Abstract
BACKGROUND: Coronary access (CA) is a major concern in redo-transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) for failing supra-annular self-expanding transcatheter aortic valves (TAVs).
AIMS: This ex vivo study evaluated the benefit of leaflet splitting (LS) on subsequent CA after redo-TAVI in anatomies deemed at high risk of unfeasible CA.
METHODS: Ex vivo, patient-specific models were printed three-dimensionally. Index TAVI was performed using ACURATE neo2 or Evolut PRO (TAV-1) at the standard implant depth and with different degrees of commissural misalignment (CMA). Redo-TAVI was performed using the balloon-expandable SAPIEN 3 Ultra (TAV-2) at different implant depths with commissural alignment. Selective CA was attempted for each configuration before and after LS in a pulsatile flow simulator. The leaflet splay area was assessed on the bench.
RESULTS: In matched comparisons of 128 coronary cannulations across 64 redo-TAVI configurations, the overall feasibility of CA significantly increased after LS (60.9% vs 18.7%; p<0.001). The effect of LS varied according to the sinotubular junction height, TAV-1 design, TAV-1 CMA, and TAV-2 implant depth, given TAV-2 alignment. LS enabled CA for up to CMA 45° with the ACURATE neo2 TAV-1 and up to CMA 30° with the Evolut PRO TAV-1. The combination of LS and a low TAV-2 implant provided the highest feasibility of CA after redo-TAVI. The leaflet splay area ranged from 25.60 mm2 to 37.86 mm2 depending on the TAV-1 platform and TAV-2 implant depth.
CONCLUSIONS: In high-risk anatomies, LS significantly improves CA feasibility after redo-TAVI for degenerated supra-annular self-expanding platforms. Decisions on redo-TAVI feasibility should be carefully individualised, taking into account the expected benefit of LS on CA for each scenario.
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) is expanding to younger patients with lower surgical risk and longer life expectancy12. Despite favourable data on transcatheter aortic valve (TAV) durability, the number of reinterventions for TAV degeneration is expected to grow, and redo-TAVI is emerging as a valuable option in appropriate patients3. However, redo-TAVI might be unfeasible in 1 out of 3 patients, given the potential risk of coronary obstruction (CO) and coronary access (CA) impairment related to the neoskirt created by the pinned leaflets of the index TAV, particularly in case of degenerated supra-annular self-expanding platforms456789.
Transcatheter leaflet splitting (LS), using electrosurgical Bioprosthetic Aortic Scallop Intentional Laceration to prevent Iatrogenic Coronary Artery obstruction (BASILICA) and its iterations or recent dedicated devices, has been advocated to overcome these issues10111213. However, despite preliminary observations, the efficacy of this approach with different configurations of redo-TAVI and the impact on subsequent CA feasibility are unknown141516. Whether LS might enable the boundaries of redo-TAVI to be pushed is a clinically relevant question for the lifetime management of younger patients and is a matter of debate, as the current evidence is limited to anecdotal case reports.
Bench testing can provide unique insights, making it possible to test and compare different redo-TAVI strategies in the same anatomical setting. The aim of this ex vivo simulation study was to evaluate the effects of LS and its impact on CA after redo-TAVI for degenerated supra-annular self-expanding platforms in high-risk scenarios of coronary inaccessibility.
Methods
STUDY DESIGN
This investigator-initiated study was designed and executed using ex vivo simulation, in order to allow the direct comparison of different redo-TAVI strategies in the same high-risk scenario and their impact on CA, which would not be possible in real patients. All the procedures were conducted by experienced operators using patient-specific anatomical models connected to a pulsatile flow simulator and conventional equipment in a catheterisation laboratory setting (Figure 1). This study was performed under physiological test conditions with no human or animal participants, and therefore ethics approval was not required.
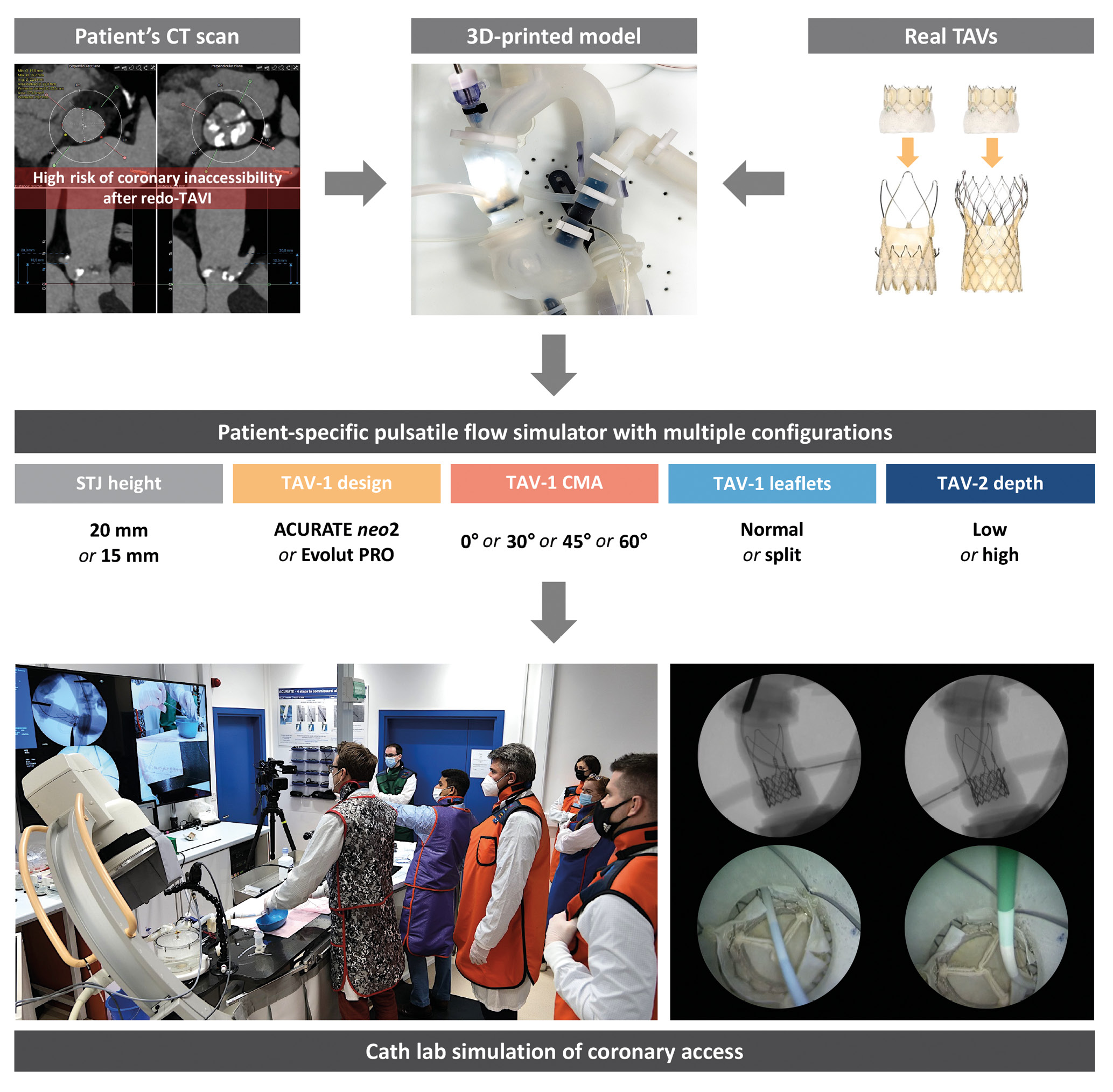
Figure 1. Study design. Development of a 3D-printed anatomical model from a patient’s CT scan and combination with different TAV configurations to test CA after redo-TAVI in a patient-specific pulsatile flow simulator under real catheterisation laboratory conditions. Patient anatomy was selected based on the high risk of coronary inaccessibility after redo-TAVI assessed by CT scan. 3D: three-dimensional; CA: coronary access; CMA: commissural misalignment; CT: computed tomography; STJ: sinotubular junction; TAV: transcatheter aortic valve; TAV-1: index TAV; TAV-2: redo-TAV; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation
ANATOMICAL MODELS
An ex vivo, three-dimensional (3D)-printed, patient-specific pulsatile flow model was developed to simulate coronary cannulation procedures after redo-TAVI. Patient anatomy was selected based on the high risk of coronary inaccessibility after redo-TAVI, as defined by computed tomography (CT): (1) coronary ostia below the neoskirt plane (NSP) defined by the redo-TAV (TAV-2) implant position inside the index TAV (TAV-1), and (2) a valve-to-aorta (VTA) distance <2 mm at the level of the NSP5. The risk of CO due to sinus sequestration was considered high in cases where the NSP was above the sinotubular junction (STJ)5. The original CT scan was electrocardiographically gated, contrast-enhanced, and used a <1 mm slice thickness. The native aortic valve was tricuspid, with symmetric cusps and no coronary eccentricity. Raw data from baseline pre-TAVI CT were exported in the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) format. The aorta, left ventricular blood pool, and left and right coronary arteries were segmented using semiautomatic segmentation algorithms with added manual corrections (Slicer 3D software; available at https://www.slicer.org). The segmentations were converted into 3D mesh images which were then converted into patient-specific 3D digital models. The native patient-specific aortic root anatomy had an STJ height of 20 mm (model A). This model was digitally edited to create an additional anatomy with an STJ height of 15 mm (model B), while maintaining anatomical proportions, in order to account for the difference in the TAV-1 design and the manufacturers’ recommended implant depths and to minimise confounding anatomical variations (Supplementary Figure 1). PolyJet technology was used to 3D print the models (J720 3D printer; Stratasys). Each 3D-printed model was assembled within a pulsatile flow circuit at physiological temperature and pressure to simulate coronary cannulation procedures under real catheterisation laboratory conditions. The overall geometry of the pulsatile flow simulator was also created from the patient’s CT and consisted of full-length aorta, aortic arch and iliofemoral axes.
REDO-TAVI CONFIGURATIONS
Multiple redo-TAVI configurations were tested in each anatomical model. The ACURATE neo2 (Boston Scientific) size small (S) and the 26 mm Evolut PRO (Medtronic) supra-annular, self-expanding valves were alternatively used as the degenerated TAV-1, while a 23 mm SAPIEN 3 Ultra (Edwards Lifesciences) intra-annular, balloon-expandable valve was used as the TAV-2 for redo-TAVI. The implant depth of the TAV-1 was 7 mm for the ACURATE neo2 and 3 mm for the Evolut PRO, according to the device manufacturers’ recommendations. Different degrees of commissural misalignment (CMA) were used for both TAV-1 platforms in all cases: 0° (commissural alignment), 30° (mild CMA), 45° (moderate CMA), and 60° (severe CMA), according to the ALIGN-TAVR definitions17. LS was performed on the bench with a straight cut in the middle of each leaflet facing the coronary ostium. Redo-TAVI was performed on the bench, avoiding TAV-2 severe CMA and alternatively targeting low and high TAV-2 implant depths. Specifically, the TAV-2 outflow was alternatively aligned to node 4 or node 6 of the index Evolut PRO, and to the top of the upper crown or to the base of the commissural posts of the index ACURATE neo2, in low and high TAV-2 implants, respectively1819. All TAV-2 were deployed with nominal volume as per the manufacturers’ recommendations.
CORONARY CANNULATION PROCEDURES
CA was independently attempted in the pulsatile flow model by 2 experienced operators under fluoroscopic guidance after redo-TAVI in each configuration, before and after TAV-1 LS. All cannulations were performed via the femoral access route. Catheter choice and coronary cannulation techniques after TAVI followed the valve-specific recommendations202122. The operators were allowed to choose among a prespecified set of different 6 Fr guiding catheters: Judkins left (JL) 4, JL5, Amplatz left (AL) 1, extra backup (EBU), multipurpose angiographic (MPA) for the left coronary artery (LCA); and Judkins right (JR) 4, AL1, AL2, internal mammary (IM), MPA for the right coronary artery (RCA). An internally mounted borescope camera was used to directly visualise the movements of the catheters and their interactions with the redo-TAVI configurations from a top axial view. The operators were blinded to the borescope camera.
OUTCOMES OF CORONARY CANNULATION PROCEDURES
Selective CA, defined as complete catheter engagement of the coronary ostium, was confirmed by contrast injection and near-field borescope assessment. Unfeasibility was defined for each coronary artery as the inability to achieve selective CA with any of the prespecified catheters despite multiple attempts. The type of catheter used and the cannulation approach, assessed by far-field borescope camera, were also collected. CA outcomes were adjudicated by a physician blinded to the STJ anatomy and to procedural planning analysis. The main study objective was to assess the impact of TAV-1 LS on CA feasibility after redo-TAVI. Secondary study objectives included the assessment of the impact of STJ height, TAV-1 design, TAV-1 CMA, TAV-2 implant depth, and their combinations on the efficacy of LS. Different redo-TAVI and lifetime management strategies to secure CA were directly compared.
LEAFLET MEASUREMENTS
All the different redo-TAVI configurations were analysed using the SmartScope (OGP) vision-based measurement system. The leaflet splay area free of TAV-2 skirt was measured. The neoskirt height was determined as the distance between the TAV-1 inflow and the pinned leaflet-free edge height at the level of the TAV-2 outflow. The functional neoskirt height was calculated by subtracting 3 mm and 7 mm from the total neoskirt height for the Evolut PRO and the ACURATE neo2, respectively. The gain in functional neoskirt height obtained with LS was calculated as the distance between the top of the functional neoskirt and the lowest accessible cell of the TAV-2 at the nadir of the split leaflet of the TAV-1.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Continuous variables were reported as mean±standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile range (IQR), as appropriate. The normality of the data was verified by the Kolmogorov-Smirnov goodness-of-fit test. Group comparison was performed using the Student’s t-test, Mann-Whitney U test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test, as appropriate. Categorical variables were reported as numbers and percentages. Group comparison was performed using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. Matched comparison of feasibility classification before and after different interventions was performed with McNemar’s test and Cochran’s Q test or with Dunn’s test and the Bonferroni correction, as appropriate. Two-sided p-values<0.05 were considered statistically significant. The statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics version 24 (IBM). The graphs were generated with GraphPad Prism software (version 6; GraphPad Software).
Results
CT ASSESSMENT
According to CT analysis, without LS, CA was predicted to be unfeasible in 64/64 (100%) configurations, and the risk of CO was considered high in 32/64 (50.0%) configurations. Based on the assumption that an angle >20° between the coronary ostium and TAV-1 commissural post (TAV-1 CMA <45°) would be necessary to warrant efficacy14, LS would prevent CO in 16/32 (50.0%) of these high-risk cases.
IMPACT OF LS ON CA AFTER REDO-TAVI
Overall, 128 coronary cannulations were performed in 64 different redo-TAVI configurations. The 2 operators achieved the primary outcome of selective CA in the same configurations. The impact of LS on CA feasibility after redo-TAVI was analysed using pairwise comparisons in order to adjust for the effect of STJ height, TAV-1 design, TAV-1 degree of CMA, and TAV-2 implant depth. The results of each matched comparison have been visually illustrated in a feasibility matrix (Table 1). Without LS, selective CA was obtained in 12/64 (18.7%) cases. In all these cases, CA was achieved only with the combination of the ACURATE neo2 and a low TAV-2 implantation, up to TAV-1 CMA 45°. The addition of LS significantly increased the overall feasibility of CA from 12/64 (18.7%) to 39/64 (60.9%) cases in matched comparisons (p<0.001). LS produced a significant increase of CA feasibility across different STJ anatomies, TAV-1 platforms, TAV-1 degrees of CMA, and TAV-2 implant depths. However, the effect of the intervention varied according to specific combinations of the above-mentioned parameters (Central illustration). Coronary cannulation was performed through the frame of the TAV-1 in all cases. According to the specific configuration, for both TAV-1 platforms, coronary cannulation after LS was possible either above the TAV-2 frame or through the TAV-2 frame (Figure 2). In 15/39 (38.4%) cases overall, coronary cannulation after LS was only possible through the TAV-2 frame, owing to TAV-2 commissural alignment. The JL4 (87.5%) and the JR4 (100%) were the most used guiding catheters for LCA and RCA engagement, respectively.
Table 1. CA feasibility matrix.
| Configuration | TAV-1 normal leaflets | TAV-1 split leaflets | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STJ height | TAV-1 type | TAV-1 CMA | TAV-2 implant depth | LCA | RCA | LCA | RCA |
| 15 mm | ACURATE neo2 | 0° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | ||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | |||||
| 30° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | ||||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | |||||
| 45° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | ||||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | * | * | |||
| 60° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | ||||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | * | * | |||
| Evolut PRO | 0° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | * | * | |||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | |||||
| 30° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | * | * | ||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | |||||
| 45° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | * | * | * | * | ||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | * | * | |||
| 60° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | * | * | * | * | ||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | * | * | |||
| 20 mm | ACURATE neo2 | 0° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | ||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | |||||||
| 30° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | ||||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | |||||||
| 45° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | ||||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | |||||||
| 60° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | ||||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | |||||||
| Evolut PRO | 0° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | |||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | |||||
| 30° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | ||||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | |||||
| 45° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | ||||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | * | * | |||
| 60° | SAPIEN 3 Ultra low | ||||||
| SAPIEN 3 Ultra high | * | * | * | * | |||
| The CA feasibility matrix shows the observed feasibility of coronary cannulation (green boxes) for each tested redo-TAVI configuration. CA was deemed unfeasible in all cases without LS. The predicted high risk of CO (*) is highlighted. CA: coronary access; CMA: commissural misalignment; CO: coronary obstruction; LCA: left coronary artery; LS: leaflet splitting; RCA: right coronary artery; STJ: sinotubular junction; TAV: transcatheter aortic valve; TAV-1: index TAV; TAV-2: redo-TAV; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation | |||||||
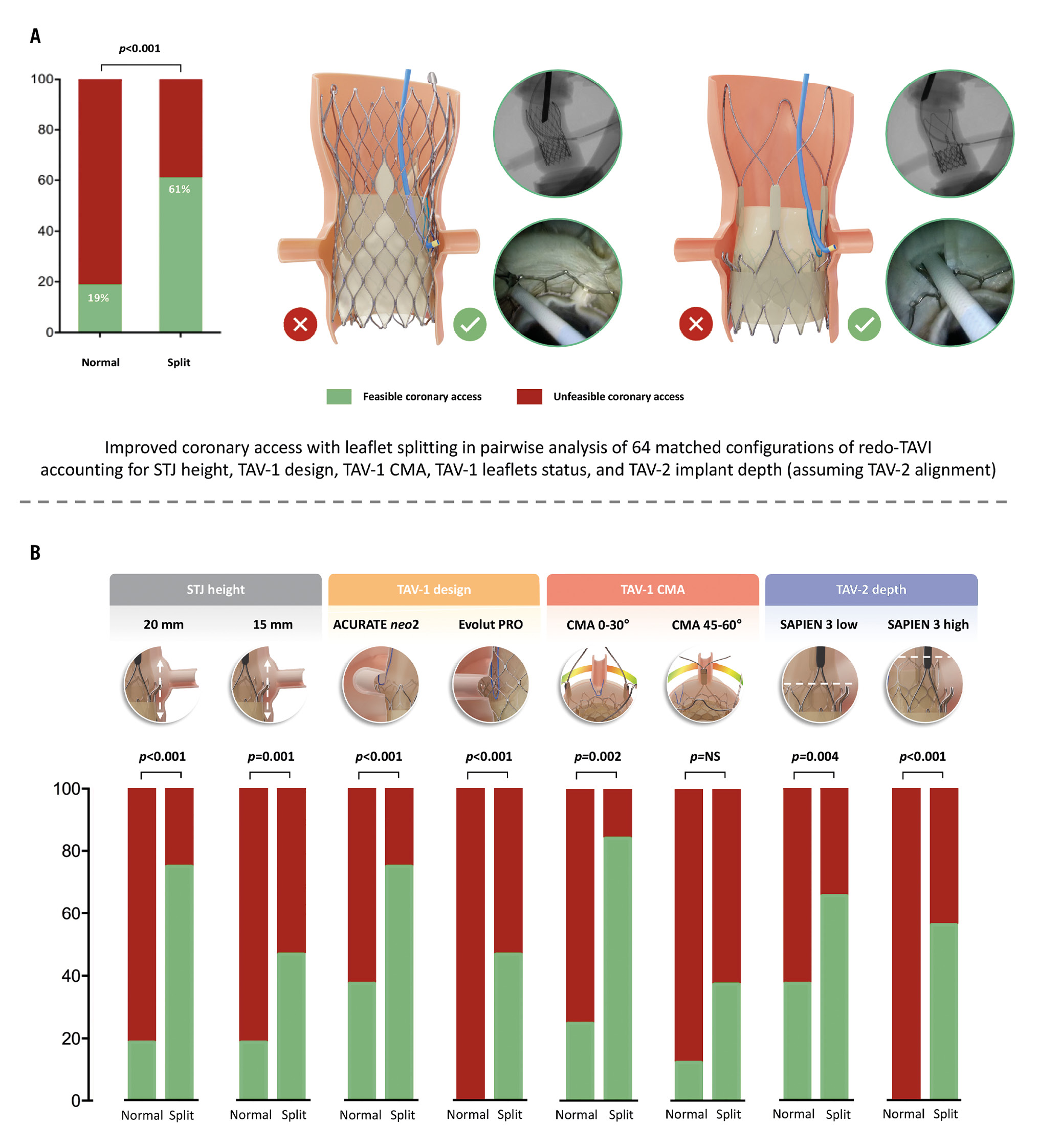
Central illustration. Impact of leaflet splitting on CA after redo-TAVI with a balloon-expandable valve in degenerated supra-annular self-expanding platforms in high-risk scenarios of coronary inaccessibility. A) The feasibility of CA after redo-TAVI with leaflet splitting. B) Anatomical and procedural variables affecting the efficacy of leaflet splitting on coronary access after redo-TAVI. CA: coronary access; CMA: commissural misalignment; NS: not significant; STJ: sinotubular junction; TAV: transcatheter aortic valve; TAV-1: index TAV; TAV-2: redo-TAV; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation
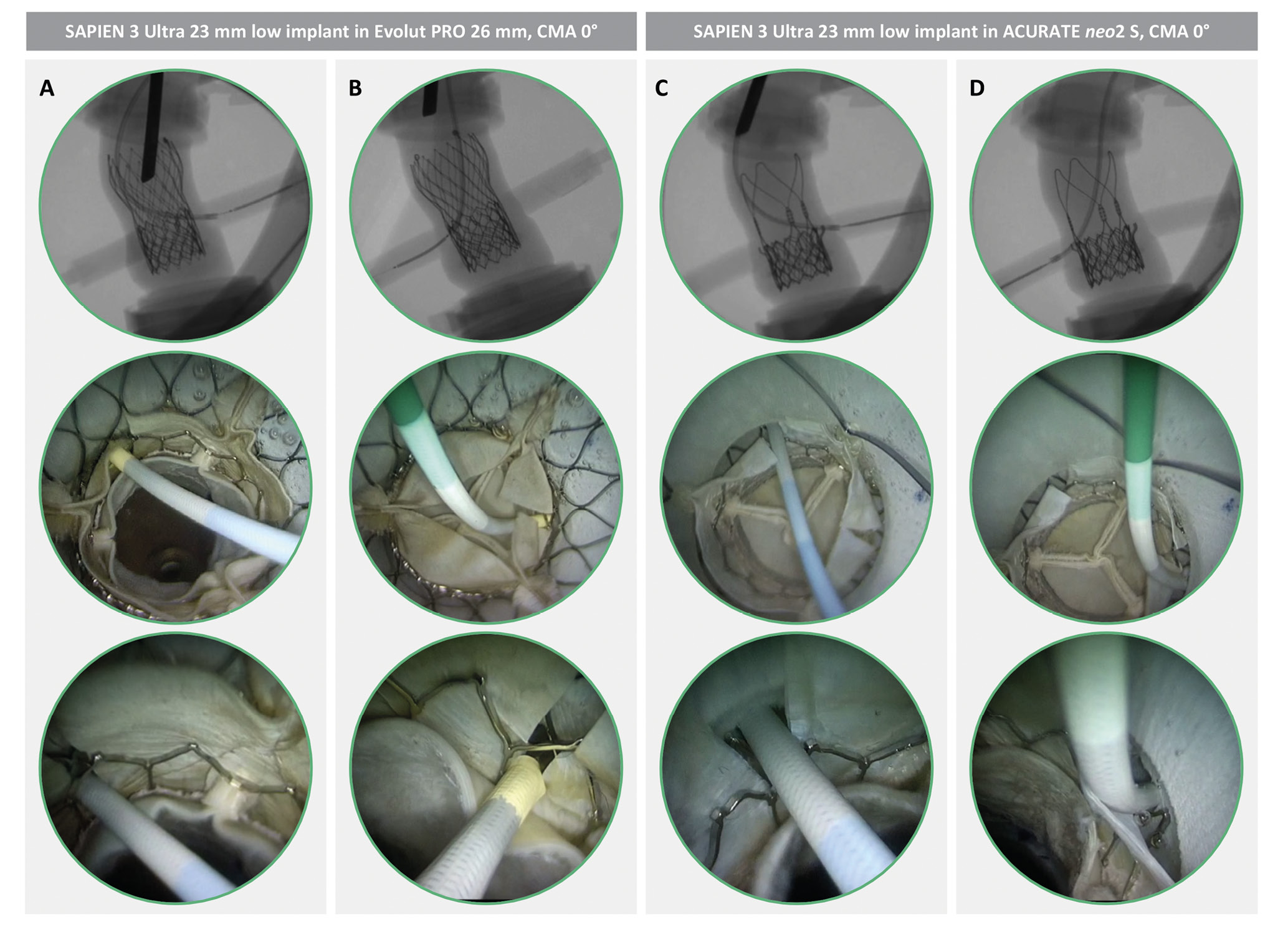
Figure 2. CA simulation after redo-TAVI with LS. Different TAV-1 platforms are shown in matched redo-TAVI configurations in the same anatomy (STJ height 15 mm). CA is obtained through the TAV-1 split leaflet, either through the TAV-2 frame (A and B) or above the TAV-2 frame (C and D). CA: coronary access; CMA: commissural misalignment; LS: leaflet splitting; S: small; STJ: sinotubular junction; TAV: transcatheter aortic valve; TAV-1: index TAV; TAV-2: redo-TAV; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation
COMPARISON OF REDO-TAVI STRATEGIES
The possible treatment combinations for redo-TAVI optimisation were analysed using pairwise comparisons with the aim of identifying those providing the highest rate of CA.
The effect of LS and TAV-2 implant depth modulation was evaluated adjusting for STJ height and the TAV-1 degree of CMA. For the ACURATE neo2 TAV-1 platform, the combinations of LS plus low TAV-2 implant (p<0.001), LS plus high TAV-2 implant (p<0.001), and no LS plus low TAV-2 implant (p<0.001) provided a significantly higher proportion of feasible cases, as compared to no LS plus high TAV-2 implant. For the Evolut PRO TAV-1, the combination of LS plus low TAV-2 implant resulted in a significantly higher proportion of feasible cases, as compared to no LS plus low TAV-2 implant (p=0.001) and no LS plus high TAV-2 implant (p=0.001) (Supplementary Figure 2).
The effect of the TAV-1 degree of CMA on LS efficacy was assessed adjusting for STJ height and TAV-2 implant depth. For the ACURATE neo2 TAV-1, the addition of LS led to a significantly higher proportion of feasible CA for CMA 0° to 45° (p<0.001) compared to CMA 60°. For the Evolut PRO TAV-1, the addition of LS led to a significantly higher proportion of feasible CA only for CMA 0° (p=0.004) and 30° (p=0.030) compared to CMA 60° (Supplementary Figure 3).
LEAFLET MEASUREMENTS
The leaflet splay area free of TAV-2 skirt changed according to the TAV-1 design and the TAV-2 implant depth. ACURATE neo2 showed a larger leaflet splay area compared to Evolut PRO. The TAV-2 implant depth had a greater effect on leaflet splay area for ACURATE neo2, with a larger leaflet splay area when the TAV-2 was implanted in a high position compared to a low position. For both TAV-1, the gain in functional neoskirt height was greater in cases with a high TAV-2 implant (Figure 3).
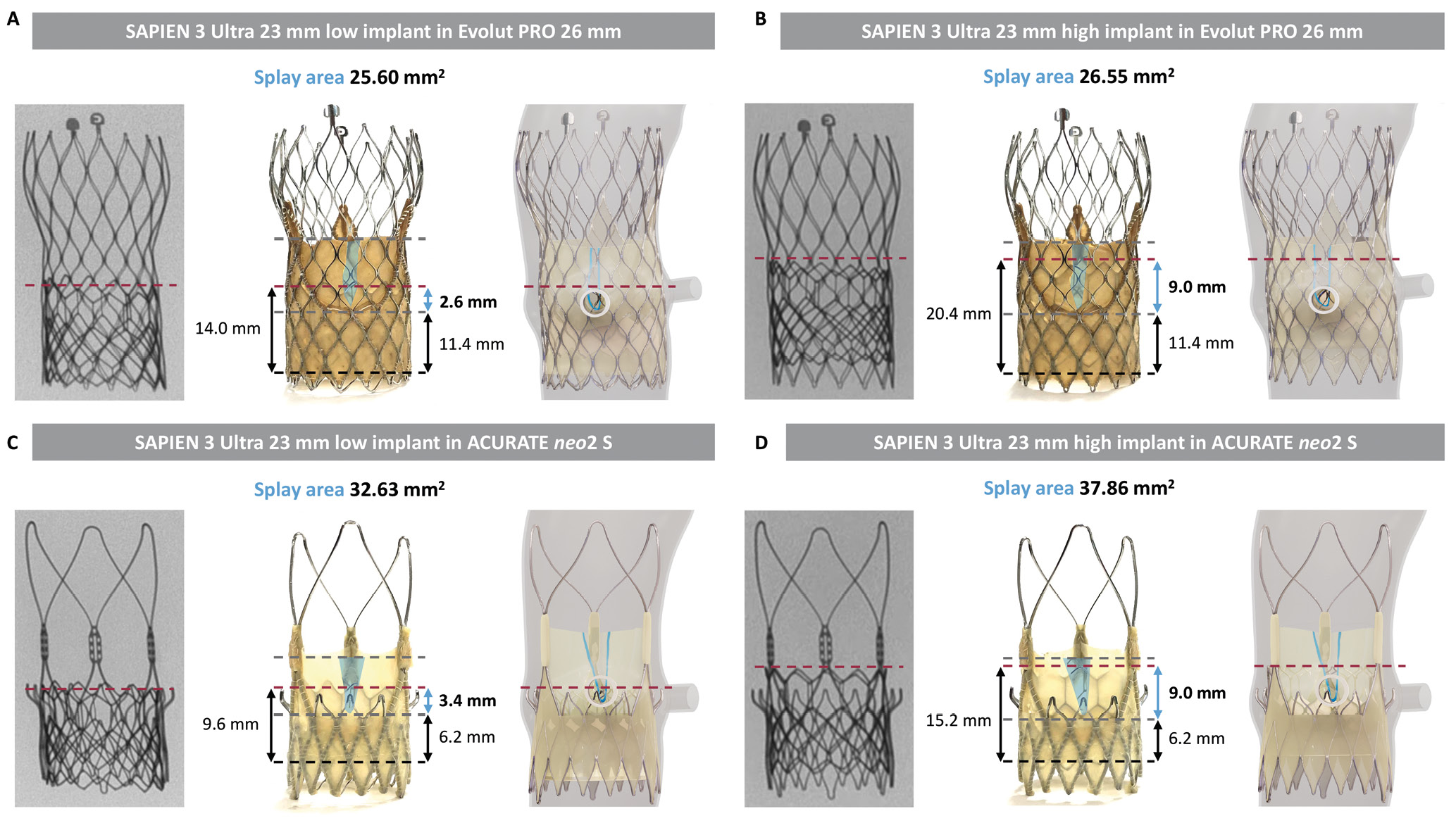
Figure 3. Leaflet measurements before and after splitting for different redo-TAVI combinations. (A) and (B) show the measurements with the SAPIEN 3 Ultra implanted in the Evolut PRO, while (C) and (D) show those with the SAPIEN 3 Ultra implanted in the ACURATE neo2 S, in low and high positions. TAV-1 implant depth (black line), TAV-1 leaflet base and top (grey lines), and TAV-2 position (red line) are marked. Leaflet splay area (blue area), functional neoskirt (black arrows) and functional neoskirt gain (blue arrow) are illustrated. A simulation of the anatomy (STJ height 15 mm) is displayed. S: small; STJ: sinotubular junction; TAV: transcatheter aortic valve; TAV-1: index TAV; TAV-2: redo-TAV; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation
Discussion
Along with the risk of CO, the risk of CA impairment is a major concern in redo-TAVI procedures, especially if the first implanted valve is a supra-annular self-expanding TAV. Current evidence is limited to virtual predictions of CA feasibility after redo-TAVI using different imaging methodologies. Angiographic analysis of 137 patients who underwent TAVI with either Evolut PRO or ACURATE neo2 predicted that CA may be unfeasible in up to 38.5% or 41.1% of patients, respectively. The presence of a narrow STJ was the main anatomical predictor for unfeasible CA in this setting, regardless of annular size and coronary height4. Postprocedural CT analysis of 30 patients who underwent redo-TAVI for degenerated CoreValve (Medtronic) or Evolut TAVs predicted the rates of unfeasible CA to be between 20% and 27% depending on the TAV-2 used8. A recent CT simulation study demonstrated that up to 90.7% of patients implanted with an Evolut PRO undergoing virtual redo-TAVI with a SAPIEN 3 in a low position might require leaflet modification regardless of TAV size because of the anticipated risk of unfeasible CA23. Therefore, LS may represent an appealing solution, not only to mitigate the risk of CO, but also to facilitate future CA after redo-TAVI. LS, whether electroÂÂsurgical or mechanical, has demonstrated efficacy in preventing CO after TAVI in the setting of native valves and failed surgical aortic prostheses. However, comparatively little data exist evaluating the effectiveness of LS after redo-TAVI, and testing CA with and without LS is not possible in vivo141516.
This study provides a detailed assessment of the impact of LS on CA feasibility after redo-TAVI for degenerated supra-annular self-expanding TAVs. Furthermore, it demonstrates for the first time the anatomical and procedural factors that can impact the effectiveness of LS for CA after redo-TAVI. The unique design of this study with the use of patient-specific simulators allows for a direct comparison of different therapeutic options for redo-TAVI in the same anatomical conditions, which is impossible to test in real patients. LS produced a significant increase in CA feasibility by creating an opening in the functional neoskirt. However, the effect of the intervention varied according to specific combinations of baseline parameters and procedural factors.
When evaluating patients with failing supra-annular self-expanding TAVs, 3 non-modifiable factors should be considered to assess the feasibility of CA following redo-TAVI: (1) STJ height, (2) TAV-1 type with relative implant depth, and (3) TAV-1 degree of CMA. These factors are closely intertwined, as they synergistically define the VTA distance, the functional neoskirt height and the lowest accessible cell area of the TAV-1. The geometrical variables determine the ability to advance and manipulate a guiding catheter into the coronary sinus. During the redo-TAVI procedure, when treating supra-annular self-expanding platform degeneration with a short-frame balloon-expandable device, 3 possible actions can be taken to try and secure future CA: (1) TAV-1 leaflet modification, (2) TAV-2 implant depth modulation, and (3) TAV-2 commissural alignment. The impact of the TAV-2 implant depth has been investigated for both the Evolut R (Medtronic) and the ACURATE neo2 devices in previous bench studies using non-degenerated platforms. A low SAPIEN 3 implant inside an index Evolut R reduces the neoskirt height without compromising haemodynamics despite the higher degree of TAV-1 leaflet overhang18. Similar results in terms of haemodynamics and neoskirt height reduction have been observed for the ACURATE neo219. Furthermore, a recent CT simulation study demonstrated that SAPIEN 3 outflow positioning at Evolut node 4 would result in a higher predicted rate of feasible CA after redo-TAVI compared to positioning at node 5, irrespective of the initial Evolut implant depth24. TAV-2 alignment is a major determinant of LS efficacy. Failure to align the TAV-2 to the TAV-1, resulting in severe CMA, might jeopardise the efficacy of LS, as the TAV-1 leaflet splay would be obstructed by the TAV-2 commissural posts. Although current-generation balloon-expandable platforms do not allow for commissural alignment, next-generation devices will include this feature. The results of the present study were obtained with TAV-2 alignment, and 38.4% of the cannulations after LS were only possible through a TAV-2 frame, underscoring the relevance of this upcoming technological refinement.
Two main questions arise when considering the possibility of adding leaflet modification to the interventional “arsenal”: (1) given a specific scenario, what is the best strategy for redo-TAVI? and (2) given a specific scenario and a specific strategy for redo-TAVI, how is the efficacy of LS affected by TAV-1 CMA? Overall, the combination of leaflet splitting plus a low TAV-2 implant appeared to be the best strategy, providing the highest CA feasibility rate. However, similar rates could also be achieved with leaflet splitting plus a high TAV-2 implant and with no splitting plus a low TAV-2 implant in cases where ACURATE neo2 is the TAV-1. In the latter case, although more challenging, CA could be achieved through the increase in the VTA distance created by the gap between the neoskirt and the outer edge of the ACURATE neo2 frame19. The lowest rates of CA feasibility despite LS occurred with Evolut PRO as the TAV-1 plus a high TAV-2 implant. Therefore, when confronted with a high-risk anatomy, LS should be considered, as it will enable operators to adjust the TAV-2 implant depth if necessary, based on the STJ height and TAV-1 design, without compromising CA. On the other hand, if LS is not feasible, either because of limited local expertise with BASILICA or because of a lack of dedicated platforms, it becomes imperative to achieve a low TAV-2 implant in cases where ACURATE neo2 is the TAV-1 and to evaluate surgery as an alternative option in cases where Evolut PRO is the TAV-1 if the risk for unfeasible CA is deemed to be high. Commissural alignment has only been recently introduced in clinical practice; therefore, it is reasonable to anticipate that a significant proportion of patients requiring redo-TAVI in the near future will present with a wide spectrum of misaligned configurations17. TAV-1 CMA is thought to affect the efficacy of LS on both CO prevention and CA preservation. A recent computer simulation study hypothesised a non-linear efficacy gradient for BASILICA according to the degree of overlap between the TAV-1 commissural posts and coronary ostia, with a severe risk of CO in case of ≤20° deviation14. However, the effect of CMA on LS efficacy might vary across different TAV-1 devices. Particularly, differences in the TAV-1 stent frame might result in heterogeneous splay angles after LS, favouring open-stent frame designs1516. These considerations might call into question the theoretical ineffectiveness of LS in preventing CO in case of TAV-1 CMA ≥45°. On the other hand, they might explain why, in the present study, LS increased CA feasibility up to TAV-1 CMA 45° for the ACURATE neo2, while for the Evolut PRO the effect of CMA was more prominent, resulting in futility in case of CMA >30°.
The results of this study generate insights on how LS might expand redo-TAVI indications and might be incorporated into the lifetime management planning of aortic stenosis patients. The translational impact of these findings on clinical practice is further emphasised by the observation that the high-risk aortic anatomies tested in this study are commonly encountered, being in line with the average aortic root dimensions of patients included in the RE-ACCESS study, which showed an average STJ height of 18 mm in a large, real-world population of 300 subjects undergoing TAVI25. Nevertheless, further in vivo studies are warranted to confirm the efficacy of LS in the setting of redo-TAVI.
In conclusion, decisions on redo-TAVI feasibility should be carefully individualised, taking into account the expected benefit of LS on CA in each scenario.
Limitations
This study relied on ex vivo simulation to overcome the challenge of testing different redo-TAVI combinations in the same anatomy. Despite its robustness, the model might not fully replicate the complexity of in vivo procedures in a real catheterisation laboratory setting, potentially affecting the generalisability of the study findings. Furthermore, the study’s ex vivo nature precluded the collection of longitudinal clinical data, limiting the ability to assess the long-term implications of LS on patient outcomes over time.
All the tests were performed in high-risk anatomies for coronary inaccessibility and, therefore, may not represent the regular redo-TAVI scenario. The aim of this study was to assess the most challenging end of the spectrum of anatomical complexity, in which CA impairment and CO might coexist. However, a methodology to assess coronary perfusion ex vivo is still under development. Therefore, in the present study, the assessment of the effect of LS on CO remains theoretical, since CA unfeasibility cannot be assumed to be disruption of coronary flow (particularly with TAV-1 CMA <45°), and CA feasibility cannot be translated into preservation of coronary perfusion (particularly with TAV-1 CMA ≥45°).
The feasibility and the results of LS obtained in vivo using current technologies might be less predictable than those obtained in the present study. Indeed, while ex vivo splitting was performed by cutting the leaflet in the middle portion, in vivo splitting might be unfeasible in some cases, and the cut might either not fall in the middle of the leaflet or follow a skewed path, leading to asymmetric flaps. The mobility of in vivo degenerated leaflets might not reflect that of the ex vivo model in which the TAVs utilised were new and devoid of any calcification. The leaflet splay area measured on the bench was obtained with ideal TAV-1 expansion and TAV-2 commissural alignment, which might not necessarily occur in vivo. Furthermore, in vivo TAV-1 implant depth might differ from the nominal one adopted in this study, affecting the functional neoskirt height. In addition, while in this study the TAV-2 commissures were aligned to the TAV-1, current-generation balloon-expandable TAVs do not allow for predictable commissural alignment, increasing the risk of severe TAV-2 CMA, which might obstruct the splayed leaflet. Therefore, the results of this study reflect the best-case scenario for LS and should be considered hypothesis-generating.
Conclusions
In high-risk anatomies, LS significantly increases CA feasibility after redo-TAVI for degenerated supra-annular self-expanding platforms. The combination of STJ height, TAV-1 design and CMA, and TAV-2 implant depth and CMA affects the efficacy of LS. Further clinical studies are necessary to validate these findings and establish the clinical usefulness of LS in redo-TAVI.
Impact on daily practice
Redo-transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) in failing supra-annular transcatheter aortic valves (TAVs) might be unfeasible in 1 out of 3 patients, based on the potential risk of coronary obstruction and coronary access (CA) impairment. The efficacy of leaflet splitting (LS) in TAVs and the impact on subsequent CA feasibility after redo-TAVI are unknown. In high-risk anatomies, LS significantly increases CA feasibility after redo-TAVI for degenerated supra-annular self-expanding platforms. The combination of sinotubular junction height, index TAV design and commissural misalignment (CMA), and second TAV implant depth and CMA affects the efficacy of LS. Further studies are needed to assess the feasibility of CA after redo-TAVI with LS in vivo. Imaging-based prediction models might contribute to individualised decision-making and lifetime management planning.
Funding
This study was supported by an investigator-sponsored research grant from Boston Scientific. However, Boston Scientific was not involved in the design, planning or execution of the study, simply providing equipment.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Beneduce has received speaker fees from Abiomed and Boston Scientific. A.A. Khokhar has received speaker fees from Boston Scientific. F. Giannini has received speaker fees from Boston Scientific. W-K. Kim has been a proctor for Boston Scientific, Abbott, and Meril Life Sciences; has received speaker fees from Boston Scientific, Abbott, Edwards Lifesciences, Meril Life Sciences, and Shockwave Medical; has been an advisory board member to Boston Scientific and HID; and has received institutional fees from Boston Scientific. F. Maisano has received grant and/or institutional research support from Abbott, Medtronic, Edwards Lifesciences, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, NVT, and Terumo; has received consulting fees, personal and institutional honoraria from Abbott, Medtronic, Edwards Lifesciences, Xeltis, and Cardiovalve (Venus Medtech); has received royalty income/IP rights from Edwards Lifesciences; and has been a shareholder (including share options) of CardioGard, Magenta, SwissVortex, Transseptal Solutions, Occlufit, 4Tech, and Perifect. O. De Backer has received institutional research grants and consulting fees from Boston Scientific. D. Dudek has been a scientific advisory board member of Boston Scientific. D. Grant and L. Lynch are employees of Boston Scientific. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

