Abstract
Background: A recent randomised trial demonstrated fractional flow reserve (FFR) guidance for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was non-inferior to intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) guidance regarding clinical outcomes, with a lower frequency of PCI.
Aims: We sought to evaluate the prognosis of FFR versus IVUS guidance for PCI of intermediate coronary artery stenosis and low lesion complexity in diabetic and non-diabetic patients.
Methods: This study is a prespecified post hoc analysis from the FLAVOUR trial. The primary outcome was major adverse cardiac events (MACE) at 24 months, defined as a composite of death, myocardial infarction or any revascularisation. The secondary outcomes were target vessel failure (TVF) and each component of MACE and TVF at 24 months.
Results: Among 1,682 randomly assigned patients, 554 (32.9%) had diabetes, and the mean SYNTAX score was 8.64±6.03 at baseline. The FFR group had a lower PCI rate than the IVUS group in both diabetic (48.2% vs 69.1%; p<0.001) and non-diabetic (42.6% vs 63.3%; p<0.001) patients. At 24 months, there was no difference in the cumulative incidence of MACE between the FFR and the IVUS groups in either diabetic (9.3% vs 8.3%; p=0.90) or non-diabetic (7.5% vs 8.6%; p=0.50) patients. The cumulative incidence of TVF was also comparable between the FFR and the IVUS groups regardless of diabetic status.
Conclusions: In patients with intermediate coronary stenosis and low lesion complexity, regardless of diabetic status, FFR guidance had no significant differences in MACE or TVF with a lower frequency of PCI compared with IVUS guidance.
Diabetes mellitus is the most prevalent comorbidity among patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)1. Diabetic patients frequently present with more complex CAD − characterised by multivessel disease, diffuse lesions and lipid-rich vulnerable plaques − and have a higher prevalence of other comorbid conditions such as hypertension, renal insufficiency, and heart failure23. Moreover, diabetic patients have an elevated risk of stent-related complications, including stent thrombosis and restenosis, compared to non-diabetic patients1. Therefore, despite the improvement in clinical outcomes after PCI in the contemporary era, diabetes remains an independent predictor of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), highlighting the ongoing challenges in optimal decision-making and procedural details of PCI for diabetic patients.
Several landmark randomised trials showed that fractional flow reserve (FFR)- and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS)-guided PCI improve clinical outcomes in comparison with angiography-guided PCI456. While the fundamental principles governing the use of FFR and IVUS during PCI are inherently different, both FFR and IVUS have emerged as the most frequently used complementary techniques in the assessment and management of CAD during cardiac catheterisation. Recently, the Fractional FLow Reserve And IVUS for Clinical OUtcomes in Patients With InteRmediate Stenosis (FLAVOUR) trial found that the use of FFR or IVUS to manage patients with angiographically intermediate coronary artery stenosis resulted in comparable outcomes at 24 months, while the PCI rate was lower with FFR guidance7. To date, however, a direct comparison of FFR- and IVUS-guided PCI in diabetic patients regarding clinical outcomes has not been evaluated. We therefore examined the outcomes of FFR and IVUS guidance for PCI according to the presence of diabetes in the FLAVOUR trial.
Methods
Study population
The present analysis represents a prespecified substudy from the FLAVOUR trial (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02673424), which is an investigator-initiated, prospective, multinational, randomised controlled trial that compared FFR and IVUS guidance strategies for PCI. The study design and results have been reported previously78. In brief, the FLAVOUR trial was conducted in patients with intermediate stenosis based on visual estimation by coronary angiography. Eligible patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to undergo FFR- or IVUS-guided PCI with a 2nd-generation drug-eluting stent. Randomisation was stratified according to the trial centre and the presence or absence of diabetes mellitus. In the present study, patients were divided according to the presence of diabetes and treatment (patients who underwent PCI and those with deferred PCI and medical treatment). The protocol of the FLAVOUR trial was approved by the ethics committee at each participating site, and all patients provided written informed consent. Follow-up was performed according to the regulations of each institution and complied with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Invasive procedures and revascularisation protocol
Quantitative coronary analysis (QCA) was performed at the core laboratory (Seoul National University Hospital QCA Core Laboratory, Seoul, Republic of Korea) using a validated software program. FFR was measured using standard techniques after randomisation. After guide catheter engagement, a pressure sensor guidewire was located at the distal part of the target vessel, after calibration and equalisation to aortic pressure. Hyperaemic aortic pressure (Pa) and distal coronary arterial pressure (Pd) were measured. The FFR was calculated as the mean Pd/Pa during maximum hyperaemia. Hyperaemia was induced by intravenous infusion of adenosine or adenosine triphosphate (at a dose of 140 μg/kg/minute) or intracoronary nicorandil (2 mg). IVUS images were obtained using commercially available devices after intracoronary administration of nitroglycerine. The minimal lumen area (MLA), plaque burden and minimal stent area (MSA) were measured.
The criterion of FFR-guided PCI was an FFR of 0.80 or less. The criteria of IVUS-guided PCI were an MLA measuring either 3 mm2 or less or measuring 3-4 mm2 with a plaque burden of more than 70%7.
Clinical outcomes
The primary outcome was MACE at 24 months, defined as a composite of death, myocardial infarction, or any revascularisation according to the Academic Research Consortium consensus9. The secondary outcomes were target vessel failure (TVF) at 24 months − defined as a composite of cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction, or target vessel revascularisation (TVR) in patients with PCI − and each component of MACE and TVF.
Statistical analysis
Continuous and categorical variables are presented as mean±standard deviation and number (%), respectively. Continuous variables were compared by the t-test, whereas categorical variables were compared by the chi-square test. The time-to-first event analysis was conducted with the Kaplan-Meier method and compared by the log-rank test. For the per-patient analysis of clinical outcomes, the Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to calculate the hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The analysis was adjusted for covariates, including age, sex, and baseline characteristics that were statistically significant with a p-value lower than 0.1. A 2-sided p-value of 0.05 or less was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software, version 23 (IBM) and R programming language, version 3.6.2 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing).
Results
Baseline clinical characteristics
Among 1,682 randomly assigned patients, 554 (32.9%) patients had diabetes, and the mean SYNTAX score was 8.64±6.03. Compared with non-diabetic patients, diabetic patients had a higher body mass index and more frequent comorbidities, including hypertension, dyslipidaemia, previous PCI and lab abnormalities (Supplementary Table 1). Comparing diabetic and non-diabetic patients, the differences between the FFR and IVUS groups were minimal: diabetic patients had more frequent previous MI, and non-diabetic patients were older with higher total and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels in the FFR group, as compared to the IVUS group (Table 1). The discharge medications are shown in Supplementary Table 2. The IVUS group was more likely to be treated with antiplatelet agents compared to the FFR group, in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients, which might have mainly been contributed to by the higher PCI rate in the IVUS group.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients according to the presence of diabetes.
| Diabetes | No diabetes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFR group (n=272) | IVUS group (n=282) | p-value | FFR group (n=566) | IVUS group (n=562) | p-value | |
| Age, years | 64.9±9.2 | 65.3±9.8 | 0.62 | 65.7±9.4 | 64.5±9.9 | 0.03 |
| Male sex | 188 (69.1) | 193 (68.4) | 0.93 | 396 (70.0) | 410 (73.0) | 0.29 |
| Body mass index, kg/m² | 25.1±3.3 | 24.7±3.2 | 0.10 | 24.4±3.3 | 24.7±3.3 | 0.19 |
| Diagnosis | 0.45 | 1.00 | ||||
| Stable angina | 190 (69.9) | 206 (73.0) | 396 (70.0) | 394 (70.1) | ||
| Acute coronary syndrome | 82 (30.1) | 76 (27.0) | 170 (30.0) | 168 (29.9) | ||
| Medical history | ||||||
| Hypertension | 200 (73.5) | 203 (72.0) | 0.70 | 377 (66.6) | 367 (65.3) | 0.66 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 228 (83.8) | 224 (79.4) | 0.19 | 439 (77.6) | 431 (76.7) | 0.78 |
| Current smoking | 60 (22.1) | 57 (20.2) | 0.60 | 106 (18.7) | 98 (17.4) | 0.59 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 46 (16.9) | 59 (20.9) | 0.24 | 97 (17.1) | 88 (15.7) | 0.52 |
| Previous MI | 24 (8.8) | 11 (3.9) | 0.02 | 32 (5.7) | 28 (5.0) | 0.69 |
| Previous PCI | 69 (25.4) | 59 (20.9) | 0.23 | 96 (17.0) | 104 (18.5) | 0.53 |
| Left ventricular EF, % | 62.6±9.4 | 64.1±7.8 | 0.06 | 63.6±8.0 | 63.8±8.5 | 0.71 |
| Laboratory data | ||||||
| Haemoglobin, g/dl | 13.3±1.7 | 13.5±1.8 | 0.20 | 13.8±1.6 | 13.7±1.6 | 0.88 |
| White cell count, per mm3 | 6,671±1,858 | 6,745±2,055 | 0.66 | 6,409±1,838 | 6,424±1,874 | 0.89 |
| Creatinine, mg/dl | 1.0±1.3 | 1.0±1.4 | 0.77 | 0.9±0.4 | 0.9±0.5 | 0.96 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dl | 150.8±43.9 | 150.7±41.1 | 0.98 | 159.4±44.1 | 152.8±41.9 | 0.01 |
| High-density lipoprotein | 43.9±10.8 | 43.5±10.7 | 0.63 | 46.1±11.1 | 45.6±11.8 | 0.45 |
| Low-density lipoprotein | 82.1±35.7 | 81.0±30.3 | 0.69 | 90.2±35.6 | 84.8±34.9 | 0.01 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dl | 149.7±103.1 | 151.4±108.9 | 0.85 | 138.2±73.3 | 134.2±84.9 | 0.40 |
| Data are presented as mean±standard deviation or as n (%). EF: ejection fraction; FFR: fractional flow reserve; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; MI: myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention | ||||||
Baseline procedural characteristics
Diabetic patients had more frequent multivessel disease, a higher baseline SYNTAX score, smaller MLA, and a larger plaque burden compared to non-diabetic patients. This was associated with a higher PCI rate with the use of longer and smaller stents in diabetic patients (Supplementary Table 3). The procedural characteristics according to the presence of diabetes are shown in Table 2. The IVUS group had a higher PCI rate than the FFR group in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients, which led to more stent implantation. However, when comparing the total number and total length of stents among those who underwent PCI, there were no significant differences in either group.
Table 2. Baseline procedural characteristics according to the presence of diabetes.
| Diabetes | No diabetes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFR group | IVUS group | p-value | FFR group | IVUS group | p-value | |
| Angiographic findings | ||||||
| No. of patients | 272 | 282 | 566 | 562 | ||
| Multivessel disease | 155 (57.0) | 170 (60.3) | 0.44 | 290 (51.2) | 260 (46.3) | 0.10 |
| Diseased vessels | 0.23 | 0.15 | ||||
| Non-obstructive | 4 (1.5) | 2 (0.7) | 11 (1.9) | 14 (2.5) | ||
| 1 vessel | 113 (41.5) | 110 (39.0) | 265 (46.8) | 288 (51.2) | ||
| 2 vessels | 95 (34.9) | 96 (34.0) | 200 (35.3) | 177 (31.5) | ||
| 3 vessels | 60 (22.1) | 74 (26.2) | 90 (15.9) | 83 (14.8) | ||
| Trial target vessels | 0.23 | 0.001 | ||||
| 1 vessel | 255 (93.8) | 257 (91.1) | 508 (89.8) | 534 (95.0) | ||
| 2 vessels | 16 (5.9) | 23 (8.2) | 53 (9.4) | 26 (4.6) | ||
| 3 vessels | 1 (0.4) | 2 (0.7) | 5 (0.9) | 2 (0.4) | ||
| Patients who underwent PCI | ||||||
| Any procedure | 131 (48.2) | 195 (69.1) | <0.001 | 241 (42.6) | 356 (63.3) | <0.001 |
| Multivessel | 25 (9.2) | 53 (18.8) | 0.001 | 41 (7.2) | 72 (12.8) | 0.002 |
| Stent data | ||||||
| Total no. per patient | 0.7±0.9 | 1.0±0.9 | <0.001 | 0.6±0.8 | 0.9±1.0 | <0.001 |
| Total length per patient, mm | 18.6±26.6 | 27.0±27.3 | <0.001 | 15.5±22.7 | 24.3±28.6 | <0.001 |
| Total no. per patient who underwent PCI | 1.4±0.9 | 1.5±0.8 | 0.41 | 1.4±0.7 | 1.4±0.8 | 0.23 |
| Total length per patient who underwent PCI, mm | 38.6±26.5 | 39.1±24.6 | 0.88 | 36.4±21.3 | 38.3±27.4 | 0.35 |
| SYNTAX score | ||||||
| At baseline | 9.2±6.5 | 9.5±6.5 | 0.57 | 8.0±5.4 | 8.6±6.1 | 0.11 |
| After PCI | 5.7±4.9 | 5.0±5.2 | 0.11 | 5.3±4.4 | 4.5±4.4 | 0.003 |
| Target vessel findings | ||||||
| No. of vessels | 290 | 309 | 629 | 592 | ||
| Diameter of stenosis, % | 57.3±9.9 | 56.5±10.2 | 0.36 | 56.4±10.2 | 57.1±10.1 | 0.23 |
| Target vessel PCI | 106/290 (36.6) | 189/309 (61.2) | <0.001 | 199/629 (31.6) | 337/592 (56.9) | <0.001 |
| Stent data | ||||||
| Total no. per stented vessel | 1.2±0.5 | 1.2±0.4 | 0.18 | 1.2±0.4 | 1.2±0.4 | 0.60 |
| Total length per stented vessel, mm | 34.1±18.9 | 30.0±14.3 | 0.05 | 32.0±13.3 | 30.7±13.5 | 0.30 |
| Diameter per stented vessel, mm | 3.06±0.41 | 3.15±0.43 | 0.09 | 3.13±0.44 | 3.21±0.43 | 0.04 |
| IVUS findings | ||||||
| Minimal lumen area, mm2 | — | 3.3±1.1 | — | 3.5±1.4 | ||
| Plaque burden, % | — | 71.2±9.8 | — | 69.5±10.4 | ||
| Minimal stent area after PCI, mm2 | — | 6.8±2.1 | — | 7.1±2.2 | ||
| FFR findings | ||||||
| At baseline | 0.83±0.10 | — | 0.83±0.09 | — | ||
| After PCI | 0.88±0.05 | — | 0.88±0.06 | — | ||
| Data are presented as mean±standard deviation, n (%) or n/N (%). FFR: fractional flow reserve; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention | ||||||
Clinical outcomes
Among the entire population, there were no significant differences in MACE, TVF or other clinical outcomes at the 24-month time-to-event analysis between the diabetic and non-diabetic patients (Supplementary Figure 1, Supplementary Table 4). When divided according to diabetic status, there was no significant difference in MACE between the FFR and the IVUS group in either diabetic (9.3% vs 8.3%, HR 0.96, 95% CI: 0.54-1.73; p=0.90) or non-diabetic (7.5% vs 8.6%, HR 1.16, 95% CI: 0.76-1.76; p=0.50) patients (p for interaction=0.62) (Figure 1, Table 3). The cumulative incidence of TVF was also comparable in the two groups in both diabetic (2.9% vs 3.6%, HR 1.35, 95% CI: 0.51-3.56; p=0.55) and non-diabetic (3.4% vs 2.7%, HR 0.79, 95% CI: 0.40-1.56; p=0.49) patients (p for interaction=0.38) (Supplementary Figure 2, Table 3).
A subgroup analysis was performed in patients who received PCI and in those who received medical treatment with PCI deferred. In both subgroups, there were no significant differences in MACE or TVF between the FFR and the IVUS groups in either diabetic or non-diabetic patients (Figure 2, Figure 3, Supplementary Table 5, Supplementary Table 6). In non-diabetic patients who underwent PCI, the cumulative incidence of TVR was higher in the FFR group compared with the IVUS group, with a marginal interaction (5.1% vs 2.0%, HR 0.36, 95% CI: 0.14-0.92; p for interaction=0.07) (Supplementary Table 6).
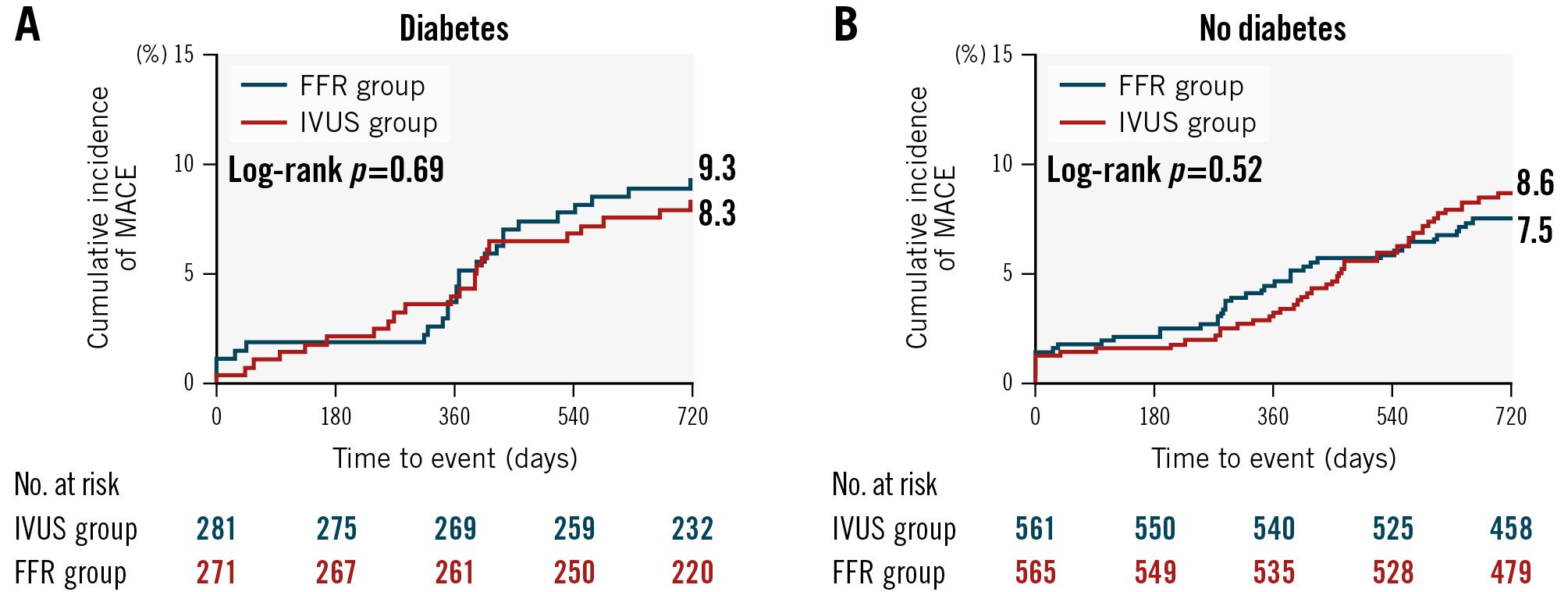
Figure 1. Cumulative incidence of MACE at 24 months between the FFR and IVUS groups according to the presence of diabetes. A) Diabetic patients and (B) non-diabetic patients. FFR: fractional flow reserve; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; MACE: major adverse cardiac events
Table 3. Primary and secondary outcomes according to the presence of diabetes.
| Diabetes | No diabetes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFR group (n=272) | IVUS group (n=282) | Adjusted HR*(95% CI) | p-value | FFR group (n=566) | IVUS group (n=562) | Adjusted HR*(95% CI) | p-value | p for interaction | |
| Primary outcome | |||||||||
| MACE | 25 (9.3) | 23 (8.3) | 0.96 (0.54-1.73) | 0.90 | 42 (7.5) | 48 (8.6) | 1.16 (0.76-1.76) | 0.50 | 0.62 |
| Secondary outcomes | |||||||||
| TVF | 8 (2.9) | 10 (3.6) | 1.35 (0.51-3.56) | 0.55 | 19 (3.4) | 15 (2.7) | 0.79 (0.40-1.56) | 0.49 | 0.38 |
| All-cause death | 2 (0.7) | 5 (1.8) | 2.22 (0.42-11.82) | 0.35 | 9 (1.6) | 14 (2.5) | 1.54 (0.66-3.56) | 0.32 | 0.69 |
| Cardiacdeath or TVMI | 2 (0.7) | 1 (0.4) | 0.58 (0.05-7.12) | 0.67 | 8 (1.4) | 12 (2.2) | 1.47 (0.60-3.61) | 0.40 | 0.36 |
| MI | 5 (1.8) | 3 (1.1) | 0.70 (0.16-3.15) | 0.64 | 11 (2.0) | 11 (2.0) | 1.11 (0.48-2.60) | 0.80 | 0.63 |
| Revascularisation | |||||||||
| Any | 20 (7.4) | 17 (6.2) | 0.93 (0.48-1.82) | 0.84 | 27 (4.9) | 27 (4.9) | 0.97 (0.56-1.65) | 0.90 | 0.94 |
| Ischaemia-driven | 14 (5.2) | 13 (4.7) | 0.86 (0.41-1.84) | 0.71 | 24 (4.3) | 20 (3.6) | 0.79 (0.43-1.43) | 0.43 | 0.78 |
| Target vessel | 8 (3.0) | 7 (2.5) | 0.91 (0.32-2.54) | 0.85 | 19 (3.4) | 13 (2.4) | 0.64 (0.31-1.30) | 0.22 | 0.66 |
| Data are presented as n (%). *Adjusted for age, male sex, previous MI, total cholesterol, and trial target vessels. CI: confidence interval; FFR: fractional flow reserve; HR: hazard ratio; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; MACE: major adverse cardiac events; MI: myocardial infarction; TVF: target vessel failure; TVMI: target vessel myocardial infarction | |||||||||
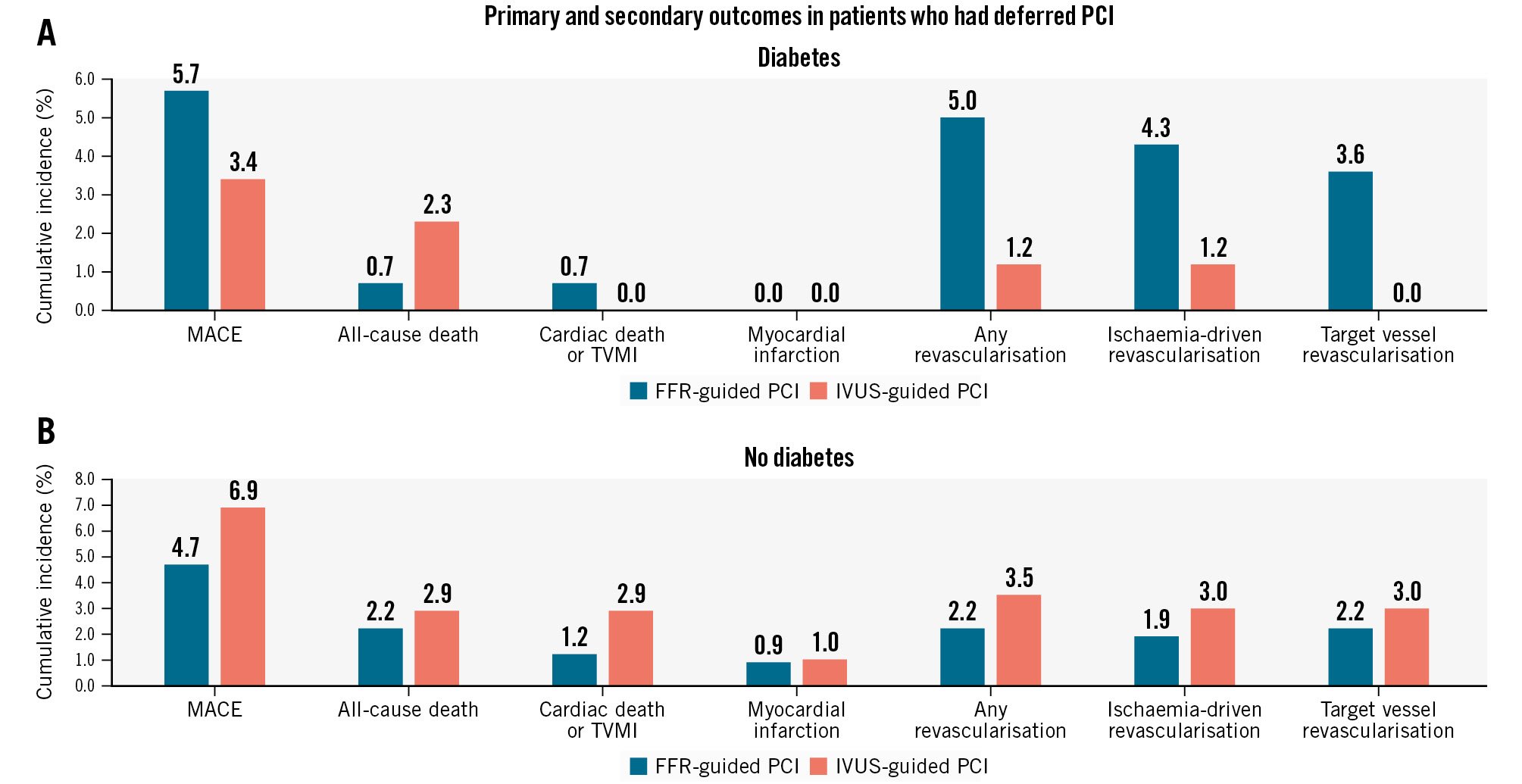
Figure 2. Occurrence rate of the primary and secondary outcomes in patients who had deferred PCI with medical treatment according to the presence of diabetes. A) Diabetic patients and (B) non-diabetic patients. FFR: fractional flow reserve; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; MACE: major adverse cardiac events; TVMI: target vessel myocardial infarction

Figure 3. Occurrence rate of the primary and secondary outcomes in patients who underwent PCI according to the presence of diabetes. A) Diabetic patients and (B) non-diabetic patients. FFR: fractional flow reserve; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; MACE: major adverse cardiac events; TVMI: target vessel myocardial infarction
Discussion
This prespecified substudy from the FLAVOUR trial assessed the outcomes of lesion selection for PCI guided by FFR versus IVUS according to the presence of diabetes (Central illustration). The main findings of our study were as follows: (1) there were no significant differences in MACE or TVF between the FFR and IVUS group in either diabetic or non-diabetic patients. 2) The IVUS group had more frequent stent implantation and administration of antiplatelet agents than the FFR group regardless of the presence of diabetes. 3) In the subgroup analysis in patients who received medical treatment only or PCI, there were no significant differences in MACE or TVF between the two groups in either diabetic or non-diabetic patients. Among non-diabetic patients who underwent PCI, the TVR rate was higher in the FFR group compared with the IVUS group, with a marginal interaction.
In line with the previous literature13, diabetic patients in our study had a higher incidence of unfavourable clinical characteristics compared with non-diabetic patients. In addition, compared to non-diabetic patients, diabetic patients had a higher incidence of adverse procedural characteristics, including more frequent multivessel disease, higher baseline SYNTAX score, larger plaque burden and smaller MLA. These characteristics were associated with a higher PCI rate with smaller stents. As the aforementioned factors are well-known high-risk factors for CAD, we must stress the importance of determining the specific strategy to use for PCI guidance in diabetic patients.
A small number of studies have evaluated the unique characteristics of physiological assessment in diabetic patients with CAD. A recent study showed that routine integration of FFR for the management of CAD in diabetic patients may be associated with a high rate of treatment reclassification10. Interestingly, FFR-based deferral identified patients with a lower risk of MACE at 12 months, compared with those undergoing revascularisation, among patients with diabetes10. Another coronary physiological index, the quantitative flow ratio (QFR)-guided lesion selection strategy, improved PCI outcomes compared with standard angiography guidance, regardless of the presence of diabetes, in the FAVOR III substudy11. Moreover, there are a few studies regarding the benefit and prognosis of imaging-guided PCI according to the presence of diabetes12131415. These studies reported that diabetic patients showed more negative remodelling at the lesion, greater plaque volume and burden, more frequent necrotic lipid core and thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA), macrophage infiltration, and focal calcification in the intracoronary imaging, which were all associated with a higher rate of adverse events during follow-up1415.
However, so far, a study regarding the comparative impact of intracoronary imaging- or physiology-guided decision-making for coronary revascularisation according to the presence of diabetes is lacking. Before such a comparison, the differential purpose of FFR and IVUS should be appreciated1617. FFR is generally used for revascularisation decision-making and IVUS is used for the PCI planning and stent optimisation. Despite this inherent difference, our study showed no significant difference in the 24-month MACE rate between FFR and IVUS guidance regardless of the presence of diabetes. Our data suggest that it is feasible to use either of these strategies to guide PCI regardless of diabetic status. In particular, our data might have prompt real-world implications for interventional cardiologists who treat diabetic patients with only either FFR or IVUS available.
As has been shown in previous studies71819, the IVUS group had a higher PCI rate and more prescription of dual antiplatelet agents than the FFR group, regardless of the presence of diabetes in the present study. Nevertheless, there were no significant differences in MACE or TVF between FFR and IVUS guidance according to the presence of diabetes. This was also consistent in the subgroups of patients who received medical treatment with deferred PCI and those who underwent PCI. This infers that, other than the higher usage of stents in the IVUS group, IVUS guidance is not associated with a higher clinical event rate, i.e., restenosis. A longer follow-up may be needed to compare the impact of the additional PCI in the IVUS group. This may increase the number of deferred lesions treated by FFR guidance, which would otherwise have been treated by IVUS guidance, and vice versa.
From the secondary outcome analysis of the subgroup who underwent PCI in our study, the TVR rate was higher in the FFR group compared with the IVUS group, with a marginal interaction observed only in non-diabetic patients. A similar trend was shown in previous subgroup analyses of large randomised clinical trials. These studies reported that imaging-guided PCI led to a lower risk of clinical events compared to angiography guidance in non-diabetic patients, but not in diabetic patients56. Considering all of these results together, it might suggest that imaging-guided stent optimisation of culprit vessel PCI is more important in patients with low plaque burden and focal lesions (e.g., non-diabetic patients) than in patients with high plaque burden and diffuse lesions (e.g., diabetic patients). However, we acknowledge that this is a hypothesis that needs to be proven by future studies with larger sample sizes.
In patients who received medical treatment with deferred PCI by FFR or IVUS guidance, diabetes is well known to be a poor prognostic factor of adverse clinical outcomes142021. The COMBINE OCT-FFR trial showed that TCFA was detected in 25% of FFR-negative lesions in diabetic patients which were associated with a 5-fold higher risk of MACE despite the absence of ischaemia15. Furthermore, a recent study showed that anatomical-functional discordance of intermediate coronary artery stenosis assessed by IVUS and QFR is more exacerbated in patients with diabetes than in non-diabetic patients22. Although our data showed no difference in clinical outcomes between the FFR group and the IVUS group in diabetic patients, a combined use of physiology and imaging guidance for PCI might be needed for improving clinical outcomes in diabetic patients. Further larger studies might be able to determine the optimal role of FFR and IVUS evaluation in CAD patients with diabetes, especially in high-risk populations.
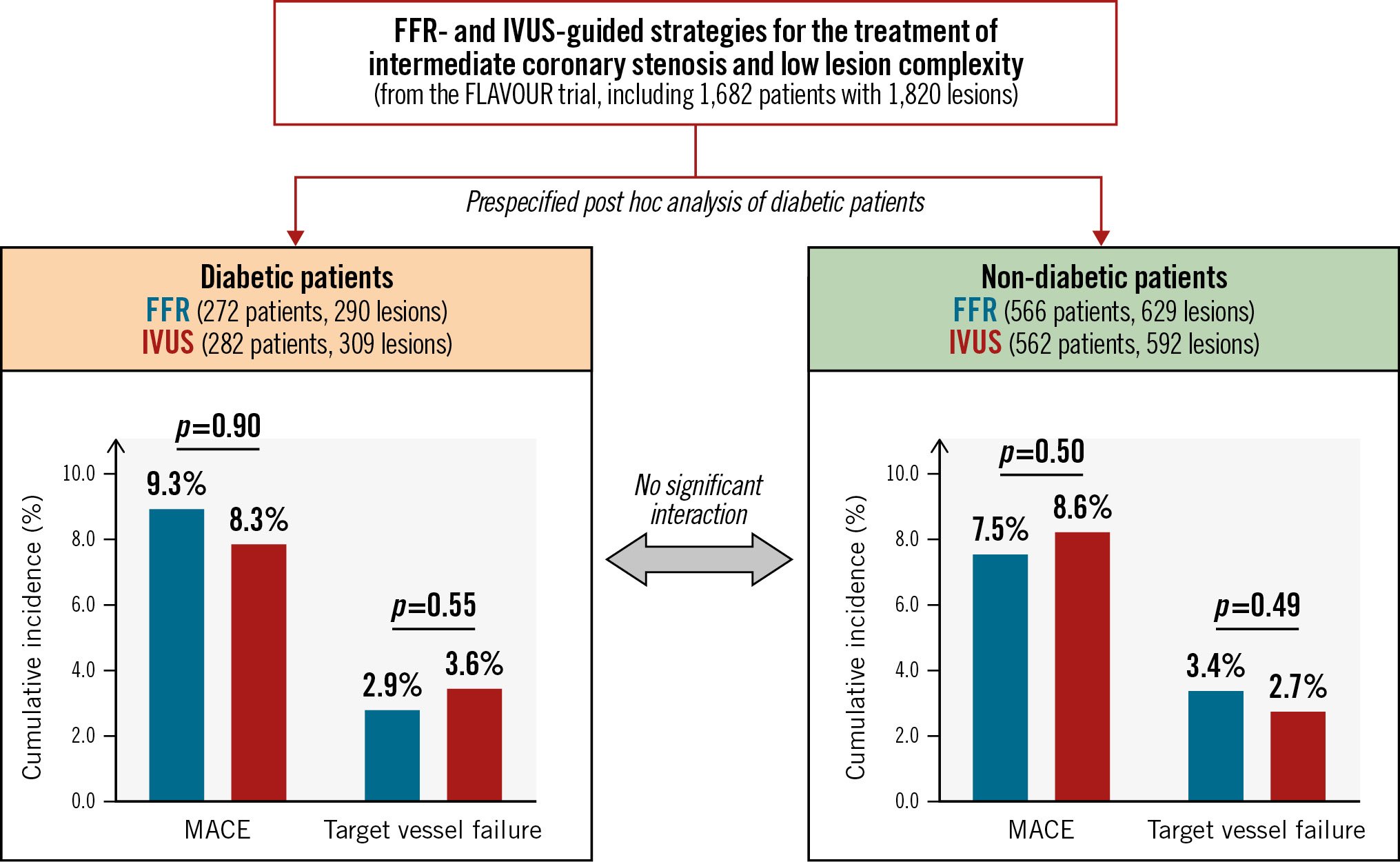
Central illustration. Clinical outcomes between the FFR- and IVUS-guided strategies based on the presence of diabetes. In the patients with intermediate coronary stenosis and low lesion complexity, there were no significant differences in MACE or target vessel failure between the FFR- and IVUS-guided strategies in either diabetic or non-diabetic patients. FFR: fractional flow reserve; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; MACE: major adverse cardiac events
Limitations
A few limitations should be noted in our study. First, since the FLAVOUR trial was designed to show non-inferiority, the sample size was limited, and a post hoc analysis is likely to lack power for revealing any significant findings different from the original trial. Specifically, event rates, such as for revascularisation and stent thrombosis, were lower. However, we focused on the subtle findings that could give physicians insight on evaluating intermediate lesions in patients with diabetes. Second, although diabetes is a high-risk feature which presents as complex CAD, the FLAVOUR trial population included low-risk patients with intermediate coronary artery stenosis, indicating anatomically low lesion complexity7. Therefore, the results for FFR and IVUS usage may not be extended to the evaluation of higher-risk complex CAD. Finally, detailed data regarding diabetes type − such as insulin dependency, duration of diabetes, class and dose of oral hypoglycaemic agents, and the level of glycated haemoglobin − were lacking, all of which might have provided further helpful information.
Conclusions
In patients with intermediate coronary artery stenosis and low lesion complexity, FFR guidance had no significant differences in MACE or TVF, with a lower frequency of stent implantation compared with IVUS guidance regardless of the presence of diabetes.
Impact on daily practice
Despite the improvement in clinical outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in the contemporary era, diabetes remains an independent predictor of major adverse cardiac events (MACE). In patients with intermediate coronary artery stenosis and low lesion complexity, regardless of diabetic status, fractional flow reserve (FFR) guidance had no significant differences in MACE or target vessel failure with a lower frequency of PCI compared with intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) guidance. Our results suggest that it is feasible to use any one of these strategies to guide PCI regardless of the presence of diabetes. In particular, our data might have prompt real-world implications for interventional cardiologists who treat diabetic patients with only either FFR or IVUS available.
Funding
The FLAVOUR trial was funded by Boston Scientific. It was also supported by grants from the Patient-Centered Clinical Research Coordinating Center (HI19C0481 and HC19C0305) funded by the Ministry of Health &Welfare and from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (RS-2023-00215667), Republic of Korea. The study funders had no role in trial design, data collection, analysis and interpretation, or writing of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
B.-K. Koo received institutional research grants from Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Philips. J.-Y. Hahn received institutional research grants from Abbott, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Daiichi Sankyo, Medtronic, and the National Evidence-Based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea. C.-W. Nam received an institutional research grant from Abbott. The other authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to the submitted work to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

