
Abstract
Aims: Bioabsorbable polymer drug-eluting stents (DES) may reduce the inflammation and delayed healing associated with some permanent polymer-coated DES. Whether late clinical outcomes are improved, particularly among patients with medically treated diabetes, is unknown. Therefore, we analysed outcomes from a pre-specified substudy of the EVOLVE II trial to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the SYNERGY stent in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Methods and results: SYNERGY is a thin-strut, platinum-chromium everolimus-eluting stent with an ultra-thin bioabsorbable poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) abluminal polymer. The EVOLVE II randomised, controlled trial proved the non-inferiority of the SYNERGY versus the PROMUS Element Plus stent for one-year target lesion failure (TLF: ischaemia-driven target lesion revascularisation [ID-TLR], target vessel myocardial infarction [TVMI], or cardiac death). The pre-specified EVOLVE II diabetes substudy prospectively pooled randomised patients with diabetes (N=263) with a sequential single-arm diabetic cohort (n=203). The substudy primary endpoint was one-year TLF compared with a pre-specified performance goal (14.5%). The primary endpoint occurred in 7.5% of SYNERGY-treated patients with diabetes, significantly less than the performance goal (p<0.0001). The two-year rate of TLF was 11.2% (cardiac death 1.5%, TVMI 6.4%, ID-TLR 6.8%) and definite/probable stent thrombosis occurred in 1.1% of patients.
Conclusions: The EVOLVE II diabetes substudy demonstrates the efficacy and safety of the SYNERGY stent in patients with medically treated diabetes. Clinical Trial Registration Information: NCT01665053 (http://clinicaltrials.gov/)
Abbreviations
ARC: Academic Research Consortium
BMS: bare metal stent
DES: drug-eluting stent
EES: everolimus-eluting stent
ID-TLR: ischaemia-driven target lesion revascularisation
MI: myocardial infarction
NSTEMI: non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction
PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
PG: performance goal
PLGA: poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide)
PVDF-HFP: polyvinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene
QCA: quantitative coronary angiography
RCT: randomised controlled trial
RVD: reference vessel diameter
ST: stent thrombosis
TLF: target lesion failure
TVF: target vessel failure
TVMI: target vessel myocardial infarction
ULN: upper limit of normal
Introduction
Patients with diabetes mellitus are at increased risk for adverse ischaemic events following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), including myocardial infarction (MI), stent thrombosis and restenosis1,2 due to a higher level of underlying vascular inflammation, the presence of a prothrombotic state, as well as more complex clinical and angiographic features3,4. Furthermore, both periprocedural and late clinical outcomes following PCI in patients with diabetes have been correlated with the severity of diabetes (as reflected by treatment regimen: insulin versus no insulin)2,5 as well as the level of glucose control (as reflected by HbA1c or fasting blood glucose levels)6,7. Although iterations in metallic drug-eluting stents (DES), including novel metal alloy composition, reduced strut thickness and improved polymer biocompatibility and/or resorption, have improved outcomes compared with early-generation DES8,9, concerns remain regarding incomplete endothelial coverage/stent healing, polymer hypersensitivity, neoatherosclerosis and stent fracture10-12. Importantly, the presence of diabetes remains a significant independent predictor of target lesion failure (TLF; composite occurrence of cardiac-related death, target vessel MI [TVMI] and ischaemia-driven target lesion revascularisation [ID-TLR]) events following PCI with second-generation everolimus-eluting stents (EES) as well as bioresorbable vascular scaffolds2,13. Recently, the SYNERGY™ bioresorbable polymer everolimus-eluting stent (Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA) demonstrated comparable one and two-year rates of TLF when compared with the permanent polymer (PVDF-HFP) EES14. Furthermore, the rate of stent thrombosis beyond 24 hours post PCI (to two years) was extremely low following SYNERGY implantation. Whether the presence of diabetes differentially affects clinical outcomes associated with specific DES types is not known and has been the subject of debate. Thus, a pre-specified, formal substudy of the EVOLVE II trial was performed to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of the SYNERGY stent in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Methods
The EVOLVE II diabetes substudy is a prospective, multicentre study conducted as part of the EVOLVE II (registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov, identifier: NCT01665053) randomised, controlled, single-blind, non-inferiority trial described previously14. As pre-specified, the EVOLVE II diabetes substudy pooled patients with diabetes: 1) randomised to the SYNERGY arm of the EVOLVE II randomised controlled trial (RCT), and 2) enrolled in the non-randomised single-arm diabetes study following completion of EVOLVE II RCT enrolment. The study was conducted in accordance with the US Food and Drug Administration’s Guidance for Industry E6 Good Clinical Practice: Consolidated Guidance, the Declaration of Helsinki, the International Conference on Harmonisation, and all local regulations, as appropriate. Institutional review boards at each centre approved the study protocol and all patients provided written informed consent before performance of any study-specific tests or procedures.
DEVICE DESCRIPTION
The SYNERGY everolimus-eluting stent consists of a thin-strut (74 μm), platinum-chromium stent platform with an ultra-thin (4 mm) bioabsorbable poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) polymer (PLGA) which elutes everolimus and is applied to the abluminal surface. Everolimus is eluted within 90 days and polymer resorption is usually complete within four months14,15.
PATIENT SELECTION, PROCEDURE, AND FOLLOW-UP
Patients in the EVOLVE II diabetes substudy were eligible to participate if they had medically treated diabetes and met the inclusion/exclusion criteria for the EVOLVE II RCT14. Per protocol, patients were treated with a P2Y12 inhibitor for at least six months following the index procedure. After the first year of follow-up, only patients who received study stents were followed (to five years after the index procedure).
ENDPOINTS
The primary endpoint for the EVOLVE II diabetes substudy was the rate of 12-month TLF, with TVMI defined as CK-MB >3x the upper limit of normal (ULN). Additional clinical endpoints included individual components of TLF, target vessel failure (TVF: all deaths, all MI and target vessel revascularisation), all-cause death, and stent thrombosis (ST: defined by the Academic Research Consortium [ARC] definite or probable criteria)14,16. All major adverse cardiac events (MACE) were adjudicated by an independent clinical events committee. Ongoing dynamic data safety monitoring by an independent data monitoring committee was performed. All procedural and follow-up angiograms up to two years were systematically assessed for longitudinal stent deformation by an independent quantitative coronary angiographic (QCA) core laboratory (Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA, USA).
STATISTICAL METHODS
The primary endpoint was 12-month TLF compared to a performance goal (PG) of 7% based on previous experience with everolimus-eluting stents in patients with diabetes17-20. The EVOLVE II non-Q-wave MI definition was based on CK-MB >3x ULN and would result in higher rates of non-Q-wave MI compared to several studies used to derive the PG. An analysis of prior trials where both CK and CK-MB were measured estimated that this lower threshold definition would increase the observed MI rate by ~3%21,22, leading to an expected one-year TLF rate of 10% (7.0%+3.0%). Both the PG and the 4.5% margin were developed in collaboration with the US Food and Drug Administration. The 4.5% margin represents 45% of the expected TLF rate and is consistent with non-inferiority margins used in previous indication expansion studies23,24. Thus, the PG was set at 14.5% (10%+delta 4.5%). Enrolment of 460 patients would provide 80% power. Comparisons were made using a one-group Clopper-Pearson test25 to determine if SYNERGY attained less than the pre-specified PG with respect to 12-month TLF (one-sided p<0.025 for significance). Clinical outcomes to two years were analysed by acute coronary syndrome (ACS) versus stable ischaemic heart disease status and stent type (SYNERGY or PROMUS Element™ Plus; Boston Scientific). PROMUS Element Plus patients were derived solely from the RCT cohort. Continuous variables were estimated as mean±standard deviation and compared with the use of the Student’s t-test. Discrete variables were reported as counts and percentages; cumulative event rates were estimated by the Kaplan-Meier method.
Results
PATIENTS AND ENROLMENT
Patients with diabetes randomised to the SYNERGY arm in the EVOLVE II RCT (263 patients enrolled at 125 sites in 16 countries between November 2012 and August 2013) were pooled with patients enrolled in the single-arm diabetes study (203 patients from 48 sites in 12 countries between August and December 2013) for a total of 466 patients with diabetes with intention to be treated with SYNERGY stents (Figure 1). Follow-up at 12 months was available in 97.6% of patients (455/466); four patients withdrew consent and seven patients missed their 12-month clinical visit. At two-year follow-up, the pre-specified safety cohort (those patients who received a SYNERGY stent) was analysed. Three patients were not included in the safety cohort as they did not receive the SYNERGY stent, five patients withdrew consent, and 10 patients missed their two-year visit, resulting in complete follow-up being available in 96.8% of patients.
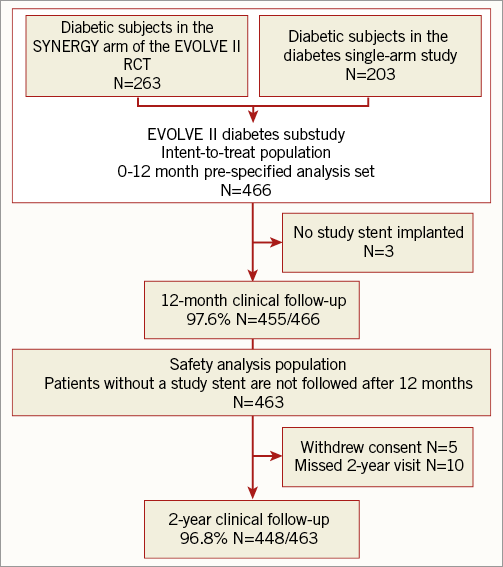
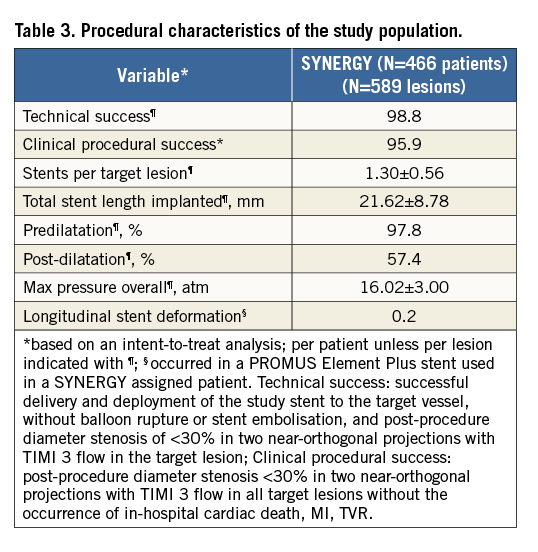
Figure 1. Patient disposition in the EVOLVE II diabetes substudy.
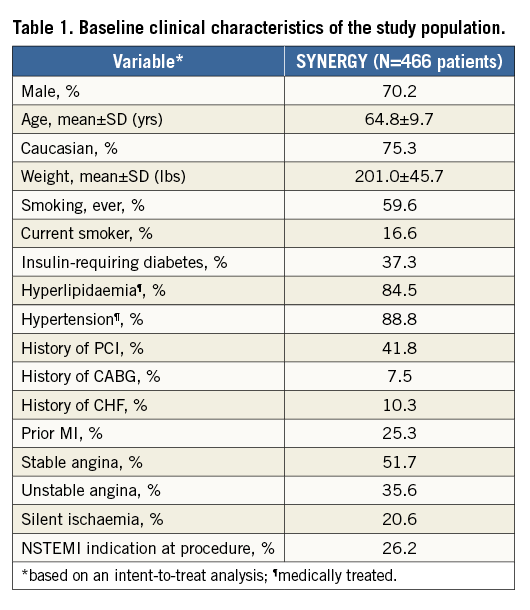
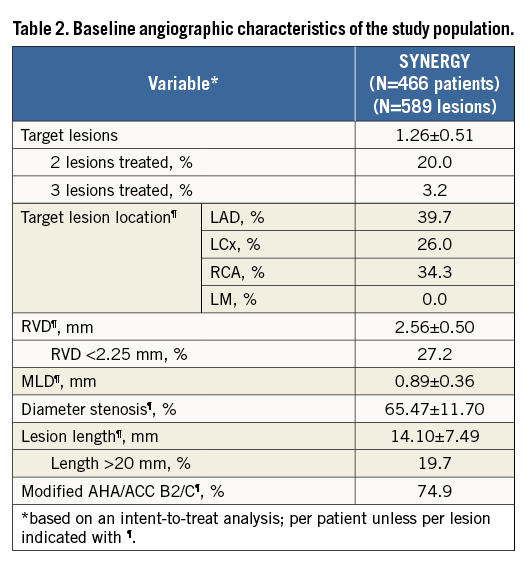
Baseline demographics and clinical characteristics of patients in the EVOLVE II diabetes substudy are shown in Table 1. Mean age was approximately 65 years, nearly 30% of patients were female, and 37.3% were treated with insulin. Baseline QCA parameters are shown in Table 2. Technical and clinical procedural success was high (Table 3). Longitudinal stent deformation was observed in one PROMUS Element Plus stent used to treat a patient assigned to SYNERGY (randomisation error) and no longitudinal stent deformation was observed in any SYNERGY stent (Table 3). Dual antiplatelet therapy (aspirin plus a P2Y12 inhibitor) adherence was 99.1% at discharge, 96.9% at six months, 86.1% at 12 months and 46.0% at two years. Aspirin adherence was 99.6% at discharge, 98.0% at six months, 97.5% at 12 months, and 96.6% at two years. Although the predominant P2Y12 inhibitor was clopidogrel, at discharge, six months, 12 months and two years prasugrel adherence was 17.5%, 14.2%, 11.7% and 4.6%, respectively, while ticagrelor adherence was 10.4%, 9.1%, 8.1% and 3.0%, respectively.
PRIMARY ENDPOINT
The primary endpoint of 12-month TLF was met in both intent-to-treat (TLF 7.5%, one-sided 97.5% upper confidence limit [UCL]=10.4%) as well as per-protocol analyses (TLF 7.4%, one-sided 97.5% UCL=10.2%) with both UCLs being significantly less (p<0.0001) than the 14.5% performance goal (Figure 2A)14. The time-to-event TLF rate at two years was 11.2% for patients with diabetes mellitus treated with SYNERGY in the EVOLVE II diabetes substudy and 9.4% for all SYNERGY stent-treated patients enrolled in the EVOLVE II trial (Figure 2B). The inset shows a one-year landmark analysis of TLF in the EVOLVE II diabetes substudy. The rate of TLF in PROMUS Element Plus-treated patients with diabetes in the EVOLVE II RCT was 9.2%.
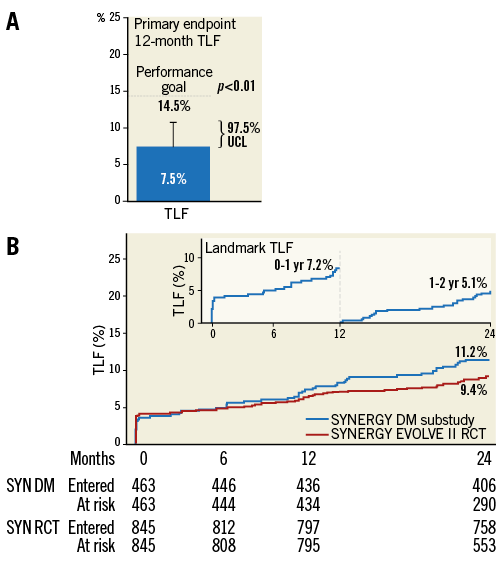
Figure 2. Primary endpoint analysis. A) The primary endpoint of 12-month TLF. Outcomes in the intent-to-treat patient population are shown. B) Time-to-event rate of TLF in the safety cohort patient population at two years. The inset shows a one-year landmark analysis of TLF in the EVOLVE II diabetes substudy.
OTHER CLINICAL OUTCOMES
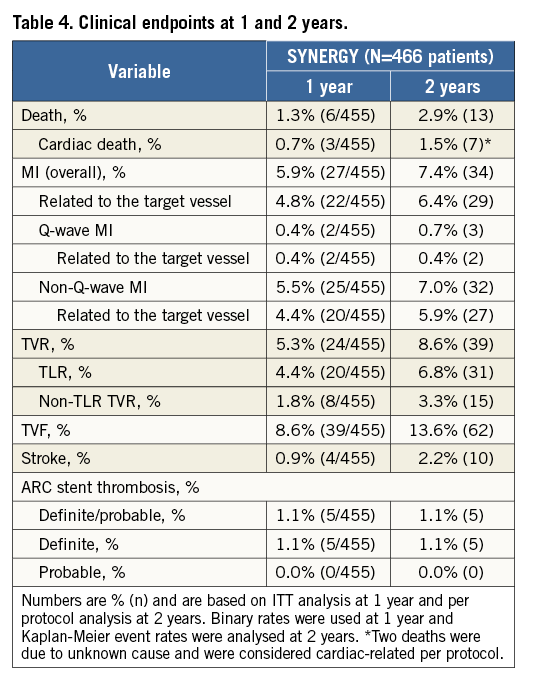
The individual components of TLF and other clinical endpoints at one and two-year follow-up are shown in Table 4 18. There were seven cardiac and six non-cardiac deaths, yielding a cardiac death rate of 1.5% in the EVOLVE II diabetes substudy. The overall rate of MI was 7.4% (6.4% were target vessel-related), with the major portion of MI being non-Q-wave MI (n=32); most non-Q-wave MI were periprocedural (Table 4). TLR occurred in 6.8% of patients (n=31) and non-TLR-TVR in 3.3% of patients (n=15). The rates of TLF and its components in PROMUS Element Plus-treated patients with diabetes were: TLF 9.2%, cardiac death 1.7%, target vessel-related MI 5.0%, and TLR 5.0%. Five patients experienced a definite stent thrombosis within two years (1.1%) in the EVOLVE II diabetes substudy and there were no probable stent thromboses. Most stent thromboses occurred acutely (4/5 within 24 hours and one on day 5 following the index procedure). There were no definite or probable late or very late ST in the EVOLVE II diabetes substudy.
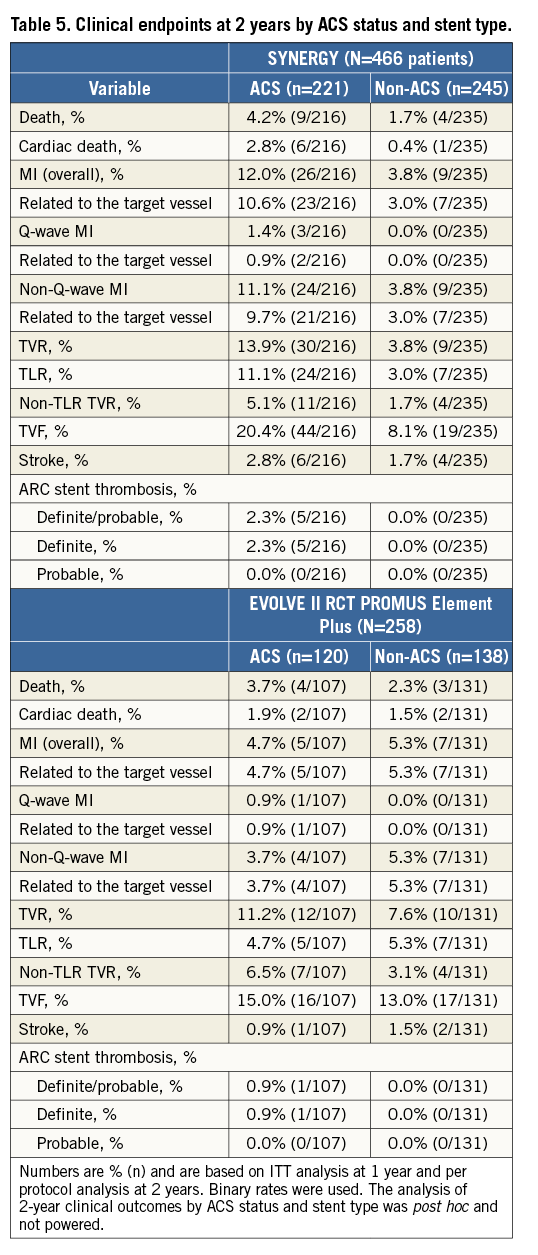
The EVOLVE II diabetes substudy patient population was complex and included 41% of patients with ACS (MI or unstable angina). At one year, TLF was increased in ACS patients with diabetes (10.5%) compared to non-ACS patients (4.7%, p=0.02); at two years, TLF was 17.6% in ACS patients vs. 6.0% of non-ACS patients (p=0.003). All clinical outcomes to two years by ACS status and stent type (SYNERGY or PROMUS Element Plus) are shown in Table 5.
Discussion
This pre-specified, powered EVOLVE II substudy supports the efficacy and safety of the bioabsorbable polymer everolimus-eluting SYNERGY stent in patients with diabetes mellitus. The major observations of this study include the following. 1) The powered primary endpoint of the study (TLF at one year) was met with one-sided 97.5% upper confidence limits significantly below the pre-specified PG in both intent-to-treat and per-protocol analyses. 2) Overall rates of TLF, MI, ID-TLR and stent thrombosis appear remarkably low at one- and two-year follow-up despite the clinical and angiographic complexity of the study population. In this regard, rates of TLF at one and two years following SYNERGY stent treatment in the diabetic substudy (7.5% and 11.2%, respectively, by ITT) appear comparable to those observed in the overall population of SYNERGY stent-treated patients (6.7% and 9.4%, respectively) enrolled in the EVOLVE II trial18. This observation is remarkable in the context of the rather large percentages of patients with diabetes mellitus in the current analysis who required insulin treatment (37%), had NSTEMI (26%) as the indication for PCI or had multiple target lesions treated (23%). This level of clinical complexity is further compounded by angiographic (QCA) characteristics which include the prevalence of very small target vessels (<2.25 mm reference vessel diameter [RVD]) in 27%, long target lesion length (>20 mm) in 20%, and complex target lesion morphology (modified AHA/ACC B2/C criteria) in 75% of patients with diabetes, respectively. Indeed, each of these clinical and angiographic characteristics has been identified by previous studies as a significant independent predictor of stent thrombosis and/or ID-TLR26,27. Despite the high prevalence of insulin treatment, acute myocardial infarction and very small vessels, stent thrombosis was not observed beyond the first five days following SYNERGY stent deployment. This observation is consistent with the absence of late or very late thrombosis to two-year follow-up after SYNERGY stent deployment in both the overall EVOLVE II trial as well as the EVOLVE first human use experience28 up to five years, and may reflect more rapid and complete stent healing with this device28. The absence of late/very late stent thrombosis in the present cohort is striking, although the play of chance for a low frequency adverse outcome cannot be excluded. The SYNERGY stent incorporates multiple design elements specifically aimed towards rapid and complete stent coverage/healing and reduced thrombosis, including thin, platinum-chromium (PtCr) metal alloy struts, ultra-thin PLGA polymer limited to the abluminal strut surface and rapid polymer resorption within four months14,15. Abluminal-only polymer distribution (versus conformal) has been demonstrated to enhance the time course and extent as well as the function and maturation of endothelial cell stent coverage15,29. Similarly, bare metal PtCr enhanced endothelial coverage and reduced platelet adhesion and activation when compared in cell assay with PtCr covered by permanent PVDF polymer29,30. Finally, the time course of polymer resorption may influence the occurrence of thrombotic events as well as the required duration of dual antiplatelet therapy. In the recent PANDA III randomised trial comparing two bioresorbable polymer, sirolimus-eluting metallic DES, the device with more rapidly absorbed (three months) PLGA polymer had significantly fewer stent thromboses at one-year follow-up than the device with more slowly resorbed (nine months) PLA polymer31. In the EVOLVE II trial, stent thrombosis was not observed after the first week following PCI regardless of diabetic status or clinical complexity. In the Swedish Angiography and Angioplasty Registry (SCAAR), definite stent thrombosis was not observed beyond six months following SYNERGY stent deployment regardless of whether PCI was performed for acute coronary syndrome indication or not. Stent thrombosis occurring in the acute/subacute time frame, as observed in the present study, most often reflects mechanical or technical issues of underexpansion, malapposition, necrotic core plaque prolapse and/or unrecognised stent marginal dissection that may, at least in part, be mitigated by improved deployment technique32. The results of the current analysis of patients with diabetes mellitus, although promising, will need to be replicated in larger groups of high-risk patients over even longer periods of time.
Study limitations
Several potential study limitations should be noted. First, this study is a single-arm evaluation without a randomised comparator. The results observed with SYNERGY, although promising, cannot be compared with other stent platforms. Second, this study pools two separate groups of patients (one randomised to SYNERGY, one not randomised). Importantly, both groups of patients with diabetes were subject to the same clinical and angiographic enrolment criteria, under the same protocol with the same central, independent clinical events committee (CEC) adjudication of events. Consecutive (non-randomised) treatment of patients with diabetes using the SYNERGY stent was performed to enrich the statistical power of this study subpopulation with specific intent to expand the label for this device. Third, the analysis of two-year clinical outcomes by ACS status and stent type was post hoc and not powered. Finally, complete follow-up is limited to two years at this time.
Conclusions
This pre-specified, powered substudy of patients with diabetes mellitus treated with the SYNERGY stent supports the efficacy and safety of this device to two-year follow-up and supports an expanded indication for SYNERGY in this high-risk patient cohort.
| Impact on daily practice This pre-specified, powered EVOLVE II trial substudy in patients with medically treated diabetes mellitus demonstrates the efficacy and safety of the SYNERGY stent and supports an expanded indication of SYNERGY to include this complex patient subgroup. |
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Kristine Roy, PhD, and Songtao Jiang, MSc (both Boston Scientific Corporation), for assistance in manuscript preparation and statistical analysis.
Funding
The EVOLVE II trial was sponsored and funded by Boston Scientific Corporation.
Conflict of interest statement
D. Kereiakes has received consultancy fees from BSC and Abbott Vascular. I. Meredith has received honoraria for speaking/consultancy from Boston Scientific. A. Erglis has received consultancy fees from BSC and Abbott Vascular. J. Airaksinen has received lecture fees from Bayer, Cardiome, Pfizer and Boehringer Ingelheim. S. Windecker has received research grants to the institution from Abbott, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Johnson & Johnson, Medtronic, Edwards, and St. Jude. T. Christen and K. Dawkins are full-time employees with equity in Boston Scientific. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

