The current report provides a six-year overview of trends for coronary interventions from the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI) registries1. From 2010 to 2015, significant changes in coronary interventions occurred after compelling clinical evidence for practice change became available and subsequent guideline recommendations were published2. The radial artery has become the preferred vascular access, being chosen in two thirds of the procedures (Table 1). The average number of PCI per operator has slightly increased, though complex procedures such as PCI of the left main, chronic total occlusions and with rotational atherectomy have remained unchanged.
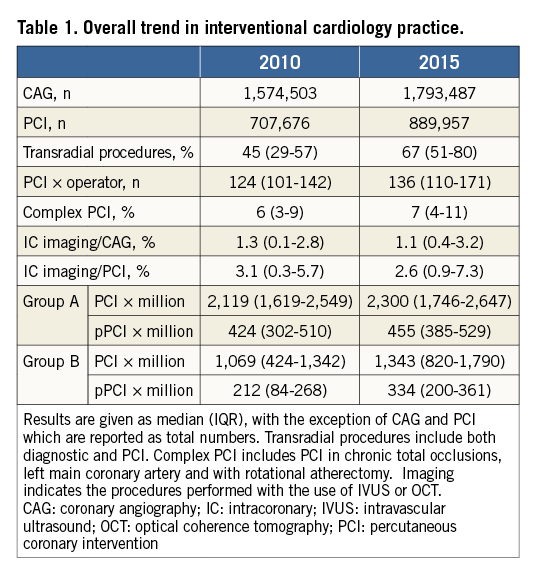
Trends in total PCI and primary PCI (pPCI) numbers followed two main patterns: a stable, slow growing pattern in Group A and a pattern of rapid growth in coronary interventions in Group B. This difference in PCI growth was most likely linked to the median number of PCI at the beginning of the observation period: in countries of Group A twice as many PCI and pPCI per million inhabitants were reported in 2010 as compared with countries of Group B (Table 1). Yet, over the subsequent six years, countries of Group B had an exponential growth especially in pPCI (Figure 1). Overall, the monitored countries have reached or come closer to the 600 pPCI per million inhabitants recommended by the Stent for Life initiative3.
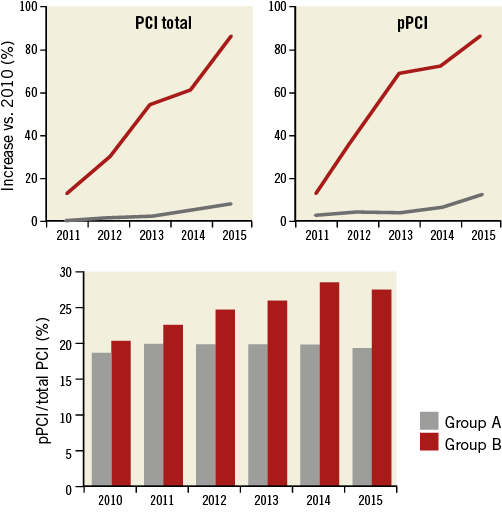
Figure 1. Trends in PCI and primary PCI (pPCI) from 2010 to 2015. Upper panels: PCI total and pPCI are expressed as increase versus 2010 per million inhabitants. Lower panel: ratio of pPCI to total PCI. Countries of Group A: Belgium, Denmark, France, Israel, Italy, Poland, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, UK. Countries of Group B: Egypt, Kazakhstan, Macedonia, Portugal, Serbia.
Strong evidence in favour of the use of drug-eluting stents (DES) has become available both in elective and in acute coronary syndrome patients1. This was associated with a high DES penetration rate (above 70% in most of the countries) with a growth ranging between 20% and 50% (Figure 2). However, reimbursement issues still represented the main obstacle in some countries.
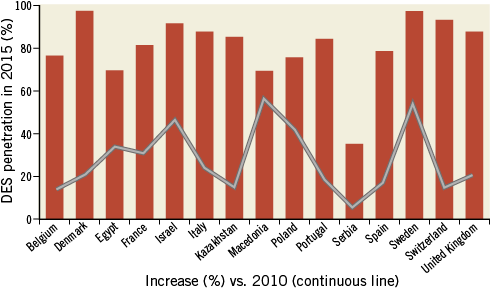
Figure 2. Penetration of drug-eluting stents (DES) in 2015 (bars), and rate of DES adoption (continuous line) from 2010 to 2015 in the 15 countries providing data on DES implantation. DES data unavailable for Turkey.
Finally, despite the lack of reimbursement in many countries, the use of intracoronary physiology techniques doubled from 2010 to 2015, though it still remained lower than 6% and 20% of the total volume of coronary angiography and of PCI, respectively (Figure 3). Given the less strong evidence, a stable and rather low trend in the adoption of intracoronary imaging techniques was observed during the period analysed (Table 1).
Figure 3. Rate of invasive physiologic assessment (IC physiology) overall (black line) and in the individual participating countries (coloured lines). Upper panel: IC physiology corrected by total number of coronary angiographies. Lower panel: IC physiology corrected by total number of PCI (after excluding pPCI).
Despite inherent limitations linked to the heterogeneous data collection, this six-year overview of the EAPCI registries demonstrates a good overall adoption of novel therapies and implementation of guideline recommendations. Budget constraints and limited reimbursement policies still represent the main reasons for the scattered rate of adoption and implementation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

