Introduction
Preprocedural coronary computed tomography angiography (CTA) can identify calcification and tortuosity, and accurately determine the occlusion length, which may facilitate chronic total occlusion (CTO) crossing. A major limitation of offline CTA is lack of real-time guidance during percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). This limitation can be overcome using CTA co-registration with a real-time fluoroscopy system.
Methods
CTA/fluoroscopy fusion was used in 27 of 146 cases (18%) performed in 2018-2019, by two experienced operators, at two centres participating in the PROGRESS-CTO registry (NCT02061436). We compared the clinical, angiographic and technical characteristics and procedural outcomes of the patients who underwent CTO PCI with versus without CTA/fluoroscopy fusion guidance.
A coronary CTA and 2D coronary angiography co-registration system (syngo CTO Guidance; Siemens Healthineers, Forchheim, Germany) was used for the CTA/fluoroscopy co-registration. Previously acquired CTA data sets are imported into the system. The tool automatically identifies the coronary arteries and extracts the centrelines. After registration, the CTA volume is aligned to the C-arm’s coordinate system.
Results
The patients’ baseline clinical characteristics were similar in the two groups. Mean patient age was 66±9 years for both groups and most patients were male (93% vs 78%, p=0.065 with and without CTA/fluoroscopy co-registration guidance, respectively).
For the CTA/fusion group, the median radiation dose for CTA scanning was 4.7 (3.1–7.9) mSv and the CT-RECTOR score was 2.9±1.1. CTA studies were obtained within 15 (6, 29) days before CTO PCI. A prior CTO PCI attempt had been performed more frequently in cases with CTA/fluoroscopy fusion (37% vs 13%, p=0.003). The right coronary artery was the most common target vessel for both groups (56% vs 45%, p=0.912). The mean J-CTO score (3.3±1.1 vs 2.7±1.2, p=0.009) and PROGRESS-CTO complications score (3.8±1.8 vs 3.0±2.0, p=0.040) were both higher in the CTA/fluoroscopy fusion group. The most common indication for performing CTA/fluoroscopy fusion was to clarify proximal cap ambiguity (63%) (Figure 1), followed by facilitation of intra-CTO wire advancement (true lumen or subintimal) (56%) and re-entry (15%). Antegrade/dissection re-entry (ADR) was the most common successful crossing technique for the CTA/fluoroscopy fusion group (37%) and antegrade wiring (AW) for the other group (54%).
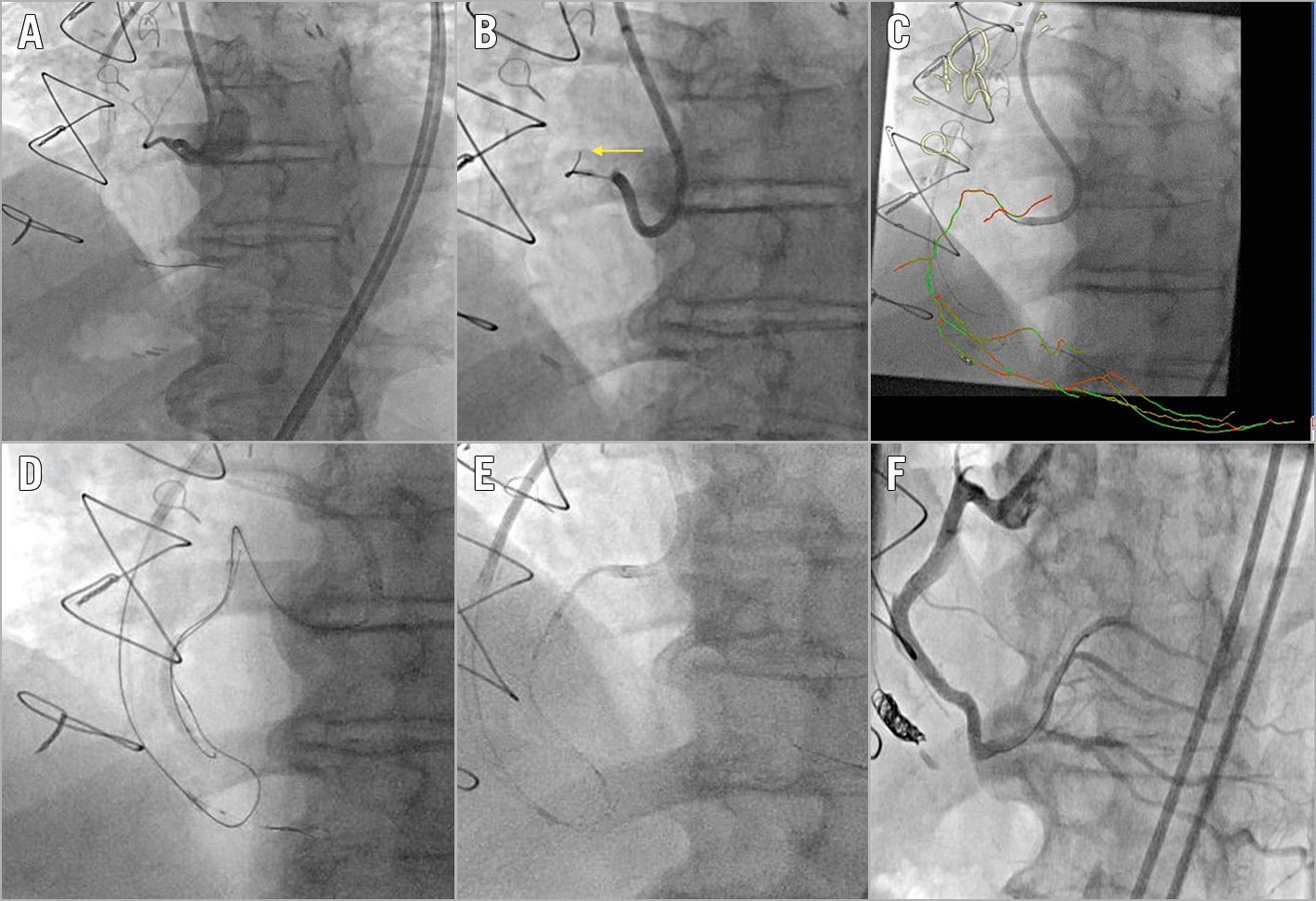
Figure 1. Computed tomography angiography (CTA)/real-time fluoroscopy fusion to clarify proximal cap ambiguity. Proximal right coronary artery (RCA) chronic total occlusion with proximal cap ambiguity due to the presence of obscuring side branches (A). The wire kept entering into the side branches (arrow) (B). Upward course of the RCA clarified with CTA/coronary fluoroscopy co-registration (C). The antegrade wire entered the subintimal space. It was then decided to proceed with reverse controlled antegrade and retrograde subintimal tracking (D). Four drug-eluting stents were implanted with the aid of a GuideLiner® guide extension (Teleflex Medical, Wayne, PA, USA) (E). Final result (F).
Technical success (81% vs 89%, p=0.279) and in-hospital major adverse cardiac events (MACE) (0 vs 2.5%, p=1.000) were similar between the two groups. Procedure time (206 [141, 277] vs 137 [141, 123] min, p=0.010) and air kerma (AK) radiation dose (2.43 [1.63, 3.97] vs 1.84 [0.94, 2.90] Gray, p=0.038) were higher for the CTA/fluoroscopy fusion group, while there was no difference in contrast volume (210 [155, 270] vs 237 |163, 314] ml, p=0.101).
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the largest to date evaluating the use of real-time CTA/fluoroscopy fusion in CTO interventions. The major findings of our study are that CTA/fluoroscopy fusion: (a) was used in highly complex lesions; (b) was mainly used to resolve proximal cap ambiguity and facilitate CTO wire advancement; (c) was associated with high technical success; and that (d) ADR was the most common final successful crossing technique.
Roguin et al were the first to evaluate the feasibility of CTA/fusion co-registration in five patients with CTO lesions, focusing on AW cases1. Ghoshhajra et al compared the clinical and angiographic characteristics and procedural outcomes of 24 patients who underwent CTO PCI under CTA/fluoroscopy fusion guidance with 24 consecutive CTO PCI patients treated without real-time CTA fusion2. The lesions in the CTA/fluoroscopy fusion group were more complex. In that study, technical success was 83%; one in-hospital MACE was recorded in each group. CTA/fluoroscopy fusion facilitated ADR by guiding re-entry attempts away from areas with extreme calcification.
In the present study, ADR was the most common successful crossing strategy (37%) in contrast with prior studies, in which ADR was used in the minority of cases, ranging from <2% for Japanese operators to 28% for American operators3. ADR followed AW in a considerable number of cases in the CTA/fluoroscopy fusion group, probably due to the higher lesion complexity in this group that demanded more advanced crossing techniques. CTA/fluoroscopy fusion might also reduce the need for retrograde crossing strategies by clarifying proximal cap ambiguity, identifying vessel course and facilitating intra-CTO wire advancement4. Although the J-CTO score as well as the PROGRESS-CTO complications score were significantly higher in the CTA/fluoroscopy fusion group, there was no difference in technical success or in in-hospital MACE, suggesting that CTA/fluoroscopy fusion may facilitate success while maintaining safety for PCI of complex CTOs. In addition, the incidence of coronary perforation was low in the CTA/fluoroscopy fusion group despite high lesion complexity, suggesting that coronary CTA might improve procedural safety.
Limitations
Our study is limited by the relatively small sample size, the retrospective observational design, and differences in the baseline characteristics of the two study groups.
Conclusion
CTA/fluoroscopy fusion can be performed during CTO PCI primarily for clarifying the anatomy of very complex CTO lesions and facilitating guidewire navigation through the occluded segment, with promising success and complication rates.
|
Impact on daily practice CTA/fluoroscopy fusion can facilitate CTO PCI by clarifying proximal ambiguity and guiding antegrade wiring, antegrade dissection and re-entry attempts. Furthermore, it can potentially reduce the need for retrograde crossing, which is a higher-risk procedural strategy. |
Acknowledgements
Study data were collected and managed using Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) electronic data capture tools.
Funding
The PROGRESS-CTO registry has received support from the Abbott Northwestern Hospital Foundation, Minneapolis, MN, USA. Gift from Joseph F. and Mary M. Fleischhacker Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
F. Jaffer reports research grants (Siemens, Canon, Shockwave), consulting (Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, Philips), speaker’s fees (Biotronik, Siemens), equity interest (Intravascular Imaging, Inc.), and American College of Cardiology (Associate Editor, JACC Cardiovascular Imaging). In addition, F. Jaffer has an intravascular imaging-related patent. B. Rangan reports research grants from Infraredx, Inc., and The Spectranetics Corporation. S. Garcia reports grants from BSCI, and Edwards Lifesciences, and personal fees from Abbott Vascular, Medtronic and Edwards Lifesciences, outside the submitted work. J.L. Cavalcante reports being on the speaker’s bureau for Siemens Healthineers. N. Burke reports being a shareholder in Egg Medical and MHI Ventures, being a speaker for Opsens Medical, and receiving consulting and speaker honoraria from Abbott Vascular and Boston Scientific. E. Brilakis reports consulting/speaker honoraria from Abbott Vascular, American Heart Association (Associate Editor, Circulation), Amgen, Asahi Intecc, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Cardiovascular Innovations Foundation (Board of Directors), ControlRad, CSI, Elsevier, Infraredx, GE Healthcare, Medicure, Medtronic, Opsens, Siemens, and Teleflex, and being a shareholder in MHI Ventures and Cleerly Health. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

