Abstract
Aims: Few data regarding clinical outcomes according to severity of calcification in patients with coronary bifurcation target lesions are available. We therefore aimed to evaluate the clinical outcomes according to severity of calcification in patients with coronary bifurcation target lesions after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with drug-eluting stents (DES) using a large-scale multicentre Korean registry.
Methods and results: This prospective, multicentre, observational registry enrolled 2,897 patients undergoing PCI with DES for coronary bifurcation lesions. We compared target lesion failure (TLF), defined as a composite of cardiac death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), and target lesion revascularisation (TLR), according to severity of calcification in coronary bifurcation target lesions, assessed by an angiographic core laboratory using quantitative coronary angiography. Moderate or severe calcification of target bifurcation lesions was observed in 608 (20.9%) patients. During a median follow-up period of 36 months, moderate or severe calcification increased the adjusted risks of TLF (hazard ratio [HR] 1.31, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.03-1.68, p=0.031), TLR (HR 1.36, 95% CI: 1.04-1.79, p=0.027), and revascularisation (HR 1.39, 95% CI: 1.09-1.78, p=0.009). However, it was not associated with an increased risk of cardiac death, MI, or stent thrombosis.
Conclusions: Moderate or severe calcification of coronary bifurcation lesions is not uncommon and is associated with unfavourable long-term clinical outcomes, driven mainly by an increased frequency of repeat revascularisation.
Abbreviations
DES: drug-eluting stent(s)
MI: myocardial infarction
PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
TLF: target lesion failure
TLR: target lesion revascularisation
TVR: target vessel revascularisation
Introduction
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for the treatment of coronary bifurcation lesions is a frequently performed high-risk procedure with a high periprocedural complication rate1. Calcified coronary lesions pose a challenge for PCI due to their smaller final lumen diameters and reduced acute lumen gain with stenting compared with non-calcified lesions2. Severe calcification in native coronary arteries can even increase the risk of mortality in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery3. Coronary bifurcation and calcified lesions are related to lower procedural success rates, stent underexpansion, and a greater likelihood of in-stent restenosis4. Surprisingly, no study has investigated the effects of calcification in coronary bifurcation target lesions after PCI in the era of drug-eluting stent (DES) use. Therefore, we evaluated the clinical outcomes according to severity of calcification in patients with coronary bifurcation target lesions after PCI with DES using a large-scale multicentre Korean registry.
Methods
The COronary BIfurcation Stent (COBIS) II registry is a retrospective, multicentre, observational registry designed to reflect real-world practice in the treatment of coronary bifurcation lesions with DES. A total of 2,897 patients with bifurcation lesions treated at 18 major PCI centres in South Korea between January 2003 and December 2009 were enrolled. The inclusion criteria were: 1) coronary bifurcation lesion treated with a DES only, and 2) main vessel diameter ≥2.5 mm and side branch diameter ≥2.3 mm. Exclusion criteria were: 1) cardiogenic shock or receipt of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and 2) protected left main disease. Data collection and coronary angiography and PCI methods used in patients included in the COBIS II registry have been described previously5. Briefly, all baseline and procedural cine coronary angiograms were reviewed and analysed at the angiographic core laboratory of the Cardiac and Vascular Center, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea, using standard qualitative and quantitative methods. Bifurcation lesions were classified according to the Medina system6, and Medina type 1,1,1, 1,0,1 and 0,1,1 lesions were defined as true bifurcation lesions. The ethics committees of all participating hospitals approved the study protocol, and all patients provided written informed consent.
A total of 2,897 patients in the COBIS II registry were divided into two groups according to the presence of calcified bifurcation target lesions: 1) no or mild calcification (N=2,289), and 2) moderate or severe calcification (N=608). Moderate calcification was defined as radiopaque density noted only during the cardiac cycle and typically involving only one side of the vascular wall, and severe calcification was defined as radiopaque density noted without cardiac motion prior to contrast injection and generally involving both sides of the arterial wall7. Patients who underwent PCI received 300 mg aspirin and 300 or 600 mg clopidogrel as a loading dose before PCI. Doses of 50-70 U/kg unfractionated heparin were used before or during PCI to maintain an activated clotting time of 250-300 s. DES type, use of one or two stents, use of intravascular ultrasound, and PCI access route were chosen at the discretion of the interventional cardiologist. After PCI, 100-300 mg aspirin and 75 mg clopidogrel were prescribed daily. Patients used the two antiplatelet medications for a minimum of six months, and aspirin was prescribed indefinitely. The median duration of follow-up was 36 months (interquartile range, 25-52 months). The primary study outcome was target lesion failure (TLF), defined as the composite of cardiac death, spontaneous myocardial infarction (MI), and target lesion revascularisation (TLR). We also investigated the incidence of cardiac death or MI, target vessel revascularisation (TVR), repeat PCI, and stent thrombosis. All study outcomes were registered according to the Academic Research Consortium definitions8.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Continuous variables are presented as means±standard deviations or medians and interquartile ranges and were compared using the unpaired t-test or the Mann-Whitney rank-sum test. Discrete variables are expressed as counts and percentages and were analysed with Pearson’s chi-squared test or Fisher’s exact test. We constructed Kaplan-Meier curves for comparison of the primary outcome between the two groups, and differences were assessed with the log-rank test. Cox proportional hazards regression with adjustment for covariates was used to assess clinical outcomes. The variables which had a p-value ≤0.05 in univariate Cox regression analysis and centre identifier (composed of 18 numerals for each centre) were included in the multivariate Cox regression analysis: lesion location (left main vs. non-left main bifurcation), stenting technique (one- vs. two-stent technique), side branch predilatation, diabetes mellitus, history of cerebrovascular accident, history of PCI, multivessel disease, use of non-compliant balloon after stenting, and true bifurcation. However, a proportional hazards assumption test using the Schoenfeld residual method (analysis by Cox regression and bivariate correlation analysis) showed that the proportional hazards assumption was violated; therefore, we performed time-dependent Cox regression analysis using the above-mentioned variables. All analyses were two-tailed, and all variables were considered significant at a value of p<0.05. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS for Windows, Version 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
Results
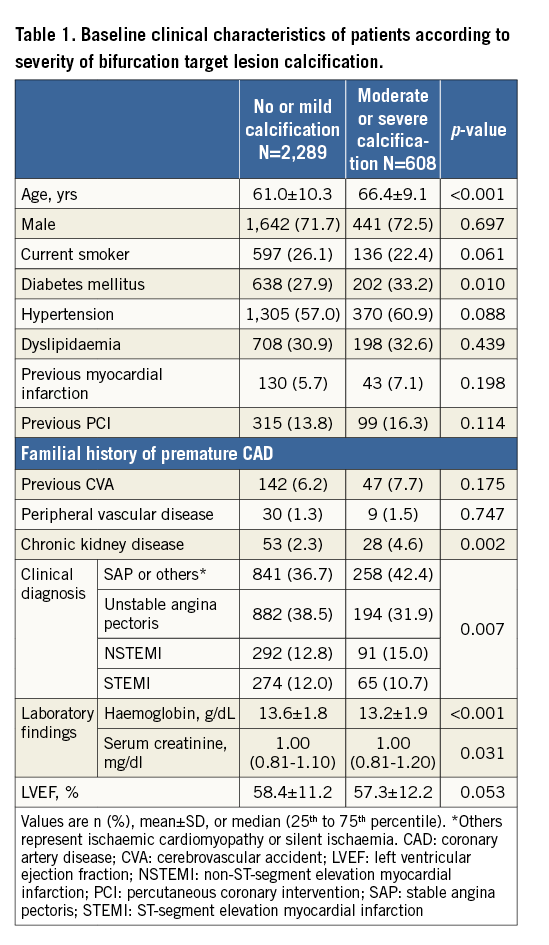
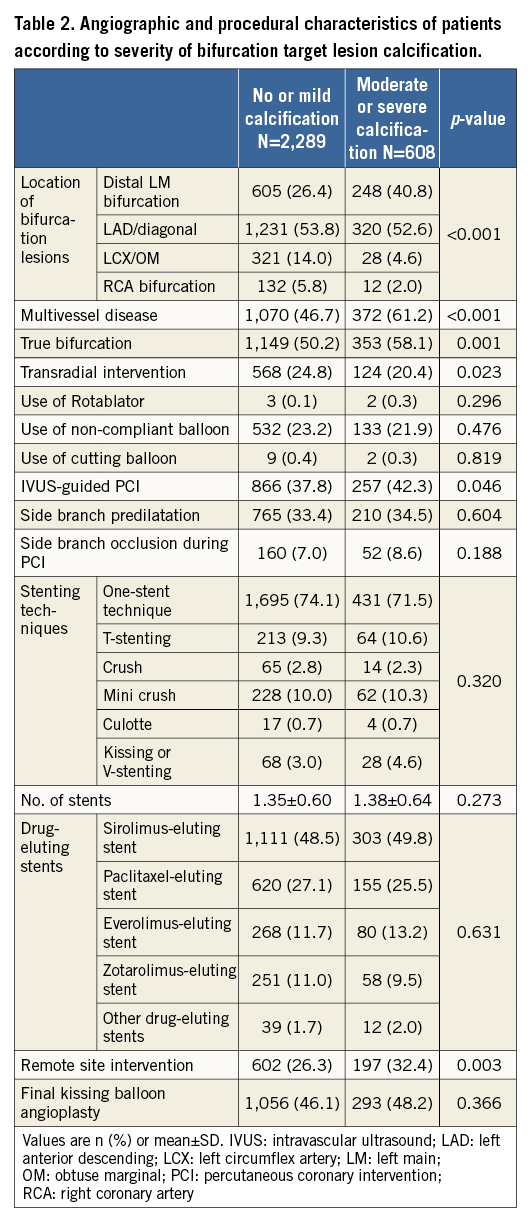
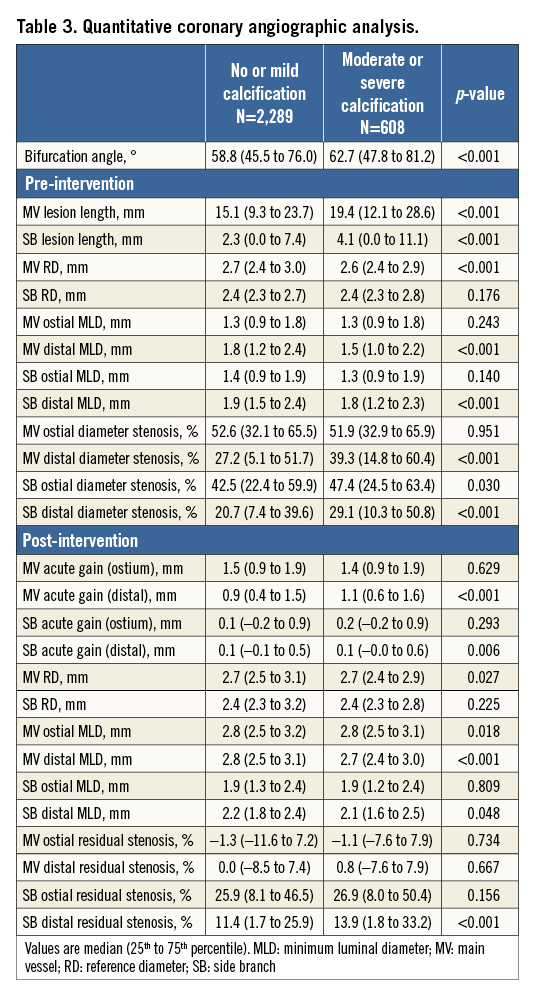
The baseline clinical, angiographic, and procedural characteristics of the study participants are summarised in Table 1 and Table 2. Patients with moderate or severe calcification were older (61.0±10.3 vs. 66.4±9.1 years, p<0.001). Past medical history was comparable in the two groups, except for higher rates of diabetes mellitus (27.9% vs. 33.2%, p=0.010) and chronic kidney disease (2.3% vs. 4.6%, p=0.002) in patients with moderate or severe calcification. Stable angina pectoris was the most common initial diagnosis in the moderate or severe calcification group (42.4%), whereas unstable angina pectoris was the most common diagnosis in the no or mild calcification group (38.5%). The moderate or severe calcification group had more distal left main bifurcation lesions (26.4% vs. 40.8%), and more true bifurcation lesions and multivessel disease. The two-stent technique and final kissing balloon angioplasty were performed at similar frequencies in both groups; however, the moderate or severe calcification group had an increased rate of intravascular-guided PCI compared with the no or mild calcification group. Table 3 shows quantitative coronary angiographic data. The bifurcation angle was larger, and lesion length in the main vessel or side branch was greater, in the moderate or severe calcification group.
During the three-year follow-up period, the primary endpoint occurred in 218 (9.5%) patients in the no or mild calcification group and in 78 (12.8%) patients in the moderate or severe calcification group (Table 4). The presence of moderate or severe calcification in bifurcation target lesions increased the three-year risks of TLF (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 1.31, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.03-1.68, p=0.031), TLR (adjusted HR 1.36, 95% CI: 1.04-1.79, p=0.027), TVR (adjusted HR 1.58, 95% CI: 1.20-2.07, p=0.001), and repeat PCI (adjusted HR 1.39, 95% CI: 1.09-1.78, p=0.009). However, it was not associated with the occurrence of cardiac death, non-fatal MI, or definite or probable stent thrombosis. Kaplan-Meier estimates for TLF, cardiac death or MI, TLR, and repeat PCI are shown in Figure 1. Other independent predictors of TLF were (data not shown): use of the two-stent technique (HR 1.70, 95% CI: 1.28-2.26, p<0.001), history of cerebrovascular accident (HR 1.57, 95% CI: 1.07-2.31, p=0.021), and chronic kidney disease (HR 1.93, 95% CI: 1.16-3.21, p=0.012). However, the use of a non-compliant balloon after stenting was a protective factor for TLF occurrence (HR 0.65, 95% CI: 0.48-0.87, p=0.005). We also investigated the clinical correlates of moderate or severe bifurcation calcifications using logistic regression. Male gender (odds ratio [OR] 1.33, 95% CI: 1.07-1.66, p=0.010), old age (OR 2.37, 95% CI: 1.96-2.87, p<0.001), non-acute coronary syndrome (OR 1.31, 95% CI: 1.09-1.58, p=0.005) and history of chronic kidney disease (OR 1.73, 95% CI: 1.06-2.81, p=0.028) were correlates of moderate or severe bifurcation calcification. Variables associated with other endpoints were as follows (data not shown). Left main target lesion and chronic kidney disease were predictors of increased cardiac death or MI. TLR was associated with the two-stent technique, diabetes mellitus and a history of cerebrovascular accident, and repeat PCI were related to left main target lesion, the two-stent technique, diabetes mellitus and multivessel disease.
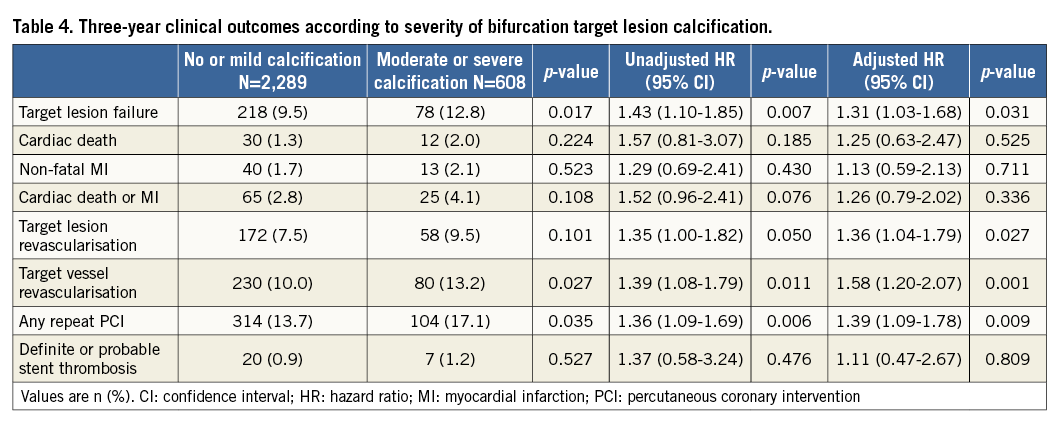
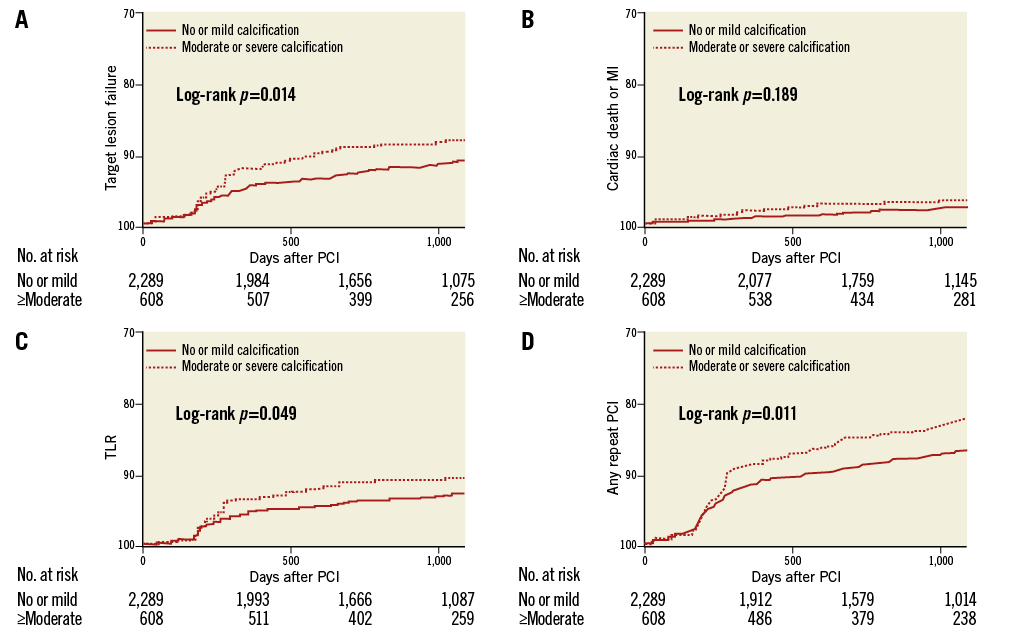
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier estimates for TLF, cardiac death or MI, TLR and any repeat PCI. The rate of target lesion failure (A), cardiac death or MI (B), TLR (C), and any repeat PCI (D) between no or mild calcification and moderate or severe calcification. MI: myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; TLF: target lesion failure; TLR: target lesion revascularisation
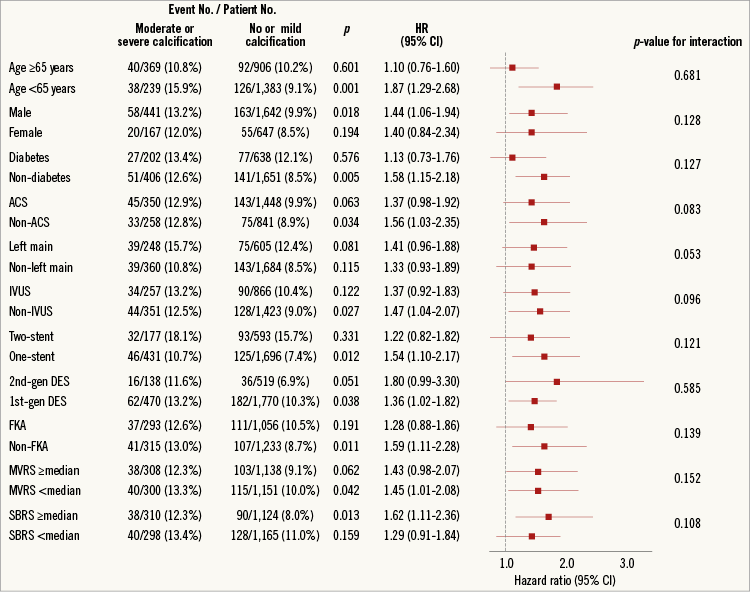
To determine whether the outcomes according to calcification grade observed in the entire study population were consistent, we performed subgroup analyses for TLF in various subgroups (Figure 2). Results showed that moderate or severe calcification was associated more with increased TLF in the non-elderly (age <65 years), males, those without diabetes, those without acute coronary syndrome, those who did not receive intravascular ultrasound-guided PCI, those who received the one-stent technique, those treated with first-generation DES, those who did not receive final kissing balloon angioplasty, those with main vessel ostium residual stenosis (%) Figure 2. Estimated hazard ratios of TLF for various subgroups. ACS: acute coronary syndrome; DES: drug-eluting stent; FKA: final kissing balloon angioplasty; IVUS: intravascular ultrasound; MVRS: main vessel ostium residual stenosis; SBRS: side branch ostium residual stenosis Discussion The current study results show that moderate or severe calcification in coronary bifurcation target lesions was associated with an increased three-year risk of TLF after PCI with DES compared with no or mild calcification. This effect was driven mainly by an increased incidence of TLR, TVR, and repeat PCI. To our knowledge, the current study is the first to investigate the impact of calcified bifurcation target lesions on clinical outcome after PCI with DES. Coronary artery calcification is an advanced stage in the atherosclerotic process whereby a soft plaque is converted to a fibrocalcified plaque, causing higher rates of procedural failure and stent underexpansion, smaller post-procedural minimal lumen diameters, less acute gain, and increased chance of in-stent restenosis9. Although the restenosis rate has been reduced markedly by the use of the most recent DES, calcified lesions continue to pose challenges for interventional cardiologists. Coronary bifurcation lesions also pose a major problem in terms of optimal PCI results. In addition to higher periprocedural complication and restenosis rates, side branch occlusion can occur during bifurcation interventions and increase the incidence of major adverse cardiac events5. Therefore, we evaluated the impact in these two high-risk lesion subsets using a large-scale multicentre registry, specifically data on PCI using DES. We found that the TLF rate was higher in the moderate or severe calcification group in terms of a higher repeat PCI rate, including TLR and TVR. Although the incidence of TLR in the current study (7.5% in the no or mild group and 9.5% in the moderate or severe group) was similar to that in previous studies which mainly enrolled patients who received PCI using first-generation DES, our results are promising, considering the use of the bifurcation PCI registry and the long-term follow-up period in our study10,11. In a recent study investigating the clinical impact of calcified lesions in patients with acute coronary syndrome, moderate or severe coronary calcification increased the risk of TLR, as well as that of cardiac death and stent thrombosis7. Another recent study by Lee et al showed that moderate or severe coronary artery calcification was associated with increased major adverse cardiac events including death compared to no or mild calcification; their results are different from our current study12. The incidence of cardiac death or non-fatal MI and definite/probable stent thrombosis was comparable in our study despite the prevalent use of first-generation DES, regardless of calcification grade. Another large-scale study which included seven stent trials also showed that patients with severe coronary target lesion calcification had worse clinical outcomes compared to those without severe coronary calcification13. Coronary bifurcation lesions themselves were not associated with increased rates of cardiac death, stent thrombosis, or TVR in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction1. Despite the use of specific devices such as orbital or rotational atherectomy devices and dedicated bifurcation stents, calcified bifurcation lesions are still obstacles for interventional cardiologists. Although some studies showed promising results of new devices for the treatment of calcified bifurcation lesions14,15, medical therapies such as statins, calcium channel blockers, and vitamins for reducing coronary artery calcium progression have shown inconsistent results16. Therefore, further large-scale randomised trials are needed to confirm the efficacy of new devices or medical therapies for calcified bifurcation lesions. Study limitations The limitations of our study include the physicians’ selection of stent type. Although all patients in our registry underwent PCI using DES, many were treated with first-generation DES, which are inferior to second-generation DES. In addition, target lesion calcification is classified dichotomously (none or mild vs. moderate or severe) in the COBIS II registry. The COBIS II registry is not a coronary calcification registry, but a bifurcation registry. Therefore, information on coronary calcification was not classified in detail. The low number of single endpoint events (per sample size) such as cardiac death and non-fatal MI might also make the findings on hard endpoints underpowered. Another limitation is the risk of selection and confounding bias due to the study design. Patients with complex lesions and those who experienced periprocedural complications may have been excluded from the study. The pattern of TLF occurrence in the Kaplan-Meier curve is also problematic. Although the one-year landmark analysis by crude analysis showed a higher incidence of TLF in the moderate-severe calcification group (130 [5.7%] vs. 50 [8.2%], p=0.021), Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a similar TLF rate at one year between the no-mild and moderate-severe calcification groups (log-rank p=0.132). These results might be related to TLR outcome and therefore a further randomised trial is needed. Finally, the retrospective design, and post hoc nature of our study resulted in differences in baseline clinical and angiographic findings between the groups. Given the limitations exposed above, the present analysis has to be considered hypothesis-generating. Conclusions Moderate or severe calcification of coronary bifurcation lesions was not uncommon (20.9%) in a large-scale real-world multicentre registry. It was associated with an unfavourable long-term clinical outcome, driven mainly by an increased frequency of repeat PCI procedures. Furthermore, a complex stenting procedure increased the risk of stent failure in these high-risk lesions. Impact on daily practice The present study showed that moderate or severe calcification in coronary bifurcation lesions is not uncommon in a real-world setting. Moreover, it increases the risk of stent failure in terms of an increased incidence of TLR, TVR, and repeat PCI procedures after PCI with DES compared with lesions with no or mild calcification. These findings suggest the need for improved PCI technology and devices. Acknowledgements This work was supported by a Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI12C0498, HI13C1527) and a National Research Foundation grant funded by the Korean Government (MEST), Republic of Korea (2015M3A9B4051063, 2015M3A9B4066496, 2015M3A9 C6031684). Conflict of interest statement The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.