Introduction
The importance of personalised medicine has been increasingly recognised over the last decade, with promises of optimising outcomes and minimising the risk of adverse events. This is also the case when dealing with tools to guide the selection and duration of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), including platelet function testing and genotyping. Guided DAPT has not been routinely adopted in clinical practice due to costs, logistical challenges, and conflicting evidence. While these approaches have shown promise in reducing the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, their clinical utility and cost-effectiveness remain to be established.
Pros
Dominick J. Angiolillo, MD, PhD; Mattia Galli, MD, PhD
The reason why a guided selection of oral P2Y12 inhibitors (clopidogrel, prasugrel, and ticagrelor) is to be unquestionably implemented in clinical practice is as simple as the answer to the following question: would you risk taking a drug knowing that there is, approximately, a one in three chance of it not achieving its full pharmacological effects? The answer is indeed negative, but due to the lack of early trial evidence, there has been scepticism about routinely adopting a guided selection of P2Y12 inhibitors in patients undergoing PCI12.
Clopidogrel is the most broadly utilised P2Y12 inhibitor and is subject to interindividual variability in platelet inhibition, with up to 30% of patients having high platelet reactivity (HPR), a modifiable risk factor associated with ischaemic events, including stent thrombosis (ST)1. Clinical and genetic factors are associated with clopidogrel response1. The CYP2C19 enzyme is key for clopidogrel metabolism, with carriers of the loss-of-function (LOF) alleles, responsible for its transcription, associated with reduced metabolism, increased HPR rates and stent thrombosis12. Although prasugrel and ticagrelor have more predictable platelet inhibition, resulting in reduced HPR rates and ischaemic events, they are associated with increased bleeding compared with clopidogrel1. These observations underscore the need for antiplatelet strategies with an optimal balance between safety and efficacy. To this extent, the use of platelet function assays to identify HPR patients or genetic testing to identify the carriers of CYP2C19 LOF alleles have been proposed to enable the selective administration of clopidogrel to responders and prasugrel/ticagrelor to non-responders2. The clinical implications of such a “guided” strategy consist of the reduction of bleeding that is associated with an unguided use of prasugrel or ticagrelor and, at the same time, the prevention of ischaemic events associated with clopidogrel non-responsiveness2. Data showing that prasugrel and ticagrelor do not reduce ischaemic events but increase bleeding compared with clopidogrel responders further strengthen the rationale for the use of a guided strategy3.
The recent randomised controlled trials (RCTs), TROPICAL-ACS, POPular Genetics, PATH-PCI and TAILOR-PCI, were designed to overcome the limitations of early RCTs (i.e., inadequate identification of clopidogrel non-responders, infrequent use of potent P2Y12 inhibitors, inclusion of low-risk patients)2. In brief, the first two RCTs compared a strategy of guided de-escalation (using platelet function and genetic testing, respectively) versus standard antiplatelet therapy in acute coronary syndrome (ACS) patients, and both met the primary endpoint for non-inferiority of net adverse clinical events (NACE); bleeding was also reduced in POPular Genetics2. The latter two RCTs tested a strategy of guided escalation (using platelet function and genetic testing, respectively) versus standard antiplatelet therapy. PATH-PCI found a significant 32% reduction of NACE and TAILOR-PCI a non-significant (p=0.06) 34% reduction of the primary composite ischaemic endpoint with a guided therapy2.
Therefore, recent individual RCTs support the use of a guided versus standard selection of P2Y12 inhibitors, both in an acute and stable setting. Residual concerns remain on their low statistical power for individual ischaemic and bleeding endpoints. Indeed, studies on guided de-escalation used a non-inferiority design and primary composite endpoints including both ischaemic and bleeding events. Moreover, TAILOR-PCI, the largest available trial, had insufficient statistical power due to the lower-than-expected rate of events and the use of an ambitious 85% power to show a 50% reduction of the primary endpoint. However, a recent analysis of the trial looking at cumulative events, hence with greater power, showed that a genetic-guided strategy resulted in a statistically significant reduction in cumulative ischaemic events without differences in bleeding. A comprehensive meta-analysis, which allowed the limited power of the individual trials to be overcome, showed guided de-escalation to be associated with a 19% reduction of bleeding without any trade-off in ischaemic events, and a guided escalation was associated with a 26% reduction of major adverse cardiovascular events, a 27% reduction of cardiovascular death, a 29% reduction of myocardial infarction and a 38% reduction of ST without any trade-off in bleeding events4. Moreover, a network meta-analysis exploring the comparative effects of a guided de-escalation versus standard prasugrel or ticagrelor in ACS showed a guided de-escalation to be associated with the most favourable balance between safety and efficacy (Figure 1)5.
In conclusion, the rationale, feasibility and compelling evidence of providing the optimal safety-efficacy profile indicates that a guided selection of P2Y12 inhibitors is ready for prime time.
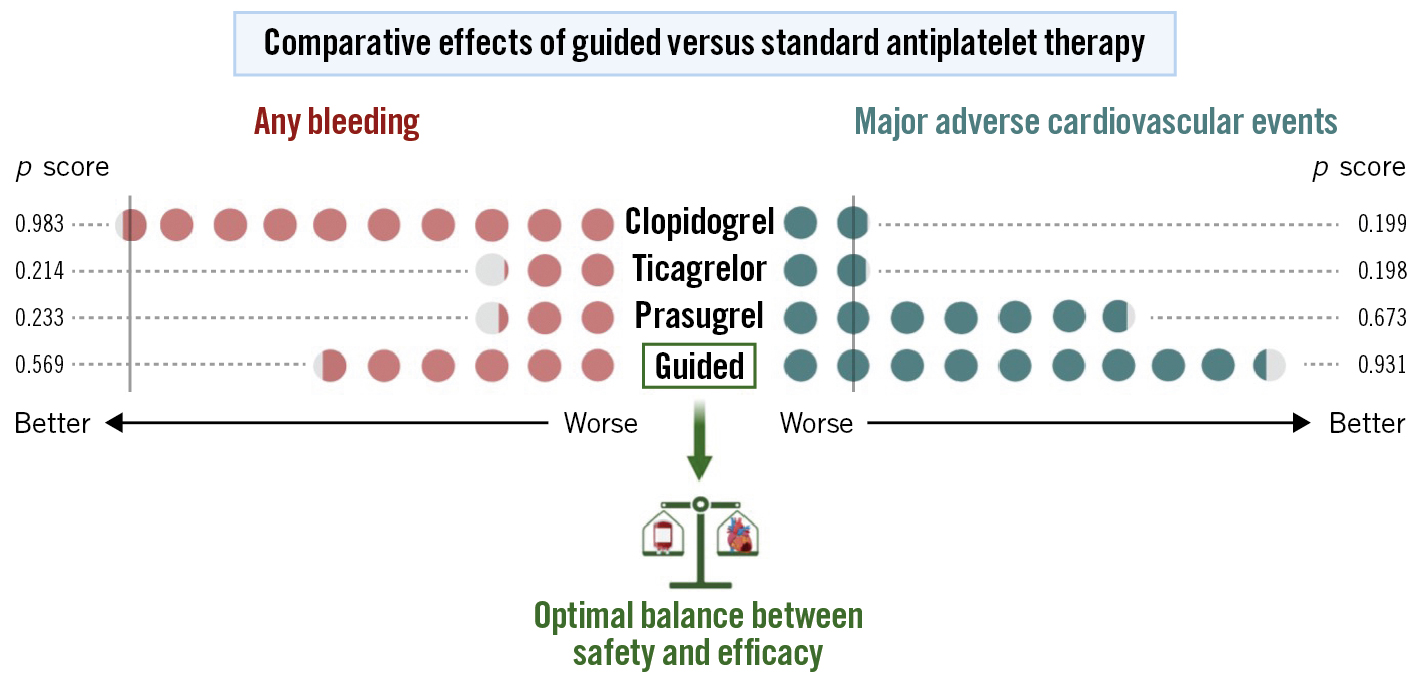
Figure 1. Comparative effects of guided versus standard antiplatelet therapy. A frequentist network meta-analysis allows for the ranking of treatments according to p scores (range 0 to 1: the higher the score, the better the treatment’s performance). Guided selection of antiplatelet therapy was shown to be the strategy with the most favourable balance between safety and efficacy compared to standard dual antiplatelet therapy with either clopidogrel, prasugrel or ticagrelor. Vertical grey line: reference strategy (clopidogrel). Modified by Galli et al5.
Conflict of interest statement
D.J. Angiolillo declares that he has received consulting fees or honoraria from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Biosensors, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chiesi, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Haemonetics, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Vectura; he also declares that his institution has received research grants from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Biosensors, CeloNova, CSL Behring, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Idorsia, Janssen, Matsutani Chemical Industry Co., Merck, Novartis, and the Scott R. MacKenzie Foundation. M. Galli declares that he has received consulting fees from Terumo.
Cons
Marco Valgimigli, MD, PhD; Antonio Landi, MD
The use of platelet function testing (PFT) or genotype-guided selection of DAPT is justified by the large interindividual response to clopidogrel, which leads to a suboptimal or even no response in a sizable proportion of patients, depending on the timing, type of assessment and patient profile. Ticagrelor and prasugrel, however, have a more predictable P2Y12 inhibitory effect, are widely available and are (or are becoming) available in generic formulations. Therefore, the use of screening tests to guide the selection of P2Y12 inhibitors appears, nowadays, to be not only supported by limited data, but also superseded. This statement is reflected in the lack of clinical implementation of this approach outside RCTs and is further supported by additional considerations.
The results of individual RCTs on guided therapy are inconclusive because of the lack of adequate statistical power to assess ischaemic endpoints. A meta-analysis of those trials provides apparent support to the concept of intensified antiplatelet therapy on the basis of PFT6. However, interpretation of this analysis is hampered by multiple limitations, including the universal use of clopidogrel in ACS patients, considerable differences in the platelet function devices, cut-offs and intervention strategies, and the role of periprocedural myocardial infarction (MI) in driving an overall MI reduction6. While clopidogrel remains the standard-of-care P2Y12 inhibitor in patients with chronic coronary syndrome (CCS), the rate of ischaemic events in these patients is low. Furthermore, among the CCS patients at high ischaemic risk, direct use of ticagrelor or prasugrel instead of clopidogrel is more practical, is supported by guidelines, and might be used as a monotherapy option after 1-month DAPT, especially in high bleeding risk patients78. In ACS subjects, the use of PFT and genotype-guided DAPT de-escalation after a short course of potent DAPT is not convincing either. Firstly, unguided de-escalation reduces bleeding risk without an apparent increase in ischaemic endpoints compared with DAPT continuation, similar to the effects of guided de-escalation in trials. Secondly, 12-month potent DAPT is no longer the standard-of-care treatment in ACS patients. A recent meta-analysis of 24,096 ACS or PCI patients (n=6 trials) demonstrated that P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy (mainly ticagrelor) after 1- to 3-month DAPT halved the risk of major bleeding, is associated with lower cardiovascular death and showed no increase in non-fatal ischaemic endpoints9. A recent network meta-analysis of 43 trials (n=189,261 participants) showed that ticagrelor monotherapy was associated with lower mortality, without a bleeding risk trade-off compared with DAPT10.
The results of these trials, along with the progressive ageing of the population and increased awareness of the importance of bleeding risk prevention after ACS or PCI, have led to new thinking wherein a combination of antithrombotics should be avoided or minimised. In this framework, DAPT should at least be de-escalated, but probably better withheld, soon after ACS or PCI. A direct comparative study between guided or unguided DAPT de-escalation versus P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy is desirable but, to the best of our knowledge, not planned. On the other hand, multiple investigations are now assessing the risks and benefits of even earlier aspirin withdrawal after ACS/PCI and continuation with potent P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy. The use of PFT or genotype-guided selection of DAPT or even a type of P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy is not the future, rather the past. It is cumbersome, expensive, requires expertise and has never been entirely supported by data. This lack of evidence might not reflect lack of benefit but rather lack of properly powered and adequately controlled studies. One thing is for sure, the cardiology community will not embrace a more complicated treatment paradigm until compelling evidence exists.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Valgimigli reports grants and/or personal fees from AstraZeneca, Terumo, Alvimedica/CID, Abbott Vascular, Daiichi Sankyo, Bayer, CoreFLOW, Idorsia Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Universität Basel Department Klinische Forschung, Vifor, Bristol-Myers Squibb SA, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Vesalio, Novartis, Chiesi, and PhaseBio, outside the submitted work. The other author has no conflicts of interest to declare.

