Abstract
Background: Safe deferral of revascularisation is a key aspect of physiology-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). While recent evidence gathered in the FAVOR III Europe trial showed that quantitative flow ratio (QFR) guidance did not meet non-inferiority to fractional flow reserve (FFR) guidance, it remains unknown if QFR might have a specific value in revascularisation deferral.
Aims: We aimed to evaluate the safety of coronary revascularisation deferral based on QFR as compared with FFR.
Methods: Patients randomised in the FAVOR III trial in whom PCI was deferred in at least one coronary artery, based on QFR or FFR>0.80, were included in the present substudy. The primary outcome was the 1-year rate of major adverse cardiac events (MACE), with results reported for two subsets of deferred patients: (1) any study lesion deferral and (2) complete study lesion deferral.
Results: A total of 523 patients (55.2%) in the QFR group and 599 patients (65.3%) in the FFR group had at least one coronary revascularisation deferral. Of these, 433 patients (82.8%) and 511 (85.3%) patients, respectively, had complete study lesion deferral. In the “complete study lesion deferral” patient group, the occurrence of MACE was significantly higher in QFR-deferred patients as compared with FFR-deferred patients (24 [5.6%] vs 14 [2.8%], adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 2.07, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.07-4.03; p=0.03). In the subgroup of “any study lesion deferral”, the MACE rate was 5.6% vs 3.6% (QFR vs FFR), adjusted HR 1.55, 95% CI: 0.88-2.73; p=0.13.
Conclusions: QFR-based deferral of coronary artery revascularisation resulted in a higher incidence of 1-year MACE as compared with FFR-based deferral.
A functional evaluation is recommended for revascularisation decision-making in intermediate coronary artery stenosis1. Over the last 25 years, functional evaluations have been performed using intracoronary pressure-based indices like fractional flow reserve (FFR)23 and non-hyperaemic pressure ratios45. In the quest for increased implementation of physiology-guided coronary revascularisation, several new angiography-based modalities for FFR computation have been developed6. The attractiveness of these new angiography-based modalities stems from not requiring dedicated guidewires, avoiding coronary instrumentation, and improving the diagnostic workflow with the possibility of offline analyses of previously acquired angiograms.
Quantitative flow ratio (QFR) is the angiography-based modality for FFR estimation with the most evidence available, including two randomised clinical outcomes trials78. Based on early favourable validation studies9101112 and the randomised FAVOR III China trial reporting the superiority of QFR as compared with angiography alone7, recent European clinical practice guidelines endorsed QFR for guiding the decision to revascularise intermediate coronary stenosis1. Yet the subsequently published randomised FAVOR III Europe trial showed that a QFR-guided strategy did not meet non-inferiority to FFR with respect to major adverse cardiac events (MACE)8.
A large part of the clinical benefit derived from physiology-based revascularisation results from the avoidance of unneeded coronary interventions. The safety of physiology-based revascularisation deferral strategies is well established for wire-based indices1314 but is unknown for QFR. Previous studies on QFR reported a high negative predictive value91011, suggesting that QFR may be a valuable tool for revascularisation deferral. Thus, the aim of this subanalysis of the FAVOR III Europe trial was to evaluate the safety of revascularisation deferral based on QFR as compared with FFR.
Methods
Study design
The FAVOR III Europe trial design (Supplementary Appendix 1) has been described in detail elsewhere15. In brief, the FAVOR III Europe trial was an investigator-driven randomised, multicentre, open-label, controlled trial conducted at 34 European centres. The trial was approved by The Central Jutland Committees on Health Research Ethics and by the national or local ethics committees for the participating sites. The present study constitutes a post hoc subanalysis of the FAVOR III Europe trial, its main objective being to compare clinical outcomes following deferral by QFR to those following deferral by FFR.
Study population
A total of 2,000 patients presenting with either (1) chronic coronary syndrome (CCS) or (2) acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and an indication for invasive coronary angiography (ICA) were enrolled in the FAVOR III Europe trial. All patients had at least one intermediate non-culprit coronary stenosis (40-90% diameter stenosis [DS] by visual estimate) with an indication for physiology-guided revascularisation. The complete list of inclusion and exclusion criteria was published previously15. All patients provided written informed consent. Patients were randomised 1:1 to either a QFR-guided or an FFR-guided diagnostic strategy, aiming for full revascularisation. Revascularisation was deferred if QFR or FFR was>0.80. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) was performed if QFR or FFR was ≤0.80.
Only patients with successful QFR or FFR measurements with respect to allocation were included in this substudy. Patients in whom the revascularisation approach was not aligned with the results of the QFR or FFR measurements were excluded from our analysis. Deferred patients were categorised in two groups: (1) “any study lesion deferral”, where at least one study lesion was deferred based on QFR or FFR, and (2) “complete study lesion deferral”, where all study lesions were deferred based on QFR or FFR. A study lesion was defined as any intermediate lesion (40-90% DS) measured by QFR or FFR. Both groups included patients with revascularisation of angiographically severe stenosis (>90% diameter stenosis) which had not been assessed by QFR or FFR. Analysis of patients with complete deferral by QFR and FFR and with no treatment of stenosis >90% DS is presented in Supplementary Appendix 2 and Supplementary Table 1. Please see Figure 1 for the patient flowchart.
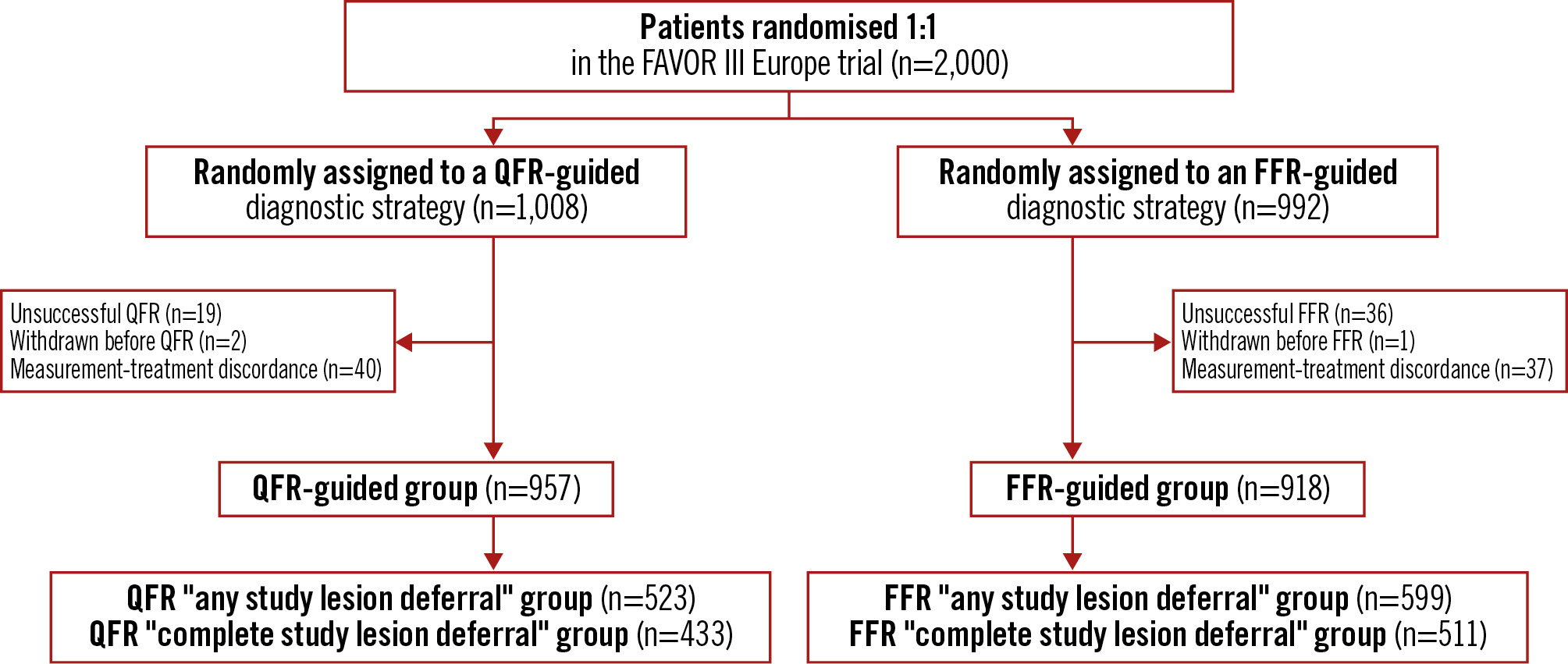
Figure 1. Patient flowchart. A total of 2,000 patients were enrolled in the FAVOR III Europe trial and randomised 1:1 to a QFR-guided strategy or an FFR-guided strategy. The “any study lesion deferral” group comprises patients with deferral of at least one study lesion based on QFR or FFR. The “complete study lesion deferral” group comprises patients with deferral of all study lesions based on QFR or FFR. FFR: fractional flow reserve; QFR: quantitative flow ratio
Procedures
QFR was performed using the Medis Suite application QAngio XA 3D QFR analysis solution (V. 2.0; Medis Medical Imaging). Medical staff performing QFR study analysis were required to (1) complete certification by the QFR vendor and (2) perform study-specific training exceeding the vendor’s requirements, as described previously15. Additionally, feedback on QFR study analyses was provided case by case throughout enrolment. Measurement of FFR was performed according to clinical recommendations. For both QFR and FFR, the prespecified threshold for revascularisation deferral was>0.80.
Endpoints
The main endpoint of the present substudy was the 1-year rate of MACE, defined as all-cause death, myocardial infarction (MI) or unplanned coronary revascularisation. Secondary endpoints included the individual components of MACE, target vessel failure (TVF), subclassifications of MI, and revascularisation at 1 year. All events are reported for both the “any study lesion deferral” group and the “complete study lesion deferral” group. Clinical outcomes after deferral based on a “grey zone” approach were explored for patients with QFR>0.85 and were compared with deferred patients in the FFR group according to standard clinical practice.
Statistical analysis
Baseline and procedural characteristics for the deferred population are reported as mean±standard deviation or median and interquartile range for continuous variables, and numbers (percentages) for categorical variables. Continuous variables were compared by the 2-sample t-test or Mann-Whitney U test if data followed a non-normal distribution. Categorical variables were compared using the χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test if any cell numbers were small.
For the main endpoint (MACE) and other clinical endpoints, 1-year Kaplan-Meier estimates, hazard ratios (HRs), and 95% 2-sided confidence intervals (CIs) based on Cox analysis are reported. For the primary endpoint, cumulative hazard curves are presented. In addition, adjusted HRs were calculated using a multivariable Cox model. Adjustment was performed for the following baseline characteristics: age, sex, body mass index, clinical presentation (CCS vs ACS), number of diseased vessels, number of study lesions, diabetes, treatment for hypertension, treatment for hyperlipidaemia, smoking status and previous PCI. Only the significant variables were retained in the final models. Both unadjusted and adjusted results are presented in the tables, while adjusted HRs are presented throughout the text. Proportional hazards assumption was assessed using log-log plots and plots of observed versus predicted values. Participants who withdrew consent before 1 year were censored from the date of withdrawal or latest contact before withdrawal. All analyses were performed using Stata software, version 18 (StataCorp).
Results
Study population
A total of 2,000 patients were enrolled in the FAVOR III Europe trial, with 1,008 assigned to QFR guidance and 992 to FFR guidance. Among these, 987 patients (97.9%) in the QFR group and 955 patients (96.3%) in the FFR group had measurements acquired successfully for QFR or FFR, and 77 patients (40 in the QFR group and 37 in the FFR group) could not be assessed for the subanalysis as the revascularisation approach was not aligned with the diagnostic result. Overall, the median QFR value was lower than the median FFR value, resulting in a more frequent occurrence of revascularisation deferral in patients allocated to FFR guidance. This resulted in a more than 15% absolute difference in group size for the “any study lesion deferral” group, with 523 patients (55.2%) in the QFR-based deferral group and 599 (65.3%) patients in the FFR-based deferral group. Of these patients, 84% were included in the “complete study lesion deferral” group, comprising 433 patients (82.8%) with QFR-based deferral and 511 patients (85.3%) with FFR-based deferral of all study lesions. Baseline characteristics of FFR- and QFR-based deferral categories are listed in Table 1.
No major differences in patient characteristics were found between the QFR and FFR groups, including sex, age, presence of risk factors or previous PCI. Likewise, the percentage of patients with recent or current ACS was similar in the QFR- and FFR-based deferral groups.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of deferred patients.
| Characteristics | Any study lesion deferral | Complete study lesion deferral | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QFR group (n=523) | FFR group (n=599) | p-value | QFR group (N=433) | FFR group (N=511) | p-value | |
| Age, years | 66.0±10.3 | 66.4±10.4 | 0.58 | 65.7±10.4 | 66.6±10.5 | 0.21 |
| Female | 120 (22.9) | 163 (27.2) | 0.10 | 105 (24.2) | 142 (27.8) | 0.22 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 27.9±4.5 | 27.6±4.5 | 0.23 | 28.1±4.5 | 27.5±4.6 | 0.074 |
| Diabetes | 131 (25.0) | 146 (24.5) | 0.83 | 107 (24.7) | 121 (23.8) | 0.75 |
| Current smoker | 138 (27.6) | 161 (28.2) | 0.75 | 109 (26.3) | 136 (28.0) | 0.58 |
| Antihypertensive treatment | 415 (79.3) | 451 (75.5) | 0.13 | 343 (79.2) | 385 (75.6) | 0.19 |
| Statin treatment | 379 (72.6) | 432 (72.1) | 0.86 | 309 (71.5) | 365 (71.4) | 0.97 |
| Family history of IHD | 161 (32.2) | 166 (29.6) | 0.36 | 129 (31.1) | 140 (29.5) | 0.62 |
| History of PCI | 241 (46.3) | 296 (49.4) | 0.31 | 196 (45.6) | 247 (48.3) | 0.40 |
| History of CABG | 2 (0.4) | 3 (0.5) | 0.77 | 1 (0.2) | 3 (0.6) | 0.41 |
| Angina CCS class* | 0.37 | 0.40 | ||||
| 0 | 138 (26.6) | 172 (29.4) | 112 (26.0) | 146 (29.1) | ||
| I | 180 (34.7) | 188 (32.1) | 157 (36.4) | 165 (32.9) | ||
| II | 157 (30.3) | 170 (29.1) | 127 (29.5) | 149 (29.7) | ||
| III | 31 (6.0) | 30 (5.1) | 24 (5.6) | 21 (4.2) | ||
| IV | 13 (2.5) | 25 (4.3) | 11 (2.6) | 20 (4.0) | ||
| Clinical indication | 0.28 | 0.43 | ||||
| Chronic coronary syndrome | 352 (69.2) | 373 (64.6) | 292 (69.2) | 320 (65.2) | ||
| Secondary evaluation after NSTEMI or STEMI | 116 (22.8) | 149 (25.8) | 92 (21.8) | 122 (24.8) | ||
| NSTEMI at randomisation | 41 (8.1) | 55 (9.5) | 38 (9.0) | 49 (10.0) | ||
| Number of diseased vessels | 0.28 | 0.19 | ||||
| 1 | 250 (47.8) | 314 (52.4) | 246 (56.8) | 310 (60.7) | ||
| 2 | 205 (39.2) | 218 (36.4) | 147 (33.9) | 169 (33.1) | ||
| 3 | 68 (13.0) | 67 (11.2) | 40 (9.2) | 32 (6.3) | ||
| Values are n (%) or mean±standard deviation. *Angina CCS class: the CCS grading of angina pectoris: 0: no angina; 1: angina only with strenuous activity; 2: angina with moderate exertion; 3: angina with mild exertion; 4: angina at rest. BMI: body mass index; CABG: coronary artery bypass grafting; CCS: Canadian Cardiovascular Society; FFR: fractional flow reserve; IHD: ischaemic heart disease; NSTEMI: non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; QFR: quantitative flow ratio; STEMI: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction | ||||||
Procedural characteristics
Procedural characteristics are found in Table 2. Of all the intermediate study lesions measured in the “any study lesion deferral” group, 625 lesions (86.8%) were deferred in the QFR-based deferral group and 722 (88.2%) lesions were deferred in the FFR-based deferral group. The location of deferred lesions differed between the groups, with more right coronary artery lesions and fewer circumflex coronary artery/obtuse marginal branch lesions being deferred by QFR. More patients in the FFR-deferred groups had no stent implantation (as in >90% DS lesions and/or measured study lesions), with the difference being statistically significant in the “any study lesion deferral” group. The total procedure time, fluoroscopy time and use of contrast were lower with the QFR diagnostic strategy, despite more stent implantations.
Table 2. Procedural characteristics.
| Any study lesion deferral | Complete study lesion deferral | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QFR group (n=523) | FFR group (n=599) | p-value | QFR group (N=433) | FFR group (N=511) | p-value | |
| Total no. of study lesions | 720 | 819 | NA | 514 | 611 | NA |
| Total no. of study lesions per patient† | 1.69±0.81 | 1.68±0.83 | 0.76 | 1.21±0.49 | 1.22±0.48 | 0.73 |
| Number of lesions deferred by QFR or FFR | 625/720 (86.8) | 722/819 (88.2) | 0.42 | 514/514 (100) | 611/611 (100) | 1.00 |
| Number of lesions deferred by QFR or FFR per patient† | 1.41±0.67 | 1.39±0.67 | 0.67 | 1.21±0.49 | 1.22±0.48 | 0.73 |
| Vessel type for deferred lesions* | ||||||
| LAD and diagonal branches | 258 (41.3) | 292 (40.3) | 0.72 | 226 (44.0) | 274 (44.8) | 0.77 |
| RCA | 211 (33.8) | 200 (27.7) | 0.016 | 172 (33.5) | 167 (27.3) | 0.0018 |
| Cx and OM branches | 147 (23.5) | 218 (30.2) | 0.006 | 111 (21.6) | 161 (26.4) | 0.064 |
| IB | 9 (1.4) | 13 (1.8) | 0.60 | 5 (1.0) | 9 (1.5) | 0.45 |
| FFR or QFR measured in deferred lesions* | 0.90 [0.85, 0.93] | 0.89 [0.85, 0.92] | 0.003 | 0.90 [0.85, 0.93] | 0.89 [0.84, 0.93] | 0.006 |
| Revascularisation of study lesion(s) with 40-90% DS | 90 (17.2) | 88 (14.7) | 0.25 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NA |
| Revascularisation of lesion(s) with >90% DS | 124 (23.7) | 130 (21.7) | 0.42 | 115 (26.8) | 116 (22.7) | 0.15 |
| Total number of stents implanted per patient† | 0.64±0.95 | 0.55±0.93 | 0.03 | 0.41±0.78 | 0.35±0.77 | 0.08 |
| Total procedure time, minutes | 41 [26, 60] | 45 [30, 60] | 0.071 | 38 [24, 55] | 41 [27, 59] | 0.010 |
| Total fluoroscopy time, minutes | 7 [3.2, 13] | 9.3 [5.3, 15] | <0.001 | 5.8 [3, 11] | 8 [5, 13] | <0.001 |
| Total contrast use, mL | 100 [65, 160] | 110 [72, 170] | 0.074 | 90 [60, 140] | 100 [70, 150] | 0.003 |
| Values are presented as n (%), n/N (%), mean±SD, or median [IQR]. *Lesion-level analysis. †Non-normal distribution. Means and standard deviations are provided, but the variables were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test. Cx: circumflex coronary artery; DS: diameter stenosis; FFR: fractional flow reserve; IB: intermediate branch; IQR: interquartile range; LAD: left anterior descending artery; NA: not applicable; OM: obtuse marginal artery; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; QFR: quantitative flow ratio; RCA: right coronary artery; SD: standard deviation | ||||||
Clinical outcomes
Main outcomes
In the “complete study lesion deferral” group, MACE occurred in 24 patients (5.6%) in the QFR group and in 14 patients (2.8%) in the FFR group (adjusted HR 2.07, 95% CI: 1.07-4.03; p=0.03) at 1 year.
In the “any study lesion deferral” group, MACE occurred in 29 patients (5.6%) in the QFR group and in 21 patients (3.6%) in the FFR group (adjusted HR 1.55, 95% CI: 0.88-2.73; p=0.13) at 1 year. Cumulative incidence curves for both groups are presented in the Central illustration.
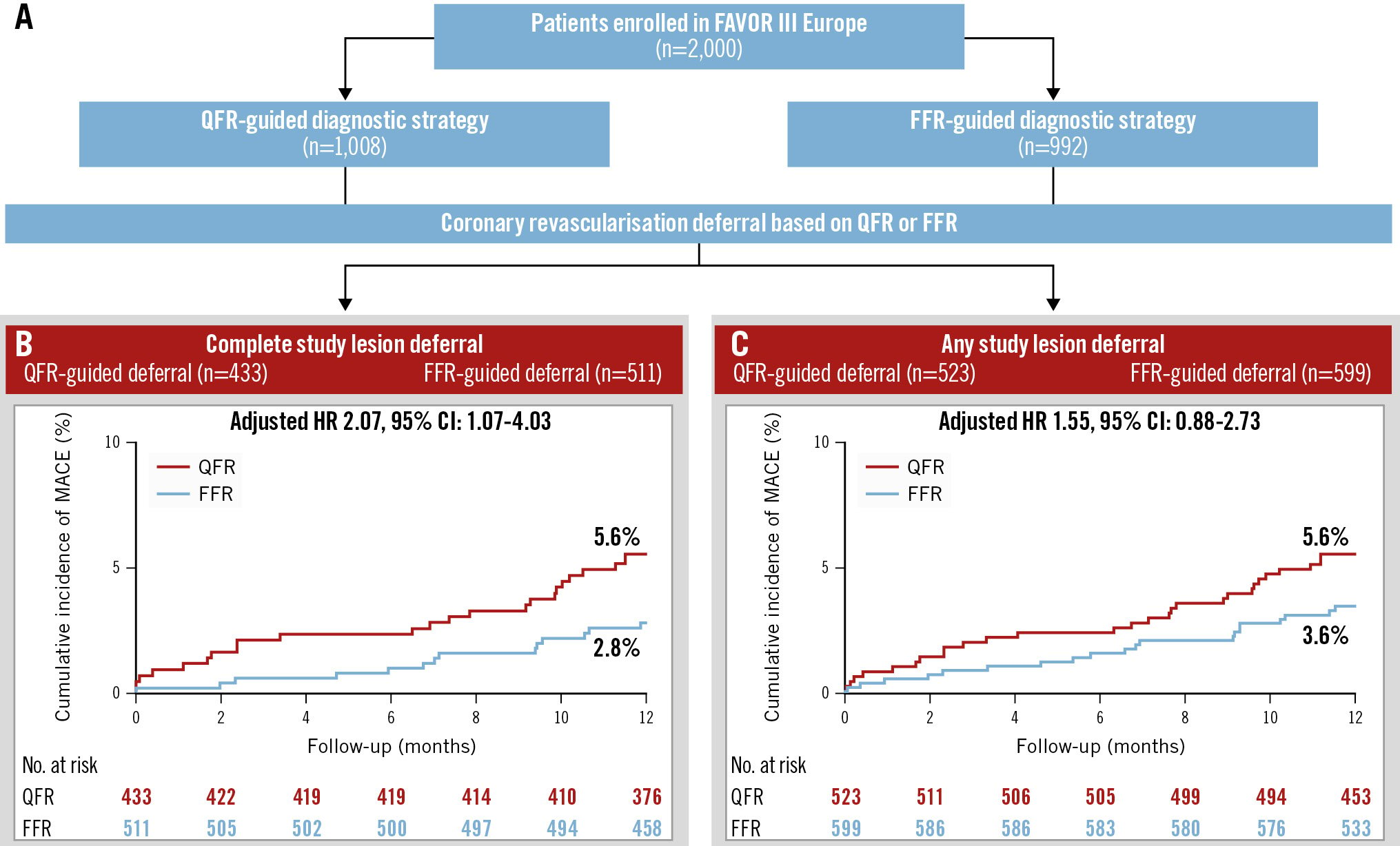
Central illustration. A FAVOR III Europe substudy: clinical outcomes of patients deferred by QFR or FFR. Patients enrolled in the FAVOR III Europe trial with coronary revascularisation deferral based on QFR or FFR were included. Results are reported for the following two groups: (1) any study lesion deferral: at least one intermediate coronary stenosis deferred by QFR or FFR; (2) complete study lesion deferral: all intermediate coronary stenosis deferred by QFR or FFR. Baseline characteristics were similar between the QFR and FFR groups, with 25% of patients being female, 65% presenting with chronic coronary syndrome, and 50% in the “any study lesion deferral” group and 59% in the “complete study lesion deferral” group having single-vessel disease. CI: confidence interval; FFR: fractional flow reserve; HR: hazard ratio; MACE: major adverse cardiac events; QFR: quantitative flow ratio
Secondary endpoints
The HRs for the individual components of MACE and other secondary clinical endpoints can be found in Table 3 and Table 4. Unplanned revascularisation was the biggest contributor to the total MACE rate, both numerically and in terms of driving a difference between QFR- and FFR-deferred groups (any study lesion deferral: 19 [3.7%] vs 14 [2.4%], adjusted HR 1.52, 95% CI: 0.76-3.04; p=0.23; complete study lesion deferral: 17 [4.0%] vs 9 [1.8%], adjusted HR 2.21, 95% CI: 0.98-4.96; p=0.06).
In the “complete study lesion deferral” group, the rate of TVF that was definitely or possibly related to a vessel with deferred treatment of a stenosis was significantly higher following QFR-based deferral as compared with FFR: 16 (3.7%) versus 9 (1.8%), adjusted HR 2.27, 95% CI: 1.00-5.16; p=0.049. The direction of all other secondary clinical endpoints supported the main results.
All primary and secondary clinical endpoints were calculated for a third deferral group including patients with complete deferral of both study lesions and >90% DS lesions. The results support our findings in favour of FFR-based deferral (Supplementary Table 1).
Table 3. Hazard ratios for clinical endpoints at 1 year – “any study lesion deferral” group.
| Total (n=1,122) | QFR-based deferral (n=523) | FFR-based deferral (n=599) | Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI) |
p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MACE | 50 | 29 (5.6) | 21 (3.6) | 1.60 (0.91-2.80) | 1.55 (0.88-2.73) | 0.13 |
| All-cause death | 12 | 7 (1.4) | 5 (0.9) | 1.61 (0.51-5.06) | 1.71 (0.54-5.39) | 0.36 |
| Any MI | 22 | 12 (2.3) | 10 (1.7) | 1.38 (0.60-3.20) | 1.41 (0.61-3.27) | 0.42 |
| Any unplanned revascularisation | 33 | 19 (3.7) | 14 (2.4) | 1.57 (0.79-3.13) | 1.52 (0.76-3.04) | 0.23 |
| Cardiac death | 9 | 5 (1.0) | 4 (0.7) | 1.43 (0.38-5.34) | 1.43 (0.38-5.34) | 0.59 |
| TVMI | 21 | 11 (2.1) | 10 (1.7) | 1.27 (0.54-2.98) | 1.29 (0.55-3.05) | 0.56 |
| TVF | 40 | 21 (4.1) | 19 (3.2) | 1.27 (0.69-2.37) | 1.29 (0.69-2.40) | 0.42 |
| TVF – study vessels only | 34 | 19 (3.7) | 15 (2.5) | 1.46 (0.74-2.87) | 1.46 (0.74-2.88) | 0.27 |
| Spontaneous MI with confirmed origin in deferred vessel | 7 | 5 (1.0) | 2 (0.3) | 2.87 (0.56-14.79) | 2.87 (0.56-14.79) | 0.21 |
| Unplanned revascularisation of deferred lesions | 17 | 10 (2.0) | 7 (1.2) | 1.64 (0.62-4.31) | 1.64 (0.62-4.31) | 0.32 |
| Numbers are presented as Kaplan-Meier estimates (%). *The reported p-values are for the adjusted HR results. TVMI includes MI related to any target vessel, including all vessels with measured study lesions, vessels with treated >90% DS lesions, and MI of unknown coronary vessel origin as per regular endpoint definitions 30. TVF is a composite of cardiac death, TVMI or TVR. Target vessels include all measured study lesions and treated >90% DS lesions. MI or revascularisation of unknown coronary vessel origin was also included as per regular endpoint definitions30. “TVF – study lesions only” is defined as per TVF above but only includes measured study lesions as target vessels, excluding treated >90% DS lesions. MI and revascularisation of unknown coronary vessel origin were also included per regular endpoint definitions 30. CI: confidence interval; DS: diameter stenosis; FFR: fractional flow reserve; HR: hazard ratio; MACE: major adverse cardiac events; MI: myocardial infarction; QFR: quantitative flow ratio; TVF: target vessel failure; TVMI: target vessel myocardial infarction; TVR: target vessel revascularisation | ||||||
Table 4. Hazard ratios for clinical endpoints at 1 year – “complete study lesion deferral” group.
| Total (N=944) |
QFR-based deferral (N=433) | FFR-based deferral (N=511) |
Unadjusted HR |
Adjusted HR (95% CI) |
p-value* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MACE | 38 | 24 (5.6) | 14 (2.8) | 2.05 (1.06-3.97) | 2.07 (1.07-4.03) | 0.03 |
| All-cause death | 9 | 5 (1.2) | 4 (0.8) | 1.47 (0.40-5.48) | 1.47 (0.40-5.48) | 0.56 |
| Any MI | 17 | 10 (2.3) | 7 (1.4) | 1.69 (0.65-4.45) | 1.67 (0.64-4.39) | 0.30 |
| Any unplanned revascularisation | 26 | 17 (4.0) | 9 (1.8) | 2.26 (1.01-5.06) | 2.21 (0.98-4.96) | 0.06 |
| Cardiac death | 7 | 4 (0.9) | 3 (0.6) | 1.57 (0.35-7.02) | 1.57 (0.35-7.02) | 0.55 |
| TVMI | 16 | 9 (2.1) | 7 (1.4) | 1.52 (0.57-4.09) | 1.50 (0.56-4.03) | 0.42 |
| TVF | 30 | 18 (4.2) | 12 (3.4) | 1.79 (0.86-3.71) | 1.84 (0.89-3.83) | 0.10 |
| TVF – study vessels only | 25 | 16 (3.7) | 9 (1.8) | 2.12 (0.93-4.79) | 2.27 (1.00-5.16) | 0.049 |
| Spontaneous MI with confirmed origin in deferred vessel | 5 | 4 (0.9) | 1 (0.2) | 4.74 (0.53-42.39) | 4.74 (0.53-42.39) | 0.16 |
| Unplanned revascularisation of deferred lesions | 13 | 9 (2.1) | 4 (0.8) | 2.67 (0.82-8.66) | 2.67 (0.82-8.66) | 0.10 |
| Numbers are presented as Kaplan-Meier estimates (%). *The reported p-values are for the adjusted HR results. TVMI includes MI related to any target vessel, including all vessels with measured study lesions, vessels with treated >90% DS lesions, and MI of unknown coronary vessel origin per regular endpoint definitions 30. TVF is a composite of cardiac death, TVMI or TVR. Target vessels include all measured study lesions and treated >90% DS lesions. MI or revascularisation of unknown coronary vessel origin was also included per regular endpoint definitions 30. “TVF – study lesions only” is defined as TVF above but only including measured study lesions as target vessels, excluding treated >90% DS lesions. MI and revascularisation of unknown coronary vessel origin were also included per regular endpoint definitions 30. CI: confidence interval; DS: diameter stenosis; FFR: fractional flow reserve; HR: hazard ratio; MACE: major adverse cardiac events; MI: myocardial infarction; QFR: quantitative flow ratio; TVF: target vessel failure; TVMI: target vessel myocardial infarction; TVR: target vessel revascularisation | ||||||
“Grey zone” hybrid approach
Applying a 0.85 limit for deferral by QFR, the 1-year event rate for QFR versus FFR was 4.1% versus 2.8% (unadjusted HR 1.49, 95% CI: 0.71-3.13; p=0.29) in the “complete study lesion deferral” group and 3.5% versus 3.6% (unadjusted HR 0.97, 95% CI: 0.48-1.93; p=0.93) in the “any study lesion deferral” group (Figure 2).
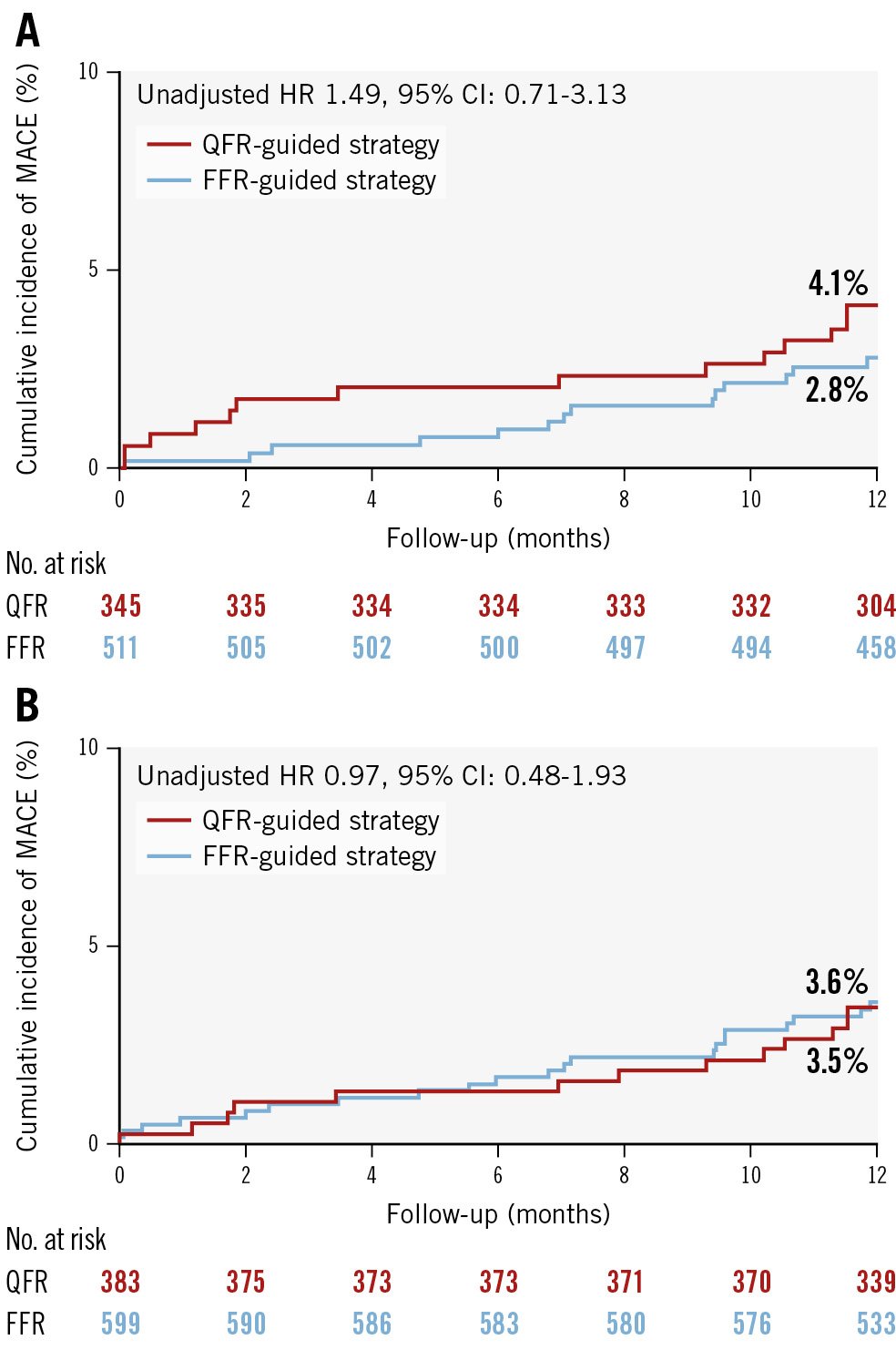
Figure 2. Cumulative incidence curve for the primary endpoint in exploratory grey zone subgroups. Cumulative incidence curves for the complete (A) and any (B) study lesion deferral groups. In this exploratory grey zone subanalysis, QFR deferral was restricted to patients deferred based on QFR values outside of the grey zone (QFR >0.85). The FFR group remains unchanged and includes deferral by FFR based on the usual cutoff value of FFR >0.80, as per standard clinical practice. CI: confidence interval; FFR: fractional flow reserve; HR: hazard ratio; MACE: major adverse cardiac events; QFR: quantitative flow ratio
Discussion
The main conclusion of this FAVOR III Europe substudy is that QFR-guided deferral of intermediate coronary stenoses was associated with more major adverse cardiac events at 1 year, especially in terms of unplanned revascularisations, than FFR-guided deferral.
Why is safety of deferral important?
Safety of revascularisation deferral is a cornerstone in physiology-guided PCI. Previous studies on FFR and instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR) have shown that physiology-guided PCI results in fewer lesions being treated than with angiography-guided PCI34513. In addition, results from large registries also support the safety of PCI deferral by FFR1617 and iFR18. A large study combining the DEFINE-FLAIR and iFR-SWEDEHEART populations demonstrated that revascularisation deferral of intermediate lesions was equally safe based on iFR and FFR guidance at one year14. Long-term follow-up data from each of the major iFR trials did not report any safety concerns in the deferred populations1920. All this supports the concept that physiology serves as a gatekeeper for necessary coronary revascularisation, sparing the consequences of unneeded interventions.
Quantitative flow ratio
The results of the present research may seem counterintuitive, considering the evidence accumulated prior to the FAVOR III Europe trial, which seemed to indicate that QFR could be used to defer coronary revascularisation safely. Firstly, using FFR as a reference, validation studies reported good diagnostic accuracy of QFR, with an especially high negative predictive value9101112, suggesting few false negatives. Secondly, in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease, the functional SYNTAX score based on QFR or FFR resulted in substantial agreement in terms of Heart Team treatment recommendations21, results which were later supported by findings in the DECISION QFR trial22. Finally, in the FAVOR III China trial, the superiority of QFR guidance over angiography guidance seemed to be linked to a lower number of lesions treated in the QFR arm7.
Despite this, in the FAVOR III Europe trial, deferral of revascularisation with QFR led to higher MACE rates than deferral by FFR8. While the direction of our findings was similar for both the “any study lesion deferral” and “complete study lesion deferral” groups, more pronounced differences were seen in the “complete study lesion deferral” group, suggesting an additive effect of more deferrals in one patient. The main endpoint results were supported by the directional findings of target vessel failure, also in favour of deferral by FFR. When evaluating a QFR-guided revascularisation strategy we must remember that, in some patients with multivessel disease, QFR was used simultaneously for setting the indication for revascularisation in one vessel while supporting deferral in another (vessel), based on the QFR values. As QFR values were overall lower than FFR values and, therefore, more lesions were treated following QFR guidance, a higher number of lesions were treated in patients with at least one QFR-based deferral (Table 2). The question might arise regarding whether this excess of revascularisation in the QFR arm might account for the observed worse patient outcomes, thus interfering with the main objective of this subanalysis, namely assessing the safety of PCI deferral. Yet, as shown in Table 4, patients in whom QFR led to PCI deferral in all interrogated lesions, therefore being free of this potential interference, showed higher rates of TVF of deferred lesions than equivalent ones in the FFR arm. This supports the concept that revascularisation deferral was not as safe when QFR was used for decision-making. The differences in favour of FFR were consistent across deferral categories and vessel-related outcomes, supporting the concern that excess events in the QFR group are caused by clinically relevant false negative measurements.
We explored the outcomes of a hybrid “grey zone” strategy with deferral based on a QFR threshold that ensures a high negative predictive value. This approach was applied to iFR in the past, before trials showed equipoise with FFR23. With an increased 5-year mortality rate in iFR-guided patients receiving revascularisation, this discussion may yet again be relevant for iFR, which still seems to be a safe tool for deferral2024. As for QFR, a hybrid approach was suggested after early positive results in paired comparisons with FFR. As cutoff values from 0.83-0.87 have been proposed for deferral by QFR1225, the exploratory analysis in FAVOR III Europe was performed with the originally defined limit of 0.85262728. No definitive conclusions were derived from this exploratory subanalysis of a hybrid QFR-FFR strategy. Possible clinical implementation of this strategy would require further investigation.
Possible explanations
Differences in the performance of QFR and FFR may be related to the considerable differences in the nature of a pressure-wire based method and a computer-based method. The latter may be less sensitive to patient-specific changes in, for example, microcirculation29 or identification of high-risk plaque. This remains speculation and a topic for further investigation.
As most of the events, and differences in events, were caused by unplanned revascularisations, the explanation may rather simply be the poorer performance of QFR, with too many clinically relevant false negatives in a clinical, multicentre setting, and the reliance on in-procedure QFR analysis.
Limitations
This is a post hoc analysis and hence only hypothesis generating. The unbalanced deferral in the main trial increases the risk of baseline differences between groups, although baseline and procedural data appear quite similar. The low event rates, global endpoints and multiple comparisons without adjustment for multiplicity increase the risk of type I and II errors. Physicians and patients were not blinded to the allocated diagnostic strategy. As QFR was the experimental method, this may have led to more re-evaluations and subsequently more unplanned revascularisations in the QFR-deferred groups.
Conclusions
In a large, multicentre, clinical setting, QFR-based deferral of coronary artery revascularisation resulted in a higher incidence of MACE as compared with FFR-based deferral. This difference was mainly driven by unplanned revascularisations.
Impact on daily practice
The results of the current subanalysis suggest that a routine quantitative flow ratio (QFR) strategy does not provide the same safe revascularisation deferral of intermediate coronary stenosis as fractional flow reserve (FFR). Further investigation is required to determine whether a hybrid QFR-FFR approach is safe and effective. Long-term follow-up will provide a better perspective of the consequences of our findings. Core laboratory reanalysis of the FAVOR III Europe QFR and FFR data may provide additional information on whether the in-procedure QFR-based deferral was rightly indicated or was based on false negative values.
Acknowledgements
We thank physicians and hospital staff enrolling patients in the FAVOR III Europe trial, and patients accepting enrolment. Furthermore, we thank our data managers, Martin Amadeus Rahbek and Jakob Hjort, Aarhus University, Denmark, for their important contributions.
B.K. Andersen thanks the entire team at Hospital Clínico San Carlos, Madrid, Spain, for welcoming her on her research exchange stay when preparing this work for submission. B.K. Andersen thanks Aarhus University Hospital and Augustinus Fonden for their financial support of the research exchange stay in Madrid.
Funding
The FAVOR III Europe trial was funded in part by Medis Medical Imaging, the Netherlands, and Aarhus University, Denmark. Neither of them had any role in the design, conduct or reporting of the FAVOR III trial nor did they have any influence on the decision to perform the present substudy, design, data analysis, interpretation, writing of the paper, or decision to submit the paper for publication.
Conflict of interest statement
B.K. Andersen: institutional research grant from Medis Medical Imaging. N.R. Holm: institutional research grants from Abbott, B. Braun, Biosensors, Boston Scientific, and Medis Medical Imaging; and speaker fees from Abbott and EPS Vascular. A. Erriquez: educational grants from Philips, Abbott, and MLCTO; support for course participation from CoreAalst; and speaker fees from Eukon. T. Råmunddal: consultant and proctoring honoraria from Boston Scientific, EPS Vascular, and Cardirad. E.H. Christiansen: institutional research grants from Abbott, Biosensors, Meril Life Sciences, and Medis Medical Imaging; and speaker fees from Abbott and EPS Vascular. J. Escaned: personal fees as speaker and/or advisory board member from Abbott, Boston Scientific, Medis Medical Imaging, and Philips. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

