Abstract
BACKGROUND: Coronary intravascular lithotripsy (IVL) safely facilitates stent implantation in severely calcified lesions.
AIMS: This analysis sought to determine the relative impact of IVL on acute and long-term outcomes specifically in calcified nodules (CNs).
METHODS: Individual patient-level data (N=155) were pooled from the Disrupt CAD optical coherence tomography (OCT) substudies. Severely calcified lesions with and without CNs were compared by OCT for acute procedural results and for target lesion failure (TLF) at 2 years − a composite of cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction, and ischaemia-driven target lesion revascularisation.
Results: A CN was identified in 18.7% (29/155) of lesions. When comparing lesions with and without CNs, there were no significant differences in preprocedure minimal lumen area or diameter stenosis; however, the mean calcium angle and calcium volume were greater in CN lesions. Despite a higher calcium burden, the final minimal stent area (CN: 5.7 mm2 [interquartile range [IQR] 4.4, 8.3] vs non-CN: 5.7 mm2 [IQR 4.7, 7.2]; p=0.80) and stent expansion (CN: 79.3% [IQR 64.3, 87.0] vs 80.2% [IQR 68.9, 92.4]; p=0.30) were comparable between the two groups. In the CN group, the final stent area and expansion at CN sites were 7.6 mm2 (IQR 5.5, 8.5) and 89.7% (IQR 79.8, 102.5), respectively. The cumulative incidence of TLF at 2 years was 13.9% and 8.0% in the CN and non-CN groups, respectively (p=0.32).
CONCLUSIONS: Despite a greater calcium volume in CNs, IVL use was associated with comparable stent expansion and luminal gain in both CN and non-CN lesions. Further studies powered for clinical outcomes comparing different plaque modification techniques in this lesion subset are warranted.
Coronary artery calcification (CAC) adversely affects the outcomes of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) by hindering device crossing1, causing the delamination of drug and polymer coatings from stents2, altering elution kinetics and drug delivery3 and impairing stent apposition and expansion4. These challenges are exaggerated by calcified nodules (CNs)56. CNs have a unique plaque morphology, in which an area of nodular calcification protrudes into the lumen of the coronary artery, with or without disruption of the fibrous cap. While CNs are reported to be an infrequent cause of acute coronary syndromes7, the predominant clinical impact of CNs is poor technical and procedural success during PCI, leading to suboptimal clinical outcomes68910.
Intravascular lithotripsy (IVL) is a technique in which multiple lithotripsy emitters mounted on a traditional catheter platform deliver localised pulsatile sonic pressure waves to circumferentially modify vascular calcium. In the Disrupt CAD studies11121314, we demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of IVL as a novel treatment strategy to modify vascular compliance in calcified plaque in the coronary arteries11. Recently, we first reported the acute procedural outcomes of IVL-assisted PCI in CNs, demonstrating IVL’s safety and effectiveness15. Nonetheless, little is known regarding the long-term clinical outcomes of IVL-assisted PCI for CNs. Therefore, in this patient-level pooled analysis of the Disrupt CAD III and IV optical coherence tomography (OCT) substudies, we sought to compare the outcomes after IVL-assisted PCI of de novo severely calcified coronary lesions with and without CNs.
Methods
STUDY DESIGN, PATIENTS, AND PROCEDURE
The study design, detailed inclusion criteria, procedural details, and outcomes of the Disrupt CAD III and IV studies have been described previously1314. Briefly, all were prospective, multicentre, single-arm studies which evaluated the procedural and long-term clinical outcomes after IVL-assisted PCI with stent implantation in patients with severely calcified de novo coronary lesions. The Disrupt CAD OCT study was a prespecified substudy. Subject eligibility criteria were similar across all studies1314. Each study was approved by the institutional review board or ethics committee at participating centres, and all patients provided written informed consent. Prior to stent implantation, the IVL balloon (Shockwave Medical), sized 1:1 to the reference artery vessel diameter (RVD), was inflated to 4 atm, to allow contact with the vessel wall but minimise static barotrauma, and 10 pulses were delivered, followed by further dilatation to the nominal pressure of 6 atm. If lesion preparation was incomplete despite delivery of the maximum number of pulses, further IVL catheters with the same or a different diameter could be used. Subsequent stent implantation and PCI optimisation was performed at the discretion of the operator.
OCT IMAGE ACQUISITION AND ANALYSIS
OCT was performed using a commercially available frequency domain OCT system (ILUMIEN OPTIS [Abbott]). The Disrupt CAD III and IV studies were analysed at an independent angiographic and OCT core laboratory (Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York, NY, USA) using common definitions.
Details of calcification quantification have been described previously1617. Briefly, quantitative indices of calcification were evaluated and measured in each OCT frame at 1 mm intervals at the lesion level. Calcium location was defined as superficial if the luminal leading edge of calcification was located within 0.5 mm from the surface of plaque. Calcification arc, thickness, and length were measured as previously described1617. Calcium volume index was then calculated as mean calcium arc×calcium length (°×mm). Calcium fracture was identified as a new disruption/discontinuity in the calcium sheet identified on OCT. The number of fractures per lesion was determined by tracing the fracture lines for continuity frame by frame throughout the lesion, and cross-checked with the longitudinal OCT image. OCT parameters were also analysed at the site of CNs. CNs were subdefined as (1) eruptive if the lesion exhibited evidence of fibrous cap discontinuity and/or thrombus, over a calcified plaque characterised by protruding calcification into the lumen18, or (2) non-eruptive if a smoother uniform protruding calcified mass was present with a thicker continuous fibrous cap19. The luminal area was measured by tracing the luminal border on each cross-section, which, after IVL, included marking the lumen contour in continuity with the additional luminal border generated by the fractures, from which the acute luminal gain post-IVL was calculated1617. OCT was used to calculate the asymmetry index, over the length of the stent (minimum/maximum stent diameter), and the eccentricity index, at any one cross-section (minimum/maximum stent diameter in the same cross-section). A CN was considered deformable if there was a visual change from the baseline OCT to the final OCT where the CN protrusion within the lumen decreased and the asymmetry index and eccentricity index were>0.7.
CLINICAL STUDY ENDPOINTS
The clinical study endpoints were definite/probable stent thrombosis and target lesion failure (TLF) at 2 years − a composite of cardiac death, target vessel myocardial infarction (TVMI), and ischaemia-driven target lesion revascularisation (ID-TLR). Details about the prespecified endpoints and definitions have been described elsewhere1314. In brief, periprocedural myocardial infarction (MI) was defined as a peak creatine kinase myocardial band (CK-MB) level >3 times the upper limit of a normal lab value with or without new pathological Q waves, consistent with a prior pivotal atherectomy study20. Spontaneous MI was defined using the Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction21. An independent clinical events committee (CEC; Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York, NY, USA) adjudicated all clinical events. An independent data safety monitoring board (Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York, NY, USA) reviewed data safety and integrity and the overall conduct of the study on a periodic basis.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The primary analysis population was by intention-to-treat, and patients were divided into two groups according to the presence of CNs. Data were subjected to the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test to determine distribution. Continuous variables are described as mean±standard deviation and were compared by t-tests if parametric and as median with interquartile range (IQR) and were compared by the Mann-Whitney U test if non-parametric. The cumulative incidences of clinical events were presented as Kaplan-Meier estimates and compared using a log-rank test. A value of p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed with SAS, version 9.4 or higher (SAS Institute), and STATA 18.0 (StataCorp).
Results
PATIENTS AND PROCEDURES
From the Disrupt CAD III and IV OCT substudies conducted at 21 sites in 3 countries between January 2019 and April 2020, a total of 155 patients with 2-year clinical outcomes were pooled for the present analysis. Among them, OCT-defined CNs were identified in 29 patients (18.7%).
Table 1 presents baseline and procedural characteristics. Notably, CNs were more prevalent in patients with renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance <60 ml/min/1.73 m2). There was more predilatation in the CN group, but the use of IVL, post-dilatation and the number of stents were similar between the two groups. Angiographic characteristics are presented in Table 2. CNs were most commonly located in the right coronary artery. Following PCI, the RVD increased in all lesions but was larger in the CN group, with greater acute luminal gain than in the non-CN group. Treatment of both CN and non-CN calcified lesions with IVL was safe without any occurrences of slow flow, no reflow, abrupt closure, flow-limiting dissections, or perforation in either group.
Table 1. Baseline and procedural characteristics.
| CN (N=29) | Non-CN (N=126) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||
| Age, years | 71.9±8.8 | 73.4±9.0 | 0.40 |
| Male | 28 (96.6) | 96 (76.2) | 0.01 |
| Cardiovascular risk factors | |||
| Hypertension | 24 (82.8) | 107 (84.9) | 0.77 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 26 (89.7) | 109 (86.5) | 0.65 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 14 (48.3) | 50 (39.7) | 0.40 |
| Current or former smoker | 18 (62.1) | 75 (59.5) | 0.80 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 28.3±5.8 | 26.9±5.0 | 0.17 |
| Prior myocardial infarction | 9 (31.0) | 21 (16.7) | 0.08 |
| Renal insufficiency* | 5 (17.2) | 2 (1.6) | <0.001 |
| Procedural characteristics | |||
| Predilatation | 15 (51.7) | 32 (25.4) | <0.001 |
| Patients undergoing IVL | |||
| Maximum inflation pressure, atm | 6.0±0.0 | 6.0±0.4 | 0.63 |
| Number of catheters | 1.5±0.6 | 1.4±0.6 | 0.54 |
| Number of pulses | 93.0±44.2 | 87.9±44.1 | 0.57 |
| Stent delivery | 29 (100) | 126 (100) | 1.00 |
| Number of stents implanted | 1.3±0.5 | 1.3±0.5 | 0.95 |
| Total stent length, mm | 34.7±12.9 | 34.8±12.3 | 0.96 |
| Post-stent dilatation | 29 (100) | 126 (100) | -- |
| Maximum inflation pressure, atm | 18.3±2.9 | 18.2±2.7 | 0.84 |
| Total procedure time, min | 71.0±26.1 | 57.3±22.4 | <0.001 |
| Contrast volume, mL | 179.7±51.8 | 197.0±66.5 | 0.19 |
| Hospital stay, days | 1.0 (0.0, 1.0) | 0.9 (0.0, 1.0) | 0.74 |
| Data are presented as number (%), mean±standard deviation, or median (interquartile range [Q1, Q3]). *Creatinine clearance <60 ml/min/1.73 m2 as calculated by the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula. CN: calcified nodule; IVL: intravascular lithotripsy; Q1: first quartile; Q3: third quartile | |||
Table 2. Angiographic characteristics (core laboratory).
| CN (N=29) | Non-CN (N=126) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target vessel | <0.001 | ||
| Left anterior descending artery | 8 (27.6) | 100 (79.4) | |
| Circumflex artery | 4 (13.8) | 5 (4.0) | |
| Right coronary artery | 16 (55.2) | 21 (16.7) | |
| Left main artery | 1 (3.4) | 0 (0) | |
| Severe calcification | 29 (100) | 126 (100) | - |
| Lesion location | 0.45 | ||
| Proximal | 12 (41.4) | 66 (52.8) | |
| Mid | 10 (34.5) | 29 (30.4) | |
| Distal | 7 (24.1) | 20 (16.0) | |
| Ostial | 0 (0) | 1 (0.8) | |
| Calcification length, mm | 57.6 (45.2, 71.3) | 47.0 (36.4, 60.9) | 0.02 |
| Baseline QCA | |||
| Lesion length, mm | 28.3±10.8 | 27.8±11.1 | 0.82 |
| Reference vessel diameter, mm | 3.1±0.4 | 3.0±0.4 | 0.22 |
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 1.1±0.4 | 1.1±0.3 | 0.57 |
| Diameter stenosis, % | 65.9±12.2 | 62.9±10.0 | 0.18 |
| Post-PCI final QCA (in-stent) | |||
| Reference vessel diameter, mm | 3.4 (2.9, 3.6) | 3.0 (2.8, 3.3) | 0.03 |
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 2.90 (2.6, 3.2) | 2.66 (2.4, 3.0) | 0.02 |
| Diameter stenosis, % | 10.3 (7.2, 16.9) | 11.0 (6.1, 16.1) | 0.89 |
| Stent length, mm | 32.9 (23.8, 37.9) | 32.8 (22.9, 37.9) | 0.87 |
| Acute gain, mm | 1.7 (1.5, 2.1) | 1.5 (1.3, 1.9) | 0.01 |
| Diameter stenosis ≤30% | 28 (96.6) | 121 (96.0) | 1.00 |
| Post-PCI final complications* | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| Data are presented as number (%), mean±standard deviation, or median (interquartile range [Q1, Q3]). *Includes flow-limiting dissection, slow flow or no reflow, abrupt closure, or perforation. CN: calcified nodule; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; Q1: first quartile; Q3: third quartile; QCA: quantitative coronary angiography | |||
OCT ANALYSIS
Serial OCT measurements are presented in Table 3. The mean calcium arc (CN 164.2° [IQR 130.2, 247.9] vs non-CN 129.2° [IQR 101.9, 164.8]; p<0.001) and calcium volume index (CN 4,558.0°×mm [IQR 3,763.0, 6,250.0] vs non-CN 3,126.5°×mm [1,916.0, 4,678.0]; p<0.001) were significantly higher in CN lesions. The differential impact of IVL at the sites of pre-PCI minimal lumen area (MLA), max calcium arc site and final minimal stent area (MSA) comparing CN and non-CN lesions are also presented in Table 3. There were no significant differences in stent area, stent expansion, post-stent residual area stenosis, acute gain or incidence of calcium fracture between groups at any of these sites (Central illustration). The stent asymmetry index was lower in the CN group (CN 0.58 [IQR 0.54, 0.61] vs non-CN 0.64 [IQR 0.59, 0.70]; p<0.001) with the proportion of lesions with an asymmetry index <0.7 higher in the CN group (100% vs 72.7%; p=0.002). Correspondingly, the lowest stent eccentricity index was also lower in the CN group (CN 0.64 [IQR 0.58, 0.68] vs non-CN 0.73 [IQR 0.69, 0.77]; p<0.001), with the proportion of lesions with the lowest eccentricity index of <0.7 being higher in the CN group (88.5% vs 28.1%; p<0.001). There was a trend towards overall greater calcium fracture (CN 80.8% vs non-CN 62.5%; p=0.07) and number of calcium fractures per lesion (CN 3.0 [IQR 2.0, 5.0] vs non-CN 2.0 [IQR 1.0, 3.0]; p=0.06) in the CN group (Table 3). The fracture length was greater in the CN group. Irrespective of the presence or absence of a CN, the final MSA was never at the site of maximum calcification from the pre-PCI OCT.
CNs were colocated at the sites of pre-PCI MLA and post-PCI MSA in 51.7% and 42.3% of cases, respectively. Table 4 presents post-PCI OCT findings at the CN site. At the CN site, the pre-PCI lumen area was 2.3 mm2 (IQR 1.7, 4.1) and post-PCI stent area was 7.6 mm2 (IQR 5.5, 8.5) with stent expansion of 89.7% (IQR 79.8, 102.5) and an eccentricity index of 0.66 (IQR 0.61, 0.74). Calcium fracture at the CN site was seen in 23.1%, and deformability was identified in 80.8% of all CN lesions. All eruptive nodules were deformable, but of the non-eruptive nodules, 61.5% were deformable and 38.5% were not. As such, more non-eruptive nodules were colocated at the lowest eccentricity site. Representative examples of the effects of IVL in a calcified lesion and a non-deformable non-eruptive CN are shown in Figure 1 and Supplementary Figure 1, respectively.
Table 3. Serial measurements by OCT (core laboratory).
| CN (N=29) | Non-CN (N=126) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-PCI | |||
| Lesion length, mm | 27.6 (21.4, 36.8) | 32.3 (23.4, 37.8) | 0.16 |
| Lumen area, mm2 | |||
| MLA | 1.9 (1.3, 2.4) | 1.8 (1.4, 2.4) | 0.62 |
| Lumen area at max calcium site | 4.6 (3.7, 6.0) | 3.4 (2.5, 4.6) | <0.001 |
| Lumen area at CN site | 2.3 (1.7, 4.1) | - | - |
| Lumen area at final MSA site | 3.5 (2.2, 5.9) | 3.5 (2.2, 4.9) | 0.69 |
| Area stenosis, % | |||
| Area stenosis at pre-PCI MLA site | 77.8 (65.9, 80.4) | 73.6 (66.7, 79.0) | 0.37 |
| Area stenosis at max calcium site | 49.4 (28.5, 57.0) | 52.8 (30.7, 67.8) | 0.09 |
| Area stenosis at CN site | 66.0 (56.0, 79.1) | - | - |
| Area stenosis at final MSA site | 47.2 (36.9, 57.0) | 54.0 (29.0, 68.7) | 0.91 |
| Calcium thickness, mm | |||
| Max thickness at pre-PCI MLA site | 1.1 (0.9, 1.2) | 0.8 (0.5, 1.0) | <0.001 |
| Max thickness at max calcium site | 1.1 (0.8, 1.2) | 1.0 (0.8, 1.1) | 0.43 |
| Max thickness at CN site | 1.2 (1.2, 1.3) | - | - |
| Max thickness at final MSA site | 1.1 (1.0, 1.2) | 0.8 (0.7, 1.0) | <0.001 |
| Mean calcium arc, ° | 164.2 (130.2, 247.9) | 129.2 (101.9, 164.8) | <0.001 |
| Calcium length, mm | 28.0 (22.0, 35.0) | 25.0 (17.0, 32.0) | 0.08 |
| Calcium volume index, °×mm | 4,558.0 (3,763.0, 6,250.0) | 3,126.5 (1,916.0, 4,678.0) | <0.001 |
| Post-PCI | |||
| Stent area, mm2 | |||
| MSA | 5.7 (4.4, 8.3) | 5.7 (4.7, 7.2) | 0.80 |
| Mean stent area | 7.9 (6.5, 10.1) | 7.7 (6.4, 9.2) | 0.41 |
| Stent area at pre-PCI MLA site | 5.8 (4.4, 8.4) | 5.8 (4.7, 7.4) | 0.76 |
| Stent area at max calcium site | 7.7 (6.4, 9.4) | 7.3 (5.9, 9.0) | 0.43 |
| Stent expansion, % | |||
| Minimal stent expansion | 79.3 (64.3, 87.0) | 80.2 (68.9, 92.4) | 0.30 |
| Mean stent expansion | 99.6 (89.4, 117.1) | 104.3 (91.1, 118.3) | 0.59 |
| Stent expansion at pre-PCI MLA site | 80.1 (64.3, 87.7) | 81.7 (68.9, 93.7) | 0.19 |
| Stent expansion at max calcium site | 97.9 (76.0, 115.1) | 100.3 (83.4, 118.3) | 0.54 |
| Area stenosis, % | |||
| Area stenosis at final MSA site | 13.9 (7.9, 31.2) | 15.6 (2.5, 28.6) | 0.33 |
| Area stenosis at pre-PCI MLA site | 16.9 (11.4, 31.2) | 16.2 (4.6, 28.9) | 0.23 |
| Area stenosis at max calcium site | −6.7 (−24.4, 12.7) | −8.3 (−28.6, 10.2) | 0.67 |
| Acute area gain, mm2 | |||
| Area gain at final MSA site | 2.9 (2.1, 3.8) | 2.4 (1.4, 3.4) | 0.21 |
| Area gain at pre-PCI MLA site | 4.6 (3.3, 5.7) | 3.9 (3.2, 5.2) | 0.42 |
| Area gain at max calcium site | 3.7 (2.0, 4.8) | 4.1 (3.0, 6.0) | 0.051 |
| Calcium fracture* | |||
| Any fracture | 80.8 (21/26) | 62.5 (80/128) | 0.07 |
| Any fracture at final MSA site | 12.0 (3/25) | 18.3 (17/93) | 0.56 |
| Any fracture at pre-PCI MLA site | 8.3 (2/24) | 12.1 (11/91) | 1.00 |
| Any fracture at max calcium site | 57.7 (15/26) | 39.0 (48/123) | 0.30 |
| ≥3 fractures | 46.2 (12/26) | 29.7 (38/128) | 0.10 |
| Fracture length, mm | 6.6 (4.4, 10.8) | 3.6 (1.7, 6.4) | 0.01 |
| Max fracture depth, mm | 0.5 (0.4, 0.7) | 0.5 (0.3, 0.7) | 1.00 |
| Max calcium arc at calcium fracture, ° | 289.0 (201.0, 330.0) | 232.0 (167.0, 300.0) | 0.12 |
| Min calcium arc at calcium fracture, ° | 171.0 (143.0, 200.0) | 165.0 (137.0, 221.0) | 0.70 |
| Number of calcium fracture per lesion | 3.0 (2.0, 5.0) | 2.0 (1.0, 3.0) | 0.06 |
| Lumen gain at fracture site, mm2 | 4.1±1.9 | 4.5±1.9 | 0.36 |
| Presence of any malapposition | 100 (26/26) | 84.4 (108/128) | 0.03 |
| Stent asymmetry index | 0.58 (0.54, 0.61) | 0.64 (0.59, 0.70) | <0.001 |
| Lowest stent eccentricity index | 0.64 (0.58, 0.68) | 0.73 (0.69, 0.77) | <0.001 |
| Data are presented as % (n/N), mean±standard deviation, or median (interquartile range [Q1, Q3]). *Total number varies based on the analysability of OCT for the different outcomes. CN: calcified nodule; max: maximum; MLA: minimal lumen area; MSA: minimal stent area; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; Q1: first quartile; Q3: third quartile | |||
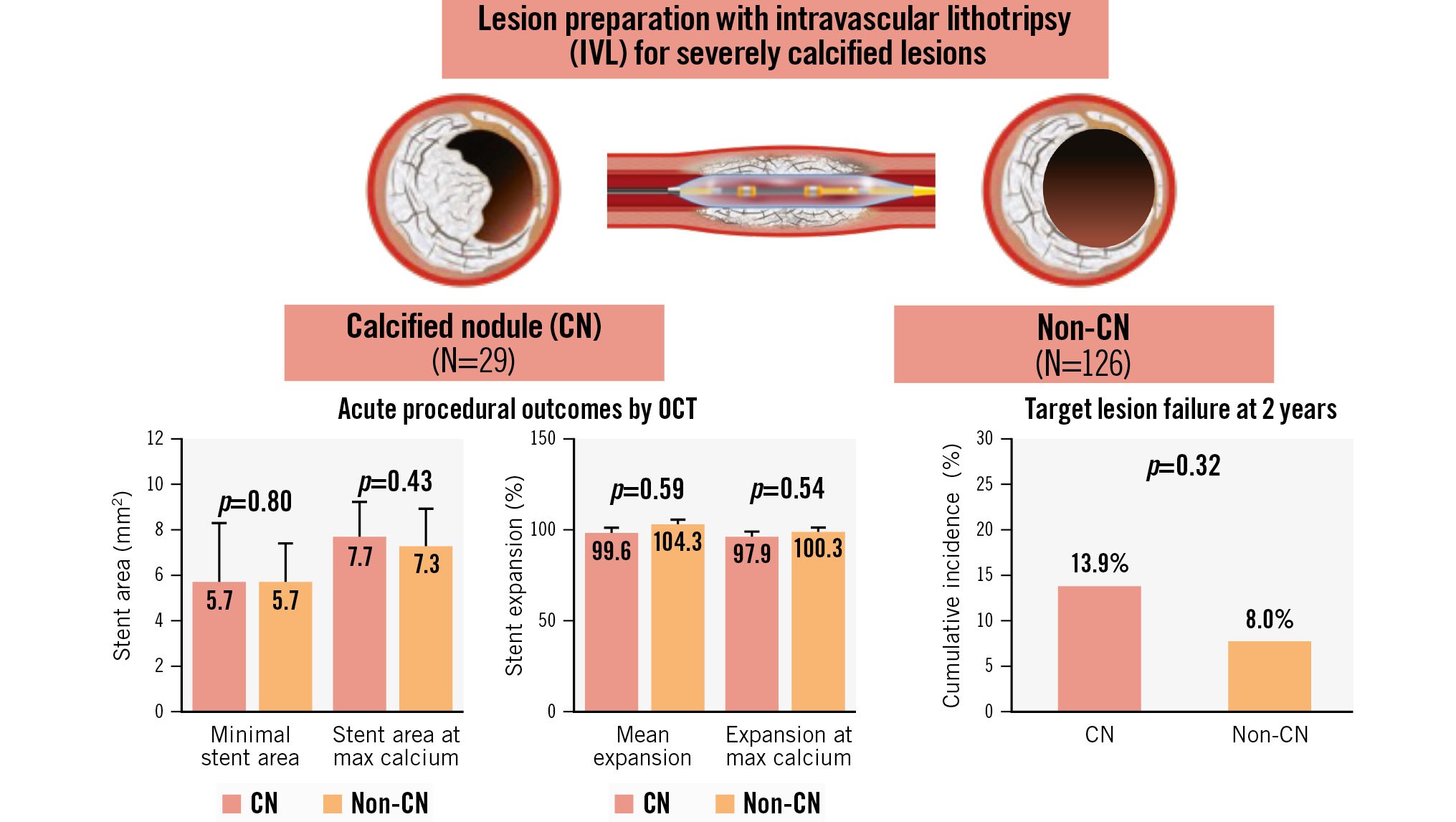
Central illustration. Disrupt CAD III-IV OCT substudies (N=155 from 21 sites in 3 countries). From the Disrupt CAD III and IV studies, the individual patient-level data of 155 patients who underwent IVL-assisted PCI were pooled. Among them, a CN was identified in 18.7% (29/155) of lesions. After PCI, there were no differences in stent expansion or final minimal stent area when comparing CN lesions and non-CN lesions, despite a higher calcium burden in CN lesions. The cumulative incidence of TLF at 2 years was similar between the CN and non-CN groups. CN: calcified nodule; IVL: intravascular lithotripsy; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; OCT: optical coherence tomography; TLF: target lesion failure
Table 4. Post-PCI OCT characteristics of CN site (core laboratory).
| CN (N=26*) | Eruptive CN (N=13*) | Non-eruptive CN (N=13*) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deformed CN | 80.8 (21) | 100 (13) | 61.5 (8) |
| Non-deformed CN | 19.2 (5) | 0 (0) | 38.5 (5) |
| Colocated with MSA site | 42.3 (11) | 38.5 (5) | 46.2 (6) |
| Colocated with the lowest eccentricity site | 57.7 (15) | 38.5 (5) | 76.9 (10) |
| Area stenosis, % | 3.2 (−3.8, 17.2) | 1.7 (−8.3, 14.3) | 7.4 (−1.9, 20.6) |
| Stent area, mm2 | 7.6 (5.5, 8.5) | 7.8 (7.1, 8.4) | 6.7 (4.9, 8.7) |
| Stent expansion, % | 89.7 (79.8, 102.5) | 97.7 (81.7, 102.7) | 83.5 (73.4, 98.0) |
| Stent eccentricity | 0.66 (0.61, 0.74) | 0.71 (0.69, 0.78) | 0.64 (0.56, 0.66) |
| Presence of calcium fracture | 23.1 (6) | 30.8 (4) | 15.4 (2) |
| Data are presented as % (n) or median (interquartile range [Q1, Q3]). *There were no post-PCI OCT images in 3 CN lesions. CN: calcified nodule; MLA: minimal lumen area; MSA: minimal stent area; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; Q1: first quartile; Q3: third quartile | |||
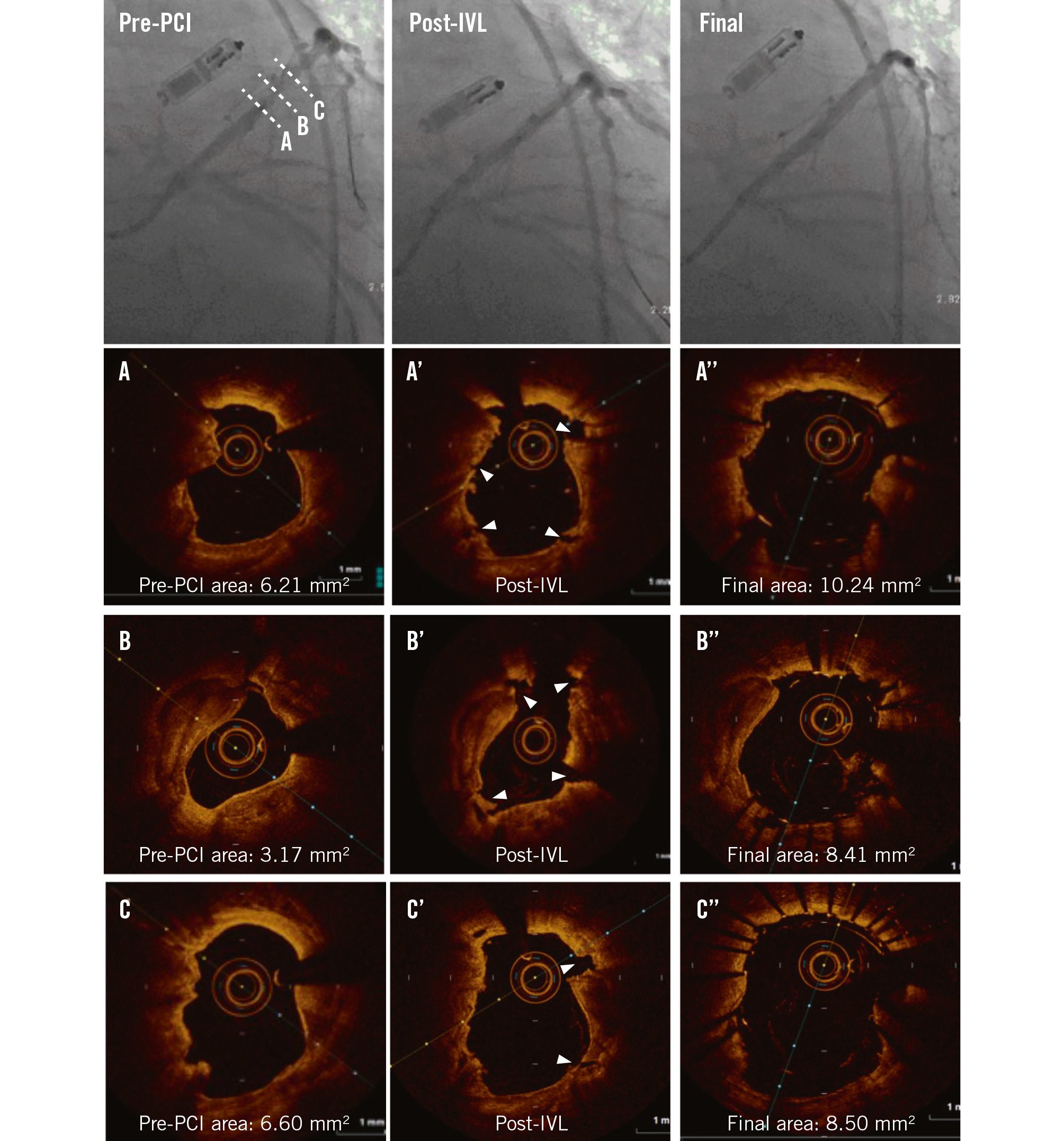
Figure 1. Impact of intravascular lithotripsy on a calcified nodule. Pre-PCI angiography identifies a calcified lesion in the left anterior descending artery. Coregistered OCT cross-sections represent (A) the non-eruptive calcified nodule, (B) maximum calcification, and (C) the distal segment of the calcified lesion. A’-C’) Coregistered images following IVL. Note the multiple fractures (white arrowheads). A’’-C’’) Coregistered images following stent implantation showing sufficient luminal gains. IVL: intravascular lithotripsy; MLA: minimal lumen area; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
CLINICAL OUTCOMES
Table 5 shows 2-year clinical outcomes after IVL-assisted PCI according to the presence of CNs. The cumulative incidence of TLF at 2 years was 13.9% and 8.0% in the CN and non-CN groups, respectively (p=0.32) (Figure 2). One patient in the CN group had definite stent thrombosis 22 days after the index procedure. The cumulative incidence of TLF at 2 years was similar between lesions with eruptive versus non-eruptive CNs (14.3% vs 13.3%, respectively; p=0.94) (Supplementary Table 1).
Table 5. Clinical outcomes at 2 years after IVL-assisted PCI according to the presence of CN.
| CN (N=29) | No CN (N=126) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target lesion failure | 13.9 (4) | 8.0 (10) | 0.32 |
| Cardiac death | 0 (0) | 0.8 (1) | 0.63 |
| Target vessel MI | 13.9 (4) | 7.2 (9) | 0.24 |
| Q wave MI | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | - |
| Non-Q wave MI | 13.9 (4) | 7.2 (9) | 0.24 |
| Ischaemia-driven TLR | 6.9 (2) | 2.4 (3) | 0.21 |
| Stent thrombosis* | 3.4 (1) | 0 (0) | 0.04 |
| Data are presented as % (n). The cumulative incidences of clinical outcomes are presented as Kaplan-Meier estimates. *Definite and probable. CN: calcified nodule; IVL: intravascular lithotripsy; MI: myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; TLR: target lesion revascularisation | |||
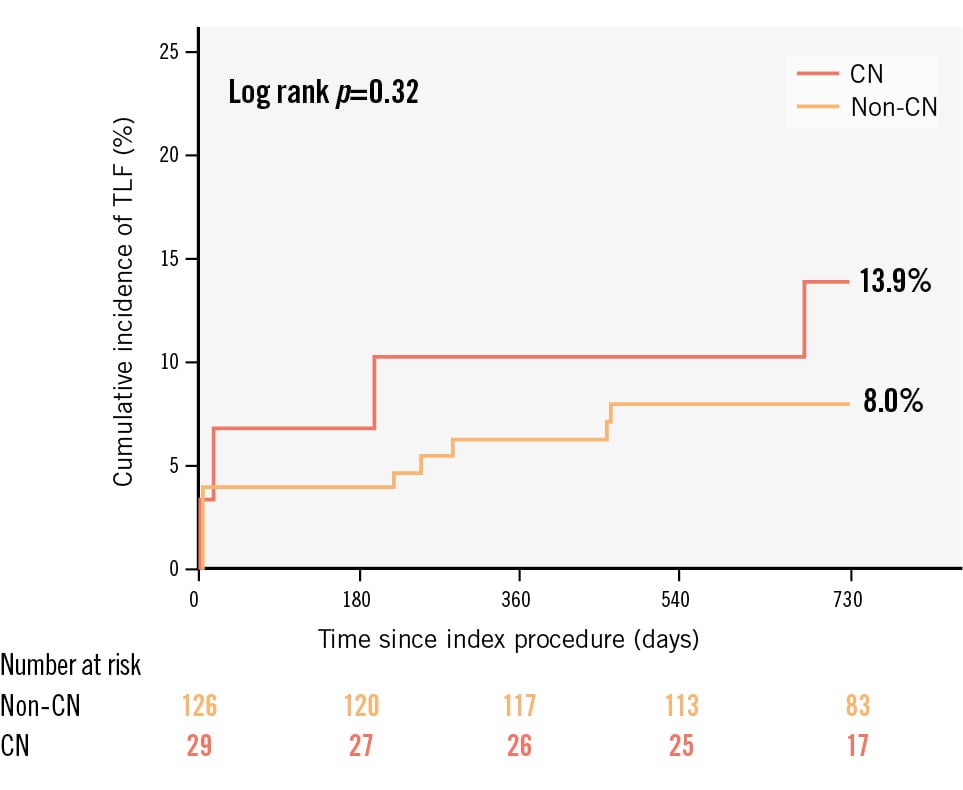
Figure 2. Comparison of TLF at 2 years according to the presence of a CN. Kaplan-Meier curves and cumulative incidence of TLF at 2 years were compared according to the presence of a CN after IVL-assisted PCI. CN: calcified nodule; IVL: intravascular lithotripsy; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; TLF: target lesion failure
Discussion
We report the following important findings: (1) IVL was a feasible frontline preparation tool for severe CAC with CNs, with the IVL catheter successfully crossing the lesion, delivering IVL therapy and facilitating delivery of stents in all cases. 2) IVL was highly effective in treating CNs, with no differences in MSA or stent expansion between CN and non-CN groups and no reported immediate complications including flow-limiting dissections, perforations, abrupt closures, or slow flow or no reflow. 3) TLF at 2 years was 13.9% in the CN group, with no cardiac deaths and only one stent thrombosis event.
Severe CAC classifies a lesion as complex22 and is known to lead to a greater incidence of complications and PCI failure2324. Acutely, calcification may impact PCI success in a number of ways including friction between a drug-eluting stent and CAC leading to stent polymer damage, impaired drug transmission from polymer to tissue124, physical impedance to stent expansion25262728, and strut malapposition29. CNs represent a unique subset of severe CAC in which these aforementioned challenges are exaggerated, often leading to poor acute procedural outcomes. To date, rotational or orbital atherectomy has been favoured in published algorithms for plaque modification of CNs30. Theoretically, the rotational or, perhaps even more favourably, orbital motion may debulk the nodule and facilitate device delivery. However, evidence to support the debulking effectiveness of these devices in CNs is very limited6831. The present study confirms that IVL is mechanistically effective as a frontline preparation tool for the treatment of severe CAC with CNs. The IVL catheter crossed the lesion, delivered therapy and facilitated stent delivery in all cases, resulting in acceptable stent areas and expansion.
Despite the greater burden of calcium in CNs, we found no differences in residual area stenosis, stent area, stent expansion, or acute gain comparing CN and non-CN lesions at the sites of pre-IVL MLA, maximum calcium arc site or final MSA. Furthermore, the post-PCI stent area and expansion at the site of the CNs were in an acceptable range. Several reasons may explain these findings. First, the degree of calcium ablation after rotational and orbital atherectomy depends on guidewire bias directing the burr against the lesion32. This process may be less effective in some CNs where the vessel and lumen area are large or where the burr size is small. On the contrary, plaque modification using IVL is not subject to guidewire bias; therefore, irrespective of the RVD and MLA, energy is distributed circumferentially, thus modifying calcium in a more uniform manner. Second, the total burden of calcium and number of fractures were higher in the CN group compared with the non-CN group. We have shown previously that the predominant mechanism of action of IVL is calcium fracture and that the magnitude of fractures is proportional to the total burden of calcium1216. This is particularly relevant in the context of CNs, as the proximal and distal segments flanking the CN are known to have a high burden of calcium7. Given the larger vessel size and lumen area of the flanking segments, coupled with large calcium arcs, the unbiased mechanism of action of IVL favours calcium modification throughout the lesion rather than just in the CN itself. Histological data, showing that the CN itself is composed of a significantly higher proportion of necrotic core compared to collagenous sheet calcium, support the concept that complete lesion preparation, rather than isolated treatment of the nodule, is critical for optimal lesion preparation.
In heavily calcified lesions, the presence of a CN increases the risk of clinically driven target lesion revascularisation, stent thrombosis and major adverse cardiac events (MACE) up to 5 years of follow-up6. Even in the setting of advanced lesion preparation with rotational atherectomy, clinical outcomes continue to be worse in CNs compared with non-CN lesions6. These results suggest an inherently elevated risk of adverse clinical outcomes in patients with CNs undergoing PCI. This can in part be explained by (1) the location of the CNs at the site of hinge motion where the risk of stent failure increases and (2) their association with cardiovascular risk factors such as chronic kidney disease and diabetes33. To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first to demonstrate durable long-term clinical outcomes after any advanced lesion preparation strategy in lesions with CNs. Moreover, consistent with the pooled data from the Disrupt CAD trials34, IVL was safe for the treatment of CNs. Considering the inherent risk of PCI for patients with CNs and more frequent comorbidities, it was not surprising that the event rate was numerically higher in the CN group than the non-CN group, but this difference did not reach statistical significance. Furthermore, the event rate in the CN group was lower than what has been reported in the past635. Nevertheless, it should be noted that the present study was not powered for clinical outcomes, and a possible type 2 error could not be ruled out given the small number of patients in the CN group. Therefore, adequately powered studies for clinical outcomes are warranted to investigate whether IVL treatment can improve post-PCI outcomes compared with other plaque modification techniques in this highly malignant lesion subset.
While assessment of calcium by intravascular ultrasound is limited in ≈90% of calcified lesions due to acoustic shadowing, OCT allows visualisation of the outer layer of calcification in ≈80% of calcified lesions19. However, OCT imaging of CNs is limited by attenuation, and thus we could not qualitatively identify which non-eruptive nodules would be deformable by OCT. The presence of surface thrombus7, intra-CN haemorrhage36, necrotic core7 and thick calcium19 may all give a similar signal attenuation. Nevertheless, we were able to differentiate eruptive CNs from non-eruptive CNs. Given that eruptive CNs were universally deformable with IVL pretreatment15, OCT may have a therapeutic advantage in intravascular imaging of CNs. This finding is not only biologically plausible, given the high burden of deformable lipid and necrotic core in eruptive CNs7, but also has potentially important clinical implications given the ≈6.5-fold increased MACE hazard of eruptive versus non-eruptive nodules at 1 year in non-culprit vessels5. Similar to our recent report15, qualitative assessment of OCT identified distinct patterns of stent expansion based on the deformability of the CN. In total, approximately 80% of all CNs could be deformed after IVL, facilitating more symmetric and concentric stent deployment. Eruptive nodules were universally deformable, while approximately 2/3 of non-eruptive nodules were deformable. The 1/3 of non-eruptive nodules that were non-deformed resulted in more eccentric stent expansion. The different treatment response may be related to the histopathological characteristics of non-eruptive nodules: those with progression of underlying calcified disease are less likely deformable than those with progression of underlying lipidic disease. While previous studies have shown that asymmetry and eccentricity do not impact clinical outcome3738, to the best of our knowledge, these parameters have never been examined in a cohort of only severely calcified lesions. Nonetheless, our findings are reassuring in that the asymmetry and eccentricity following lesion preparation with IVL, even in CNs, do not present a clear hazard, with acceptable long-term clinical outcomes. While we did not detect a difference in clinical outcomes between the CN subtypes, the number of subjects was small, and PCI outcomes according to CN subtypes thus represent a meaningful future area of investigation.
Limitations
Despite serial OCT imaging and core laboratory analysis, our study has several limitations. First, this is a retrospective pooled analysis of non-randomised observational cohort studies without comparators such as speciality balloons or atherectomy. As such, the results should be considered hypothesis-generating. Second, as discussed above, the present study was not powered for clinical outcomes, and only a small number of patients were included in the CN group. Third, while we understand that the burden of calcification flanking the CN segment is critical to lesion preparation for stenting, the significance of partial thickness fractures in CNs is uncertain. Whether these fractures are markers of more extensive fractures that cannot be visualised by OCT due to signal attenuation remains to be determined. Indeed, in the Disrupt CAD III study, one postulated mechanism for no difference in stent expansion between lesions with versus without calcium fracture13 was the presence of non-linear fractures, not visible by OCT, but seen on microcomputational tomography and confirmed by histology34.
Conclusion
Despite the greater burden of calcification in CNs, IVL use was associated with comparable stent expansion and luminal gains in both lesions with and without CNs. Further studies powered for clinical outcomes comparing different plaque modification techniques in this lesion subset are warranted.
Impact on daily practice
Despite a greater calcium volume in severely calcified coronary lesions with calcified nodules (CNs) compared with those without CNs, intravascular lithotripsy-assisted stent implantation was associated with comparable outcomes in both CN and non-CN lesions. Further studies powered for clinical outcomes comparing different plaque modification techniques in this lesion subset are warranted.
Funding
This analysis was funded by Shockwave Medical.
Conflict of interest statement
Z.A. Ali reports institutional grants from Abbott, Abiomed, ACIST Medical, Boston Scientific, Cardiovascular Systems Inc., Medtronic, Opsens Medical, Philips, and Shockwave Medical; personal fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, and Boston Scientific; and equity in Elucid, Lifelink, SpectraWAVE, Shockwave Medical, and VitalConnect. B. Honton reports research grant from Shockwave Medical; consulting fees from Shockwave Medical and Abbott; and payment or honoraria from Terumo, Abbott, and Medtronic. D.J. Kereiakes reports personal consulting fees from Shockwave Medical, Elixir Medical, and Boston Scientific. J. Hokama has received consulting fees/honoraria from Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Abiomed; is an employee of Shockwave Medical; and has received equity/stock options from Shockwave Medical. S. Saito is a consultant for Japan Lifeline. C. Di Mario reports research grants from Amgen, CSL Behring, Chiesi, Daiichi Sankyo, Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, and Shockwave Medical. N. Gonzalo reports a research grant from Abbott; and consultancy and speaker fees from Abbott, Boston Scientific, Philips, and Shockwave Medical. R.F. Riley reports honoraria from Boston Scientific, Asahi Intecc, and Medtronic. A. Maehara reports grant support from Abbott and Boston Scientific; and consultant fees from Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Conavi Medical, Inc. M. Matsumura reports consulting fees from Terumo and Boston Scientific. G.W. Stone has received speaker honoraria from Medtronic, Pulnovo, and Infraredx; and has served as a consultant to Valfix, TherOx, Robocath, HeartFlow, Ablative Solutions, Vectorious, Miracor, Neovasc, Abiomed, Ancora, Elucid Bio, Occlutech, CorFlow, Apollo Therapeutics, Impulse Dynamics, Cardiomech, Gore, Amgen, Adona Medical, and Millennia Biopharma; and has equity/options in Ancora, Cagent, Applied Therapeutics, Biostar family of funds, SpectraWAVE, Orchestra Biomed, Aria, Cardiac Success, Valfix, and Xenter; his daughter is an employee at Medtronic; institutional disclosure: his employer, Mount Sinai Hospital, receives research support from Abbott, Abiomed, Bioventrix, Cardiovascular Systems Inc, Philips, Biosense Webster, Shockwave Medical, Vascular Dynamics, Pulnovo, and V-wave. J.M. Hill reports speaker honoraria and institutional grants from Abbott, Abiomed, Boston Scientific, and Shockwave Medical; and equity from Shockwave Medical. N.E.J. West is an employee of Shockwave Medical. All the other authors report nothing to disclose relevant to the present manuscript.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

