Abstract
Background: Transcatheter tricuspid valve replacement (TTVR) is rapidly emerging as a therapeutic option amongst patients with secondary tricuspid regurgitation. Historical data from surgical tricuspid valve replacement (TVR) studies may serve as a benchmark for the development of TTVR trials.
Aims: The aim of the study was to investigate the early and late outcomes following isolated surgical TVR.
Methods: Multiple electronic databases were searched to identify studies on isolated surgical TVR. The prespecified primary endpoint was operative mortality; secondary endpoints were early and late outcomes. Overall estimates of proportions and incidence rates with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated using random-effects models. Multiple sensitivity analyses accounting for baseline characteristics, country and the operative period were applied.
Results: A total of 35 studies (5,316 patients) were included in this meta-analysis. The operative period ranged from 1974 to 2019. The overall rate of operative mortality was 12% (95% CI: 9-15), with higher mortality for patients who were operated on before 1995, who had prior cardiac surgeries, or who had liver disease. The most frequent clinical events were pacemaker implantation (10% [95% CI: 6-16]), bleeding (12% [95% CI: 8-17]), acute kidney injury (15% [95% CI: 9-24]) and respiratory complications (15% [95% CI: 12-20]). At follow-up analysis of the bioprosthetic TVR, there was an incidence rate per 100 person-years of 6 (95% CI: 2-13) for death and 8 (95% CI: 5-13) for recurrence of significant tricuspid regurgitation.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis provides an overview of the historical clinical outcomes following isolated surgical TVR. These findings can support the development of future clinical trials in the tricuspid space by providing thresholds for clinical outcomes.
Introduction
"One of the most valuable things any person can learn is the art of using the knowledge and experience of others".
Napoleon Hill
The presence of clinically significant tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is common and is independently associated with excess mortality12. Also, right-sided heart failure is an important public health problem, and several publications support its early treatment3. However, symptomatic TR continues to be undertreated in comparison to left-sided valvular diseases4. This has been mainly attributed to the high mortality and morbidity rates of tricuspid valve (TV) surgery.
The TV has challenging anatomical features that are known predictors of procedural failure and limit the broad application of repair techniques. In contrast to mitral valve surgery, the great majority of TV patients (59%) undergo surgical replacement35. Isolated tricuspid valve replacement (TVR) has been found to have an overall mortality risk of ~10%, and this figure has not significantly changed over time56. Considering the unwavering mortality risk associated with TV surgery, the sizeable gap between patients with TV disease and those undergoing definitive correction is unlikely to be filled by surgery; therefore, several transcatheter solutions are under investigation to address this unmet clinical need at a lower procedural risk78.
Given the growing interest in transcatheter tricuspid valve replacement (TTVR), a more profound understanding of the historical surgical data is fundamental and may serve as a benchmark for developing future therapies9. To date, no randomised controlled trials or systematic literature analyses have examined this procedure. With this background, we performed an up-to-date comprehensive meta-analysis to provide a quantitative assessment of evidence regarding the outcomes after isolated surgical TVR.
Methods
The protocol of this meta-analysis has been registered in PROSPERO (international prospective register of systematic reviews; CRD42021284309) and was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) and the Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) reporting guidelines (Supplementary Appendix 1, Supplementary Appendix 2)1011. Given the nature of the work, ethical approval was not required.
Search strategy and study selection
Randomised trials and observational studies on isolated surgical TVR were evaluated for inclusion in this meta-analysis. Prespecified criteria to consider the studies eligible for inclusion were: 1) they reported separate outcome data for patients undergoing isolated TVR; 2) they included at least 10 patients; 3) there were no overlapping populations; 4) there were no exclusively congenital TV diseases; 5) there were no paediatric populations. With the aim of investigating all the literature on isolated TVR as a benchmark for TTVR, we excluded the following from the analyses: 1) patients undergoing surgical tricuspid valve repair and 2) non-isolated TVR. No restriction on the publication date was applied.
A systematic search of the literature was performed in PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, and Web of Science, from the database's inception up to the final search date of October 10th, 2021. In addition, the reference lists of prior systematic reviews and included articles were screened to find further potentially relevant studies (backward snowballing). The search strings are available in Supplementary Appendix 3. The data underlying this article will be shared upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two reviewers (A. Scotti, M. Sturla) independently searched the electronic bibliographic databases. After the removal of duplicates, the title and abstract were screened to exclude non-relevant studies; subsequently, the full text of the remaining results was retrieved for further appraisal. Discrepancies were discussed and resolved with a senior reviewer (A. Latib). A dedicated electronic database was used for data extraction and included: sample size, operative data, baseline patient characteristics, procedural complications and late outcomes.
Two independent reviewers (A.Scotti, M. Sturla) performed the Risk of Bias In Non-randomised Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I) assessment tool from the Cochrane handbook assessment for observational studies12.
Outcomes measures
The prespecified primary endpoint was operative mortality, defined as any death that occurred within 30 days after TVR or during the index hospitalisation. Secondary endpoints were early events (stroke, acute kidney injury, renal replacement therapy, bleeding, respiratory complications, pacemaker implantation, and wound infection), late mortality, TV reintervention (surgical or percutaneous), valve thrombosis, structural valve deterioration, and recurrence of at least moderate TR at follow-up. The full list of characteristic and outcome definitions is available in the Supplementary Appendix 4.
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics were presented as pooled, weighted means or proportions and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Whenever applicable, the mean±standard deviation was calculated from the reported median and interquartile range according to Wan et al13. Study-level and pooled estimates were reported as proportions or incidence rates with 95% CI, for early and late outcomes, respectively. A random-effects model using the logit transformation with the "empirical Bayes" (Paule-Mandel) estimator was applied for the meta-analysis of proportions1415. A random-effects model using the log transformation and the maximum-likelihood estimator was used to calculate incidence rates. To account for heterogeneity in follow-up, overall incidence rates were estimated per 100 person-years. If available, the collection of the numbers of actual observations at follow-up was preferred over the whole sample size, avoiding assumptions about any participants for whom the outcome was not measured16. The indirect methods by Tierney and colleagues were adopted to retrieve missing data (i.e., events, time at risk) for incidence rate estimates; when the available information was insufficient, data were retrieved from Kaplan-Meier curves using follow-up time, estimated rates, and numbers at risk assuming random (non-informative) censoring17. A continuity correction of 0.5 has been applied for studies having either zero or all events (i.e., an event probability of either 0 or 1).
Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using Cochran’s Q test and I² values. I² values of less than 25%, 25-50%, or more than 50% were regarded as being indicative of low, moderate or high heterogeneity, respectively18. Publication bias and small-study effect were assessed by visual inspection of funnel plots and using Begg’s test. A Baujat plot, which is a scatter plot with the contribution of each study to the overall heterogeneity (as measured by Cochran’s Q test) on the x-axis and the standardised difference of the overall treatment effect with and without each study on the y-axis, is provided19.
As a sensitivity analysis, a random intercept logistic regression model was used for the meta-analysis of proportions2021. The potential interaction among continents or operative periods (before 1995 versus after 1995, i.e., median operative time) and treatment effect was investigated with subgroup analyses for the primary endpoint. For this purpose, random-effects models were performed validating the confidence intervals by adjustment according to the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman method22.
Meta-regressions were performed to evaluate the potential impact of several characteristics (year of publication, operative period, continent, estimated risk of bias, age, left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction, prevalence of females, diabetes mellitus, atrial fibrillation, hypertension, TVR with bioprostheses, endocarditis, secondary TR, liver disease, and previous cardiac surgery) on the outcomes of interest. Cumulative and leave-one-out sensitivity analyses were conducted to show how each study might affect the overall estimates. Further sensitivity analyses included the calculation of proportions and incidence rates with 95% CI using fixed-effects models with the Mantel-Haenszel method. Statistical significance was set at a p-value <0.05 (2-sided). All analyses were performed with R, version 4.0.2 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing), packages meta and metafor.
Results
Search results
The search strategy results and study selection process are illustrated in Figure 1 and Supplementary Appendix 2. Thirty-five observational studies were found to be eligible for inclusion in this meta-analysis32324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354. The main features of the included studies are presented in Table 1. The operative period was up to 2019, and the most represented countries were the USA and China. Apart from 6 studies that showed in-hospital outcomes, the others reported up to 14 years of mean follow-up time.
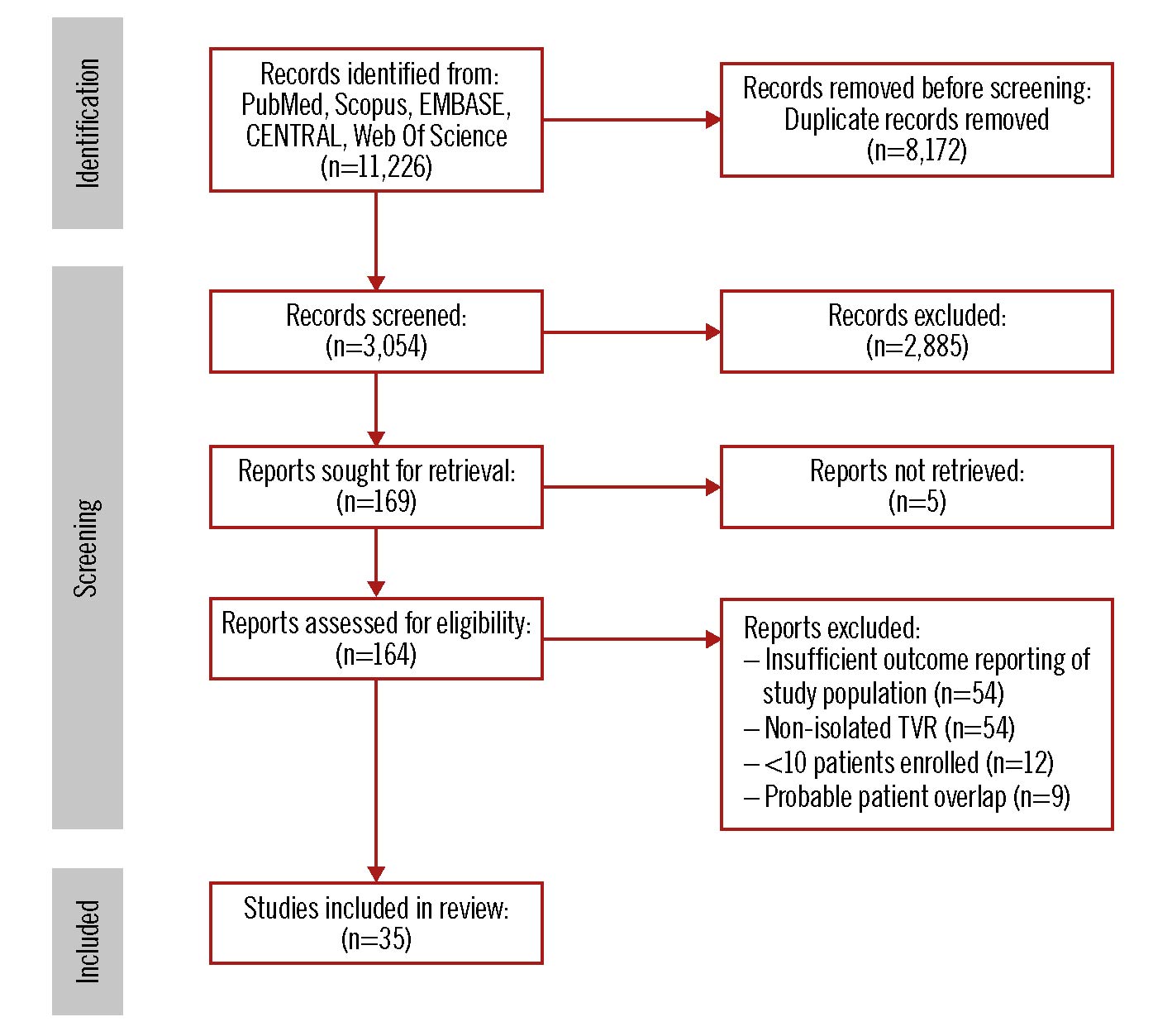
Figure 1. Flowchart of the study selection progress. TVR: tricuspid valve replacement
Table 1. Key study features.
|
Study |
Year |
Patients |
Bioprosthetic valve (%) |
Operative time |
Country |
Multicentre (n) |
Follow-up§ (years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sanfelippo et al |
1976 |
15 |
0 (0) |
Up to 1972 |
USA |
No |
4 |
|
Glower et al* |
1995 |
35 |
35 (100) |
1974-1993 |
USA |
No |
In-hospital |
|
Ian Munro et al |
1995 |
30 |
NR |
1975-1992 |
Canada |
No |
4 |
|
Do et al |
2000 |
29 |
26 (90) |
1978-1998 |
Canada |
No |
6 |
|
Mangoni et al |
2001 |
15 |
5 (33) |
1984-1994 |
USA |
No |
3 |
|
Maleszka et al |
2004 |
20 |
5 (25) |
1985-2002 |
Germany |
No |
3 |
|
Solomon et al |
2004 |
33 |
25 (76) |
1996-2002 |
N. Zealand |
No |
5 |
|
Iscan et al |
2007 |
20 |
NR |
1987-2004 |
Turkey |
No |
6 |
|
Tokunaga et al* |
2008 |
31 |
27 (87) |
1975-2004 |
Japan |
No |
8 |
|
Capoun et al |
2010 |
11 |
8 (73) |
1999-2009 |
UK |
No |
2 |
|
Baraki et al* |
2013 |
18 |
14 (78) |
1996-2012 |
Germany |
No |
6 |
|
Kim et al* |
2013 |
14 |
10 (71) |
1996-2010 |
Republic of Korea |
No |
3 |
|
Bevan et al |
2014 |
29 |
23 (79) |
1995-2011 |
N. Zealand |
No |
14 |
|
Buzzatti et al |
2014 |
61 |
NR |
1997-2012 |
Italy |
No |
5 |
|
Farag et al |
2017 |
68 |
36 (53) |
1995-2011 |
Germany |
No |
NR |
|
Hanedan et al* |
2017 |
30 |
10 (33) |
2004-2011 |
Turkey |
No |
2 |
|
Rossello et al |
2017 |
25 |
0 (0) |
1996-2012 |
Spain |
No |
5 |
|
Çakıcı et al |
2018 |
25 |
22 (88) |
2010-2016 |
Turkey |
No |
2 |
|
Chen et al* |
2018 |
118 |
102 (86) |
2003-2016 |
China |
No |
In-hospital |
|
Fang et al* |
2018 |
90 |
74 (82) |
2007-2016 |
China |
No |
9 |
|
Moutakiallah et al |
2018 |
11 |
5 (45) |
2000-2017 |
Morocco |
No |
6 |
|
Di Mauro et al |
2019 |
80 |
54 (68) |
1979-2018 |
Italy |
Yes (21) |
19 |
|
Kundi et al* |
2019 |
2,670 |
1,737 (65) |
2003-2014 |
USA |
Yes (841) |
1 |
|
Liang et al* |
2019 |
76 |
43 (57) |
2010-2017 |
China |
No |
4 |
|
Chen et al* |
2020 |
107 |
25 (23) |
2009-2017 |
China |
No |
5 |
|
Dreyfus et al |
2020 |
273 |
264 (97) |
2007-2017 |
France |
Yes (12) |
3 |
|
Sánchez-Espín G et al* |
2020 |
56 |
48 (86) |
1996-2017 |
Spain |
No |
4 |
|
Wong et al |
2020 |
137 |
NR |
2000-2013 |
Taiwan |
Yes (NA) |
4 |
|
Yan et al* |
2020 |
49 |
49 (100) |
2012-2019 |
China |
No |
2 |
|
Kawsara et al* |
2021 |
552 |
468 (85) |
2016-2017 |
USA |
Yes (NA) |
In-hospital |
|
Lee et al |
2021 |
216 |
NR |
2000-2013 |
Taiwan |
Yes (NA) |
4 |
|
Leviner et al |
2021 |
33 |
31 (94) |
2007-2018 |
Israel |
Yes (2) |
4 |
|
Liu et al* |
2021 |
186 |
145 (78) |
1999-2018 |
China |
Yes (2) |
11 |
|
Park et al |
2021 |
106 |
23 (22) |
1996-2018 |
Republic of Korea |
No |
4 |
|
Tafti et al# |
2021 |
47 |
41 (87) |
2010-2018 |
Iran |
No |
5 |
|
§Mean follow-up. *Studies reporting outcome data for bioprosthetic valve group. #Reported data were clarified and confirmed upon contacting corresponding authors. NA: not applicable; NR: not reported |
|||||||
A total of 5,316 patients undergoing isolated TVR were analysed. The baseline characteristics of the study population are reported in Supplementary Table 1. The mean age was 53 (95% CI: 49-56) years, and the majority (63% [95% CI: 57-69]) were female. Six out of 10 patients (60% [95% CI: 27-85]) had previous cardiac surgery. The pooled mean LV ejection fraction was within normal limits (58% [95% CI: 54-61]). Comorbidities, such as diabetes, hypertension and liver disease, were present in less than one-third of patients.
Risk of bias and publication bias
The risk of bias was assessed for every observational study, as shown in Supplementary Table 2. The majority of included studies presented an overall moderate risk of bias. Possible concerns were raised for some studies in the domain of “bias due to confounding” because baseline prognostic characteristics were found to influence the choice of intervention (i.e., TVR).
Visual inspection of the funnel plot and the Begg’s and Mazumdar’s rank correlation tests indicated the absence of significant publication bias and small-study effects. The Baujat plot identified the studies by Tafti et al and Sanfelippo et al as introducing significative heterogeneity and the results of Kundi et al45 as having a higher impact on the summary estimate (Supplementary Figure 1).
Outcomes
The overall random-effects rate of operative mortality, the primary endpoint, was 12% (95% CI: 9-15), with a high degree of heterogeneity (I2: 68%) (Figure 2).
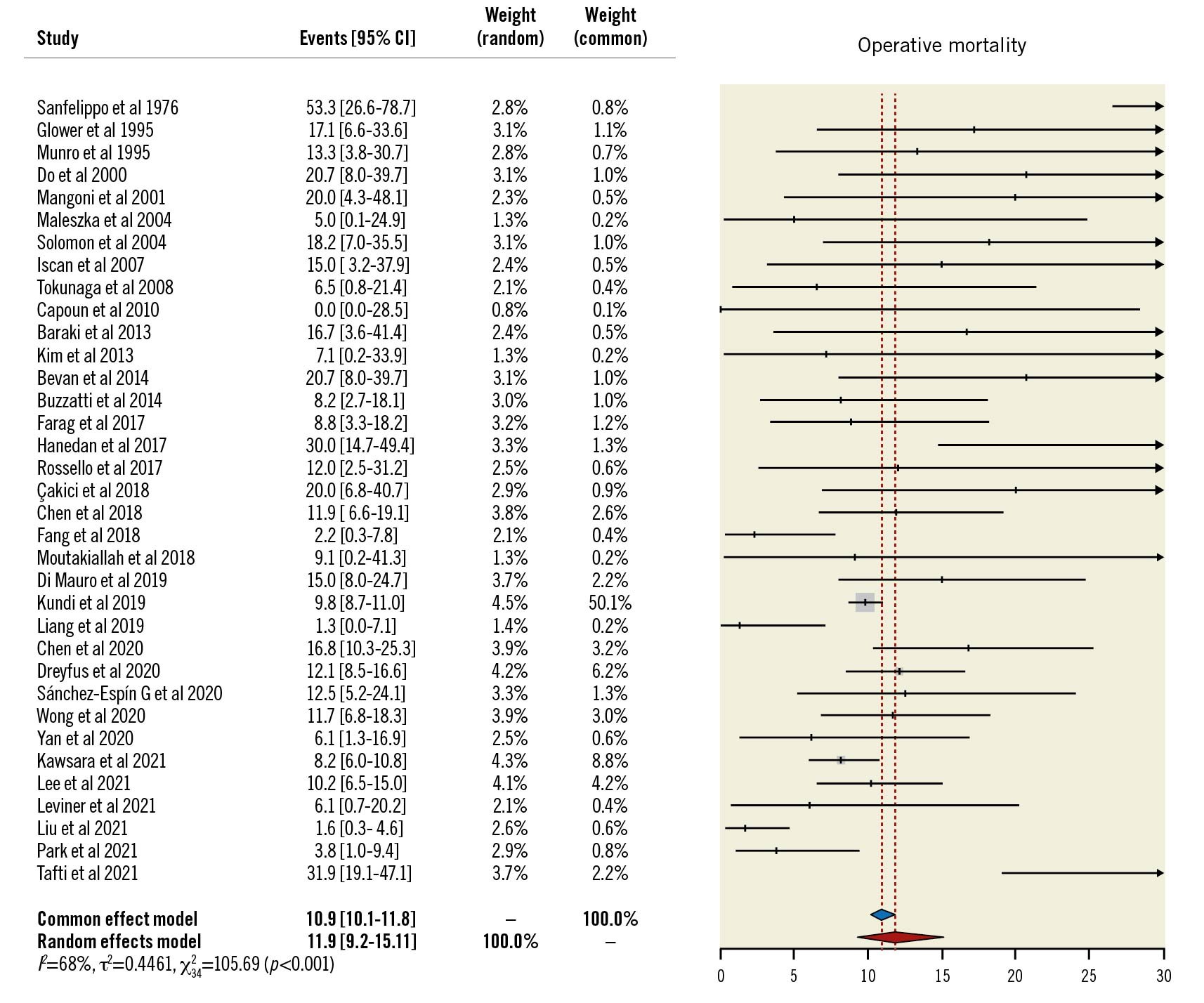
Figure 2. Primary endpoint. Forest plot of operative mortality. CI: confidence interval
Secondary endpoints were divided into early and late outcomes. Among the early outcomes, we found a 2% (95% CI: 1-4) rate of stroke, 15% (95% CI: 9-24) of acute kidney injury, 7% (95% CI: 3-15) of renal replacement therapy, 12% (95% CI: 8-17) of bleeding, 15% (95% CI: 12-20) of respiratory complications, 10% (95% CI: 6-16) of pacemaker implantation, and 3% (95% CI: 2-6) of wound infection (Table 2). Late outcomes are reported as incidence rates per 100 person-years and are as follows: 6 (95% CI: 4-9) for mortality, 2 (95% CI: 1-3) for the need for percutaneous or surgical reinterventions, 3 (95% CI: 1-6) for structural valve deterioration, 1 (95% CI: 0-2) for valve thrombosis, and 5 (95% CI: 2-13) for the recurrence of moderate or greater TR (Table 2).
Table 2. Early and late outcomes – random effects models.
|
Outcome |
Proportion/incidence (95% CI) |
I2 % |
N. of studies |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Early outcomes |
|||
|
Bleeding |
12 (8-17) |
83 (<0.01) |
17 |
|
Acute kidney injury |
15 (9-24) |
89 (<0.01) |
11 |
|
Renal replacement therapy |
7 (3-15) |
63 (0.01) |
7 |
|
Pacemaker implantation |
10 (6-16) |
75 (<0.01) |
13 |
|
Respiratory complication |
15 (12-20) |
0 (0.56) |
7 |
|
Stroke |
2 (1-4) |
74 (<0.01) |
9 |
|
Wound infection |
3 (2-6) |
81 (<0.01) |
10 |
|
Late outcomes |
|||
|
Late mortality* |
6 (4-9) |
96 (<0.01) |
23 |
|
Reintervention* |
2 (1-3) |
64 (<0.01) |
15 |
|
Structural valve deterioration* |
3 (1-6) |
82 (<0.01) |
9 |
|
Valve thrombosis* |
1 (0-2) |
49 (0.07) |
8 |
|
Recurrence of TR ≥2* |
5 (2-13) |
85 (<0.01) |
4 |
|
Bioprostheses |
|||
|
Late mortality* |
6 (2-13) |
97 (<0.01) |
8 |
|
Reintervention* |
1 (1-3) |
77 (<0.01) |
5 |
|
Structural valve deterioration* |
3 (1-9) |
91 (<0.01) |
4 |
|
Valve thrombosis* |
0 (0-1) |
68 (0.04) |
3 |
|
Recurrence of TR ≥2* |
8 (5-13) |
33 (0.22) |
3 |
|
*per 100 person-years. CI: confidence interval; TR: tricuspid regurgitation |
|||
Bioprostheses
A total of 14 studies reported outcome data for patients undergoing TVR with bioprostheses (Supplementary Table 3). Late outcomes after bio-TVR differed from those observed in the overall cohort for a higher rate of significant TR recurrence (8 [95% CI: 5-13] per 100 person-years), with a similar incidence rate of mortality (6 [95% CI: 2-13] per 100 person-years) (Table 2).
SUBGROUP ANALYSIS AND META-REGRESSION
A subgroup analysis of the primary endpoint, stratifying for the operative period (i.e., before 1995 versus after 1995), found that the mortality rate of 18% (95% CI: 8-35) from the studies examining procedures performed before 1995 was greater than the 11% (95% CI: 8-14) obtained from operations carried out after that date (Figure 3). However, the estimated mortality computed for the most recent studies was similar to the overall one. While investigating the influence of hospital locations (i.e., by continent) on operative mortality, the findings were consistent with the primary analysis, with no significant differences among the 3 subgroups (i.e., North America, Europe, Asia).
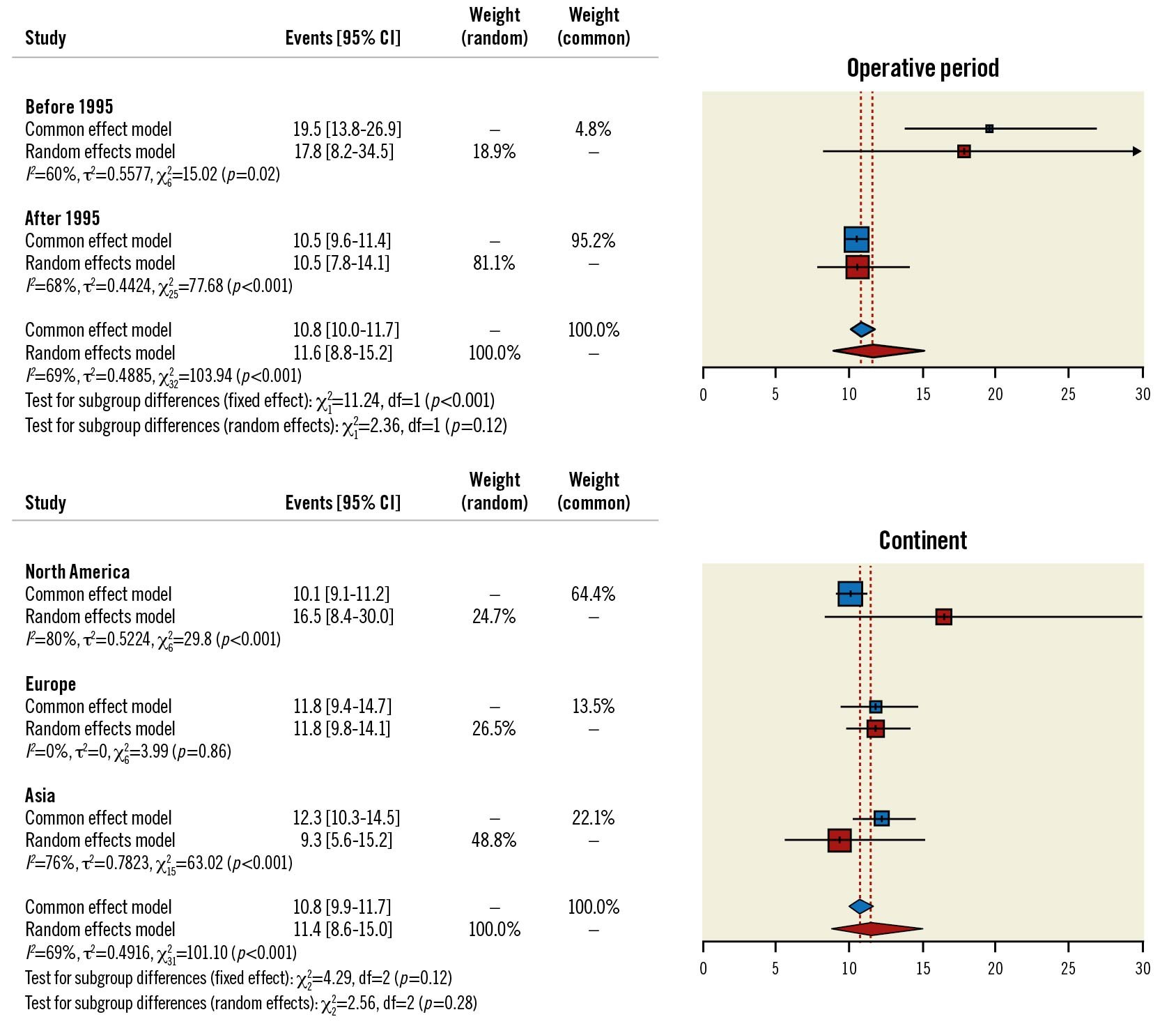
Figure 3. Subgroup meta-analysis. Forest plot of subgroup meta-analysis investigating the impact of the operative period* and continent# on the primary endpoint. * The studies by Iscan et al and Di Mauro et al were excluded because of their operative period. #Africa (n=1) and Oceania (n=2) were excluded because of their underrepresentation. CI: confidence interval
Meta-regression analysis detected a significant impact of previous cardiac surgery, liver disease, and the year of publication on the overall estimate of operative mortality (Supplementary Table 4, Supplementary Figure 2). A trend for lower hospital mortality was apparent with increasing values of left ventricular ejection. Further meta-regression analyses found no significant interactions of baseline clinical and echocardiographic characteristics, risk of bias, endocarditis aetiology and the type of prosthetic valve with the primary endpoint rates.
Sensitivity analyses
The overall estimates of primary and secondary endpoints were computed excluding the studies with patients having an endocarditis aetiology of their tricuspid valve disease, and the results were consistent with the primary analysis for every investigated outcome (Supplementary Table 5). Using fixed-effects models for the overall cohort, the only difference was in late mortality, whose estimate was mainly influenced by the study of Kundi et al45 (19 [95% CI: 18-20] per 100 person-years) (Supplementary Table 6). An alternative meta-analysis using a random intercept logistic-regression model was performed and resulted in similar results compared to the primary analysis (Supplementary Figure 3). Leave-one-out random-effects meta-analyses were used to assess the absence of significant influential studies on the primary endpoint (Supplementary Figure 4). A cumulative meta-analysis confirmed the higher rates of operative mortality for older studies (Supplementary Figure 5).
Discussion
This large systematic review and meta-analysis of 5,316 patients provides an overview of outcomes after isolated surgical TVR (Central illustration). With the aim of guiding future perspectives in the development of transcatheter systems, there are several important takeaways from our study: 1) the overall operative mortality and the need for permanent pacemaker implantation in patients undergoing isolated TVR were 12% (95% CI: 9-15) and 10% (95% CI: 6-16), respectively; 2) long-term data concerning device durability deepen the knowledge regarding the extended efficacy of the bioprosthetic implantation on the TV; 3) providing the first systematic assessment of isolated TVR, this analysis gives critical insight and sets a benchmark for anticipated future TTVR trials.
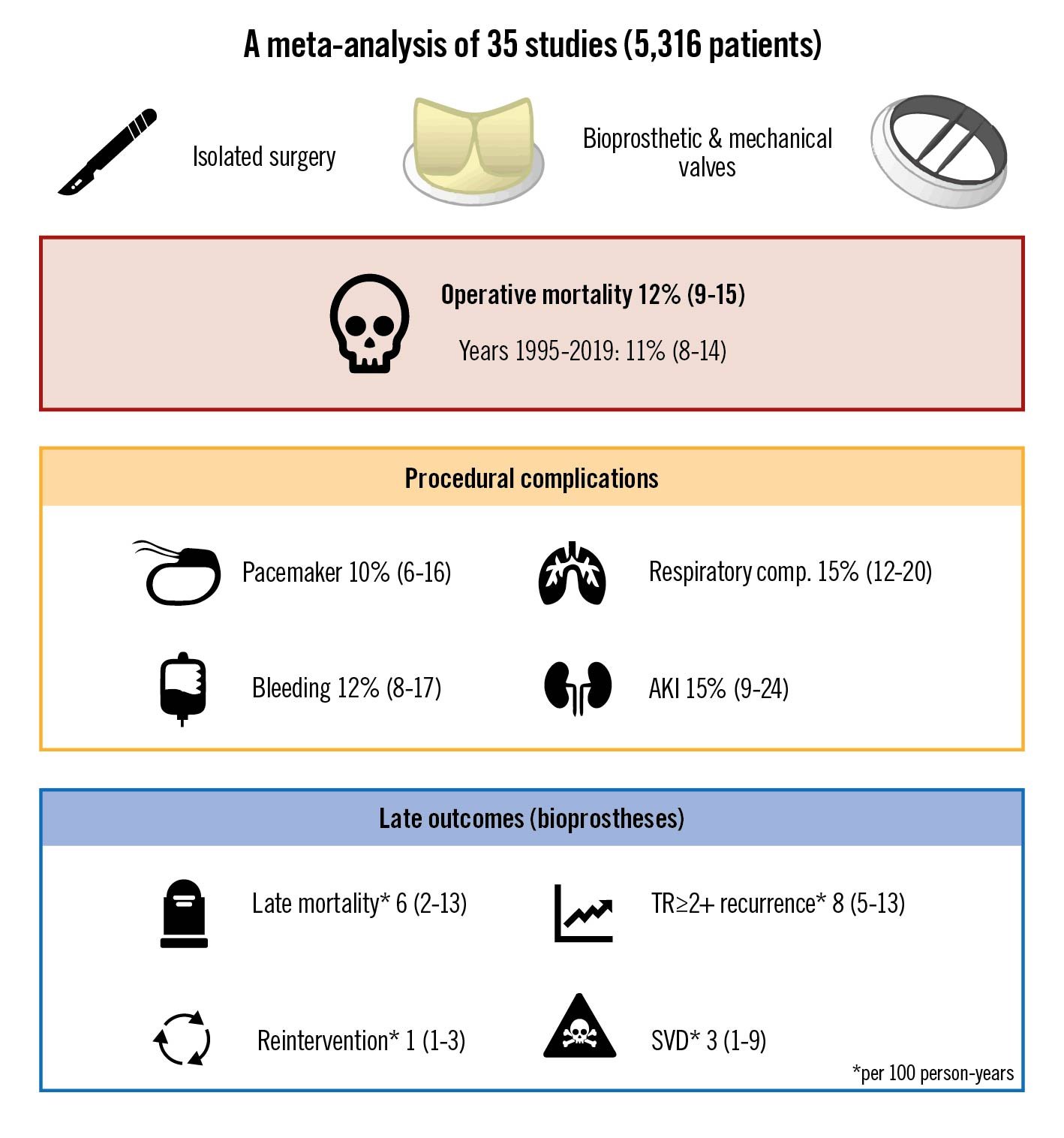
Central illustration. Surgical outcomes of isolated tricuspid valve replacement. The 35 included studies investigated isolated surgical tricuspid valve replacement. The pooled outcomes for 5,316 patients are reported as proportions and incidence rates (late) with confidence intervals. AKI: acute kidney injury; SVD: structural valve deterioration; TR: tricuspid regurgitation
Although no data restriction has been applied in the screening phase, a total of 35 studies throughout all the existing literature reported data on isolated surgical TVR. This limited amount of evidence is partially due to the considerable mortality rate of TV surgery6. The risk of treating these patients combined with the perception that TR has minimal prognostic impact are the reasons for the marked undertreatment of TR. However, recent evidence has demonstrated that untreated TR is associated with worse outcomes12. Moreover, the natural history of TV disease inexorably leads to progressive right heart failure (HF), resulting in excess mortality and recurrent hospitalisations. If we combine these adverse outcomes with the increasing prevalence of significant TR in an ageing population, it is clear that we are facing an important public health problem.
The absence of evidence-based trial data, the heterogeneous nature of TV disease and the unknown ideal timing for surgery makes it difficult to provide concrete recommendations for TV surgery. Indeed, guideline recommendations are currently based upon expert opinions, with the strongest classes of recommendation assigned to cases undergoing left-sided valve surgery. Isolated TV surgery is reserved for patients with primary TR who have signs and symptoms of right-sided HF (IIa) or progressive right ventricular dilation or systolic dysfunction (IIb), and for patients with severe secondary TR who have signs and symptoms of right-sided HF with a poor response to medical therapy and annular dilation (IIa), or prior left-sided valve surgery and the absence of severe pulmonary hypertension or severe right ventricular dysfunction (IIb)55.
Therefore, the aim of this study was to fill this critical gap. The use of bioprostheses is currently the preferred approach, with a growing trend3, and constitutes an option for emerging TTVR systems. Despite this, the choice to include trials investigating TVR with mechanical valves was made on the basis of several factors. First, there is no impact of prosthetic valve selection on the surgical technique or the periprocedural medical therapy, such as the anticoagulation regimen. Indeed, the incidences of early outcomes were consistent when comparing the bioprosthetic-only group with the overall one, and no effects of valve type were detected on the primary endpoint (Table 2, Supplementary Table 4). Second, the inclusion of studies which did not discriminate between bioprosthetic and mechanical valves allowed us to provide more robust results. This is observed by the addition of 21 studies and 2,529 patients (regarding primary endpoint data) to the overall population, making this analysis the largest and most comprehensive assessment on isolated TVR to date.
Operative mortality
The overall estimated operative mortality was 12%, with a CI ranging from 9 to 15%. After the exclusion of studies with an operative period prior to 1995, the estimated operative mortality for the most recent ones (i.e., after 1995) was in line with the overall one previously reported (11% [95% CI: 8-14]). This finding identifies isolated TVR as having a considerable surgical risk even in recent times, especially when compared to the replacement of other cardiac valves.
Since high-risk patients with aortic valve disease are nowadays treated with the transcatheter solution, data from clinical trials report operative mortality rates for isolated surgical aortic valve replacement of 0.9-1.3% and 1.7-4.1%, for low- and intermediate-risk, respectively56575859. On the other hand, isolated mitral valve replacement in ~150,000 patients in US hospitals was found to have an operative mortality rate as low as 4%60.
The discrepancy between right- and left-sided surgery might be explained by several concomitant factors. First, patients with TV diseases, especially in the case of secondary TR, present with poor functional classes and significant comorbidities, such as a long history of atrial fibrillation and pulmonary hypertension. Second, isolated TVR is usually performed after previous interventions, particularly on left-sided valves. Third, the timing is usually too late: right ventricular function is already impaired and associated with signs of advanced right HF such as liver dysfunction3. Indeed, even if hypothesis-generating, the results of the meta-regression analysis found a history of prior cardiac surgery and the presence of liver disease as having a significant impact on the overall estimate of operative mortality. These findings support the insights derived from both surgical and transcatheter TV procedures6162.
Early outcomes
>The procedural complication rates shown in Table 2, in addition to operative mortality, contribute to the reluctance to perform an isolated TVR. While most are common to all major invasive cardiac interventions, the risk of having to implant a permanent pacemaker is typical of this surgery. Since the atrioventricular node is in close proximity to the septal leaflet of the TV, its manipulation can lead to trauma of the surrounding area with subsequent heart block. On the contrary, the risk of stroke could be related to other concomitant factors. Prosthetic valves are associated with thromboembolism, but due to the position of the TV this phenomenon would result mostly in pulmonary emboli, unlike left-sided valve replacements which would lead to strokes.
Late outcomes for bioprosthetic TVR
The incidence rate of mortality after a bioprosthetic TVR was found to be 6 per 100 person-years in the random-effects model, and 22 per 100 person-years in the fixed-effects model (Table 2, Supplementary Table 5). This discrepancy is due to the great heterogeneity among the studies, which, as a result of being observational, included populations with different characteristics that might have influenced this outcome. This is reflected in the discordance of existing literature on the role of TVR on survival. While some studies report an improved survival rate after TV surgery, even in patients with TR and congestive HF63, others found no difference in long-term survival regardless of whether patients with isolated severe TR underwent surgery or medical therapy alone, after accounting for immortal time bias64.
The recurrence of at least moderate TR in the follow-up was not negligible (8 [95% CI: 5-13] per 100 person-years). However, this was accompanied by a much lower rate of reintervention (1 [95% CI: 1-3] per 100 person-years). This could reasonably be due to the growing risk of an already very compromised population having to undergo further major cardiac surgery.
Future perspectives
Epidemiological data show that secondary TR is the most prevalent aetiology in patients undergoing surgical interventions (92.6%) and the one with the lowest indication rates for surgical correction (53.2%)65. As a matter of fact, isolated TV surgery was performed only in 5% of patients included in the EuroSCORE II database66.
In this context, emerging percutaneous procedures appear to be an attractive solution for this substantial unmet clinical need. However, in order to advance TTVR technology, clinical researchers and regulatory bodies need comparative data from surgical isolated TVR. Our results provide a comprehensive extraction of published data surrounding isolated TVR. Results of either mechanical or bioprosthetic TVR are applicable to early outcomes, while results from only bioprosthetic TVR can be used for insight into TTVR durability studies. Among all TVR, the outcome data for operative mortality and permanent pacemaker implantation, critical outcomes of interest in the development of TTVR devices, should be set as the thresholds for outcomes to be utilised in prospective TTVR trials.
Of note, patients undergoing surgical TVR were relatively young (mean age 53 years), with good left ventricular function (mean ejection fraction 58%), and with few comorbidities, such as diabetes (13%), hypertension (23%), or liver disease (31%). These figures underline a selection bias in the surgical series, which include only patients deemed at an acceptable surgical risk and exclude the most advanced population. This warrants precaution when generalising the results of this meta-analysis to extreme-risk patients, such as those treated in compassionate-use studies of pioneering TTVR devices789. However, despite the baseline risk profile of patients and the absence of an appropriate learning curve, the outcomes observed in these studies are promising. As soon as further data proves TTVR to be efficacious and acceptably safe, it will be possible to push even more in favour of this technology. For this purpose, having an in-depth knowledge of surgical TVR, with its results and pitfalls, is essential for a rigorous evaluation and to promote those developing percutaneous therapies by serving as the legitimate benchmark.
Limitations
The results of the present meta-analysis have to be interpreted whilst acknowledging the following limitations. Since no randomised controlled trials investigated surgical TVR, all the included studies were observational and, thus, susceptible to error regarding patient selection and characteristics. As such, the results were affected by significant degrees of heterogeneity and should be interpreted according to their range distribution rather than point estimates. This is a study-level meta-analysis, and its findings are average pooled rates. The computation of person-years at risk was performed using study-level follow-up time when no data on the dropout date or number of days were available. Since a patient-level analysis for these 35 studies was not feasible, meta-regression analyses tested study-level characteristics, and their results should be considered as hypothesis-generating. The population was heterogeneous in terms of TV disease aetiologies, prior cardiac surgeries, and surgical experience or hospital operating volume. However, given the paucity of published evidence, the findings of this meta-analysis depict the full spectrum of patients undergoing isolated TVR.
Conclusions
This systematic review and meta-analysis provides an overview of the early and late outcomes after isolated surgical TVR. The results can support patients and doctors in the clinical decision-making for TVR and may serve as a benchmark for developing percutaneous therapies.
Impact on daily practice
Transcatheter tricuspid valve replacement (TTVR) is rapidly emerging as a therapeutic option amongst patients with secondary tricuspid regurgitation. The findings of this meta-analysis can support the clinical decision-making for tricuspid valve replacement (TVR) and may set the threshold for outcomes to be utilised in prospective TTVR trials. Surgical long-term TVR data may serve as a benchmark for developing TTVR systems. Late outcomes may inform on the bioprosthetic durability of the tricuspid valve.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

