Abstract
Background: Long-term clinical outcomes after pulmonary artery denervation (PADN) in patients with Group 1 pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) have not been reported.
Aims: We aimed to investigate the effect of PADN on 1-year outcomes in patients with PAH.
Methods: In the multicentre PADN-CFDA trial, 128 patients with Group 1 PAH were randomly assigned to PADN plus a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE-5i) versus a sham PADN procedure plus a PDE-5i. The principal endpoint of interest for the present study was clinical worsening at 1 year after randomisation, the composite of worsening of PAH (increase in WHO functional class, need for additional PAH treatments or PAH-related hospitalisation), atrial septostomy, listing for lung transplantation, or all-cause death.
Results: One-year clinical follow-up was available in all patients. At 1 year, clinical worsening had occurred in 3 (4.8%) patients in the PADN plus PDE-5i group and in 15 patients (23.1%) in the sham plus PDE-5i group (adjusted hazard ratio: 0.17; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.05-0.60; p=0.006), driven by significantly increased rates of PAH-related hospitalisations, worsening functional class and the requirement for additional PAH treatments in the sham group. Results were consistent in high-risk, intermediate-risk and low-risk patients (pinteraction=0.186). Patients treated with PADN plus PDE-5i had an improvement in the between-group change in the six-minute walking distance (6MWD) from baseline to 1 year of 81.2 m (95% CI: 50.3-112.2; p<0.001) compared with PDE-5i treatment alone.
Conclusions: In this multicentre sham-controlled randomised trial, PADN treatment for Group 1 PAH significantly reduced clinical worsening and improved the 6MWD during 1-year follow-up in patients treated with a PDE-5i.
Introduction
Group 1 pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) as classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) is a chronic, progressive disorder of the cardiopulmonary circulation, with an estimated prevalence of 10.6-12.4 cases per million12345. In the last decade, PAH-specific medications have been shown to improve clinical outcomes in PAH6. However, these medications are expensive, difficult to administer, fraught with side-effects, and do not prevent disease progression in most patients7. The 1-, 2-, and 3-year mortality rates among patients with PAH in the Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-term PAH Disease Management (REVEAL) were 10%, 19%, and 25%, respectively, before 2010, and 8%, 16%, and 21%, respectively, between 2015 and 20208910.
Pulmonary artery denervation (PADN) which uses radiofrequency energy to ablate the pulmonary arterial sympathetic nerves has emerged as a safe and potentially effective therapy in patients with PAH11. However, only 2 prior observational studies have reported the long-term clinical outcomes after PADN to assess the durability of the procedure1213, and neither study randomised their patients. The PADN-CFDA trial14 was a sham-controlled, multicentre trial designed for regulatory approval of PADN in China for Group 1 PAH patients. We have previously reported the 6-month outcomes from this study14. To better understand the long-term effects of PADN, we herein report the 1-year outcomes from the PADN-CFDA trial.
Methods
Study design and patient population
The design of the multicentre, randomised, sham-controlled PADN-CFDA trial has been described elsewhere14. The study was approved by the institutional review board at each participating site, and all patients signed informed consent. Inclusion and exclusion criteria have also been previously described14. In brief, eligible participants aged 18 to 70 years with symptomatic WHO Group 1 PAH who were not yet being treated with any PAH-specific drugs because of insurance or other logistical issues were enrolled and randomised. For diagnosis, PAH required a mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) ≥25 mmHg with pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) >3 Wood units (WU) and pulmonary arterial wedge pressure (PAWP) <15 mmHg by right heart catheterisation, with a negative acute vasoreactivity test (for patients with idiopathic, heritable, or drug-induced PAH). After right heart catheterisation, eligible patients were randomised in a 1:1 ratio to receive PADN plus a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE-5i, either sildenafil or tadalafil per site discretion) or a sham PADN procedure plus a PDE-5i. The PDE-5i was administered open-label to all patients and initiated before the PADN procedure. Sildenafil was initiated at 25 mg three times daily. Tadalafil was initiated at 20 mg once daily for 1 week and was then increased to 40 mg once daily if tolerated. Thereafter, combination therapy with PAH-specific medications was permitted in both groups if patients had ongoing symptoms or clinical worsening.
Procedures
The PADN procedure has been previously described121314. The PADN system consists of a dedicated 7.5 Fr temperature-sensing ablation catheter which is delivered to the periconjunctional area between the distal main pulmonary artery trunk and the ostium of the left main pulmonary artery branch. Radiofrequency energy is emitted to ablate the sympathetic nerves around that region15.
Randomisation and masking
Randomisation in block sizes of 6 was implemented through a central interactive web response system. As previously described, the sham procedure was carefully performed according to a script to mimic the PADN procedure, with the PADN catheter inserted into the pulmonary artery without delivery of radiofrequency energy14. Patients, their families and all post-procedure healthcare providers remained blinded to the randomisation arm until the primary 6-month endpoint was reached. A questionnaire to assess the success of blinding was administered post-procedure to all patients. As previously reported14, most patients in both the PADN and sham groups believed they had received active PADN treatment (61/63 [96.8%] vs 62/65 [95.4%], respectively). Patient unblinding was performed at 6 months after randomisation.
Follow-up and assessments
Office visits were scheduled for all patients at 7, 30, 180 and 365 days. Baseline and follow-up echocardiography and right heart catheterisation were performed at 6 months, as previously reported14. The need for rehospitalisation was determined by a patient’s referring physician and not research personnel. A standardised script using the Patient Functional Classification Self-Report (PH-FC-SR)16 was utilised when telephone contact was conducted. Patients at low risk and in a stable clinical condition as determined by the phone call had their in-person visit postponed to a later date. On the other hand, high-risk patients were followed more closely, and weekly or biweekly check-in calls were performed to monitor clinical conditions. Patients with worsening symptoms and/or congestive heart failure were hospitalised using safety control procedures or through the emergency department.
Endpoints
The principal endpoint of interest for the present study was the time to first clinical worsening, defined as the composite of worsening of PAH, atrial septostomy, listing for lung transplantation or all-cause death, within 1 year after randomisation. Worsening of PAH was defined as an increase in World Health Organization functional class (WHO-FC), need for additional PAH treatments (including combination medical therapy) or PAH-related hospitalisation. Of note, the 6-month definition of worsening of PAH had previously included a six-minute walking distance (6MWD) decrease >15% from baseline as a component, rather than an increase in WHO-FC. However, because of the inability of patients to travel to their local hospital for the 6MWD test during the COVID-19 pandemic, this component was changed for the 1-year endpoint to an increase in WHO-FC, which could be assessed during a telephone call. WHO-FC I=symptom-free at rest and during exercise. WHO-FC II=no symptoms at rest, but some daily activities such as making the bed or grocery shopping causes dyspnoea or chest discomfort. WHO-FC III=no symptoms at rest, but normal chores are greatly limited because of dyspnoea or fatigue. WHO-FC IV=symptoms at rest and severe symptoms with activity. Secondary endpoints included the components of clinical worsening as well as the between-group change in 6MWD. All primary and secondary outcomes were evaluated by an independent clinical events committee using original source documents, blinded to treatment assignment.
The consistency of the primary outcome of clinical worsening was also assessed in 12 prespecified subgroups, including among low-, intermediate- and high-risk groups according to the REVEAL Lite 2 risk score, which was developed and has been validated to predict 1-year mortality in patients with PAH17. The REVEAL Lite 2 score includes six non-invasive variables: WHO-FC, systolic blood pressure and heart rate, 6MWD, natriuretic peptide levels, and renal insufficiency (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] <60 mL/min/1.73 m2)17.
Statistical analysis
The calculation of sample size has been previously described14. Differences between groups in continuous variables were expressed as mean±standard deviation (SD) if data were normally distributed or median (interquartile range [IQR]) for non-normally distributed data and were evaluated with the t-test or the Wilcoxon rank-sum score, respectively. The χ2 or Fisher’s exact tests were used to analyse categorical variables which were expressed as percentages. Time-to-first event curves were generated using Kaplan-Meier analysis. Patients were censored at the time of their latest follow-up. The differences in relative risk between groups were expressed as hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI), generated using Cox proportional hazards regression. Multivariable Cox analysis was performed to identify the independent predictors of 1-year clinical worsening. In addition to treatment group, the following covariates were entered into these models on the basis of their associations with the outcomes of interest: baseline 6MWD, use of monotherapy and combination PAH medications, cardiac output from right heart catheterisation, and the REVEAL Lite 2 scores17. Missing baseline and outcomes data were not replaced. The between-group change in 6MWD from baseline to 1 year was analysed using mixed-model repeated measures (MMRM) methods assuming that missing data were missing at random. Treatment (PADN vs sham), PAH-specific monotherapy and combination therapy, days to the follow-up test, and treatment-by-day interaction were included in the model as fixed effects, with baseline 6MWD as a covariate. Sensitivity analyses using the MMRM model were performed adjusting for age, sex, and body mass index and with multiple imputation using the Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method18. The imputation model included treatment group, sex, age, and baseline 6MWD data for all scheduled visits.
All outcome analyses were performed in the intention-to-treat (ITT) population, including all randomised patients according to their assigned treatment regardless of the treatment received. All statistical tests were 2-sided, and a p-value of <0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. All analyses were performed with SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute).
Results
Baseline characteristics and medications
A total of 128 patients with PAH were randomised at 12 centres in China between 8 January 2018 and 22 June 2021 (Figure 1). The baseline demographic and clinical characteristics have been reported previously14 and are shown in Table 1. In brief, the mean age was 40.8±11.8 years and 106 (82.8%) patients were women. The PAH aetiology was idiopathic in 70 (54.7%) cases. At baseline, the mean 6MWD was 401±92 m, the mPAP measured by right heart catheterisation was 53.9±16.4 mmHg, the mean PVR was 10.9±5.1 WU, and the mean N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level was 2,345±3,154 pg/mL.
One-year clinical follow-up was completed in all patients, 90 (70.3%) by clinic visit and 38 (29.7%) by telephone call. A 6MWD test was not performed at 1 year in this latter group, including 21/63 (33.3%) patients assigned to PADN and 17/65 (26.2%) patients assigned to sham treatment (p=0.13). The reasons that patients were unable to complete the 1-year follow-up 6MWD are shown in Figure 1.
Medication use at baseline, 30 days and 1 year were similar between the groups (Table 2). At 30 days, PAH monotherapy (most commonly a PDE-5i) was used in most patients. At 1 year, PAH combination therapy was used in 36 (57.1%) patients in the PADN plus PDE-5i group and in 39 (60.0%) patients in the sham plus PDE-5i group (p=0.74).
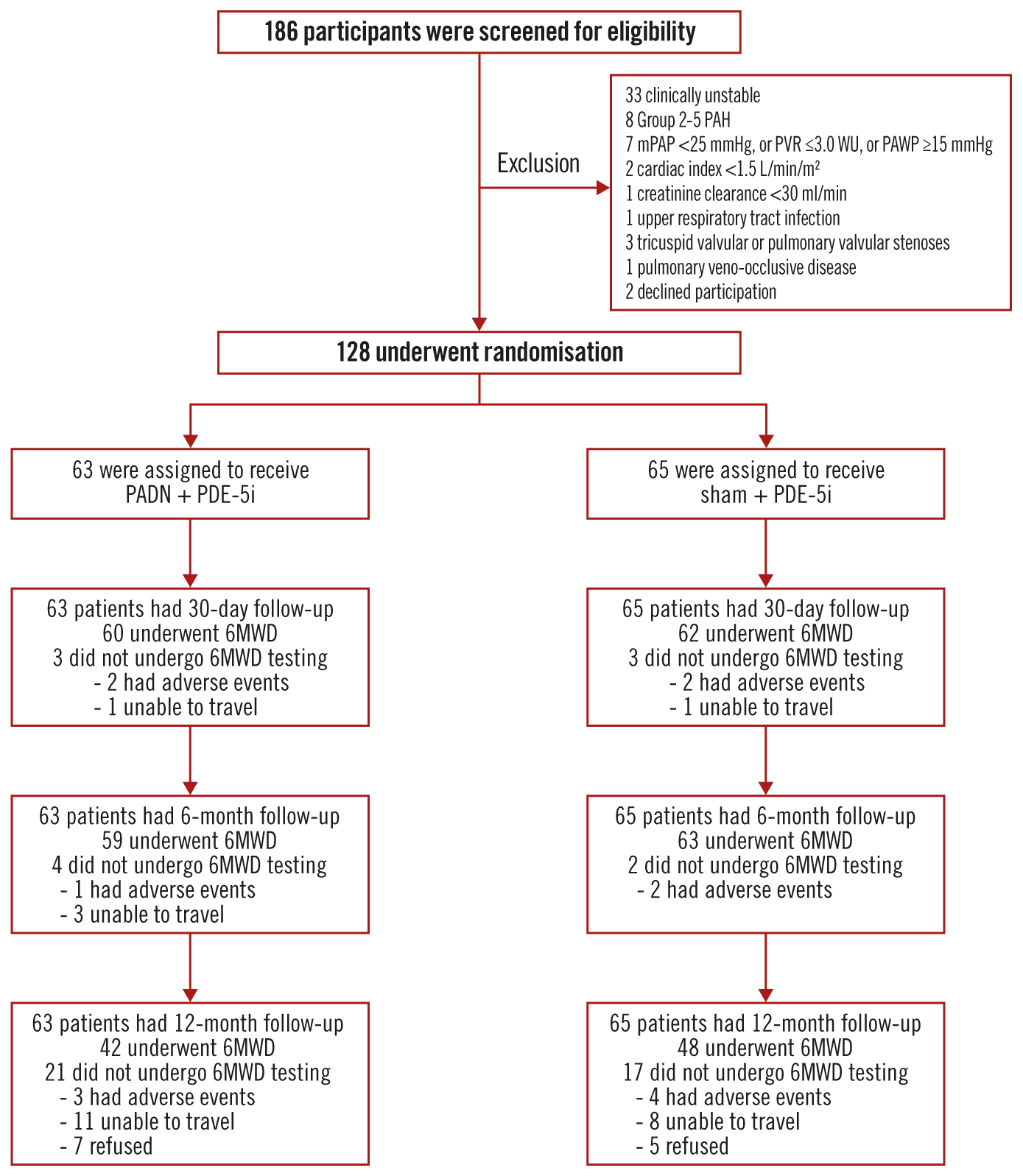
Figure 1. Screening, randomisation, and follow-up of the study participants. Among 186 patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension screened for eligibility, 128 were randomised and treated with pulmonary artery denervation (PADN) plus a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE-5i) or a sham procedure plus a PDE-5i. One-year clinical follow-up was complete in all patients, but 21 patients in the PADN plus PDE-5i group and 17 patients in the sham plus PDE-5i group did not complete a 6-minute walking distance test (6MWD) at 1 year. mPAP: mean pulmonary arterial pressure; PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension; PAWP: pulmonary arterial wedge pressure; PVR: pulmonary vascular resistance; WU: Wood units
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the randomised patients.
| PADN+PDE-5i (N=63) |
Sham+PDE-5i (N=65) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||
| Age, years | 37 (32, 48) | 39 (32, 52) | |
| Female sex | 57 (90.5) | 49 (75.4) | |
| Aetiology of PAH | |||
| Idiopathic | 36 (57.1) | 34 (52.3) | |
| Hereditary | 1 (1.6) | 1 (1.5) | |
| Associated with connective tissue disease | 14 (22.2) | 17 (26.2) | |
| Lupus | 5 (7.9) | 8 (12.3) | |
| Sjogren’s syndrome | 5 (7.9) | 5 (7.7) | |
| Systemic sclerosis | 1 (1.6) | 1 (1.5) | |
| Other | 3 (4.8) | 3 (4.6) | |
| Associated with congenital heart disease | 9 (14.3) | 13 (20.0) | |
| Associated with portal hypertension | 3 (4.8) | 0 (0) | |
| Clinical characteristics | |||
| Current smoker | 3 (4.8) | 3 (4.6) | |
| Time from diagnosis to screening, years | 3.8±5.7 | 3.1±4.9 | |
| WHO functional class | Class I | 1 (1.6) | 3 (4.6) |
| Class II | 27 (42.9) | 33 (50.8) | |
| Class III | 32 (50.8) | 27 (41.5) | |
| Class IV | 3 (4.8) | 2 (3.1) | |
| 6-minute walking distance, metres | 388±92 | 414±92 | |
| NT-proBNP, pg/mL | 1,753 (259, 3,974) | 937 (230, 2,421) | |
| Continuous data are expressed as n (%), mean±standard deviation or median (IQR). IQR: interquartile range; PADN: pulmonary artery denervation; PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension; PDE-5i: phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor; NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, WHO: World Health Organization | |||
Table 2. Medications at baseline and during follow-up.
| PADN+PDE-5i(N=63) | Sham+PDE-5i(N=65) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medications prior to enrolment | |||
| PDE-5i | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| ERA | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| PSCA | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| Diuretics | 47 (74.6) | 42 (64.6) | 0.25 |
| At 1 month | |||
| PAH-specific medications | |||
| Monotherapy | 61 (96.8) | 59 (90.8) | 0.27 |
| PDE-5i | 56 (88.9) | 56 (86.2) | - |
| ERA | 5 (7.9) | 2 (3.1) | - |
| PSCA | 0 (0) | 1 (1.5) | - |
| Dual combination therapy | 2 (3.2) | 0 (0) | 0.24 |
| PDE-5i+ERA | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| PDE-5i+PSCA | 2 (3.2) | 0 (0) | - |
| ERA+PSCA | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| Triple combination therapy(PDE-5i+ERA+PSCA) | 0 (0) | 3 (4.6) | 0.24 |
| Intolerance to PAH-specific medications | 0 (0) | 3 (4.6) | 0.24 |
| Diuretics | 13 (20.6) | 41 (63.1) | 0.15 |
| At 12 months | |||
| PAH-specific medications | |||
| Monotherapy | 22 (34.9) | 22 (33.9) | 0.90 |
| PDE-5i | 14 (22.2) | 18 (27.7) | - |
| ERA | 8 (12.7) | 4 (6.2) | - |
| PSCA | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| Dual combination therapy | 32 (50.8) | 31 (47.7) | 0.73 |
| PDE-5i+ERA | 27 (42.9) | 31 (47.7) | - |
| PDE-5i+PSCA | 2 (3.2) | 0 (0) | - |
| ERA+PSCA | 3 (4.8) | 0 (0) | - |
| Triple combination therapy(PDE-5i+ERA+PSCA) | 4 (6.3) | 8 (12.3) | 0.25 |
| Intolerance to PAH-specific medications | 1 (1.6) | 4 (6.2) | 0.37 |
| Diuretics | 34 (54.8) | 35 (53.8) | 0.85 |
| Binary data are n (%). CI: confidence interval; ERA: endothelin receptor antagonist; PADN: pulmonary arterial hypertension; PAH: pulmonary artery denervation; PDE-5i: phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor; PSCA: prostacyclin analogues | |||
Clinical outcomes
At 1-year follow-up, clinical worsening had occurred in 18 (14.1%) patients, including 3 (4.8%) in the PADN plus PDE-5i group and 15 (23.1%) in the sham plus PDE-5i group (adjusted HR 0.17; 95% CI: 0.05-0.60; p=0.006), driven by a higher rate of worsening of PAH in the sham plus PDE-5i group (Table 3, Figure 2). This difference was maintained when worsening functional class was removed from the clinical worsening criteria (3.2% vs 18.5%; p=0.017). Considering the components of worsening of PAH, PADN reduced the 1-year rates of PAH-related rehospitalisation, worsening WHO-FC, and the requirement for additional PAH treatments (Table 3). In addition to PADN treatment (HR 0.18, 95% CI: 0.05-0.63; p=0.008), independent predictors of 1-year clinical worsening included baseline 6MWD (HR per 50 m decrease 1.46, 95% CI: 1.03-2.08; p=0.04) and the REVEAL Lite 2 risk score (HR per 1 point increase 1.35, 95% CI: 1.07-1.79; p=0.04). The reduction in 1-year clinical worsening with PADN compared to sham treatment was consistent across numerous subgroups examined, including in low-risk, intermediate-risk and high-risk patients according to the REVEAL Lite 2 risk scores (pinteraction=0.186) (Figure 3). Only 1 patient died during follow-up, a 32-year-old woman with a 3-year history of idiopathic PAH who died 352 days after randomisation to the sham control group while on dual combination therapy. Neither atrial septostomy nor lung transplantation were performed in any patient.
Table 3. Clinical worsening at 1-year follow-up.
| PADN+PDE-5i (N=63) | Sham+PDE-5i (N=65) | Hazard ratio (95% CI) | Adjusted hazard ratio* (95% CI) | Adjusted p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical worsening | 3 (4.8) | 15 (23.1) | 0.19 (0.06-0.66) | 0.17 (0.05-0.60) | 0.006 |
| Worsening of PAH | 3 (4.8) | 15 (23.1) | 0.19 (0.06-0.66) | 0.17 (0.05-0.60) | 0.006 |
| PAH-related rehospitalisation | 1 (1.6) | 10 (15.4) | 0.10 (0.01-0.75) | 0.07 (0.01-0.58) | 0.01 |
| Worsening WHO-FC | 3 (4.8) | 14 (21.5) | 0.20 (0.06-0.68) | 0.19 (0.05-0.70) | 0.01 |
| Requirement for additional PAH treatments | 2 (3.2) | 12 (18.5) | 0.16 (0.04-0.72) | 0.13 (0.03-0.58) | 0.008 |
| Atrial septostomy | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - | - | - |
| Listing for lung transplantation | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - | - | - |
| Death, all-cause | 0 (0) | 1 (1.5) | - | - | 0.98 |
| PAH-related death | 0 (0) | 1 (1.5) | - | - | 0.98 |
| Event rates are binary n (%). *Adjusted for sex and baseline six-minute walk distance. CI: confidence interval; PADN: pulmonary artery denervation; PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension; PDE-5i: phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor; WHO-FC: World Health Organization functional class | |||||
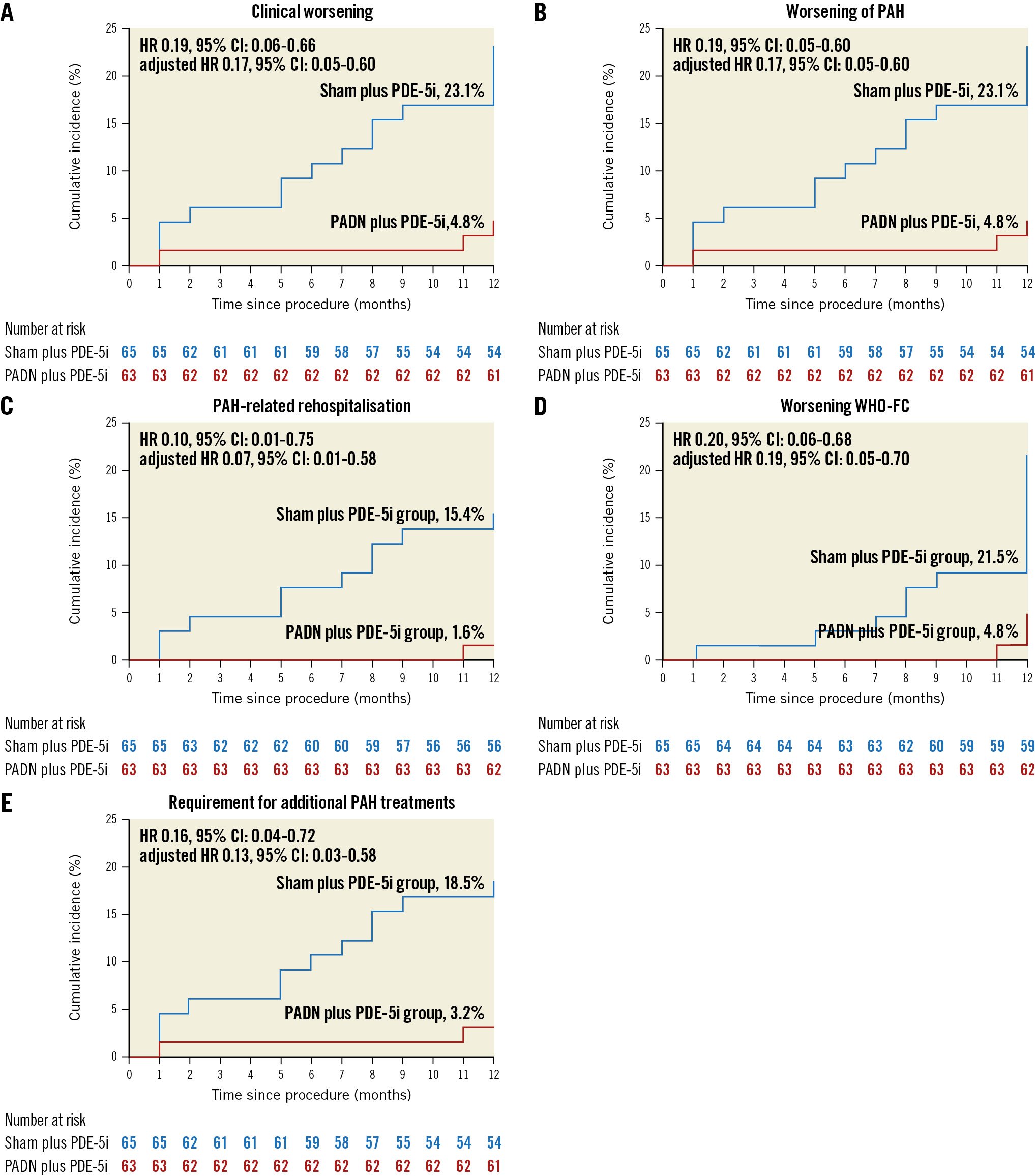
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier analysis. The cumulative 1-year hazard rates of A) clinical worsening, B) worsening of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), C) PAH-related rehospitalisations, D) WHO functional class (FC) increase, and E) requirement for additional PAH treatments after treatment with PADN and a sham procedure. CI: confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; PADN: pulmonary artery denervation; PDE-5i: phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor; WHO: World Health Organization
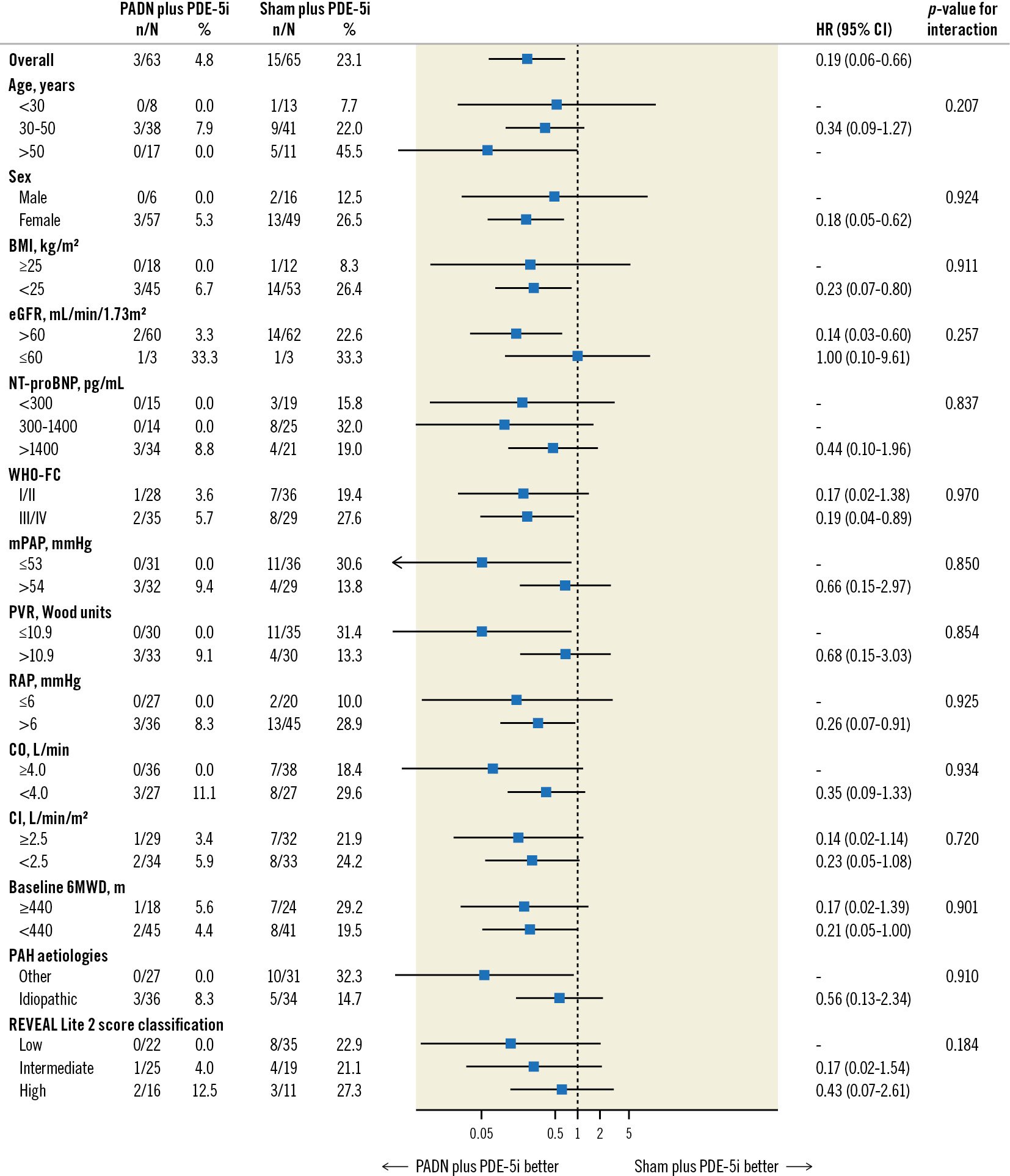
Figure 3. Subgroup analysis for the 1-year primary endpoint of clinical worsening. An interaction test of >0.05 indicates that there was no significant difference in the relative risks for clinical worsening in patients randomised to PADN plus phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE-5i) versus a sham procedure plus PDE-5i. BMI: body mass index; CI: cardiac index; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; CO: cardiac output; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; HR: hazard ratio; mPAP: mean pulmonary arterial pressure; NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; PADN: pulmonary artery denervation; PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension; PVR: pulmonary vascular resistance; RAP: right atrial pressure; REVEAL: Registry to Evaluate Early and Long-term PAH Disease Management; WHO-FC: World Health Organization functional class; 6MWD: 6-minute walking distance
Change in 6MWD from baseline to 12 months
The results of the 6MWD tests performed during follow-up are shown in Supplementary Figure 1. A between-group difference in 6MWD emerged at 30 days and widened up to 1 year. The median change in 6MWD from baseline to 1 year was 54±102 m in the PADN plus PDE-5i group and â9±127 m in the sham plus PDE-5i group (p=0.02). The adjusted between-group mean difference in the change in 6MWD from baseline to 12 months was 81.2 m (95% CI: 50.3-112.2; p<0.001), favouring the PADN group. This difference was consistent using imputed outcomes to account for missing data in the MCMC sensitivity analysis.
Discussion
The present study is the first evaluation of 1-year clinical outcomes after PADN for treatment of PAH from a randomised sham-controlled trial that was blinded for 6 months. The major findings from this study may be summarised as follows: 1) compared with a sham procedure plus treatment with a PDE-5i, PADN plus a PDE-5i substantially reduced PAH clinical worsening up to 1-year follow-up (Central illustration), driven by reductions in the 1-year rates of PAH-related rehospitalisation, worsening WHO-FC, and the requirement for additional PAH treatments; 2) the reduction in PAH clinical worsening with PADN was consistent in low-risk, intermediate-risk and high-risk patients as assessed by the REVEAL Lite 2 risk score17, and across other prespecified subgroups; 3) lower baseline 6MWD and higher REVEAL Lite 2 risk scores were independent predictors of 1-year clinical worsening, whereas treatment with PADN was the strongest predictor of freedom from clinical worsening; 4) 6MWD at 1-year follow-up increased in PADN patients, in contrast to that observed in patients treated with a sham procedure.
Few prior studies have reported 1-year or longer outcomes after PADN. In a registry study of 66 patients with different aetiologies of PAH, clinical worsening after PADN occurred in 15.2% of patients at 1-year follow-up12. In a subsequent publication, the outcomes of 120 PAH patients of different aetiologies were reported at a median follow-up of 4.8 years after PADN13. Patients were stratified by baseline WHO-FC, and the mortality rates at 1 year (2.2% vs 12.2%; p=0.087) and 3 years (6.5% vs 17.6%; p=0.102) were numerically lower in the WHO-FC I/II versus III/IV groups, respectively. The median increase of the 6MWD was 29 m in the WHO-FC I/II group compared with 60.5 m in the WHO-FC III/IV group (p=0.04). However, neither of these studies had a concurrent control arm treated with medical therapy alone, and thus the incremental benefits of PADN beyond approved PAH medications could not be estimated.
In the present multicentre, randomised, sham-controlled 6-month PADN-CFDA trial in which all patients were treated initially with background PDE-5i therapy, we assessed 1-year clinical outcomes by the occurrence of “clinical worsening”, a composite endpoint that has been used in prior clinical trials of PAH-specific medications1920. PADN resulted in a significant reduction in 1-year clinical worsening, with 80% or greater adjudicated reductions in PAH-related rehospitalisations, worsening WHO-FC, and the requirement for additional PAH treatments. Although the present trial was powered for and demonstrated an improvement in 6MWD with PADN at 6 months14, these 1-year outcomes suggest that PADN may also provide substantial clinical benefits to PAH patients.
Of note, the hazard curves favouring PADN compared with sham treatment continued to diverge up to 1 year. However, between 6 months and 1 year, the 6MWD was maintained in the PADN group, whereas it declined in the sham group (despite comparable PAH-specific medication intensification in both groups). This observation suggests that PADN mitigated the natural history of declining 6MWD in Group 1 PAH patients treated with PAH-specific medications only. However, only 70.3% of patients underwent a 6MWD assessment at 1 year. These patients likely represented a healthier group capable of exercise, and cautious interpretation of the 6MWD findings after 6 months is warranted given this selection bias.
Accurate risk prediction is essential to inform individualised treatment decisions in PAH disease management. Our results confirmed that the REVEAL Lite 2 risk score was an independent predictor of 1-year clinical worsening. In the recently published Pulmonary Hypertension Association Registry10, when categorised by the REVEAL Lite 2 score, the 1-year rates of mortality ranged from 1% in low-risk patients to 7-8% in intermediate-risk patients to 12-19% in high-risk PAH patients. In the present study of mostly low-risk and intermediate-risk PAH patients who were clinically stable despite being off all PAH-specific medications for at least 30 days before enrolment, the 1-year rates of death in the sham control and PADN groups were 1.5% and 0%, respectively. The 1-year rates of clinical worsening among low-risk, intermediate-risk, and high-risk patients by the REVEAL Lite 2 score were 0%, 4.0%, and 12.5%, respectively, after PADN (similar to our previous reports21) and substantially lower than the respective observed clinical worsening rates after sham control. The clinical outcomes of PADN were consistent across the 3 risk strata.
Lower baseline 6MWD also emerged as an independent predictor of 1-year clinical worsening, as well as being a component of the REVEAL Lite 2 score17. Similarly, in the PADN-5 trial22, 6MWD was an independent predictor for clinical worsening in patients with combined pre- and post-capillary pulmonary hypertension. Thus, consistent with approval studies of pharmacological agents23242526 and international guidelines3, field walk testing effectively evaluates baseline risk and therapeutic response in patients with PAH following PADN (Supplementary Figure 1). Finally, treatment with PADN was the strongest independent predictor of freedom from clinical worsening, suggesting that PADN may be an important therapeutic option for appropriate patients with Group 1 PAH who remain symptomatic despite drug therapy.
In the present trial, the incremental 33.9 m and 81.2 m improvements in the 6MWD with PADN from baseline to 6-month and 12-month follow-ups, respectively, compared with sham control treatment in patients principally on background monotherapy for the first 6 months were at least as good as the findings from prior trials in which combination therapy was initialised142425. More recently, the randomised STELLAR trial reported a 1 metre increase in the mean 6MWD at 6-month follow-up in the control group treated with background combination therapy (triple drug use in >60% of patients) and a 40.1 m mean improvement in the sotatercept group26.
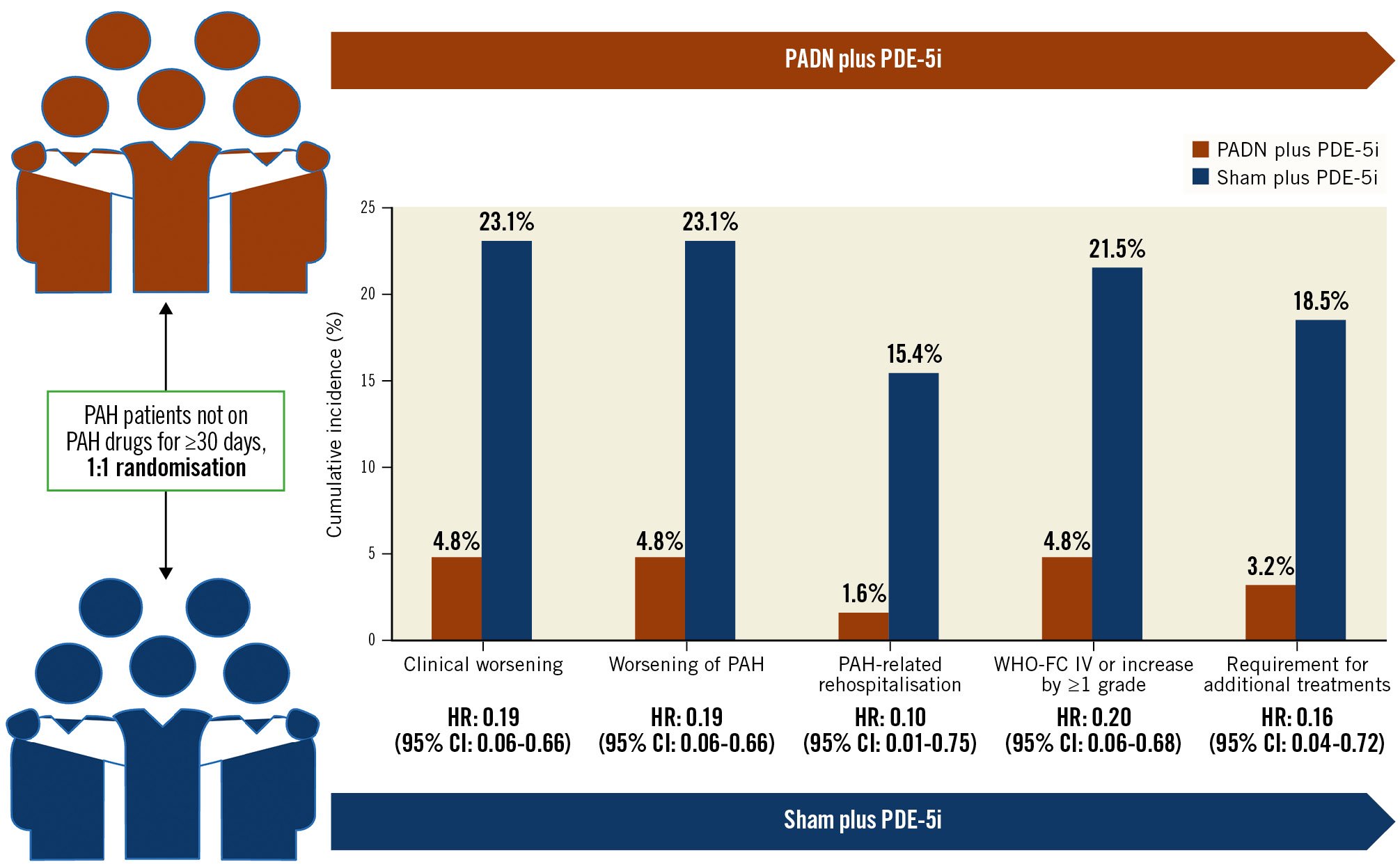
Central illustration. Change in endpoints from baseline to 12 months. CI: confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; PADN: pulmonary artery denervation; PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension; PDE-5i: phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors; WHO-FC: World Health Organization functional class
Limitations
First, the sample size of the present study was modest, and the trial was not powered for clinical outcomes. Caution is especially warranted when interpreting the results in small subgroups. Nonetheless, the large magnitude of the clinical effect during 1-year follow-up in this sham-controlled trial, with reductions in each of the 3 parameters of the clinical worsening endpoint, and consistent outcomes across low-, intermediate- and high-risk strata, provide reassurance in the validity of these findings. Second, the possibility that unblinding after 6 months influenced the 1-year outcomes cannot be excluded. However, PAH-specific medication use at 1 year was comparable in both groups, and the differences in clinical outcomes between 6 months and 1 year (after unblinding) were similar to those observed between randomisation and 6 months (before unblinding). Third, only 1 patient died during the 1-year follow-up duration in this study − a PAH-related death in the sham group − in part due to the inclusion criteria that ensured enrolment of a relatively low-risk cohort (e.g., patients untreated with PAH-specific medications for at least 30 days, without clinical instability). Although guidelines recommend initial combination therapy for Group 1 PAH3, in a large registry study, combination therapy use in China was still <45% by 202120. As such, the present trial served as a “proof-of-principle” test of the effectiveness of PADN. However, while approximately half of the patients in both groups were treated with combination PAH medication regimens during follow-up, these outcomes cannot necessarily be translated to Group 1 PAH patients who are symptomatic at baseline despite treatment with 2 or more PAH-specific drugs. However, in the TROPHY I study, a mean 42 m improvement in the 6MWD from baseline to 4-6-month follow-up was reported after treatment with an alternative ultrasound-based PADN system in patients on dual or triple combination therapy in an open-label single-arm study27, consistent with the present 6-month results. Longer-term follow-up in higher-risk patients and in greater numbers of patients are required to determine whether PADN confers a survival benefit in Group 1 PAH, especially among patients who remain symptomatic despite combination therapy. Fourth, the present trial results apply to patients with Group 1 PAH treated with a specific PADN catheter-based radiofrequency energy delivery system; whether the results would be similar in other aetiologies of PAH (e.g., secondary pulmonary hypertension due to left ventricular dysfunction or chronic pulmonary thromboembolic disease) or with other PADN systems can only be assessed in dedicated randomised trials. Finally, WHO-FC assessment replaced 6MWD testing for this 1-year analysis as the COVID-19 pandemic made in-person follow-up difficult for many patients. The rate of worsening FC was 21.5% in the sham group compared with 4.8% in the PADN group (adjusted p=0.01). However, given the increasing difference between 6 and 12 months in 6MWD favouring the PADN group, we do not believe this substitution materially affected the impression of the long-term benefits of PADN.
Conclusions
In the present multicentre, sham-controlled randomised trial in which PAH-specific background medication use was consistent between groups during follow-up, PADN resulted in a significant reduction in 1-year clinical worsening and an improvement in 6MWD in Group 1 PAH patients. Further trials are required to assess outcomes in patients who remain symptomatic despite multiple PAH-specific medications and to assess the long-term outcomes in different patient risk strata and subgroups.
Impact on daily practice
Group 1 pulmonary arterial hypertension is an incurable disease, resulting in progressive pulmonary arterial remodelling, increasing dyspnoea and fatigue, and premature death in most patients. Pulmonary artery denervation significantly reduced the risk of clinical worsening and improved 6MWD up to 1-year follow-up in patients with Group 1 pulmonary arterial hypertension initially treated with PDE-5i therapy. Pulmonary artery denervation may improve the efficacy of current pulmonary arterial hypertension therapy.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr Xiaojuan Zhang and Dr Dandan Cai (in the core lab) for their important insights on the measurements and interpretation of right heart catheterisation findings.
Funding
This trial was funded by grants from the National Scientific Foundation of China (grant numbers NSFC 91639303, NSFC 81770441 and NSFC 82121001) and Nanjing First Hospital. Pulnovo provided PADN catheters for use in the study.
Conflict of interest statement
G.W. Stone has received speaker honoraria from Medtronic, Pulnovo, Infraredx, Abiomed, Abbott, Amgen, and Boehringer Ingelheim; has served as a consultant to Daiichi Sankyo, Ablative Solutions, CorFlow, Apollo Therapeutics, CardioMech, W.L. Gore & Associates, Robocath, Miracor, Vectorious, Abiomed, Valfix, TherOx, HeartFlow, Neovasc, Ancora, Elucid Bio, Occlutech, Impulse Dynamics, Adona Medical, Millennia Biopharma, and Oxitope; and has equity/options from Ancora, Cagent, Applied Therapeutics, the Biostar family of funds, SpectraWave, Orchestra BioMed, Aria, Cardiac Success, Valfix, and Xenter; his employer, Mount Sinai Hospital, receives research support from Abbott, Abiomed, Bioventrix, Cardiovascular Systems Inc, Philips, Biosense Webster, Shockwave Medical, Vascular Dynamics, Pulnovo, and V-Wave. G.W. Stone’s daughter is an employee at IQVIA. S-L. Chen is the inventor of aPADN but not the owner of PADN patent; received speaker honoraria from MicroPort, Pulnovo, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Sanofi, and BioMed; is a Fellow at the Collaborative Innovation Center for Cardiovascular Disease Translational Medicine, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, People’s Republic of China; and received grants from the National Scientific Foundation of China. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

