
In this issue of EuroIntervention, Harnek et al report the “Very long-term outcome of coronary covered stents”. This work, which comes from the SCAAR registry, is the largest study ever published regarding the outcome following implantation of covered stents (CS)1.
The relevant findings of the study are the following:
1) At the time of this evaluation the SCAAR registry included 197,948 patients. Among this population 256 patients were treated with 366 CS. The registry included 320,784 stenting procedures performed between 2005 and 2017. These data mean that 21 patients were treated each year with these devices. To put this another way, we can say that CS were implanted in about three patients in every 2,000 percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) performed. This first observation gives us a clear picture that coronary treatment using CS is a rare situation.
2) CS were successfully delivered in 95% of the lesions. The highest rate of successful delivery was obtained with the Papyrus stent (Biotronik, Berlin, Germany) that was successfully implanted in 90% of cases.
3) No stent thrombosis was found for the equine pericardium covered stents during the entire follow-up period.
4) Immediate and follow-up adverse events were higher for patients treated with CS when compared with patients treated with non-covered stents. However, a higher rate of mortality was observed in the CS group only within the first month of follow-up, confirming a considerable use of CS in an emergency setting. Unexplained death during the first 30 days could be probable stent thrombosis.
The main reason for implanting a CS is to treat a coronary perforation, a potentially life-threatening complication that carries a mortality rate of over 7.7%2. Moreover, emergency coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is not considered a practical and effective approach to treat coronary perforations as it is able to repair the coronary rupture in only 44% of cases3. Besides coronary ruptures, other reasons for implanting a CS stent are saphenous vein graft degeneration, thrombus-rich lesions and coronary aneurysm. However, the use of CS in these latter clinical scenarios is open to debate.
Even if the present study gives a contemporary overview on the long-term outcome of CS, the results should be analysed cautiously since the final analysis is hampered by the heterogeneous clinical indications in which CS were used. The authors do not differentiate between the outcome of patients treated with CS to manage coronary perforation and the outcome of patients in which CS were used for other relatively stable clinical indications, thus mixing two different clinical contexts. As a consequence, it is not possible to draw definite conclusions about the safety and efficacy of CS compared to drug-eluting stents because of the different clinical conditions in which they are used. The negative outcome following the implantation of CS seems to be mainly driven by the clinical context and by the unfavourable prognosis of the treated population. Moreover, the higher rate of stent thrombosis observed in CS can be the result of “external” factors occurring in emergency settings: patients with coronary perforations experience a life-threatening condition with the need for heparin reversal using protamine, discontinuation of dual antiplatelet therapy; pericardial effusion following coronary perforation generates pericardial inflammation which can trigger platelet aggregation (Figure 1). Moreover, in case of coronary perforations, CS are mostly delivered in dissected and highly diseased vessels, usually after the use of rotational atherectomy or following prolonged balloon inflation attempting to seal the perforation. All these anatomical and procedural factors can influence the correct apposition, sizing of the CS and flow dynamics in the distal coronary bed, promoting thrombosis and negatively influencing the rate of long-term patency of CS when compared with drug-eluting stents implanted in elective conditions. The one-year stent thrombosis rate of 5.5% following GRAFTMASTER® (Abbott Vascular, Santa Clara, CA, USA) implantation and the 6.8% thrombosis rate following Papyrus implantation versus the 0% thrombosis rate following equine pericardium covered stent implantation need to be contextualised. Different implant indications could have contributed to these different thrombosis rates. In addition, the better deliverability of the Papyrus stent in more complex and high-risk settings could act as a negative factor, leading operators to use this device in more extreme anatomies and conditions. As we used to say, “poor deliverability is a protection against stent thrombosis”. A previous collaborative experience reported a CS thrombosis rate of 6.2% in the context of coronary perforation4. Besides the specific setting leading to covered stent implantation, we need to take into consideration the differences in thickness of each covered stent: even if GRAFTMASTER and Papyrus are both covered by polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), we cannot dismiss the fact that the half thickness of a Papyrus stent should lead to a better and faster endothelialisation. Interestingly, the authors demonstrated that the rate of CS thrombosis was not influenced by the duration of dual antiplatelet therapy4,5.
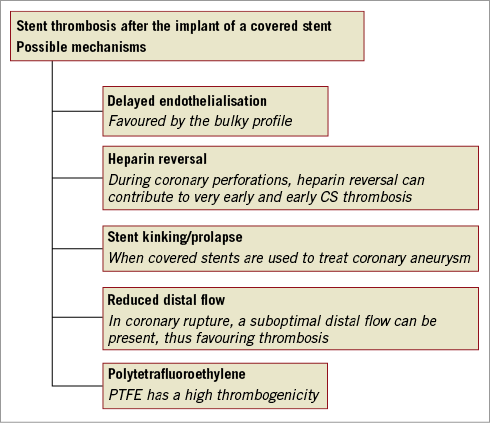
Figure 1. Possible mechanisms of covered stent thrombosis. CS: covered stents; PTFE: polytetrafluoroethylene
A novel and hypothesis-generating finding is the 0% thrombosis rate of the stent covered with equine pericardium. We can see the value of exploring the possible advantages of the low thrombosis rate of this device with dedicated studies.
While awaiting more specific data regarding the different thrombogenicity of CS devices and settings leading to implantation, we would like to deliver the following final messages:
– New-generation CS should be preferentially utilised for better deliverability and possible lower thrombogenicity.
– CS implantation to treat coronary perforations and ruptures are prime and important indications, even if affected by a high rate of adverse events.
– Elective implantation of a CS (and which device to use) should, for the moment, remain a niche indication to be carefully evaluated case by case.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

