
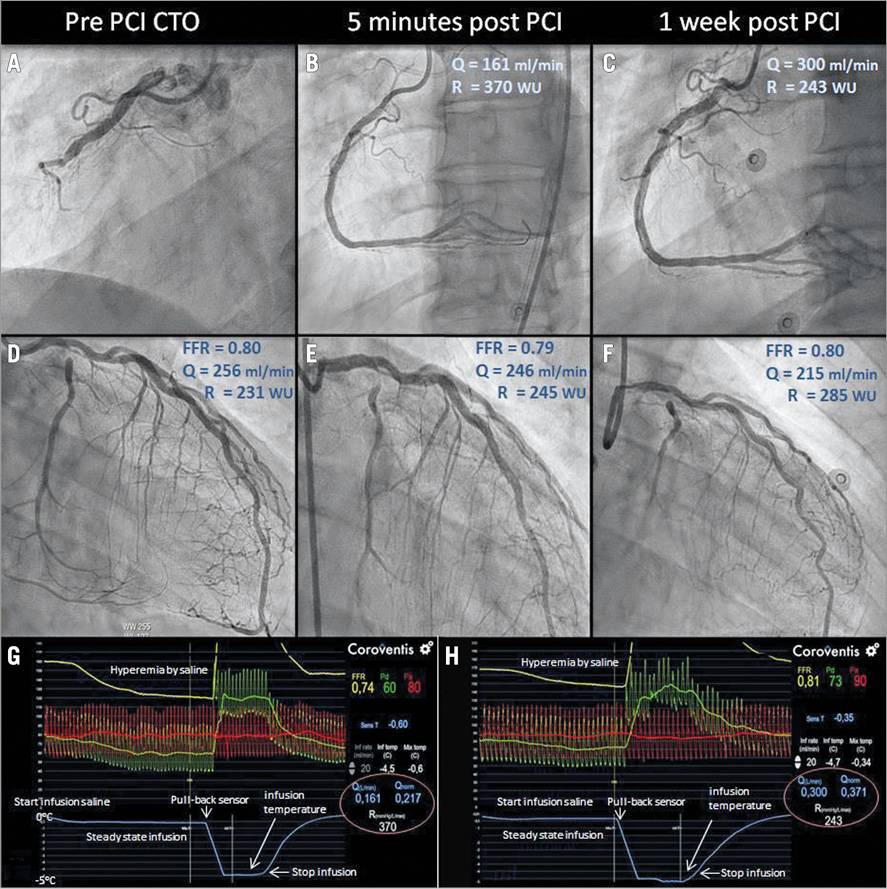
A 59-year-old male was admitted to the Catharina Hospital with unstable angina. Coronary angiography showed a chronic total occlusion (CTO) of the right coronary artery (RCA) (Panel A), and a proximal subtotal stenosis of the ramus circumflex (RCx) and septal collaterals (Rentrop grade 1) from the left anterior descending (LAD) to the RCA (Panel D). After discussion in the Heart Team, we decided not to perform percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) of the LAD due to diffuse disease, discovered during the hyperaemic pullback, and the patient was scheduled for PCI of the chronic occluded RCA. Using the new technique of thermodilution with a low rate of saline (RayFlow© infusion catheter [Hexacath Inc., Paris, France], and CoroFlow™ software [Coroventis, Uppsala, Sweden]), we measured absolute flow and resistance in the donor vessel (the LAD) before and after PCI of the CTO (Panel D, Panel E)1,2. Absolute flow in the LAD before PCI of the RCA was 256 ml/min, with a microvascular resistance of 231 Wood units (WU). Additionally, we measured flow and resistance in the RCA after successful treatment, being 161 ml/min and 370 WU, respectively (Panel B, Panel G). Staged PCI of the RCx was performed after one week and all measurements in the RCA and LAD were repeated (Panel C, Panel F, Panel H). The absolute flow in the RCA had increased now by 86% to 300 ml/min compared to one week previously, with a decrease in microvascular resistance of 33% to 243 WU. Blood flow in the LAD area had decreased to 215 ml/min, due to the decrease of perfusion territory (Panel F).
This case elegantly demonstrates how this method can be used in the cath lab to study recovery of flow after PCI of a CTO. It illustrates that the microvasculature distal to a CTO needs a number of days to recover and normalise.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

