Abstract
BACKGROUND: Whether revascularisation (REV) improves outcomes in patients with three-vessel coronary artery disease (3V-CAD) is uncertain.
AIMS: Our objective was to evaluate outcomes with REV (percutaneous coronary intervention [PCI] or coronary artery bypass graft surgery [CABG]) versus medical therapy in patients with 3V-CAD.
METHODS: ISCHEMIA participants with 3V-CAD on coronary computed tomography angiography without prior CABG were included. Outcomes following initial invasive management (INV) with REV (PCI or CABG) versus initial conservative management (CON) with medical therapy alone were evaluated. Regression modelling was used to estimate the outcomes if all participants were to undergo prompt REV versus those assigned to CON. Outcomes were cardiovascular (CV) death/myocardial infarction (MI), death, CV death, and quality of life. Bayesian posterior probability for benefit (Pr [benefit]) for 1 percentage point lower 4-year rates with REV versus CON were evaluated.
RESULTS: Among 1,236 participants with 3V-CAD (612 INV/624 CON), REV was associated with lower 4-year CV death/MI (adjusted 4-year difference: −4.4, 95% credible interval [CrI] −8.7 to −0.3 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=94.8%) when compared with CON, with similar results for PCI versus CON (−5.8, 95% CrI: −10.8 to −0.5 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=96.4%) and CABG versus CON (−3.7, 95% CrI: −8.8 to 1.5 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=84.7%). Adjusted 4-year REV versus CON differences were as follows: death −1.2 (95% CrI: −4.7 to 2.2) percentage points, CV death −2.3 (95% CrI: −5.5 to 0.8) percentage points, with similar results for PCI and for CABG. The Pr (benefit) for death with REV (PCI or CABG) versus CON was 49-63%. The adjusted 12-month Seattle Angina Questionnaire-7 summary score differences favoured REV: REV versus CON 4.6 (95% CrI: 2.7-6.4) percentage points; PCI versus CON 3.6 (95% CrI: 1.2-5.8) percentage points and CABG versus CON 4.3 (95% CrI: 1.5-6.9) percentage points with high Pr (benefit).
CONCLUSIONS: In participants with 3V-CAD, REV (either PCI or CABG) was associated with a lower 4-year CV death/MI rate and improved quality of life, with similar results for PCI versus CON and CABG versus CON. The differences in all-cause mortality between REV and CON were small with wide confidence intervals. (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01471522)
In patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), revascularisation (REV) improves angina-related quality of life (QoL)123. Whether REV improves cardiovascular outcomes in patients with stable CAD, and especially in those with three-vessel CAD (3V-CAD), is unknown and has been hotly debated45. Randomised trials in the 1970s and 1980s showed an improvement in survival with coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG) when compared with medical therapy in patients with 3V-CAD6. However, medical therapy was very limited compared with contemporary practice. The outcomes of patients with 3V-CAD in contemporary practice with guideline-directed medical therapy (GDMT) are not known.
In the ISCHEMIA trial, there was no heterogeneity of treatment effect in the comparison of randomised treatment groups (initial invasive [INV] vs initial conservative [CON] strategy) for the primary endpoint based on the number of diseased vessels on coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA)7. However, a subgroup of interest was identified in an analysis of randomised participants who had CCTA evaluable for the modified Duke prognostic index. In that prior analysis, the 4-year rate of cardiovascular (CV) death or myocardial infarction (MI) was lower with the INV strategy (INV vs CON difference 6.3% [95% confidence interval {CI}: 0.2-12.4%]; pinteraction=0.33) in the most severe CAD subgroup (defined as Duke 6: three-vessel disease [3VD] based on ≥70% stenosis or two-vessel disease [2VD] based on ≥70% stenosis including the proximal left anterior descending artery [LAD])8. However, the outcomes based on actual REV received (only 80% of participants randomised to INV were revascularised) or outcomes restricted to 3VD were not explored. Accordingly, in the current analysis we sought to evaluate what the outcomes of REV would be if all participants were to receive REV compared with CON, as well as separately evaluating percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) versus CON and CABG versus CON in the subset of participants with 3V-CAD who were randomised in the ISCHEMIA trial.
Methods
The authors declare that all supporting data are available online. A list of non-author collaborators for indexing in PubMed is included in Supplementary Appendix 1.
STUDY POPULATION
The design and principal results of the ISCHEMIA trial have previously been published79. The study was approved by the institutional review boards of the participating sites. In brief, 5,179 participants with stable CAD and site-determined moderate or severe ischaemia were randomised 1:1 to either INV, consisting of coronary angiography and REV (PCI or CABG) if suitable, plus GDMT, or to CON of GDMT alone, with coronary angiography and REV reserved for failure of GDMT. Notable exclusion criteria included participants with known left main disease, recent acute coronary syndrome, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <35% or participants with an unacceptable level of angina at enrolment. Among participants randomised to INV, 80% were revascularised: 76% of them with PCI and 24% with CABG7.
Participants who had a core laboratory-interpreted CCTA with 3V-CAD based on ≥50% stenosis severity and without prior CABG were included in the present analysis. Participants with CCTA of poor quality that were not evaluable for diseased vessels were excluded. We note that the available number of evaluable CCTA studies for this analysis is larger than in a prior ISCHEMIA trial CCTA analysis that used the modified Duke prognostic index, because that index requires assessment of whether stenosis severity is ≥70%8.
STUDY PROCEDURES
Participants randomised to INV underwent coronary angiography and were scheduled to undergo REV, if feasible, using contemporary techniques, including 2nd-generation drug-eluting stents, physiology guidance for PCI and use of at least the left internal mammary artery graft for CABG. Coronary angiography and revascularisation were only allowed in the CON group in case of refractory symptoms or a suspected primary endpoint event. Both groups received secondary prevention measures that included lifestyle and pharmacological interventions.
STUDY ENDPOINTS
Endpoints of interest were the composite of CV death or MI, composite of death or MI, other composite outcomes including stroke, and individual components of the composite outcome. Health status outcomes included symptoms, function and QoL. The definitions of outcomes have been described previously7. MI included the study’s primary definition of both procedural MI and spontaneous MI.
Participants’ health status at 12 months post-randomisation was assessed using the 7-item Seattle Angina Questionnaire (SAQ-7), the Rose Dyspnea Scale (RDS), and the European Quality of Life-5 Dimension visual analogue scale (EQ-5D VAS). The SAQ-7 encompasses 3 domains assessing angina-related health status over the previous 4 weeks, quantified by angina frequency, physical limitation, and QoL scores; a summary score was also derived integrating all 3 domains10. All scores range from 0 to 100, with higher scores denoting better health status. The RDS assesses the presence of dyspnoea with 4 common physical activities, with a score of 0 indicating no dyspnoea and a score of 4 indicating significant limitations due to dyspnoea11. The EQ-5D VAS assesses general health status; scores range from 0 to 100, with a score of 0 indicating the worst possible health and a score of 100 indicating perfect health12.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Detailed statistical methods are presented in Supplementary Appendix 2. Briefly, we studied the hypothesis that, on average, patients resembling ISCHEMIA participants with 3V-CAD and no prior CABG would benefit from a strategy of upfront REV compared to CON. Outcomes of REV and CON were based on data from the randomised INV and CON groups, respectively. INV-assigned participants were excluded if they had missing data for key invasively measured angiographic covariates (n=47). Statistical adjustments were implemented to account for this exclusion and to address the fact that not all remaining INV-assigned participants underwent prompt upfront revascularisation. We also adjusted for censoring (i.e., incomplete follow-up) in the analysis of time-to-event clinical endpoints. By making these adjustments, we sought to recover the true treatment effect that would be observed in an ideal setting of no missing angiographic covariates, no censoring, and 100% adherence to an INV strategy of prompt upfront revascularisation.
We performed separate analyses for each method of revascularisation and each endpoint. For clinical endpoints, the statistical framework was a set of discrete-time longitudinal logistic regression models adjusting for the covariates listed in Supplementary Table 1. We used these models to estimate a patient’s weekly risk as a function of time since randomisation, time since INV-assigned revascularisation, and baseline covariates. Weekly risk estimates were then combined to produce an estimate of each patient’s cumulative risk over a 4-year time horizon. This calculation was performed twice per patient. The first estimate described the patient’s risk if assigned to INV and given prompt REV. The second estimate described the patient’s risk if assigned to CON. We then averaged each of these estimates across participants to produce an overall estimate of the difference in risk under a strategy of REV compared to CON.
For QoL outcomes, the statistical framework was a set of proportional odds models. Missing health status scores were imputed using multiple imputation methods, as described in Supplementary Appendix 2. We performed separate analyses for each method of REV and for each outcome. For each analysis, we estimated separate models for INV and CON, adjusting for the covariates listed in Supplementary Table 1 as well as the baseline health status score for the given outcome. Using these models, we predicted the score for each participant in the study’s INV cohort under each treatment strategy. We then estimated the standardised outcome for each treatment strategy as the average of the predicted scores. We defined the primary measure of treatment effect for each QoL outcome to be the between-group difference in the REV versus CON, PCI versus CON, and CABG versus CON standardised outcomes at 12 months.
We used a Bayesian statistical approach to implement the above analyses. This methodology allows us to calculate the probability of various outcomes directly, making the results especially relevant and understandable in clinical and practical terms1314. For example, we were able to calculate the probability that REV produces a 4-year cumulative risk that is lower than CON by a margin of at least 1 (defined in this report for simplicity as probability for benefit [Pr{benefit}]), 3, or 5 percentage points. Details are presented in Supplementary Appendix 2.
Results
A total of 1,283 participants with no prior CABG, with a prerandomisation CCTA that was evaluable for diseased vessels, revealing 3V-CAD, were identified, among whom 47 participants randomised to INV but with missing key angiographic covariates were excluded (Supplementary Figure 1). Among the remaining 1,236 participants included in this analysis, 612 were randomised to INV and 624 to CON. Among those in the INV group, 510 (83.3%) underwent REV, including 292 who underwent PCI and 218 who underwent CABG, within 180 days post-randomisation. In the CON group, 89 participants (14.3%) underwent REV within the 4-year follow-up.
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS
Baseline characteristics of the INV versus CON groups and the comparisons of REV versus CON, PCI versus CON, and CABG versus CON are presented in Table 1, Supplementary Table 2 and Supplementary Table 3. There were no major differences except for a higher proportion of participants with prior stroke, higher estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and lower SAQ angina frequency score (more angina) among those randomised to INV compared with CON. For the PCI versus CON comparison, there were no major differences except for QoL domains, with a lower SAQ summary score, lower SAQ angina frequency score and lower SAQ QoL score, indicating worse symptoms in the PCI group. Conversely, the PCI group had lower proportions of participants with left main disease and proximal LAD disease when compared with CON (Supplementary Table 3). For the CABG versus CON comparison, there were no major differences between the groups except for a greater proportion of participants with prior stroke, a greater proportion from Europe, a lesser proportion from Asia and North America, and a greater proportion of participants with severe ischaemia and left main disease in the CABG group when compared with CON (Table 1, Supplementary Table 2, Supplementary Table 3).
There were no major differences in physiological measurements, risk factor goals, medication use at baseline and at the last visit, or procedural details between the groups, except for a greater use of clopidogrel in the PCI group and a higher medication adherence in the REV, PCI, and CABG groups when compared with the CON group at the last visit (Supplementary Table 4, Supplementary Table 5). The overall 4-year mortality rate was 9.0% for CON in patients with 3V-CAD, compared with 6.4% for CON in the overall trial, reflecting the higher anatomical risk of this subset.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics.
| INV N=612 | INV: REV N=510 | INV: PCI N=292 | INV: CABG N=218 | CON N=624 | p-value INV vs CON | p-value REV vs CON | p-value PCI vs CON | p-value CABG vs CON | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 64 (57-70) | 63 (57-69) | 63 (55-69) | 64 (59-70) | 64(57-69) | 0.56 | 0.92 | 0.28 | 0.26 |
| Male | 521/612 (85.1) | 432/510 (84.7) | 238/292 (81.5) | 194/218 (89.0) | 526/624 (84.3) | 0.74 | 0.91 | 0.34 | 0.11 |
| Hypertension | 438/610 (71.8) | 370/508 (72.8) | 212/292 (72.6) | 158/216 (73.1) | 449/622 (72.2) | 0.93 | 0.86 | 0.96 | 0.85 |
| Diabetes | 261/612 (42.6) | 216/510 (42.4) | 121/292 (41.4) | 95/218 (43.6) | 289/624 (46.3) | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.54 |
| Current smoker | 80/611 (13.1) | 59/509 (11.6) | 33/292 (11.3) | 26/217 (12.0) | 78/623 (12.5) | 0.94 | 0.85 | 0.45 | 0.69 |
| Previous myocardial infarction | 105/612 (17.2) | 85/510 (16.7) | 46/292 (15.8) | 39/218 (17.9) | 104/623 (16.7) | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.79 | 0.76 |
| Known heart failure | 20/612 (3.3) | 18/510 (3.5) | 11/292 (3.8) | 7/218 (3.2) | 13/624 (2.1) | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.49 |
| Previous stroke | 22/612 (3.6) | 19/510 (3.7) | 9/292 (3.1) | 10/218 (4.6) | 10/624 (1.6) | 0.04* | 0.04* | 0.22 | 0.03* |
| History of peripheral arterial disease | 32/610 (5.2) | 23/509 (4.5) | 12/291 (4.1) | 11/218 (5.0) | 20/621 (3.2) | 0.10 | 0.33 | 0.62 | 0.31 |
| Previous percutaneous coronary intervention | 108/611 (17.7) | 81/509 (15.9) | 50/292 (17.1) | 31/217 (14.3) | 101/624 (16.2) | 0.53 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 0.58 |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction, % | 60 (55-64) | 60 (55-65) | 60 (56-65) | 60 (55-65) | 60 (55-65) | 0.95 | 0.59 | 0.26 | 0.67 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 88 (74-103) | 88 (74-102) | 88 (73-102 | 88 (74-102) | 84 (72-98) | 0.02* | 0.03* | 0.07 | 0.09 |
| SAQ-7 summary score | 76 (62-89) | 75 (62-88) | 74 (58-88) | 77 (65-89) | 78 (64-90) | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.02* | 0.68 |
| SAQ-7 angina frequency score | 80 (70-100) | 80 (70-100) | 80 (60-100) | 80 (70-100) | 90 (70-100) | 0.02* | 0.003* | 0.0002* | 0.38 |
| SAQ-7 physical limitation score | 92 (67-100) | 92 (67-100) | 92 (67-100) | 92 (75-100) | 92 (75-100) | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.55 | 0.55 |
| SAQ-7 quality of life score | 63 (50-88) | 63 (50-85) | 63 (38-75) | 63 (50-88) | 63 (50-88) | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.04* | 0.36 |
| History of angina | 549/612 (89.7) | 457/510 (89.6) | 259/292 (88.7) | 198/218 (90.8) | 553/624 (88.6) | 0.60 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 0.44 |
| Data are presented as n/N (%) or mean (95% credible interval). *Value holds statistical significance. CABG: coronary artery bypass graft surgery; CON: conservative management; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; INV: invasive management; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; REV: revascularisation; SAQ: Seattle Angina Questionnaire | |||||||||
CLINICAL OUTCOMES: REV VERSUS CON
Compared with CON, REV was associated with a lower 4-year CV death or MI rate (4-year between-group difference: −4.4 percentage points, 95% credible interval [CrI]: −8.7 to −0.3 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=94.8%) (Figure 1, Table 2, Supplementary Table 6). REV was associated with an early procedural risk with a 6-month CV death/procedural MI (pMI) difference of 6.0 (95% CrI: 4.0 to 8.3) percentage points but lower 4-year CV death/spontaneous MI (sMI) (−8.1 percentage points, 95% CrI: −12.0 to −4.5 percentage points, Pr [benefit] >99.9%) (Supplementary Table 6). For other composite endpoints, the Pr (benefit) with REV was between 73% and 87% (Table 2, Supplementary Table 7).
In contrast, the estimated between-group differences for all-cause death (4-year between-group difference, REV minus CON, −1.2 percentage points, 95% CrI: −4.7 to 2.2 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=55.6%) (Supplementary Figure 2) and CV death (−2.3 percentage points, 95% CrI: −5.5 to 0.8 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=78.7%) (Table 2, Supplementary Figure 2, Supplementary Figure 3) were imprecise with wide credible intervals. However, the probability for harm (Pr [harm]) with REV for the all-cause death rate and CV death rate was only 10.6% and 1.9%, respectively.
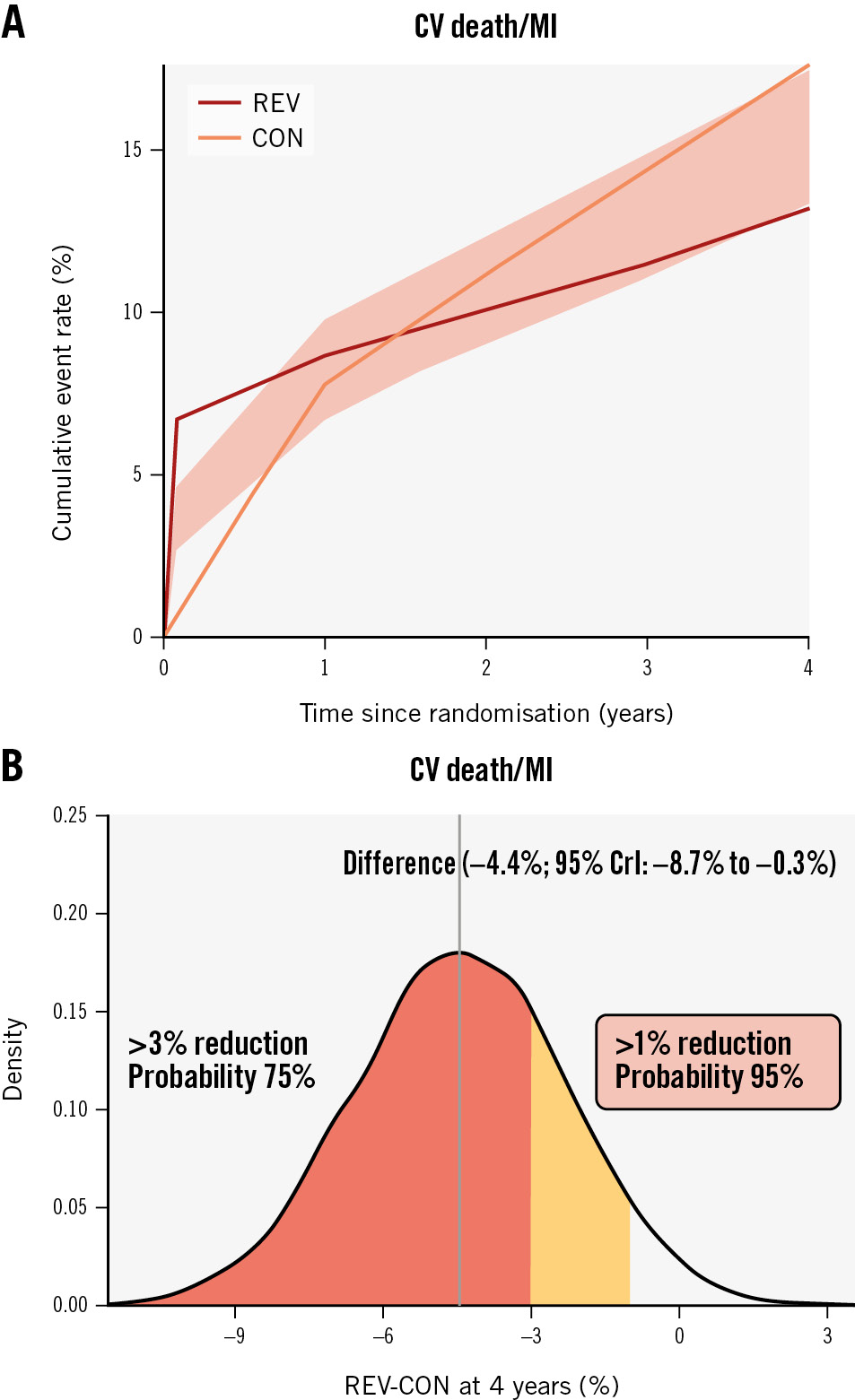
Figure 1. Revascularisation versus CON in participants with 3-vessel disease. A) Cumulative risk estimates for the outcome of CV death or MI; (B) the posterior distribution of the absolute difference in the risk of CV death or MI at 4 years for REV versus CON. The concentration of values around −4 indicates a benefit of revascularisation rather than CON by ~4 percentage points. CON: conservative strategy; CrI: credible interval; CV: cardiovascular; MI: myocardial infarction; REV: revascularisation
Table 2. Posterior probability for revascularisation, PCI or CABG versus CON in participants with 3-vessel disease.
| Treatment effect, % | CV death/MI | All death/MI | All death | CV death | All death/MI/stroke | CV death/MI/stroke |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REV vs CON | ||||||
| >5% lower | 39.5 | 23.4 | 2.0 | 4.2 | 13.6 | 25.2 |
| >3% lower | 74.7 | 56.2 | 16.0 | 31.7 | 41.4 | 59.5 |
| >1% lower | 94.8* | 85.2 | 55.6 | 78.7 | 73.4 | 87.2 |
| Any lower | 98.3* | 93.1* | 75.5 | 92.4* | 84.8 | 94.0* |
| Any higher | 1.7 | 6.9 | 24.5 | 7.6 | 15.2 | 6.0 |
| >1% higher | 0.5 | 2.6 | 10.6 | 1.9 | 7.1 | 2.1 |
| >3% higher | <0.1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | <0.1 | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| >5% higher | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.1 | <0.1 |
| PCI vs CON | ||||||
| >5% lower | 61.8 | 49.4 | 2.6 | 3.5 | 44.0 | 56.9 |
| >3% lower | 85.9 | 76.8 | 16.4 | 22.0 | 72.2 | 82.0 |
| >1% lower | 96.4* | 93.2* | 49.2 | 60.1 | 90.3* | 95.2* |
| Any lower | 98.4* | 96.4* | 67.7 | 78.2 | 95.0* | 97.9* |
| Any higher | 1.6 | 3.6 | 32.4 | 21.8 | 5.1 | 2.1 |
| >1% higher | 0.7 | 1.7 | 18.6 | 9.8 | 2.4 | 0.7 |
| >3% higher | 0.1 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| >5% higher | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| CABG vs CON | ||||||
| >5% lower | 32.0 | 18.4 | 5.3 | 17.3 | 8.7 | 17.0 |
| >3% lower | 61.0 | 43.0 | 27.1 | 57.5 | 24.7 | 40.3 |
| >1% lower | 84.7 | 69.0 | 63.1 | 90.3* | 50.0 | 67.2 |
| Any lower | 91.9* | 79.6 | 78.4 | 96.5* | 62.9 | 79.1 |
| Any higher | 8.1 | 20.4 | 21.6 | 3.5 | 37.1 | 20.8 |
| >1% higher | 3.9 | 12.1 | 10.6 | 0.9 | 26.2 | 12.6 |
| >3% higher | 0.6 | 3.4 | 1.8 | 0.1 | 9.3 | 3.7 |
| >5% higher | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.2 | <0.1 | 2.4 | 0.9 |
| The treatment effect is defined as the difference in the cumulative risk for REV, PCI or CABG vs CON at 4 years post-randomisation. *Indicates probabilities that are high (defined as >90%). CABG: coronary artery bypass graft surgery; CON: conservative management; CV: cardiovascular; MI: myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; REV: revascularisation | ||||||
CLINICAL OUTCOMES: PCI VERSUS CON
Compared with CON, PCI was associated with a lower 4-year CV death or MI rate (4-year between-group difference: −5.8 percentage points, 95% CrI: −10.8 to −0.5 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=96.4%) (Figure 2, Table 2, Supplementary Table 8). PCI was associated with an early procedural risk with a 6-month CV death/pMI difference of 3.5 (95% CrI: 1.4 to 6.1) percentage points but lower 4-year CV death/sMI (−7.4 percentage points, 95% CrI: −11.6 to −2.9 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=99.8%) (Supplementary Table 8). For other composite endpoints the Pr (benefit) with PCI was between 90% and 95% (Table 2, Supplementary Table 7).
In contrast, the estimated between-group differences for all-cause death (−0.9 percentage points, 95% CrI: −5.0 to 3.4 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=49.2%) and CV death (−1.5 percentage points, 95% CrI: −5.3 to 2.6 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=60.1%) (Table 2, Supplementary Figure 4, Supplementary Figure 5) were imprecise with wide credible intervals. However, the Pr (harm) with PCI for the all-cause death rate and CV death rate were only 18.6% and 9.8%, respectively.
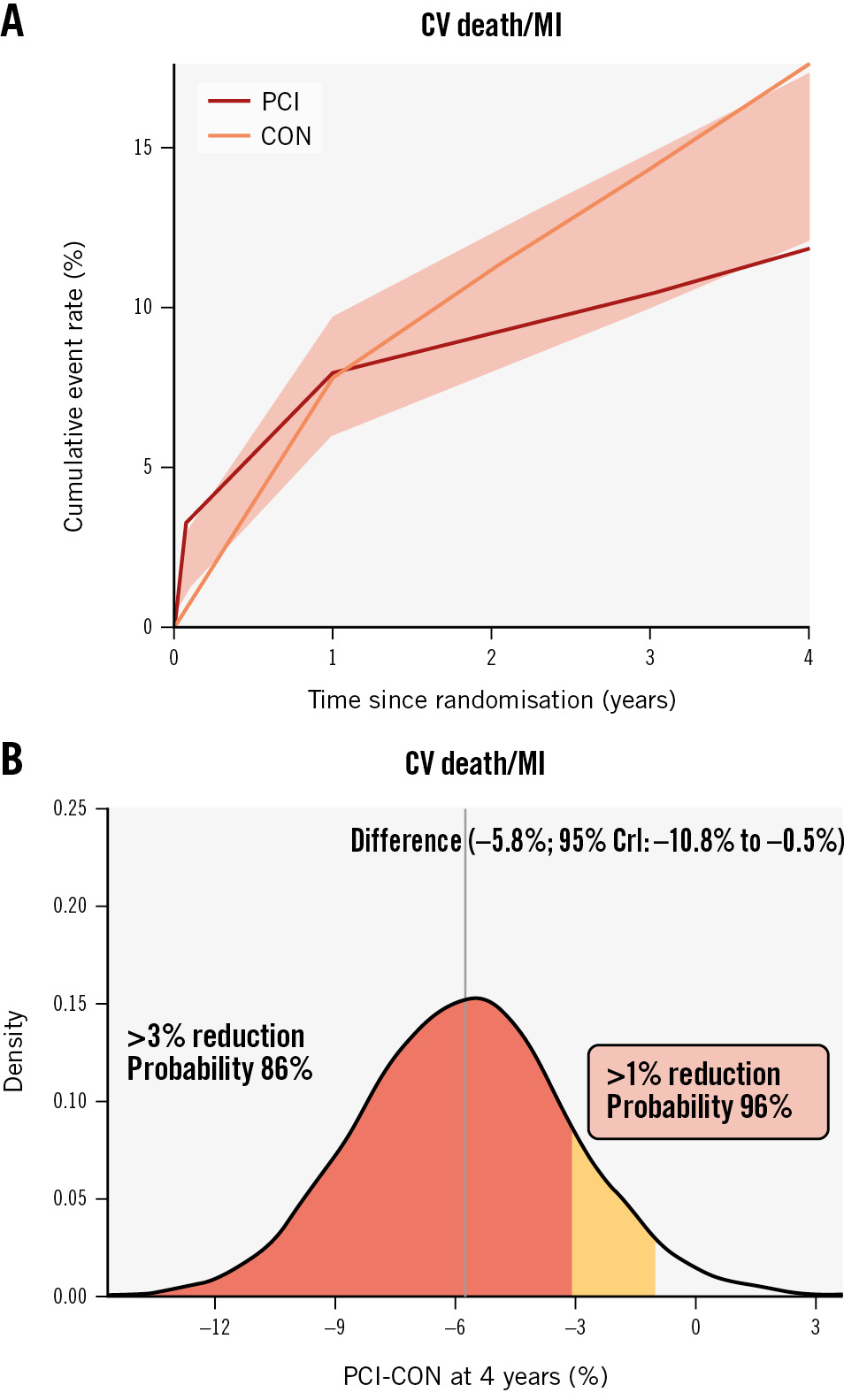
Figure 2. PCI versus CON in participants with 3-vessel disease. A) Cumulative risk estimates for the outcome of CV death or MI; (B) the posterior distribution of the absolute difference in the risk of CV death or MI at 4 years for PCI versus CON. The concentration of values around −6 indicates a benefit to PCI rather than CON by ~6 percentage points. CON: conservative strategy; CrI: credible interval; CV: cardiovascular; MI: myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
Table 2. Posterior probability for revascularisation, PCI or CABG versus CON in participants with 3-vessel disease.
| Treatment effect, % | CV death/MI | All death/MI | All death | CV death | All death/MI/stroke | CV death/MI/stroke |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REV vs CON | ||||||
| >5% lower | 39.5 | 23.4 | 2.0 | 4.2 | 13.6 | 25.2 |
| >3% lower | 74.7 | 56.2 | 16.0 | 31.7 | 41.4 | 59.5 |
| >1% lower | 94.8* | 85.2 | 55.6 | 78.7 | 73.4 | 87.2 |
| Any lower | 98.3* | 93.1* | 75.5 | 92.4* | 84.8 | 94.0* |
| Any higher | 1.7 | 6.9 | 24.5 | 7.6 | 15.2 | 6.0 |
| >1% higher | 0.5 | 2.6 | 10.6 | 1.9 | 7.1 | 2.1 |
| >3% higher | <0.1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | <0.1 | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| >5% higher | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.1 | <0.1 |
| PCI vs CON | ||||||
| >5% lower | 61.8 | 49.4 | 2.6 | 3.5 | 44.0 | 56.9 |
| >3% lower | 85.9 | 76.8 | 16.4 | 22.0 | 72.2 | 82.0 |
| >1% lower | 96.4* | 93.2* | 49.2 | 60.1 | 90.3* | 95.2* |
| Any lower | 98.4* | 96.4* | 67.7 | 78.2 | 95.0* | 97.9* |
| Any higher | 1.6 | 3.6 | 32.4 | 21.8 | 5.1 | 2.1 |
| >1% higher | 0.7 | 1.7 | 18.6 | 9.8 | 2.4 | 0.7 |
| >3% higher | 0.1 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| >5% higher | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| CABG vs CON | ||||||
| >5% lower | 32.0 | 18.4 | 5.3 | 17.3 | 8.7 | 17.0 |
| >3% lower | 61.0 | 43.0 | 27.1 | 57.5 | 24.7 | 40.3 |
| >1% lower | 84.7 | 69.0 | 63.1 | 90.3* | 50.0 | 67.2 |
| Any lower | 91.9* | 79.6 | 78.4 | 96.5* | 62.9 | 79.1 |
| Any higher | 8.1 | 20.4 | 21.6 | 3.5 | 37.1 | 20.8 |
| >1% higher | 3.9 | 12.1 | 10.6 | 0.9 | 26.2 | 12.6 |
| >3% higher | 0.6 | 3.4 | 1.8 | 0.1 | 9.3 | 3.7 |
| >5% higher | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.2 | <0.1 | 2.4 | 0.9 |
| The treatment effect is defined as the difference in the cumulative risk for REV, PCI or CABG vs CON at 4 years post-randomisation. *Indicates probabilities that are high (defined as >90%). CABG: coronary artery bypass graft surgery; CON: conservative management; CV: cardiovascular; MI: myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; REV: revascularisation | ||||||
CLINICAL OUTCOMES: CABG VERSUS CON
Compared with CON, the effect of CABG on CV death or MI (4-year between-group difference −3.7 percentage points, 95% CrI: −8.8 to 1.5 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=84.7%) was directionally similar to that observed with PCI (Figure 3, Supplementary Table 9). CABG was associated with an early procedural risk with 6-month CV death/pMI difference of 9.2 (95% CrI: 5.9 to 13.1) percentage points but lower 4-year CV death/sMI (−9.8 percentage points, 95% CrI: −13.9 to −5.6 percentage points, Pr [benefit] >99.9%) (Supplementary Table 9). For other composite endpoints, the Pr (benefit) with CABG was between 50% and 69% (Table 2, Supplementary Table 7).
In contrast, the estimated between-group differences for all-cause death (−1.7 percentage points, 95% CrI: −5.6 to 2.6 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=63.1%) (Table 2, Supplementary Figure 6) and CV death (−3.3 percentage points, 95% CrI: −6.8 to 0.3 percentage points, Pr [benefit]=90.3%) (Table 2, Supplementary Figure 7) were imprecise with wide credible intervals. However, the Pr (harm) with CABG for the all-cause death rate and CV death rate were only 10.6% and 0.9%, respectively.
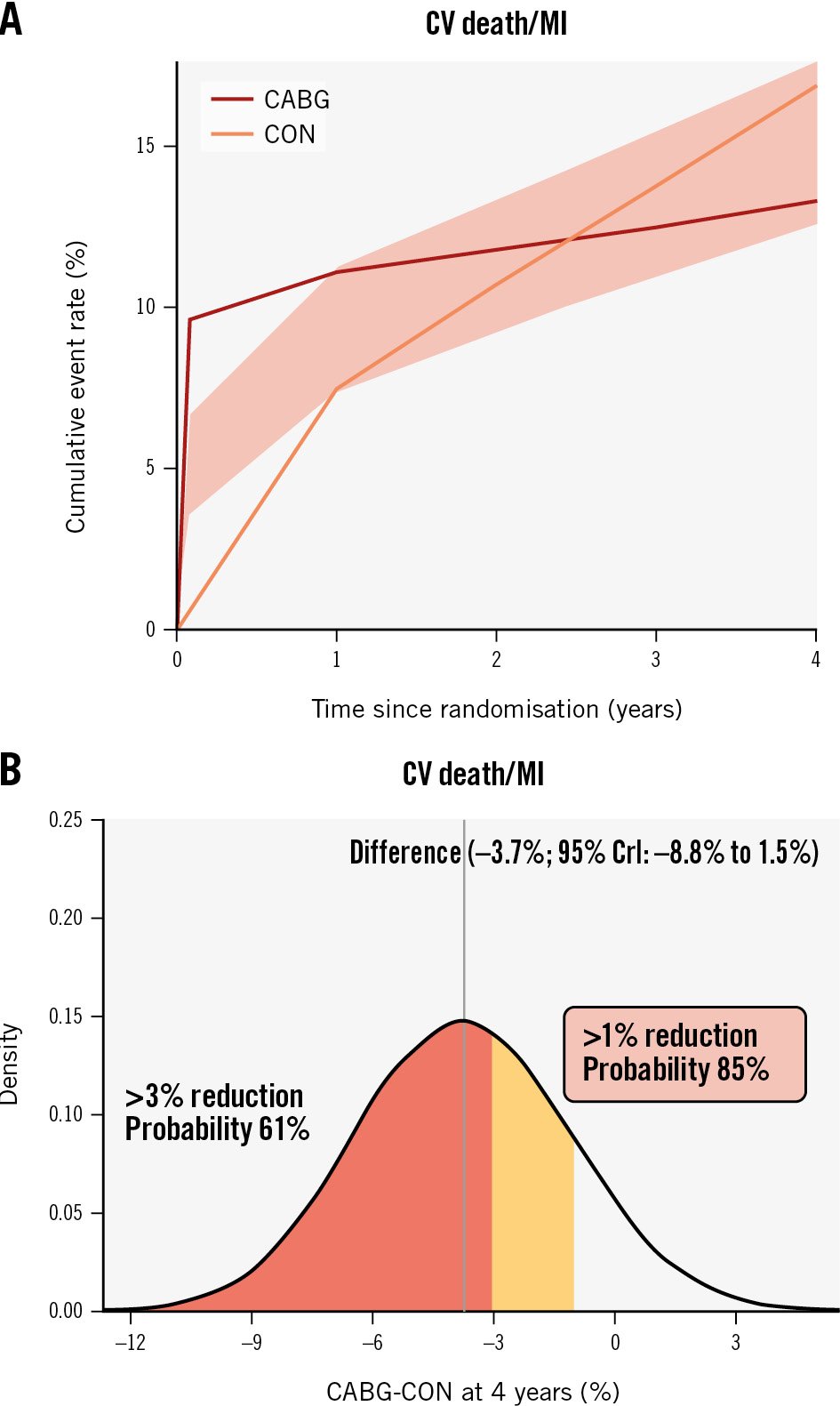
Figure 3. CABG versus CON in participants with 3-vessel disease. A) Cumulative risk estimates for the outcome of CV death or MI; (B) the posterior distribution of the absolute difference in the risk of CV death or MI at 4 years for CABG versus CON. The concentration of values around −4 indicates a benefit to CABG rather than CON by ~4 percentage points. CABG: coronary artery bypass graft surgery; CrI: credible interval; CON: conservative strategy; CV: cardiovascular; MI: myocardial infarction
Table 2. Posterior probability for revascularisation, PCI or CABG versus CON in participants with 3-vessel disease.
| Treatment effect, % | CV death/MI | All death/MI | All death | CV death | All death/MI/stroke | CV death/MI/stroke |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| REV vs CON | ||||||
| >5% lower | 39.5 | 23.4 | 2.0 | 4.2 | 13.6 | 25.2 |
| >3% lower | 74.7 | 56.2 | 16.0 | 31.7 | 41.4 | 59.5 |
| >1% lower | 94.8* | 85.2 | 55.6 | 78.7 | 73.4 | 87.2 |
| Any lower | 98.3* | 93.1* | 75.5 | 92.4* | 84.8 | 94.0* |
| Any higher | 1.7 | 6.9 | 24.5 | 7.6 | 15.2 | 6.0 |
| >1% higher | 0.5 | 2.6 | 10.6 | 1.9 | 7.1 | 2.1 |
| >3% higher | <0.1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | <0.1 | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| >5% higher | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.1 | <0.1 |
| PCI vs CON | ||||||
| >5% lower | 61.8 | 49.4 | 2.6 | 3.5 | 44.0 | 56.9 |
| >3% lower | 85.9 | 76.8 | 16.4 | 22.0 | 72.2 | 82.0 |
| >1% lower | 96.4* | 93.2* | 49.2 | 60.1 | 90.3* | 95.2* |
| Any lower | 98.4* | 96.4* | 67.7 | 78.2 | 95.0* | 97.9* |
| Any higher | 1.6 | 3.6 | 32.4 | 21.8 | 5.1 | 2.1 |
| >1% higher | 0.7 | 1.7 | 18.6 | 9.8 | 2.4 | 0.7 |
| >3% higher | 0.1 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| >5% higher | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| CABG vs CON | ||||||
| >5% lower | 32.0 | 18.4 | 5.3 | 17.3 | 8.7 | 17.0 |
| >3% lower | 61.0 | 43.0 | 27.1 | 57.5 | 24.7 | 40.3 |
| >1% lower | 84.7 | 69.0 | 63.1 | 90.3* | 50.0 | 67.2 |
| Any lower | 91.9* | 79.6 | 78.4 | 96.5* | 62.9 | 79.1 |
| Any higher | 8.1 | 20.4 | 21.6 | 3.5 | 37.1 | 20.8 |
| >1% higher | 3.9 | 12.1 | 10.6 | 0.9 | 26.2 | 12.6 |
| >3% higher | 0.6 | 3.4 | 1.8 | 0.1 | 9.3 | 3.7 |
| >5% higher | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.2 | <0.1 | 2.4 | 0.9 |
| The treatment effect is defined as the difference in the cumulative risk for REV, PCI or CABG vs CON at 4 years post-randomisation. *Indicates probabilities that are high (defined as >90%). CABG: coronary artery bypass graft surgery; CON: conservative management; CV: cardiovascular; MI: myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; REV: revascularisation | ||||||
QUALITY OF LIFE OUTCOMES
The effects of REV, PCI and CABG when compared with CON on 12-month health status are outlined in Figure 4. REV, PCI and CABG improved the 12-month SAQ-7 summary score when compared with CON. The between-group differences were 4.6 points (95% CrI: 2.7 to 6.4) for REV versus CON: 3.6 points (95% CrI: 1.2 to 5.8) for PCI versus CON and 4.3 points (95% CrI: 1.5 to 6.9) for CABG versus CON. There was a 90% probability that REV, PCI and CABG improved SAQ-7 scores by 3.4, 2.1 and 2.6 points, respectively, when compared with CON. The effects of PCI and CABG compared with CON were directionally consistent for other SAQ QoL endpoints (Figure 4).
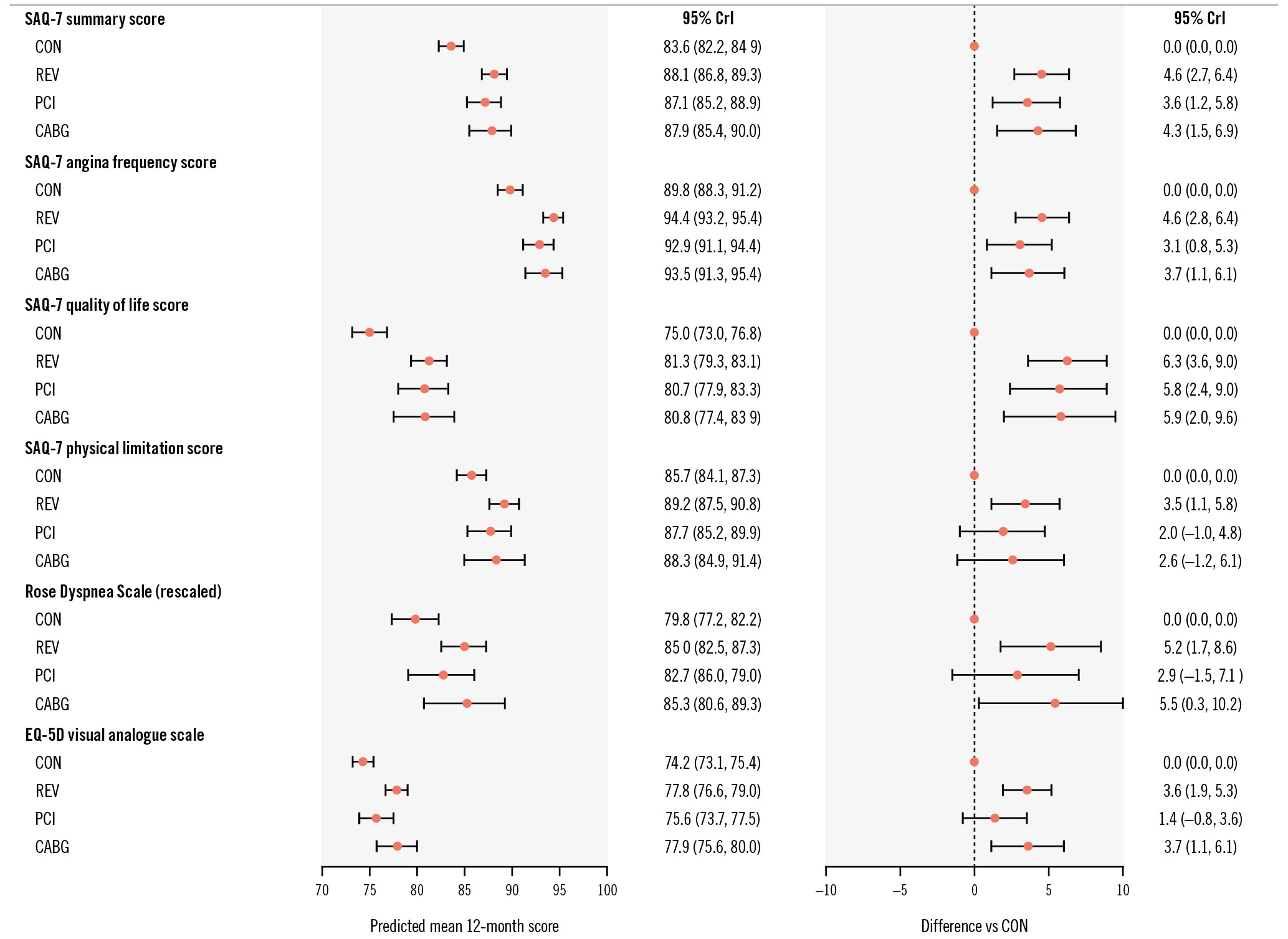
Figure 4. Effect of revascularisation, PCI, CABG versus CON on QoL outcomes. CABG: coronary artery bypass graft surgery; CON: conservative strategy; CrI: credible interval; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; QoL: quality of life; REV: revascularisation ; SAQ: Seattle Angina Questionnaire
Discussion
In this analysis, comparing outcomes with the specific mode of revascularisation received compared to the conservative strategy, among participants with 3V-CAD (≥50% stenosis) and no prior CABG in the CCTA-evaluable ISCHEMIA trial cohort, REV was associated with a >90% probability of at least a 1 percentage point lower 4-year CV death or MI rate when compared with CON. PCI had a >90% probability of at least a 1 percentage point lower 4-year CV death or MI rate when compared with CON, and CABG had an 85% probability of at least a 1 percentage point lower 4-year CV death or MI rate when compared with CON. Moreover, angina-related QoL was substantially improved by REV, PCI and CABG compared with CON (Central illustration).
However, the posterior probability of at least a 1 percentage point lower 4-year rate of all-cause death with REV, PCI or CABG was estimated at 49-63% when compared with CON. For context, a coin flip has a 50% probability of either outcome. The estimated differences in death were imprecise, with wide credible intervals indicating uncertainty. Of note, the probability for harm (at least a 1 percentage point higher rate of death over 4 years) with either revascularisation modality was 11-19%.
A meta-analysis by Yusuf et al of trials of CABG versus no CABG that were done in the 1970s and 1980s showed a mortality benefit with CABG at 5 years (p<0.001) that narrowed at 10 years (p=0.03) of follow-up6. Two of the 3 large trials included in this meta-analysis failed to show a statistically significant reduction in mortality with CABG (Supplementary Table 10). Of note, the studies included a proportion of patients with left main disease (which was excluded in ISCHEMIA). Medical therapy has greatly advanced since that time, and in ISCHEMIA, 95% of participants were on statins, 66% were on high-intensity statin therapy, the median achieved low-density lipoprotein cholesterol was 64 mg/dl, and the median achieved systolic blood pressure was 129 mmHg. Despite this, the 4-year mortality rate of 9.0% for CON in the current analysis, which excluded those without CCTA, e.g., high-risk chronic kidney disease patients, was higher than the 4-year mortality rate of 6.4% for CON in the overall trial, reflecting the higher anatomical risk subset of patients with 3V-CAD. In the current analysis, restricted to participants with 3V-CAD, REV, PCI and CABG were associated with an early procedural risk. The posterior probabilities of a 1 percentage point lower 4-year rate of death were 55.6%, 49.2% and 63.1% with REV, PCI and CABG, respectively, when compared with CON, indicating uncertainty regarding whether there is a lower rate of all-cause mortality. Randomised trials published since the meta-analysis by Yusuf et al have shown similar findings. In the BARI2D trial, neither the PCI nor the CABG stratum reduced death when compared with medical therapy (CABG vs medical therapy; p=0.33)15. Similar results of no significant difference between CABG and medical therapy for death were observed in the MASS II trial at 10 years of follow-up16 and in other trials of patients with chronic coronary disease and preserved left ventricular (LV) function (Supplementary Table 10). Meta-analyses of randomised trials in chronic coronary disease and preserved LV function have similarly shown no significant difference in overall mortality with revascularisation (PCI or CABG)17, or with CABG, when compared with medical therapy18. However, in an individual patient-level data meta-analysis of 4 randomised controlled trials (MASS I, MASS II, STICHES and BARI2D), CABG increased mortality within 30 days (hazard ratio [HR] 4.81, 95% CI: 1.95-11.83) but reduced long-term death (HR 0.79, 95% CI: 0.69-0.89) when compared with medical therapy. In the subgroup with preserved LV function (≥50%), there was a non-significant reduction in mortality with CABG (HR 0.81, 95% CI: 0.60-1.10)19.
Navarese et al, in a meta-analysis that included older trials, showed a 21% reduction (risk ratio [RR] 0.79, 95% CI: 0.67-0.93) in CV death with revascularisation, with a consistent effect even when trials of CABG were excluded20. In the current analysis from ISCHEMIA, REV, PCI and CABG were associated with an imprecise lower 4-year rate of CV death. The posterior probabilities of a 1 percentage point lower 4-year CV death rate were 78.7%, 60.1% and 90.3% with REV, PCI and CABG, respectively, versus CON. In the interim longer-term follow-up of the entire trial cohort (ISCHEMIA-EXTEND), there was a lower 7-year CV mortality (HR 0.78, 95% CI: 0.63-0.96) but a higher non-CV mortality (HR 1.44, 95% CI: 1.08-1.91) with INV compared with CON, with no difference in overall mortality21.
Finally, REV with either PCI or CABG for 3V-CAD was associated with a lower 4-year rate of the composite of CV death or MI despite an early procedural risk (Supplementary Table 6, Supplementary Table 8, Supplementary Table 9). Bayesian analysis showed that the probability of at least a 3 percentage point lower 4-year rate of CV death or MI was >80% with PCI when compared with CON and was 61% with CABG when compared with CON, whereas the probability of at least a 1 percentage point lower 4-year rate of CV death or MI was >80% with both modalities. The relatively lower posterior probability of the advantage of CABG versus CON for the outcome of CV death or MI was driven by the higher upfront risk of CV death and an even higher risk of procedural MI when compared with PCI versus CON. For the composite outcomes that excluded procedural MI, there was a >90% probability of at least a 3 percentage point lower 4-year CV death or sMI rate with PCI and at least a 5 percentage point lower 4-year CV death or sMI rate with CABG when compared with CON (Supplementary Table 7).
Finally, both PCI and CABG improved angina-related QoL when compared with CON, a critical outcome from patients’ perspectives. There was a 90% probability that REV, PCI and CABG improved SAQ-7 scores by 3.4, 2.1 and 2.6 points, respectively, when compared with CON.
Taken in aggregate, the results from this analysis and those of other contemporary trials indicate uncertainty regarding whether there is a lower rate of death with either routine prompt PCI or CABG when compared with a strategy of GDMT and revascularisation reserved for failure of medical therapy. As medical therapy has further advanced since ISCHEMIA with the use of low-dose rivaroxaban, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, the absolute difference in mortality between REV plus medical therapy versus medical therapy alone may be even lower. Nonetheless, revascularisation was safe, with a low probability of higher mortality when compared with CON. The decision to consider REV in patients with 3V-CAD should thus be based on symptom control and other outcomes including a potential reduction in the composite of CV death or MI, as well as patient preferences weighing the upfront risks of REV versus improved long-term outcomes. This is concordant with the 2021 ACC/AHA/SCAI revascularisation guidelines that downgraded CABG to a Class 2b recommendation to improve survival based on a detailed review of prior trials (such as BARI2D) and newer evidence including meta-analyses with and without ISCHEMIA4. The analysis is also concordant with the newer Class 2a recommendation by the 2021 guidelines for revascularisation to lower the risk of cardiovascular events such as spontaneous MI, unplanned urgent revascularisations, or cardiac death4. Similarly, the 2018 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) guideline on myocardial revascularisation lists 2V- or 3V-CAD with stenosis >50% as an indication for revascularisation to improve prognosis in patients with impaired LV function (LVEF ≤35%) but not in those without impaired LV function22. Patients with LVEF <35% were excluded from ISCHEMIA. Finally, the 2023 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients with Chronic Coronary Disease gave a Class 1 recommendation for CABG to improve survival in patients with multivessel disease only in the setting of severe LV dysfunction5.
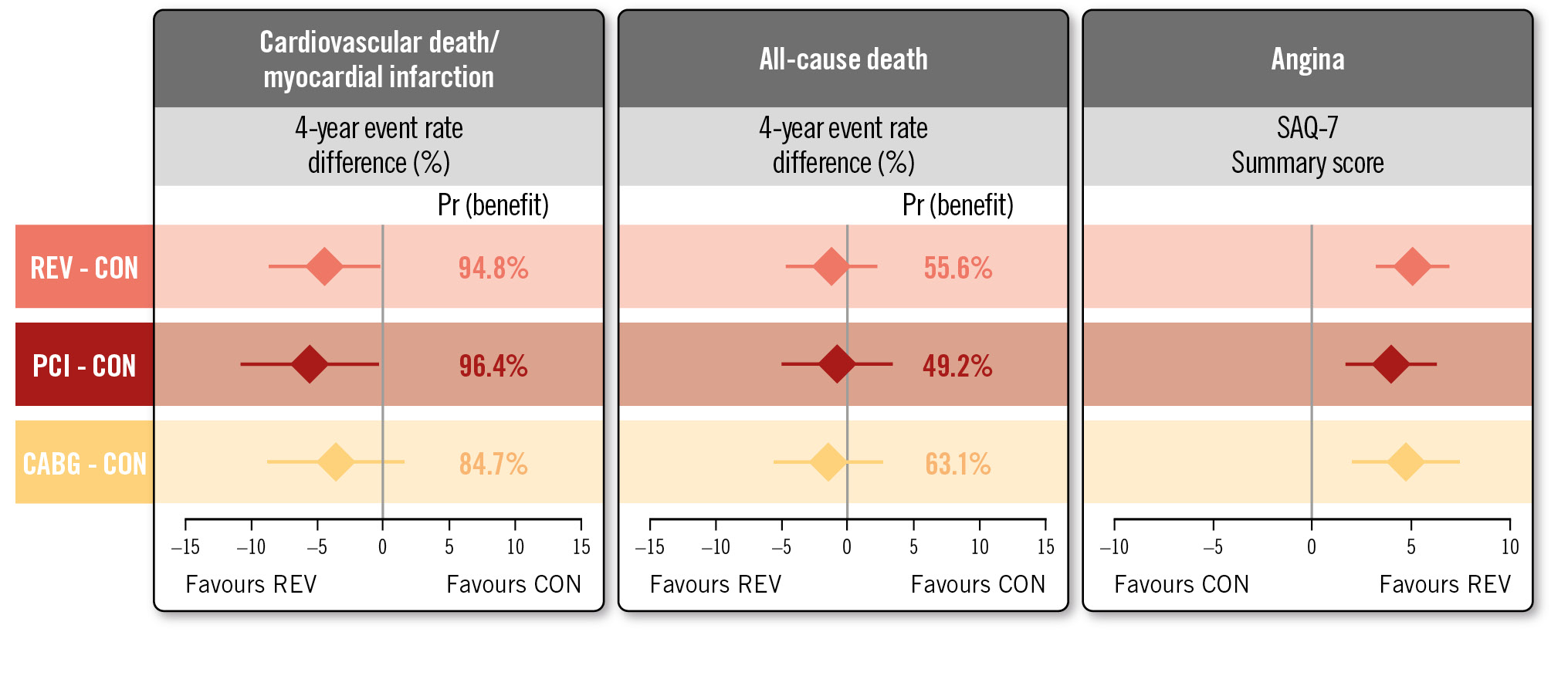
Central illustration. Effect of revascularisation, PCI, CABG versus CON on clinical and QoL outcomes in patients with 3-vessel CAD without prior CABG in the ISCHEMIA trial (N=1,236). CABG: coronary artery bypass graft surgery; CAD: coronary artery disease; CON: conservative strategy; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; Pr (benefit): probability of >1 percentage point reduction over 4 years; QoL: quality of life; REV: revascularisation; SAQ: Seattle Angina Questionnaire
Limitations
This study has a number of important limitations. First, despite using data from a randomised trial, the current ISCHEMIA analysis was observational and susceptible to bias. After randomising patients to INV versus CON, the timing of REV and the choice of PCI versus CABG for INV was left to the local Heart Team. The clinical profiles of patients selected for PCI and CABG differed from one another and from the overall INV group. We used regression modelling combined with direct standardisation to adjust for non-random treatment selection. This technique can only control for differences that were explicitly measured and incorporated in the adjustment procedure. Residual bias from unmeasured differences may have influenced the findings. An additional assumption is that all INV participants were eligible to receive REV. If REV was not an option for some INV participants due to unmeasured anatomical or clinical factors, the observed differences in outcomes may be partly a reflection of different patients rather than different treatments. Moreover, this observational analysis estimated outcomes for a patient population enrolled in ISCHEMIA. Of the 4,976 participants in the ISCHEMIA cohort with no prior CABG, 2,911 (58.5%) had a core lab-interpreted CCTA that was evaluable for the number of diseased vessels based on the 50% threshold. To extend results to the general 3V-CAD population with no prior CABG with or without an evaluable CCTA, one must assume that there were no systematic differences affecting the outcomes for participants who did versus did not have an evaluable CCTA. Notwithstanding these considerations, the results are consistent with meta-analyses of randomised trials showing lack of a significant reduction in death with REV when compared with medical therapy alone in patients with chronic coronary disease without left main involvement or LV dysfunction. Second, ISCHEMIA was not powered to demonstrate a difference in all-cause death. Given the wide credible intervals, we cannot exclude a clinically meaningful lower (or higher) mortality with either PCI or CABG in patients with 3V-CAD. Third, we used a 50% diameter stenosis severity threshold for the inclusion criteria (in addition to at least moderate ischaemia on a stress test), consistent with the majority of trials of CABG versus medical therapy listed in Supplementary Table 10 and also in the recently published FAME 3 trial24; whether the results would be different were REV restricted to more severe lesions is unknown. Fourth, the use of internal mammary artery grafting was ~92%, and it is not known if the results would have been different with greater use of this or with multiarterial grafts. Fifth, we used a CCTA definition of 3VD for entry criteria, given that patients randomised to CON did not routinely undergo coronary angiography. However, this should not differentially affect the INV and CON groups. Finally, longer-term follow-up from this trial (presently planned up to 10 years) is required to examine whether a late survival difference emerges with REV.
Conclusions
In this analysis, among participants with 3V-CAD randomised in ISCHEMIA without prior CABG, revascularisation (PCI or CABG) was associated with a lower 4-year rate of CV death or MI despite an early procedural risk. Moreover, REV improved angina-related quality of life. However, the estimated difference in the rate of death with revascularisation (PCI or CABG) compared with conservative management was imprecise, with wide credible intervals indicating uncertainty. The posterior probability of at least a 1 percentage point lower 4-year rate of death with revascularisation overall, with PCI, or with CABG was estimated at 49-63% when compared with conservative management. The probability of at least a 1 percentage point higher rate of death over 4 years with either REV modality was 11-19%.
Impact on daily practice
This post hoc analysis of participants with three-vessel coronary artery disease (3V-CAD) randomised in the ISCHEMIA trial suggests that revascularisation (with either percutaneous coronary intervention or coronary artery bypass graft surgery) was associated with a lower 4-year rate of cardiovascular death or myocardial infarction, despite early procedural risk, and with a significantly improved quality of life, but the impact on overall mortality was similar with wide confidence intervals when compared with initial conservative management. These associations should be considered in the management of patients with 3V-CAD.
Funding
NIH grants U01HL105907, U01HL105462, U01HL105561, U01HL105565, T32HL079896. This project was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and in part by Clinical Translational Science Award Nos. 11UL1 TR001445 and UL1 TR002243 from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Institutes of Health, or the Department of Health and Human Services.
Conflict of interest statement
S. Bangalore reports grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute during the conduct of the study; grants and personal fees from Abbott; personal fees from Biotronik, Pfizer, Amgen, and Reata outside of the submitted work. G. Rhodes reports NIH funding. D.J. Maron reports grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute during the conduct of the study. R. Anthopolos reports grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute during the conduct of the study. S.M. O’Brien reports grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute during the conduct of the study. D.B. Mark reports grants from National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute during the conduct of the study; and grants from HeartFlow and Merck, outside the submitted work. H.R. Reynolds reports grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute during the conduct of the study; and non-financial support from Abbott, Siemens, and BioTelemetry, outside of the submitted work. J.A. Spertus reports grants from National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Bayer, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Janssen, and United Healthcare; and grants from American College of Cardiology, outside the submitted work; in addition, he has a patent copyright to the Seattle Angina Questionnaire with royalties paid; is on the Board of Directors for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Kansas City; and reports equity in Health Outcomes Sciences. G.W. Stone has received speaker honoraria from Medtronic, Pulnovo, and Infraredx; has served as a consultant to Valfix, TherOx, Robocath, HeartFlow, Ablative Solutions, Vectorious, Miracor, Neovasc, Abiomed, Ancora, Elucid Bio, Occlutech, CorFlow, Apollo Therapeutics, Impulse Dynamics, Cardiomech, Gore Medical, Amgen, Adona Medical, and Millennia Biopharma; and has equity/options from Ancora, Cagent, Applied Therapeutics, Biostar family of funds, SpectraWAVE, Orchestra Biomed, Aria, Cardiac Success, Valfix, and Xenter; his daughter is an employee at Medtronic; for institutional disclosure, his employer, Mount Sinai Hospital, receives research support from Abbott, Abiomed, Bioventrix, Cardiovascular Systems Inc, Philips, Biosense Webster, Shockwave Medical, Vascular Dynamics, Pulnovo, and V-Wave. H.D. White reports grants from National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute during the conduct of the study; reports receiving grant support paid to the institution and fees for serving on a steering committee for the ODYSSEY OUTCOMES trial (Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcomes After an Acute Coronary Syndrome During Treatment With Alirocumab) from Sanofi-Aventis and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals; for the ACCELERATE study (A Study of Evacetrapib in High-Risk Vascular Disease) from Eli Lilly; for the STRENGTH trial (Outcomes Study to Assess Statin Residual Risk Reduction With EpaNova in High CV Risk Patients With Hypertriglyceridemia) from Omthera Pharmaceuticals; for the HEART-FID study (Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial of FCM as Treatment for Heart Failure With Iron Deficiency) from American Regent; for the CAMELLIA-TIMI study (A Study to Evaluate the Effect of Long-term Treatment With BELVIQ [Lorcaserin HC] on the Incidence of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events and Conversion to Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Obese and Overweight Subjects With Cardiovascular Disease or Multiple Cardiovascular Risk Factors) from Eisai Inc; for the dal-GenE study (Effect of Dalcetrapib vs Placebo on CV Risk in a Genetically Defined Population With a Recent ACS) from DalCor Pharma UK Inc; for the AEGIS-II study from CSL Behring; for the SCORED trial (Effect of Sotagliflozin on Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Moderate Renal Impairment Who Are at Cardiovascular Risk) and the SOLOIST-WHF trial (Effect of Sotagliflozin on Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Type2 Diabetes Post Worsening Heart Failure) from Sanofi-Aventis Australia Pty Ltd; and for the CLEAR Outcomes Study (Evaluation of Major Cardiovascular Events in Patients With, or at High Risk for, Cardiovascular Disease Who Are Statin Intolerant Treated With Bempedoic Acid. [ETC-1002] or Placebo) from Esperion Therapeutics Inc; he was on the advisory board for Genentech, Inc.; and received lecture fees from AstraZeneca. Y. Xu reports grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute during the conduct of the study. J.S. Hochman is the PI for the ISCHEMIA trial for which, in addition to support by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute grant, devices and medications were provided by Abbott, Medtronic, Abbott Laboratories (formerly St. Jude Medical, Inc.), Royal Philips NV (formerly Volcano Corporation), Arbor Pharmaceuticals, LLC, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals, LP, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., Omron Healthcare, Inc., Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Espero BioPharma, and Amgen, Inc.; and received financial donations from Arbor Pharmaceuticals LLC and AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

