Severe drug-eluting stent in-stent restenosis (ISR) in the left anterior descending (LAD) artery was treated with a 3.0×28 mm Absorb bioresorbable vascular scaffold (Absorb BVS; Abbott Vascular, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Seven-month scheduled angiography demonstrated no significant change with a fully patent treated LAD vessel with TIMI (Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction) 1 flow in the septal branch (Figure 1A).
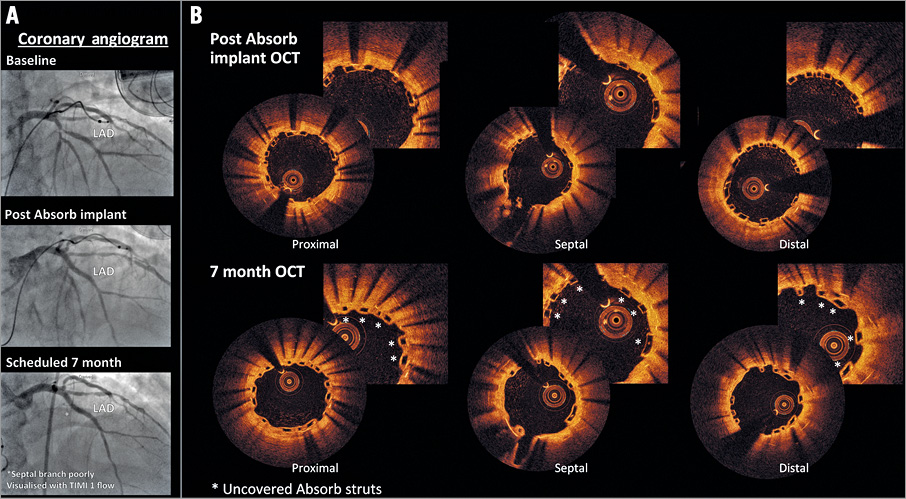
Figure 1. Baseline and seven-month coronary angiography and optical coherence tomography of drug-eluting stent-in-stent restenosis treated with the Absorb BVS.
Potential advantages of the Absorb BVS for the treatment of ISR include avoidance of multiple permanent metallic stent layers, limus-based drug elution, and allowances to treat disease beyond the stent margins.
Seven-month optical coherence tomography demonstrated incomplete healing, with a lack of a smooth luminal contour and multiple uncovered Absorb struts overlapped with metallic struts (Figure 1B). The thicker Absorb struts (156 μm), similar in thickness to first-generation drug-eluting stents, create alterations in shear stress (high shear stress on top of the strut and low shear stress behind the strut) that predisposes to a greater neointimal response and possible triggering of platelet aggregation. Furthermore, porcine studies have shown healing of overlapping Absorb BVS (strut thickness >300 microns) to be delayed at 30 days and completed at 90 days (equivalent to approximately six and 18 months in humans, respectively). In addition, the possibility of localised drug toxicity leading to delayed healing cannot be excluded: for example, most of the antiproliferative drug remains sequestered in the durable polymer of the first-generation TAXUS drug-eluting stent (Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA). Randomised trials are required to establish the potential safety and efficacy of the Absorb BVS for the treatment of ISR and the duration of dual antiplatelet therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

