Abstract
BACKGROUND: Outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for de novo ostial right coronary artery (RCA) lesions are poor.
AIMS: We used intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) to clarify the morphological patterns of de novo ostial RCA lesions and their associated clinical outcome.
METHODS: Among 5,102 RCA IVUS studies, 170 de novo ostial RCA stenoses (within 3 mm from the aorto-ostium) were identified. These were classified as 1) isolated ostial lesions (no disease extending beyond 10 mm from the ostium and without a calcified nodule [CN]); 2) ostial CN, typically with diffuse disease (disease extending beyond 10 mm); and 3) ostial lesions with diffuse disease but without a CN. The primary outcome was target lesion failure (TLF: cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction, definite stent thrombosis, and ischaemia-driven target lesion revascularisation).
RESULTS: The prevalence of an isolated ostial lesion was 11.8% (n=20), 47.6% (n=81) were ostial CN, and 40.6% (n=69) were ostial lesions with diffuse disease. Compared to ostial lesions with diffuse disease, isolated lesions were more common in women (75.0% vs 42.0%; p=0.01), and CN were associated with older age (median [first, third quartile] 76 [70, 83] vs 69 [63, 81] years old; p=0.002). The Kaplan-Meier rate of TLF at 2 years was significantly higher in patients with CN (21.6%) compared to diffuse lesions (8.2%) (p=0.04), and patients with isolated lesions had no events. A multivariable Cox proportional hazard model revealed that CN were significantly associated with TLF (hazard ratio 6.63, 95% confidence interval: 1.28-34.3; p=0.02).
CONCLUSIONS: Ostial RCA lesions have specific morphologies − detectable by IVUS − that may be associated with long-term clinical outcomes.
Although the rate of in-stent restenosis (ISR) has decreased in the current drug-eluting stent (DES) era1, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) of lesions located at the ostium of the right coronary artery (RCA) still remains challenging and is strongly associated with subsequent target lesion revascularisation2. On the one hand, de novo ostial RCA lesions have severe calcium, poor distensibility, and excessive hinge motion which may cause stent deformation and fracture, resulting in poor long-term outcomes234. On the other hand, prior literature has reported that isolated lesions have less atherosclerosis and are more frequently found in younger patients and in women567. Nevertheless, the morphology of ostial RCA lesions has not been systematically evaluated with intravascular imaging. We hypothesised that there are distinct types of ostial RCA lesions, each with different characteristics that can be detected by intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and that are related to subsequent specific outcomes.
Methods
STUDY DESIGN AND PATIENT POPULATION
This was a retrospective, observational, single-centre study conducted at New York-Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Medical Center (New York, NY, USA). An ostial RCA lesion is defined as a lesion within 3 mm of the aorto-ostial junction {8}. Inclusion criteria were 1) patients who underwent PCI for ostial RCA lesions with clinical symptoms and 2) patients with analysable IVUS images to evaluate ostial RCA morphology. Exclusion criteria were 1) in-stent restenosis, 2) prior coronary artery bypass graft to the RCA, and 3) implantation of a bare metal stent.
Patient demographics were obtained from electronic medical records. This study was approved by the institutional review board of Columbia University Medical Center; they waived informed consent for the retrospective review of records because of the minimal risk. For patients with no outcomes recorded in the electronic database, a waiver of documentation of consent was approved by the institutional review board. These subjects were then called to confirm subsequent outcomes after informed consent was obtained.
ANGIOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS AND ASSESSMENT
Quantitative and qualitative angiographic analyses were performed by experienced analysts blinded to clinical and IVUS findings (T. Sato and Y. Chen) using QAngioXA (Medis Medical Imaging) according to standardised methodology8. Only the distal reference was used to calculate angiographic diameter stenosis. Multivessel disease was defined as the presence of ≥50% luminal diameter stenosis in two or more major epicardial arteries. Procedural success was defined as stent implantation with a residual stenosis <30%9.
IVUS ANALYSIS AND ASSESSMENT
IVUS was performed using rotational imaging catheters (40 or 60 MHz Atlantis/OptiCross [Boston Scientific]; 45 MHz Revolution [Philips]; or 60 MHz Kodama HD [ACIST Medical Systems]) and motorised pullback at 0.5-1.0 mm/s. In order to obtain analysable IVUS images of sufficient quality to evaluate ostial RCA morphology, the guiding catheter was disengaged to visualise the transition from the RCA into the aorta.
IVUS analysis was performed by consensus of two experienced readers (K. Yamamoto and A. Maehara) using planimetry software (echoPlaque 4.0, INDEC Medical Systems).
Reference sites were defined as the least diseased cross-sections that were within 10 mm from the ostium. The remodelling index (RI) was calculated as the vessel area at the minimum lumen area (MLA) site divided by the distal reference vessel area10. The ostial RCA lesions were classified as one of three types: 1) isolated − isolated ostial lesions without significant distal disease, 2) calcified nodule (CN) − ostial CN with or without diffuse distal disease, and 3) diffuse − ostial lesions with diffuse distal disease without CN. An isolated ostial RCA lesion was limited to the 10 mm proximal to the aorto-ostium without a CN (Figure 1A)7. A CN was defined as irregular, convex-shaped calcium on the calcified plate (Figure 1B), with or without diffuse disease11. Diffuse lesions were ostial lesions with distal disease that did not contain a CN (Figure 1C). Post-PCI aorto-ostial stent coverage was further categorised as full (360º of visible struts at the ostium), partial (<360º of visible stent struts at the ostium), or no coverage (no visible stent struts at the ostium). Stent expansion was calculated as the minimum stent area (MSA) divided by the distal reference lumen or stent area within 10 mm distal to the ostium12. Minimum stent eccentricity was defined as the smallest minimum/maximum stent diameter ratio at a single slice within the stent.
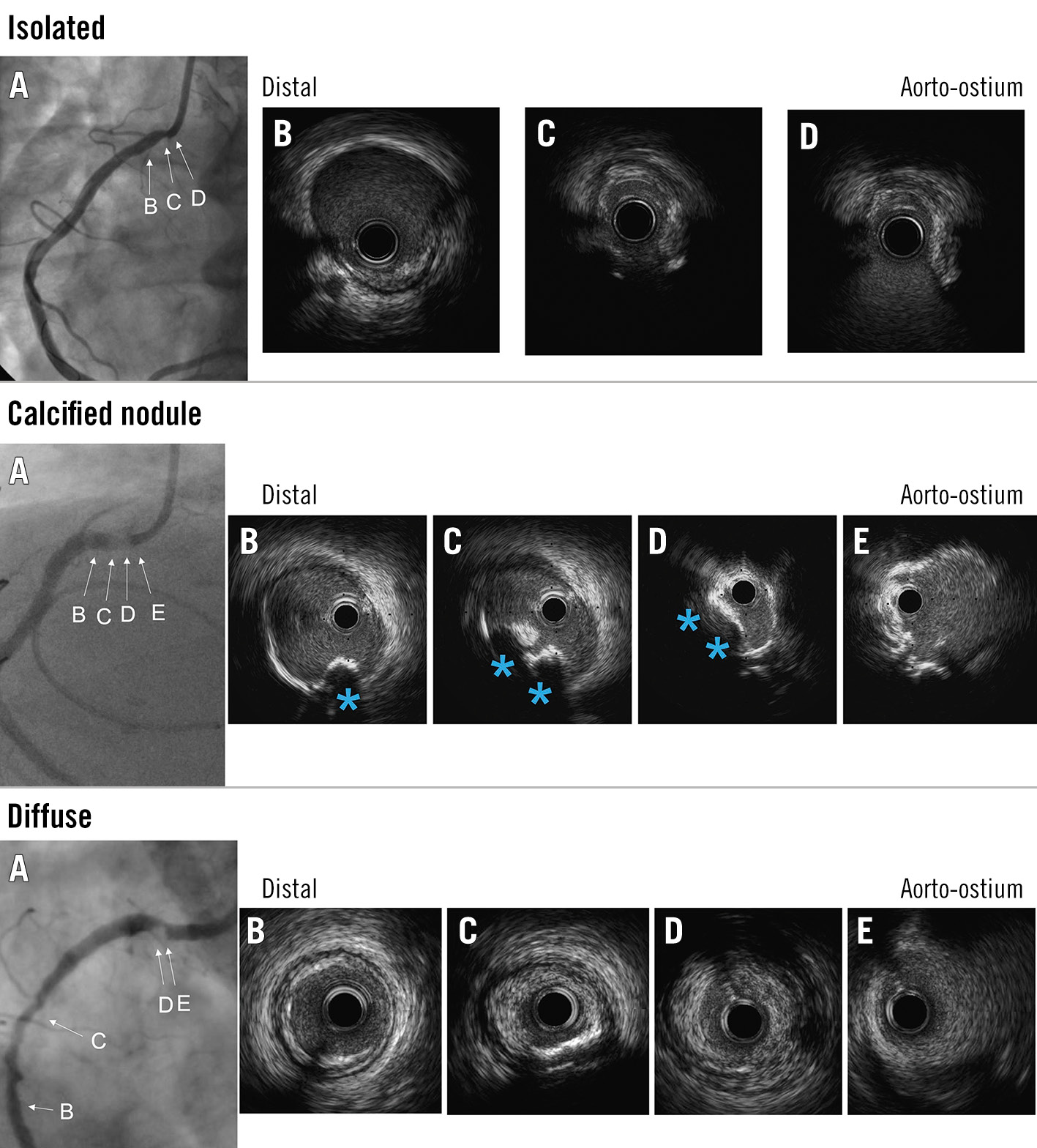
Figure 1. Representative cases of each group. In each example, the preprocedural coronary angiogram is shown (A) with the angiograms corresponding to the IVUS images (B,C,D,E). The top row shows an isolated lesion: the lesion was limited to the ostium (C,D) and showed negative remodelling (remodelling index 0.61). The middle row shows a calcified nodule: a calcified nodule (CN; blue asterisk) was seen at the ostium of the right coronary artery (B,C,D). The bottom row shows an ostial lesion with diffuse disease (diffuse lesions): non-CN plaque was seen at the ostium (D,E) as well as in the mid-segment (C). IVUS: intravascular ultrasound
CLINICAL ENDPOINTS
The primary endpoint was target lesion failure (TLF) at 2 years. TLF was defined as a composite of cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction (MI), definite stent thrombosis, or ischaemia-driven target lesion revascularisation (TLR). Clinical events were confirmed by investigators reviewing electronic medical records and/or telephone contacts.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Categorical variables are presented as count and percentage and were compared with the χ2 or Fisher’s exact test, as appropriate. Normally distributed continuous variables were compared with the Student’s t-test, and non-normally distributed continuous variables were compared with the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test. Multivariable logistic regression models were used to identify clinical factors associated with IVUS lesion morphology. The cumulative rate of TLF was estimated from Kaplan-Meier curves and compared using the log-rank test. Cox proportional hazard models were used to identify factors associated with TLF. A two-sided p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed with R statistics, version 4.0.3 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing).
Results
Between January 2005 and September 2020, IVUS was performed in 5,102 RCA lesions including 368 ostial RCA de novo lesions, from which we identified 170 lesions meeting the inclusion criteria (Supplementary Figure 1). Compared to the 106 excluded lesions with missing IVUS images, the 170 included lesions had similar clinical backgrounds except for age (median [first quartile, third quartile] 736481 years in patients with included lesions vs 696076 years in patients with excluded lesions; p=0.009) (Supplementary Table 1). Out of the 170 included lesions, 20 lesions (11.8%) were isolated, 81 lesions (47.6%) had a CN, and 69 lesions (40.6%) had diffuse distal disease. Among 81 CN lesions, there were only three lesions with disease not extending more than 10 mm from the ostium, while the other 78 CN had diffuse distal disease.
CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Clinical characteristics have been summarised in Table 1. Compared to diffuse lesions, isolated lesions were more common in women (75.0% vs 42.0%; p=0.01); and the CN group was older (76 [70, 83] vs 69 [63, 81] years old; p=0.002) (Supplementary Figure 2). The multivariable logistic model revealed that women were significantly associated with isolated lesions (odds ratio [OR] 5.86, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.60-21.5; p=0.004), whereas older age was significantly associated with CN (OR 1.63, 95% CI: 1.16-2.29 per 10-year increase; p=0.002) (Table 2).
Table 1. Clinical characteristics.
| 1. Isolated (n=20) | 2. CN (n=81) | 3. Diffuse (n=69) | p-value 1. vs 3. | p-value 2. vs 3. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 66 (63, 78) | 76 (70, 83) | 69 (63, 81) | 0.78 | 0.002 |
| Women | 15 (75.0) | 37 (45.7) | 29 (42.0) | 0.01 | 0.74 |
| Hypertension | 17 (85.0) | 71/80 (88.8) | 58/67 (86.6) | 0.99 | 0.80 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 20 (100) | 80/80 (100) | 66/67 (98.5) | 0.99 | 0.46 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 6 (30.0) | 39/80 (48.8) | 28/67 (41.9) | 0.43 | 0.41 |
| Insulin-treated | 2 (10.0) | 14/80(17.5) | 10/67 (14.9) | 0.73 | 0.82 |
| Chronic kidney disease* | 10 (50.0) | 36/80 (45.0) | 29/67 (43.3) | 0.62 | 0.87 |
| Dialysis | 1 (5.0) | 5/80 (6.3) | 2/67 (3.0) | 0.55 | 0.46 |
| Peripheral artery disease | 2 (10.0) | 21/80 (26.3) | 19/67 (28.4) | 0.14 | 0.85 |
| Prior PCI | 5 (25.0) | 27/80 (33.8) | 26/67 (38.8) | 0.30 | 0.61 |
| Prior MI | 4 (20.0) | 15/80 (18.8) | 9/67 (13.4) | 0.49 | 0.50 |
| Prior or current moderate or severe AS | 4 (20.0) | 16/80 (20.0) | 8/67 (11.9) | 0.46 | 0.26 |
| Clinical presentation at the time of PCI | 0.69 | 0.22 | |||
| STEMI | 0 (0) | 2/80 (2.5) | 0 (0) | ||
| NSTEMI | 2 (10.0) | 9/80 (11.3) | 12/67 (17.9) | ||
| Unstable angina | 9 (45.0) | 25/80 (31.3) | 26/67 (38.8) | ||
| Stable coronary artery disease | 9 (45.0) | 44/80 (55.0) | 29/67 (43.3) | ||
| Medication at discharge | |||||
| Dual antiplatelet therapy | 20 (100) | 78/78 (100) | 67/67 (100) | - | - |
| Statin | 20 (100) | 78/78 (100) | 67/67 (100) | - | - |
| ACE-I/ARB | 7 (35.0) | 31/78 (39.7) | 32/67 (47.8) | 0.44 | 0.40 |
| Beta blocker | 9 (45.0) | 43/78 (55.1) | 38/67 (56.7) | 0.45 | 0.86 |
| Values are n (%), n/N (%) or median (first, third quartile). *Defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, calculated using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease equation. ACE-I: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB: angiotensin II receptor blockers; AS: aortic stenosis; CN: calcified nodule; MI: myocardial infarction; NSTEMI: non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; STEMI: ST-elevation myocardial infarction | |||||
Table 2. Associated clinical variables for lesion morphology in the multivariable logistic regression model.
| Isolated | CN | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds ratio (95% CI) | p-value | Odds ratio (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Age, per 10 years | 0.73 (0.44-1.19) | 0.25 | 1.63 (1.16-2.29) | 0.002 |
| Women | 5.86 (1.60-21.5) | 0.004 | 0.87 (0.43-1.79) | 0.71 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.61 (0.17-2.17) | 0.44 | 1.66 (0.79-3.53) | 0.18 |
| Chronic kidney disease* | 2.49 (0.70-8.89) | 0.16 | 0.82 (0.39-1.75) | 0.60 |
| Peripheral artery disease | 0.26 (0.05-1.47) | 0.10 | 0.62 (0.27-1.41) | 0.25 |
| Prior or current moderate or severe AS | 2.57 (0.45-14.6) | 0.29 | 1.66 (0.59-4.68) | 0.33 |
| Prior MI | 1.35 (0.28-6.31) | 0.71 | 1.51 (0.58-3.93) | 0.40 |
| MI presentation | 0.53 (0.10-2.81) | 0.44 | 0.66 (0.26-1.72) | 0.40 |
| Each morphology was compared with diffuse lesions. *Defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, calculated using the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease equation. AS: aortic stenosis; CI: confidence interval; CN: calcified nodule; MI: myocardial infarction | ||||
ANGIOGRAPHICAL AND PROCEDURAL FINDINGS
Angiographic and procedural findings have been summarised in Table 3. Compared to diffuse lesions, isolated lesions had less multivessel disease (15.0% vs 62.3%; p=0.0002) and a shorter RCA lesion length (3.5 [2.7, 4.9] mm vs 5.8 [4.0, 20.3] mm; p=0.0002). CN had worse diameter stenosis (66.3 [55.4, 76.9]% vs 57.9 [49.1, 66.4]%; p=0.003).
Predilation before IVUS was required in 51 lesions (30.0%). Second-generation DES were used in most cases. All lesions were treated successfully.
Table 3. Angiographic and procedural findings.
| 1. Isolated (n=20) | 2. CN (n=81) | 3. Diffuse (n=69) | p-value 1 vs 3 | p-value 2 vs 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angiographic findings | |||||
| Multivessel disease | 3 (15.0) | 59 (72.8) | 43 (62.3) | 0.0002 | 0.22 |
| Calcification of ascending aorta | 2 (10.0) | 30 (37.0) | 18 (26.1) | 0.22 | 0.16 |
| Calcification of target lesion | 4 (20.0) | 61 (75.3) | 31 (44.9) | 0.07 | 0.0001 |
| Moderate | 3 (15.0) | 38 (46.9) | 18 (26.1) | 0.38 | 0.01 |
| Severe | 1 (5.0) | 23 (28.4) | 13 (18.8) | 0.18 | 0.19 |
| Radiolucent mass | 0 (0) | 24 (29.6) | 0 (0) | - | <0.0001 |
| Lesion length, mm | 3.5 (2.7, 4.9) | 5.2 (3.6, 9.1) | 5.8 (4.0, 20.3) | 0.0002 | 0.07 |
| Reference vessel diameter, mm | 2.60 (2.45, 2.95) | 2.89 (2.62, 3.28) | 2.94 (2.53, 3.20) | 0.20 | 0.49 |
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | |||||
| Pre-PCI | 1.30 (1.02, 1.49) | 1.03 (0.63, 1.40) | 1.17 (0.93, 1.51) | 0.60 | 0.04 |
| Post-PCI | 2.92 (2.60, 3.16) | 2.90 (2.59, 3.22) | 2.85 (2.53, 3.14) | 0.77 | 0.21 |
| Diameter stenosis, % | |||||
| Pre-PCI | 50.2 (42.5, 63.0) | 66.3 (55.4, 76.9) | 57.9 (49.1, 66.4) | 0.27 | 0.003 |
| Post-PCI | 9.1 (5.5, 13.5) | 11.1 (7.8, 16.7) | 10.5 (6.8, 14.7) | 0.28 | 0.59 |
| Procedural findings | |||||
| Max device diameter, mm | 3.5 (3.0, 4.0) | 3.5 (3.5, 4.0) | 3.5 (3.5, 4.0) | 0.39 | 0.08 |
| Balloon/artery ratio | 1.35 (1.16, 1.51) | 1.30 (1.16, 1.42) | 1.29 (1.16, 1.39) | 0.55 | 0.82 |
| Total stent length, mm | 15 (14, 17) | 22 (15, 48) | 38 (18, 61) | <0.0001 | 0.04 |
| Max inflation pressure, atm | 17 (15, 20) | 18 (16, 20) | 20 (16, 20) | 0.09 | 0.20 |
| Predilation before IVUS | 5 (25.0) | 25 (30.9) | 21 (30.4) | 0.78 | 0.99 |
| Predilation before stent implantation | 19 (95.0) | 81 (100) | 65 (94.2) | 0.99 | 0.04 |
| Stent type | 0.69 | 0.19 | |||
| 1st-generation DES | 3 (15.0) | 3 (3.7) | 7 (10.1) | ||
| 2nd-generation DES | 17 (85.0) | 78 (96.3) | 62 (89.9) | ||
| Adjunctive device | |||||
| Cutting/scoring balloon | 1 (5.0) | 10/79 (12.7) | 3/65 (4.6) | 0.99 | 0.14 |
| Rotational atherectomy | 3 (15.0) | 9/80 (11.3) | 6/67 (9.0) | 0.42 | 0.79 |
| Orbital atherectomy | 0 (0) | 1/80 (1.3) | 2/67 (3.0) | 0.99 | 0.59 |
| Intravascular lithotripsy | 0 (0) | 1/80 (1.3) | 0 (0) | - | 0.99 |
| Ostial flash | 5 (25.0) | 10/80 (12.5) | 7/67 (10.5) | 0.14 | 0.80 |
| Procedural complication* | 0 (0) | 2/80 (2.5) | 0 (0) | - | 0.50 |
| Values are n (%), n/N (%) or median (first, third quartile). *Coronary perforation that required covered stents. CN: calcified nodule; DES: drug-eluting stent; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound | |||||
IVUS ANALYSIS
IVUS findings have been summarised in Table 4. Compared to diffuse lesions, isolated lesions had more negative remodelling (remodelling index 0.82 [0.67, 0.94] vs 0.93 [0.82, 1.04]; p=0.009), less plaque burden at the MLA site (65.9 [56.5, 72.5]% vs 77.1 [70.5, 80.9]%; p<0.0001), and less reference plaque burden (35.7 [35.1, 37.3]% vs 53.0 [43.7, 63.5]%; p<0.0001). Compared with diffuse lesions, CN had more plaque burden at the MLA site (81.0 [74.3, 84.9]% vs 77.1 [70.5, 80.9]%; p=0.002), greater maximum calcium arc (283 [167, 360]° vs 130 [11, 240]°; p<0.0001), and worse stent expansion (68.0 [61.1, 79.4]% vs 79.6 [70.4, 86.7]%; p<0.0001).
Table 4. Intravascular ultrasound findings.
| 1) Isolated (n=20) | 2) CN (n=81) | 3) Diffuse (n=69) | p-value 1 vs 3 | p-value 2 vs 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Presence of calcium | 9 (45.0) | 81 (100) | 32 (46.4) | 0.99 | <0.0001 |
| Calcium in ascending aorta | 6 (30.0) | 65/79 (82.3) | 14/64 (21.9) | 0.55 | <0.0001 |
| Preprocedure | n=20 | n=62 | n=52 | ||
| Minimum lumen area, mm2 | 3.5 (2.1, 3.7) | 3.1 (2.5, 3.9) | 3.3 (2.7, 3.8) | 0.37 | 0.33 |
| Vessel area, mm2 | 10.1 (8.0, 11.5) | 15.1 (13.3, 20.7) | 14.2 (10.7, 16.3) | 0.0002 | 0.02 |
| Plaque burden, % | 65.9 (56.5, 72.5) | 81.0 (74.3, 84.9) | 77.1 (70.5, 80.9) | <0.0001 | 0.002 |
| Reference lumen area within 10 mm, mm2 | 7.6 (6.4, 9.4) | 8.0 (5.8, 10.5) | 6.8 (5.0, 8.4) | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| Reference vessel area within 10 mm, mm2 | 12.2 (10.2, 14.6) | 16.6 (13.9, 20.5) | 13.9 (12.0, 18.1) | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Reference plaque burden, % | 35.7 (35.1, 37.3) | 51.6 (45.9, 59.5) | 53.0 (43.7, 63.5) | <0.0001 | 0.81 |
| Remodelling index | 0.82 (0.67, 0.94) | 0.97 (0.87, 1.04) | 0.94 (0.83, 1.06) | 0.007 | 0.52 |
| Remodelling index <1.0 | 18 (90.0) | 38/62 (61.3) | 34/52 (65.8) | 0.04 | 0.70 |
| Lesion length, mm | 4.9 (3.7, 6.0) | 21.7 (13.9, 41.7) | 31.3 (21.0, 45.2) | <0.0001 | 0.03 |
| Maximum calcium arc, ° | 90 (0,170) | 283 (167, 360) | 130 (11, 240) | 0.20 | <0.0001 |
| Post-procedure | n=17 | n=74 | n=57 | ||
| Minimum stent area, mm2 | 8.2 (5.9, 9.3) | 7.3 (5.7, 7.3) | 7.5 (6.4, 9.7) | 0.98 | 0.07 |
| Stent expansion, % | 82.5 (76.0, 90.8) | 68.0 (61.1, 79.4) | 79.6 (70.4, 86.7) | 0.22 | <0.0001 |
| Minimum stent eccentricity index | 0.84 (0.77, 0.86) | 0.65 (0.59, 0.73) | 0.75 (0.68, 0.82) | 0.006 | <0.0001 |
| Stent coverage of ostium | 0.03 | 0.25 | |||
| Full coverage | 16/17 (94.1) | 54/68 (79.4) | 36/54 (66.7) | ||
| Partial | 1/17 (5.9) | 9/68 (13.2) | 13/54 (24.1) | ||
| No coverage | 0/17 (0) | 5/68 (7.4) | 5/54 (9.3) | ||
| Values are n (%), n/N (%) or median (first, third quartile). CN: calcified nodule | |||||
CLINICAL OUTCOMES
Clinical outcomes have been summarised in Table 5 and Figure 2. The median follow-up duration after treatment was 2.0 (0.4, 4.4) years (2.5 [1.8, 4.8] years in the isolated group, 1.8 [0.4, 4.3] years in the CN group, and 1.7 [0.3, 4.4] years in the diffuse disease group). The Kaplan-Meier rate of TLF at 2 years was higher in the CN group compared to the diffuse disease group (21.6% vs 8.2%, hazard ratio [HR] 3.06, 95% CI: 1.02-9.29; p=0.04), whereas there were no events in patients with an isolated ostial RCA lesion (p=0.22) (Supplementary Table 2). Univariate and multivariable Cox proportional hazard modelling were performed to include CN, age, chronic kidney disease, and post-PCI MSA. CN (HR 9.97 [95% CI: 2.31-43.0]; p=0.002), younger age (HR 0.57 [95% CI: 0.35-0.94]; p=0.02), and chronic kidney disease (HR 10.3 [95% CI: 2.61-40.4]; p=0.0008) were all associated with TLF (Supplementary Table 3, Table 5).
Table 5. Clinical and morphological factors associated with target lesion failure in the multivariable Cox proportional hazard model.
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|
| Calcified nodule (vs isolated or diffuse) | 9.97 (2.31-43.0) | 0.002 |
| Age, per 10 years | 0.57 (0.35-0.94) | 0.02 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 10.3 (2.61-40.4) | 0.0008 |
| Post-PCI minimum stent area, per 1 mm2 | 1.09 (0.82-1.41) | 0.53 |
| CI: confidence interval; DES: drug-eluting stent; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention | ||
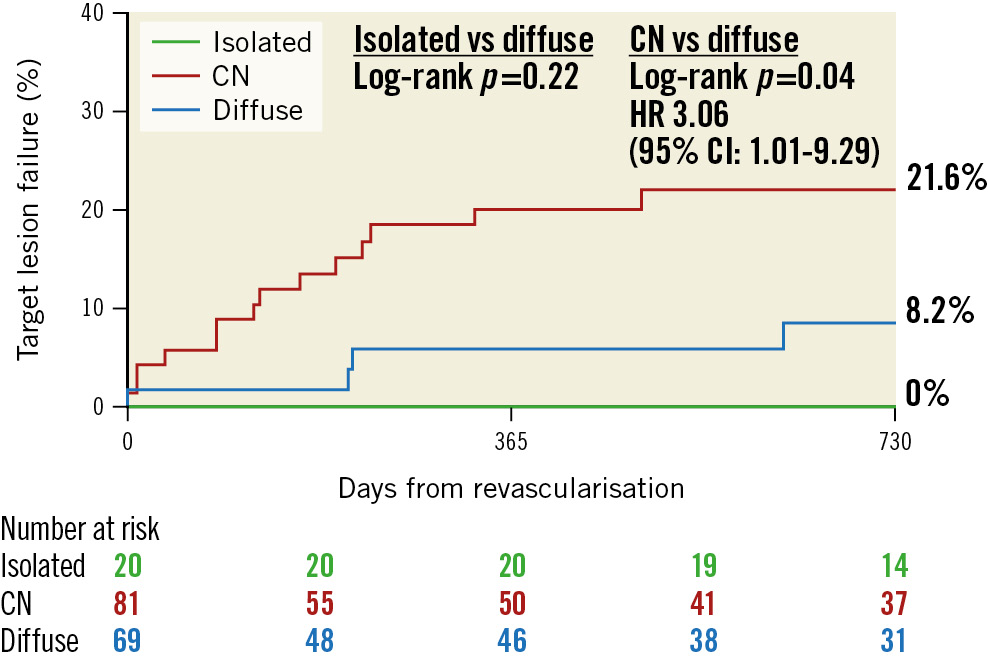
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier curve for target lesion failure among isolated, CN, and diffuse lesions. CI: confidence interval; CN: calcified nodule; HR: hazard ratio
Discussion
Historically, ostial RCA lesions have been associated with worse outcomes regardless of whether they were treated with balloon angioplasty4, directional or rotational atherectomy or laser angioplasty13, bare metal stenting14, or drug-eluting stent implantation2. Therefore, it is surprising that there have been few, if any, morphological studies of ostial RCA lesions using IVUS; imaging of aorto-ostial lesions with optical coherence tomography is difficult because the guiding catheter must be engaged in order to clear the blood-filled lumen. The key findings of the present study are as follows. There were three distinct IVUS morphologies: infrequent isolated ostial RCA lesions without significant diffuse distal disease; ostial RCA lesions with significant diffuse distal disease, but without a CN; and CNs almost always accompanied by diffuse distal disease. In terms of post-PCI outcomes, patients treated for ostial RCA lesions with CN morphology had the worst outcomes, while those with isolated disease had the best outcomes (Central illustration).
The aetiology of an ostial RCA lesion can include atherosclerosis, autoimmune aortitis (Takayasu disease or syphilis), aortic valve calcification, iatrogenic complication, and tumours561516. Histologically, an ostial RCA has a muscle bundle which independently arises from the elastin-muscle fibre of the aorta, frequently containing a circumferential sphincter-like muscle17 and a higher prevalence of fibrotic and sclerotic plaque, including smooth muscle collagen tissue and calcification and less lipid13. Previous IVUS reports revealed that negative remodelling was frequently seen in 86% of ostial RCA lesions10, consistent with our data. The present study revealed that the overall TLF rate was 13.4%, corresponding to previous reports29. Tsunoda et al reported on an IVUS analysis of 18 ostial RCA lesions comparing patients with and without subsequent restenosis. The restenosis group had more visible calcium (58% vs 5%) and a smaller stent area (8.1 mm2 vs 10.4 mm2)18.
ISOLATED LESIONS
Previous reports revealed that the prevalence of an isolated lesion varied from 8-24%, and they were more common in women 56. Barner et al included 41 patients with aorto-ostial RCA and found 10 (24%) isolated lesions, with 70% of these in women6. Darabian et al included 256 left main lesions and 36 (14.1%) aorto-ostial lesions, with 47.2% of these in women5. The present data were consistent with these previous reports.
In the current study, the 20 patients with isolated ostial lesions had no events. Isolated lesions had less calcium and larger stent expansion, which may explain the optimal outcomes19. In addition, isolated lesions were fully covered with the stents, which might contribute to less stent edge restenosis due to an uncovered stent.
CALCIFIED NODULES
CNs were found in half of the aorto-ostial RCA lesions in the present study, a higher prevalence compared to previous studies including any coronary artery segments: 5.3-17.0% by IVUS2021, 4.2-12.5% by optical coherence tomography2223, and 3.6% by pathology24. The presence of CN has been associated with an atherosclerotic background, such as older age, more plaque burden, and calcium21, which corresponds with the findings in the present study.
In the present study, CN was strongly associated with TLF. Morofuji et al reported that the presence of CN was associated with poor outcomes among patients with calcified lesions requiring atherectomy25. Nakamura et al suggested that protruding CN within a stent are an important factor in stent failure26.
DIFFUSE LESIONS WITHOUT A CALCIFIED NODULE
While isolated lesions and CN were specific categories, diffuse lesions were considered to be close to general atherosclerosis morphology. The present study revealed IVUS characteristics such as plaque burden (median 77%) and calcium arc (median 130°) were similar to previous IVUS reports2728.
In the present study, the TLF rate of diffuse lesions was 8.2%. The current second-generation DES registry reported that the 2-year TLF rate of overall vessels was 3-10%2930, which corresponds to the present study. Ostial lesions with diffuse disease without a CN had numerically worse, but statistically similar, outcomes compared to isolated lesions.
TECHNICAL ISSUES ASSOCIATED WITH IMAGING OSTIAL RCA LESIONS
To assess lesion morphology or postprocedural results by IVUS, the guide catheter needs to be disengaged10. However, there are technical difficulties with disengaging the catheter in some cases, such as a deeply inserted guiding catheter or when disengaging the catheter risks injury to the patient. The present study had 21 cases that could not be analysed because the guiding catheter was not disengaged.
Limitations
There are several limitations in the present study. First, this was a retrospective, observational study of only patients with analysable preinterventional IVUS. There was selection bias, so caution is needed during interpretation. Second, the procedure depended on each operator’s decision-making, which might have affected the outcomes. Third, as we included patients over a period of 15 years, interventional devices and techniques and medical treatment changed during the study period. However, 92% of cases were treated with second-generation DES, and clinical outcomes including only patients treated with second-generation DES were consistent with the entire cohort (Supplementary Table 2). Unfortunately, data on medication during follow-up could not be obtained. Fourth, the number of patients was small, especially in the “isolated” subgroup. Similarly, because of the small number of events, multiple outcome variables were analysed, which could have led to a type I error. Therefore, this study should be considered as hypothesis-generating, and further large-scale studies are required. Finally, even though the present study revealed the predictor of TLF after PCI for ostial RCA, optimal treatment remains unclear.
Conclusions
Ostial RCA lesions have specific morphologies detectable by IVUS: about half were CNs, a few were isolated lesions, and the rest had diffuse disease. Long-term clinical outcomes may depend on the lesion type. In particular, our data, obtained on a relatively small patient population, suggest that DES implantation in ostial RCA lesions with CNs might result in worse clinical outcomes compared to other morphologies.
Impact on daily practice
There were three distinct IVUS ostial RCA lesion morphologies: isolated ostial RCA disease, CN, and diffuse distal disease. Because the morphology may impact outcomes after DES implantation, it makes sense to evaluate ostial RCA lesion morphology with IVUS after disengagement of the guiding catheter.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Matsumura is a consultant for Terumo Corporation and Boston Scientific. K.N. Fall is a consultant for Infraredx and Boston Scientific. M. Prasad is a consultant for and is on the speakers bureau of Conavi Medical, Neovasc, Abbott, Cardinol, Chiesi, and Boehringer Ingelheim. V.G. Ng receives speaker honoraria from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. T.M. Nazif is a consultant for and receives speaker honoraria from Medtronic and Boston Scientific. S.A. Parikh has done research for Abbott, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Philips, Cordis, and Jannsen; is a consultant for Inari, Penumbra, Terumo, and Canon; and holds equity in Efemoral Medical, Advanced NanoTherapies, and Encompass Vascular. D. Karmpaliotis received speaker honoraria from Boston Scientific and Abbott; and holds equity in Saranas, SoundBite Medical Solutions, and Traverse Vascular. M.B. Leon received institutional clinical research grants from Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic. M. McEntegart received speaker honoraria from Boston Scientific, Abbott, Shockwave Medical, Teleflex, and Biosensors. J.W. Moses has equity in Orchestra BioMed and Xenter. A.J. Kirtane received institutional funding from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott, Amgen, CathWorks, CSI, Philips, ReCor Medical, Neurotronics, Biotronik, Chiesi, Bolt Medical, Magenta Medical, Canon, SoniVie, and Shockwave Medical (institutional funding includes fees paid to Columbia University and/or Cardiovascular Research Foundation for consulting and/or speaking engagements in which A.J. Kirtane controlled the content); is a consultant for IMDS; received travel expenses/meals from Amgen, Medtronic, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Abbott, CathWorks, Edwards Lifesciences, CSI, Novartis, Philips, Abiomed, ReCor Medical, Chiesi, Zoll, Shockwave Medical, and Regeneron. G.S. Mintz received speaker honoraria from Boston Scientific, Philips, SpectraWAVE, and Gentuity. A. Maehara is a consultant for Boston Scientific, Shockwave Medical, and SpectraWAVE. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

