
Abstract
Aims: We aimed to assess the effect of 10 mg/day of rosuvastatin plus eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) versus 2.5 mg/day of rosuvastatin on the extent of neoatherosclerosis using optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Methods and results: We randomly assigned 50 patients with non-obstructive neoatherosclerotic plaques detected on OCT to receive either rosuvastatin 10 mg/day and EPA 1,800 mg/day (intensive therapy group) or rosuvastatin 2.5 mg (standard therapy group). Follow-up OCT was performed one year later to evaluate serial changes in neoatherosclerosis. The serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level decreased significantly from baseline to 12-month follow-up in the intensive therapy group (89 mg/dL to 70 mg/dL; p<0.001), while no change occurred in the standard therapy group. Lipid index change and percent changes in macrophage grade were significantly lower in the intensive therapy group than in the standard therapy group (-53.6 vs 310.1, p=0.001; -37.0% vs 35.3%, p<0.001; respectively). Percent changes in lipid index and macrophage grade were positively correlated with the changes in serum LDL-C and C-reactive protein levels, and negatively correlated with the change in serum EPA/arachidonic acid and 18-hydroxyeicosapentaenoic acid (EPA bioactive metabolite) level.
Conclusions: Compared with rosuvastatin 2.5 mg/day, rosuvastatin 10 mg/day and EPA 1,800 mg/day significantly stabilised non-obstructive neoatherosclerotic plaques. Clinical Trial Registration: UMIN ID: UMIN000012576. https://upload.umin.ac.jp/cgi-open-bin/ctr_e/ctr_view.cgi?recptno=R000014711
Introduction
Recent evidence suggests the potential contribution of atheromatous changes within the neointima, namely neoatherosclerosis, to late stent thrombosis and delayed restenosis occurring after stent implantation1. The association between neoatherosclerosis and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level remains controversial. However, a retrospective observational optical coherence tomography (OCT) study which we conducted implied that patients with neoatherosclerosis identified by OCT are at high risk for late-phase clinical events, and that high LDL-C and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels may be independent determinants of neoatherosclerosis progression2.
Although previous human observational studies have implied a potential benefit of statin and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) therapy to late-phase (>1 year) stent failure prevention after coronary stent deployment3, there has been no prospective study investigating the efficacy of statin and EPA therapy on in-stent neoatherosclerosis. Accordingly, we designed the LINK-IT Trial (LesIonal evaluatioN of high-risK patIents with neoatherosclerosis Treated with rosuva-statin and eicosapentaenoic acid), a prospective, randomised OCT study to assess the effect of 10 mg/day of rosuvastatin plus EPA versus 2.5 mg/day of rosuvastatin on the extent of neoatherosclerosis.
Methods
STUDY DESIGN AND PATIENT POPULATION
The LINK-IT Trial is a prospective, randomised, open-label parallel group, single-centre study using OCT to compare in-stent neoatherosclerosis lipid index changes associated with combined treatment with moderate dose rosuvastatin (10 mg/day: the highest dose approved for ordinary use by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan) and EPA versus standard dose (2.5 mg/day) rosuvastatin for 12 months. In the present study, we enrolled patients who were detected as having neoatherosclerosis by OCT among patients who registered for the Kobe University Hospital OCT registry (Supplementary Appendix 1). The study was approved by our institutional review board and all patients gave written informed consent before enrolment.
RANDOMISATION AND INTERVENTION
Within the 24 hours following the baseline OCT examination, patients were randomly assigned to either 10 mg/day of rosuva-statin with 1,800 mg of EPA or 2.5 mg/day of rosuvastatin monotherapy. Randomisation was stratified by a web response system. The investigators who analysed the OCT findings were masked to the allocation.
PROCEDURES
We evaluated serum lipid levels and inflammatory markers and performed OCT examinations at baseline and at a 12-month follow-up2. Offline OCT analysis was performed using dedicated software (LightLab Imaging Inc., Westford, MA, USA). Neoatherosclerosis was defined as lesions with lipid-laden neointima, neointima with calcification, a thin-cap fibroatheroma-like neointima, or neointimal rupture (Figure 1),2. Lipid index was calculated as previously reported4. Macrophage accumulation was defined as confluent or punctate highly backscattering focal regions in the artery wall5. We also performed macrophage grading as previously described5. Fibrous cap was identified as a signal-rich band overlying the lipid, and fibrous cap thickness was measured for each lesion6. Lipid index and macrophage grade were determined by two independent observers (K. Kuroda and Y. Nagano) in order to determine the interobserver variability. One investigator (K. Kuroda) performed a repeat analysis three months after the first to analyse the intraobserver variability. For the above measurements, detailed OCT analysis is shown in Supplementary Appendix 1.
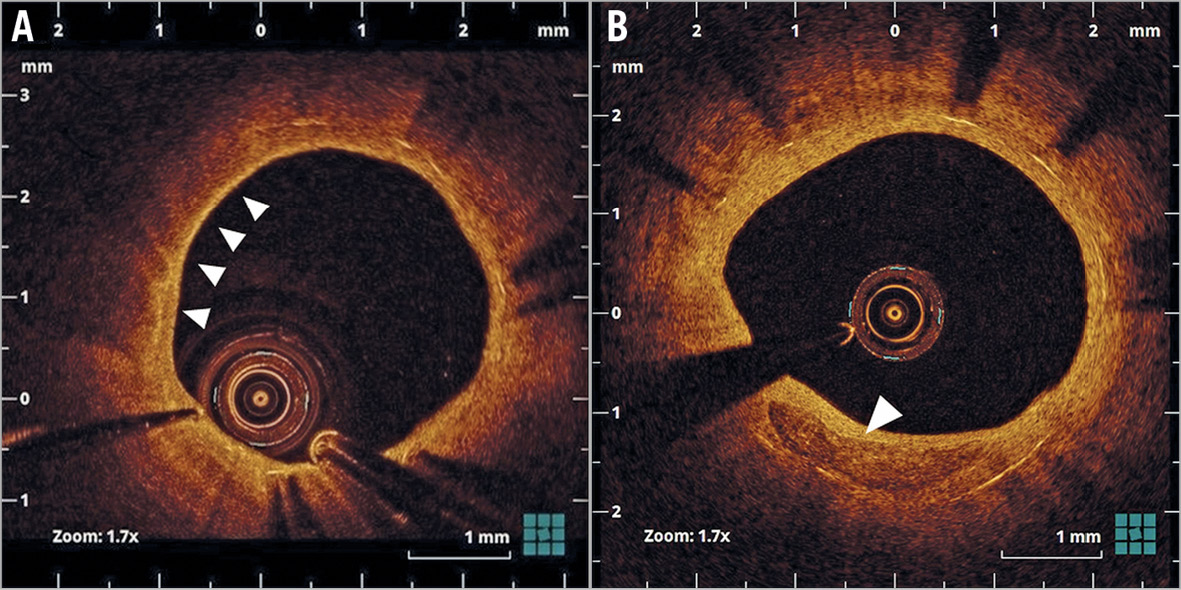
Figure 1. Representative optical coherence tomography images of neoatherosclerosis. A) Lipid-laden neointima (arrows). B) Neointima with calcification (arrow).
ENDPOINTS
The primary endpoint of the LINK-IT Trial was the change in lipid index between baseline and 12-month follow-up, as evaluated by OCT. The secondary endpoints included: 1) percent changes in lipid index and macrophage grade, and 2) percent changes in minimum fibrous cap thickness between baseline and the 12-month follow-up. Clinical events were independently evaluated by an investigator who was blinded to treatment assignments (Supplementary Appendix 1).
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS software, Version 24 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). As there are no previous reports on the effect of EPA and moderate-dose statin on the amount of neoatherosclerosis using OCT, we based our statistical analysis on the effect of EPA and moderate-dose statin on de novo atherosclerosis3. The sample size was calculated based on the assumption that the average difference in lipid index change between the groups from baseline to the 12-month follow-up was 81.5 in 30 patients. The standard deviation of lipid index growth distribution for either group was assumed to be 85.13. For a two-sided alpha level of 0.05 and a power of 80%, 17 patients were required in each group. The sample size was increased to 25 patients per group to accommodate a 15% maximum for non-parametric testing and 20% for possible missing studies or withdrawals. Qualitative data are presented with frequencies and quantitative data are shown as medians and interquartile ranges (IQR). Categorical variables were compared using the chi-square or Fisher’s exact test (for an expected cell value <5) and are presented as frequencies. Continuous variables were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test (between-group comparison) or Wilcoxon signed-rank test (if variables were compared between the baseline and 12-month follow-up) and are presented as medians and IQR. The reproducibility of lipid index and macrophage grade assessments was analysed using Bland-Altman testing. Linear mixed effects models were used to explore the influence of different variables on the percent change of lipid index and to adjust for covariates. Univariate analysis was performed first, and all variables that were statistically significant at p<0.2 were entered into the multivariate model, along with type of stent, dose of rosuvastatin, use of EPA and duration between index PCI and baseline OCT as additional covariates.
Results
TRIAL PROFILE
Among 262 registered patients between December 2013 and April 2016, neoatherosclerosis was detected in 66 patients. In cases of silent myocardial ischaemia, stable angina, or acute coronary syndrome, we included non-culprit lesions with stent implantation for this study. We excluded 16 patients - three patients in whom follow-up OCT imaging was performed <12 months after initial stent implantation, six patients whose percent diameter stenosis by coronary angiography was >50%, five patients who were previously treated with over 2.5 mg/day of rosuvastatin or another statin or EPA, and two patients who refused to consent. Finally, we included 50 patients with neoatherosclerosis detected by follow-up OCT more than one year after stent implantation and without significant angiographic stenosis (Figure 2).
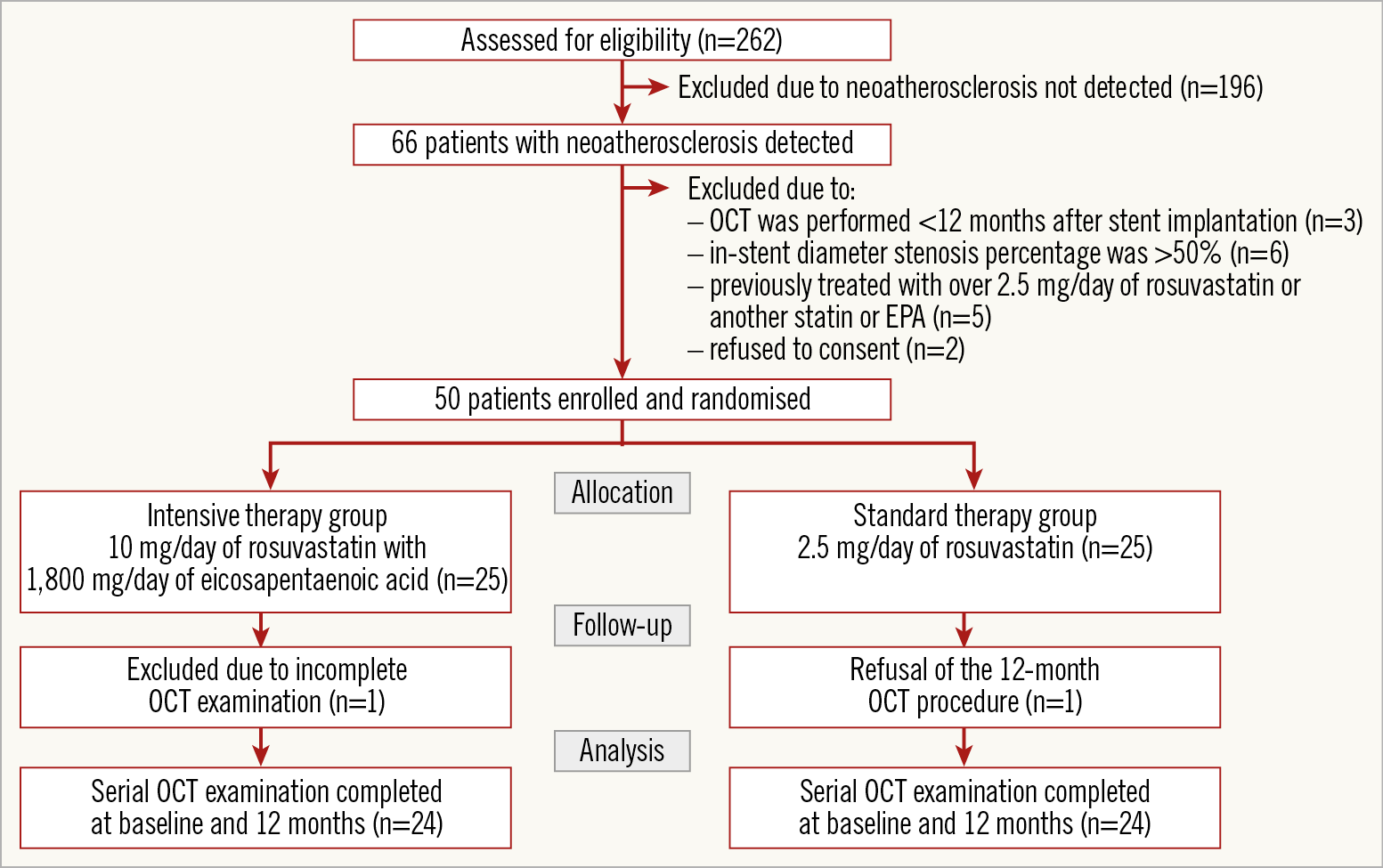
Figure 2. Study population.
PATIENT AND LESION CHARACTERISTICS
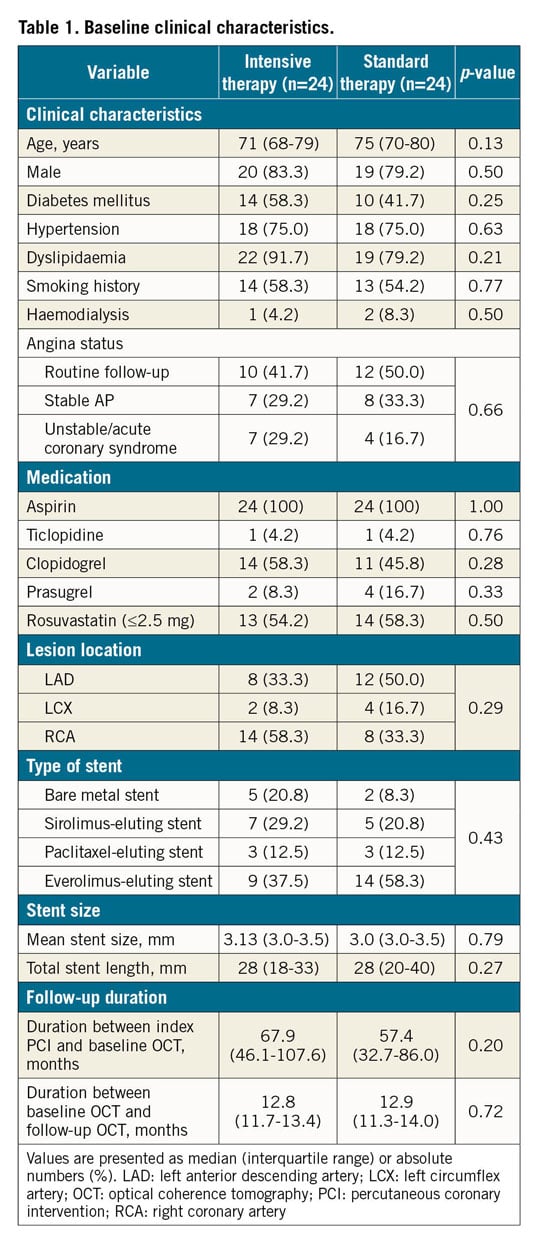
Among the 50 enrolled patients, two were excluded (incomplete OCT examination, n=1; refusal of the 12-month OCT procedure, n=1), leaving 48 patients with successful baseline and follow-up OCT examinations (24 patients in each group (Figure 2). There were no significant between-group differences in baseline patient characteristics, lesion characteristics, or concomitant medications (Table 1, Supplementary Table 1).
LABORATORY RESULTS
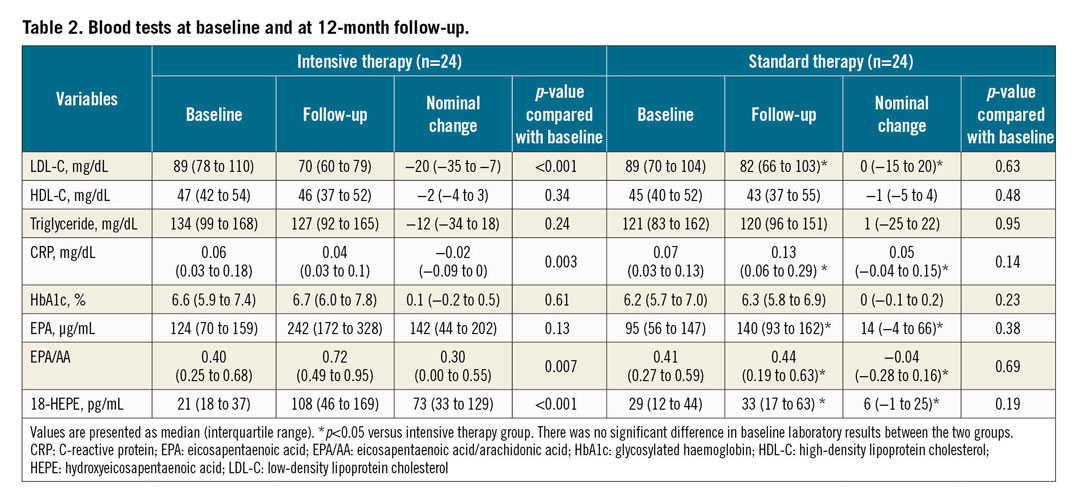
Table 2 summarises the laboratory results. There were no significant differences between the two groups in baseline laboratory data. Serum total cholesterol, LDL-C, and CRP levels decreased significantly in the intensive therapy group. No significant changes occurred in the standard therapy group. The decrease in serum LDL-C and CRP level was significantly greater in the intensive therapy group than in the standard therapy group. In the n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolites, serum EPA/arachidonic acid (EPA/AA), and 18-HEPE levels increased significantly in the intensive therapy group. Changes in EPA, EPA/AA, and 18-HEPE level were significantly greater in the intensive therapy group than in the standard therapy group.
OCT FINDINGS
Table 3 summarises the quantitative OCT findings. One patient had neointima with calcification in the standard therapy group and the other patients had lipid-laden neointima. There were no patients with plaque ruptures or thrombi. In the intensive therapy group, the lipid index did not change significantly (p=0.46) but did increase significantly in the standard therapy group (p<0.001). The lipid index change was significantly lower in the intensive therapy group than in the standard therapy group (p=0.001). The macrophage grade decreased significantly in the intensive therapy group but increased in the standard therapy group. Percent changes in the lipid index and macrophage grade were significantly lower in the intensive therapy group than in the standard therapy group (Figure 3). The fibrous cap thickness did not change significantly in the standard therapy group, while it significantly increased in the intensive therapy group. Representative OCT images are shown in Figure 4. In the intensive therapy group, the minimum lumen area and percentage of neointimal area did not change significantly. However, in the standard therapy group, the minimum lumen area was significantly reduced and the percentage of neointimal area significantly increased. There was significantly less change in the average neointimal thickness in the intensive therapy group than in the standard therapy group (Table 3).
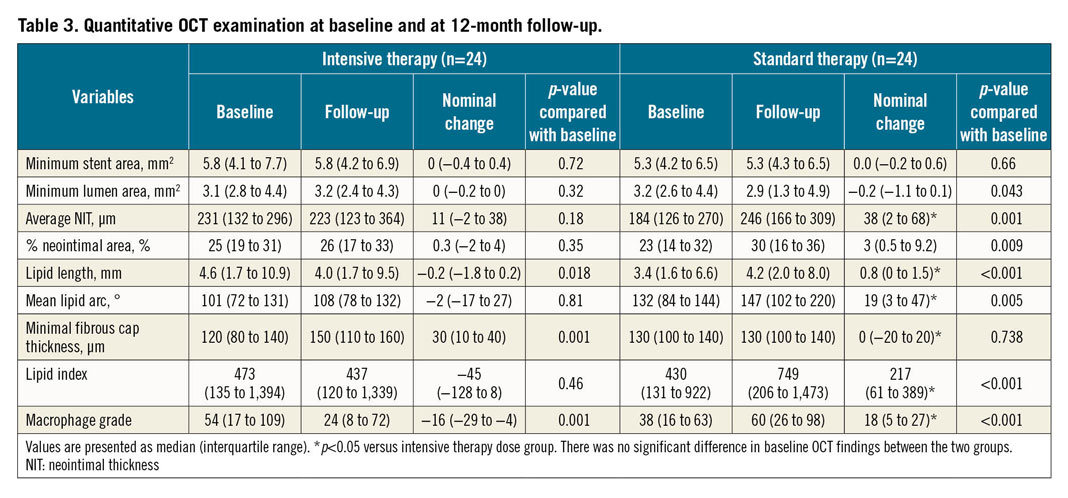
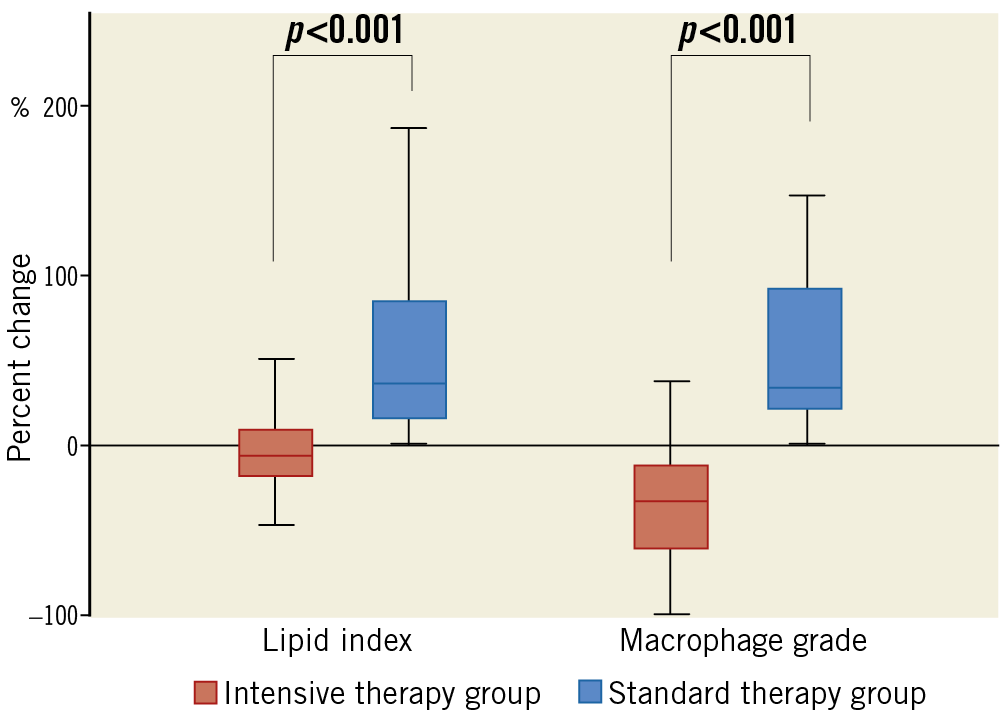
Figure 3. Percent changes in lipid index and macrophage grade.
Figure 4. Representative OCT images. In the intensive therapy group (A), the lipid arc was unchanged, and macrophage accumulation was decreased. In the standard therapy group (B), the lipid arc and macrophages increased (the white line indicates lipid, and white arrows indicate macrophages).
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN OCT FINDINGS AND LABORATORY DATA
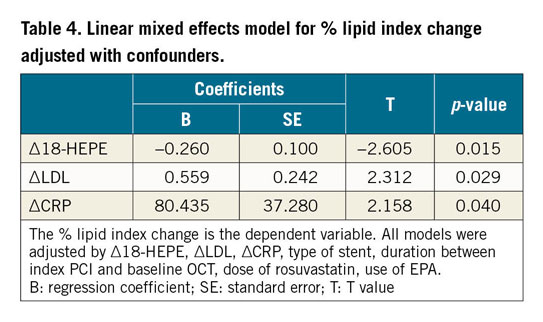
The linear mixed effects model was used to assess the independent effects of variables on the percent change of the lipid index (Table 4). In the entire patient population, multivariate analysis demonstrated that changes in LDL, CRP, and 18-HEPE levels were independently associated with a higher percent change in the lipid index.
Bland-Altman analysis revealed close agreement between the two analysts for lipid index and macrophage grade with close agreement during the measured time interval (Supplementary Figure 1).
CLINICAL OUTCOMES
Overall, eight patients required ischaemia-driven target lesion revascularisation (TLR) at the time of follow-up OCT (Supplementary Table 2). TLR incidence was significantly lower in the intensive therapy group than in the standard therapy group (4.2% vs 29.2%, p=0.024). Supplementary Table 3 summarises the comparisons of quantitative OCT findings between the patients with and without TLR. In patients with TLR, the lipid index and macrophage grade increased significantly, while no significant change was observed in patients without TLR during the follow-up. The segments requiring TLR corresponded to the neoatherosclerosis segments, and restenosis contributed to TLR in all eight cases. All patients requiring TLR had stable angina at the time of TLR; detailed OCT findings are shown in Supplementary Table 4. In all cases, neointimal thickness, lipid index, and macrophage grade increased during the 12-month follow-up, resulting in a decrease of the minimum lumen area. There were no cases with plaque rupture or thrombi.
Discussion
Neoatherosclerosis is considered a primary substrate for both late stent thrombosis and restenosis after stenting. We previously reported that patients with neoatherosclerosis identified by OCT are at high risk for late-phase clinical events, and that increased serum LDL-C and CRP levels were independent risk factors for neoatherosclerosis2. Another report indicated that, in addition to the local stent-related factors, the absence of statin use was independently associated with neoatherosclerosis in patients with a second-generation drug-eluting stent (DES)7. In CREDO-Kyoto Registry Cohort-2, the use of statins was associated with a decreased late TLR risk in patients with a sirolimus-eluting stent, while the early TLR rate was similar regardless of statin use8. However, no prospective, randomised study has investigated the effect of lipid-lowering therapy on neoatherosclerosis progression after stenting.
In our study, the minimum lumen area and percentage of neointimal area did not change significantly in the intensive therapy group. However, in the standard therapy group, the minimum lumen area was significantly reduced, and the percentage of neointimal area and average neointimal thickness increased significantly. Importantly, compared with 2.5 mg/day of rosuva-statin monotherapy, intensive therapy with 10 mg/day of rosuva-statin and 1,800 mg/day of EPA significantly suppressed in-stent lipid progression and macrophage accumulation and, compared to standard-dose statin monotherapy, significantly reduced the incidence of TLR. Although the mechanism is unknown, the use of moderate-dose rosuvastatin plus EPA significantly reduced serum LDL-C and CRP levels in comparison with standard-dose rosuvastatin monotherapy. Notably, these biomarker reductions were significantly correlated with the changes in lipid index during the follow-up period. The linear mixed effects model showed that changes in LDL, CRP and 18-HEPE levels were significantly independently associated with a higher percent change of lipid index. Therefore, we speculated that both statins and EPA played a role in the suppression of neoatherosclerosis progression. The “pleiotropic” actions of statins and the decreased LDL-C level achieved in the intensive group might be mechanisms underlying the decreased lipid index, macrophage grade, and incidence of late-phase TLR.
Another important mechanism is the anti-inflammatory function of the EPA metabolite, 18-HEPE. Recently, Endo et al demonstrated that dietary intake of EPA significantly increased the plasma concentration of 18-HEPE, an active mono-oxygenated metabolite of EPA, and that 18-HEPE acted as an anti-inflammatory and tissue-protective agent against pressure overload-induced cardiac remodelling9. The potential anti-inflammatory function of EPA has been demonstrated in a variety of inflammatory diseases, including atherosclerosis, diabetes, and arthritis10. A recent placebo-controlled study demonstrated that dietary supplementation of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids significantly decreased the circulating concentrations of inflammatory cytokines11. These data suggest that additive EPA therapy could reduce lipid accumulation in neoatherosclerosis through the anti-inflammatory effects of increased 18-HEPE concentrations.
Intensive statin treatment significantly reduces the incidence of cardiovascular events and plaque volume in patients with coronary artery disease. The ASTEROID trial demonstrated that high-intensity statin therapy using rosuvastatin 40 mg/d reduced the total atheroma volume by 6.8% over 24 months12. Although this trial used a higher statin dose than we used in our study, the dose required for optimal effect could also be affected by the patient’s race. Moderate-intensity statin therapy has been demonstrated to reduce serum LDL-C level and reverse atherosclerotic progression in Asians13. Consequently, 2.5 mg/day of rosuvastatin is the standard dose in Japan, and 10 mg/day is the highest dose approved for ordinary use by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan. Interestingly, the EASY-FIT study, which was a study of 70 Japanese patients with unstable angina pectoris and untreated dyslipidaemia, demonstrated that moderate-dose atorva-statin (20 mg/day) increased fibrous cap thickness significantly more than 5 mg/day of atorvastatin. The increase in fibrous cap thickness of de novo, native coronary plaque was correlated with the decrease in serum levels of LDL-C and high-sensitivity CRP7. Our results are consistent with those of these previous trials in that intensive statin treatment significantly increased the fibrous cap thickness of neoatherosclerosis. Our findings could potentially extend the use of moderate-dose statin therapy to high-risk patients with neoatherosclerosis. On the other hand, intensive therapy could not achieve neoatherosclerosis regression in this study. In previous serial IVUS investigations, plaque regression was achieved when LDL-C was reduced to under 70 mg/dl12. In our present study, the intensive therapy only reduced LDL levels to 70 mg/dl (median), and standard therapy reduced LDL levels to 82 mg/dl (median). These points may explain why a standard dose of rosuvastatin could not prevent the progress of neoatherosclerosis; even intensive therapy could not achieve neoatherosclerosis regression.
Limitations
Our study has several limitations. First, this was a single-centre study with a relatively small number of patients. Also, we only enrolled patients who underwent OCT imaging. Thus, a potential selection bias exists. Second, as the intensive therapy group took an increased statin dose (10 mg vs 2.5 mg daily) and EPA, our study design does not enable us to determine which medication played a central role in the suppression of the neoatherosclerosis progression which we observed. It was uncertain as to whether lipid profile modification can suppress neoatherosclerosis progression because this was the first interventional study on neoatherosclerosis, therefore we selected an increased statin dose and EPA as the maximum intensive therapy available in Japan. Currently, we hypothesise that both the increased statin dose and additive EPA therapy played important roles, as the changes in serum LDL-C, CRP, EPA/AA, and 18-HEPE levels were significantly correlated with the change in lipid index and macrophage grade. Further study is required to clarify this point. Lastly, although we showed that intensive therapy significantly reduced TLR as compared with standard therapy, the sample size was underpowered to assess clinical events.
Conclusions
In patients with non-obstructive neoatherosclerotic plaques, intensive therapy with 10 mg/day of rosuvastatin and EPA significantly suppressed the progression of neoatherosclerosis by modifying serum atherogenic lipoproteins and lipid metabolites. Our findings may provide a mechanistic insight into the efficacy of moderate-dose statin plus EPA therapy as a secondary preventative treatment in patients with coronary stents.
|
Impact on daily practice This study demonstrated that intensive lipid-lowering therapy with 10 mg/day of rosuvastatin and EPA significantly suppressed neoatherosclerosis progression by modifying serum atherogenic lipoproteins and lipid metabolites. Our findings may provide a mechanistic insight into the efficacy of moderate-dose statin plus EPA therapy as a secondary preventative treatment in patients with coronary stents. |
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

