
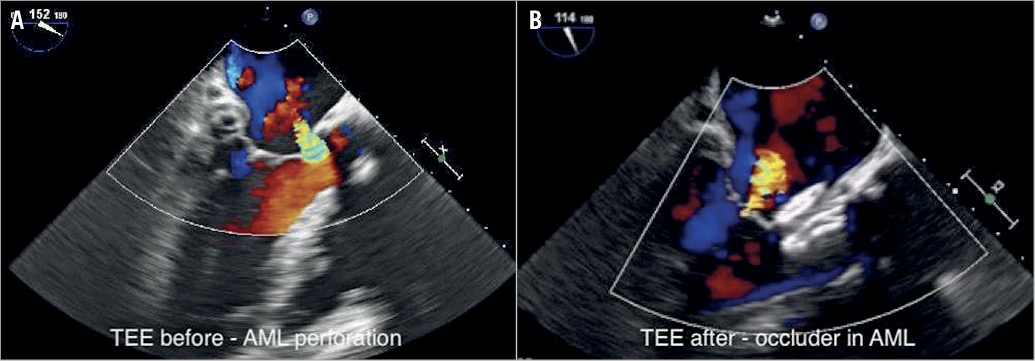
Figure 1. Mitral valve before and after intervention. A) TEE before procedure with perforation of the anterior mitral leaflet. B) TEE after procedure with occluder in the anterior mitral leaflet.
Anterior mitral leaflet perforation is a rare complication of an aortic valve replacement, typically located at the base of the leaflet1. Here we describe the case of a 69-year-old female patient who had mechanical aortic valve replacement in 2000 and bioprosthesis reimplantation because of mechanical valve dysfunction in 2017. After surgery she remained symptomatic (heart failure of NYHA Class III) because of severe mitral regurgitation due to a perforation of the anterior mitral leaflet at the base of the A2 segment caused by surgery (Figure 1A, Moving image 1). Preprocedural laboratory tests revealed haemoglobin of 11 g/dl, LDH of 413 U/l and NT-proBNP of 872 pg/ml. Endocarditis was excluded. Because of the high risk of re-reoperation and other risk factors for surgery, the Heart Team decided to attempt a percutaneous closure. After right femoral vein and transseptal puncture, a steerable sheath (Agilis™; St. Jude Medical, St. Paul, MN, USA) loaded with a 5 Fr right coronary Judkins catheter (Cordis, Milpitas, CA, USA) was used to cross the perforation with a soft J-tip Terumo guidewire (Terumo Europe, Leuven, Belgium) with 3D TEE guidance. The defect was measured in 2D to be 6x6 mm and in 3D 0.35 cm2. Over a stiff wire the Agilis sheath was exchanged for a 6 Fr Cook sheath (Cook Medical, Bloomington, IN, USA), and a 10 mm AMPLATZER™ Septal Occluder (St. Jude Medical) was implanted into the perforation, which resulted in complete sealing of the perforation (Figure 1B, Moving image 2, Moving image 3). Echocardiography confirmed normal mitral leaflet motion (Moving image 4, Moving image 5). The ventricular part of the occluder neither disturbed the aortic bioprosthesis nor created a significant pressure gradient in the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) (11 mmHg; total transvalvular gradient 13 mmHg). Procedure time was 60 minutes. One-month echocardiographic follow-up revealed a stable occluder position with complete sealing of the defect. Heart failure improved to NYHA Class II; heart failure self-assessment changed from 9/10 at baseline to 5/10 after three months. LDH decreased to 291 U/l and NT-proBNP to 411 pg/ml.
Others have used an occluder to seal a perforation of the posterior mitral leaflet, where the ventricular part of the device is not positioned in the LVOT2. Here we demonstrate that percutaneous closure can also be performed in case of anterior mitral leaflet perforation, where part of the occluder has to be placed into the LVOT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. Preprocedural regurgitation, TEE 2D long-axis view with colour Doppler.
Moving image 2. Occluder positioning, fluoroscopy.
Moving image 3. Post-procedural regurgitation, TEE 2D longaxis view with colour Doppler.
Moving image 4. Occluder positioned, TEE 2D long-axis view.
Moving image 5. Occluder positioned, TEE 3D en face view.

