
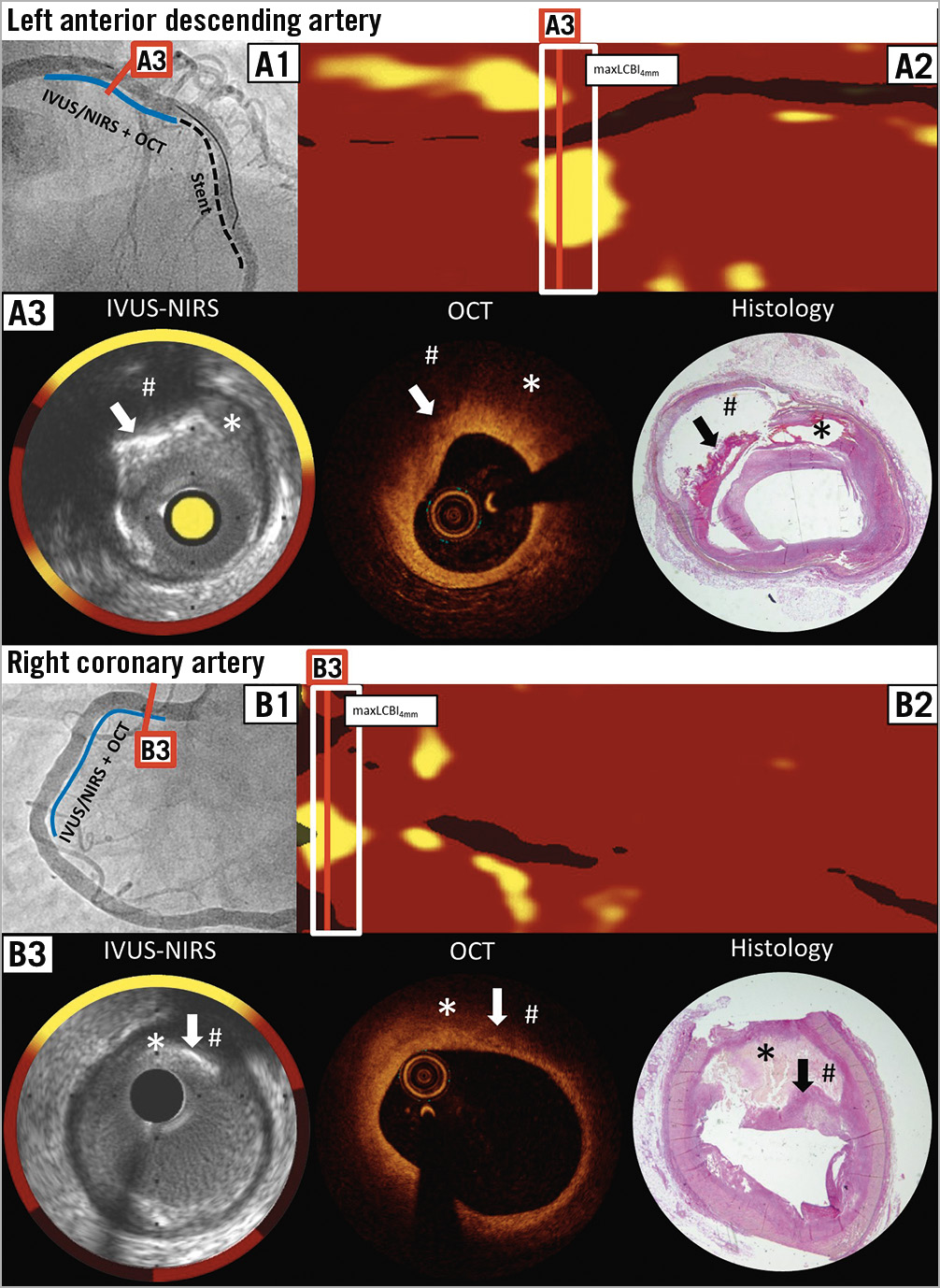
Figure 1. Matched near-infrared spectroscopy and optical coherence tomography cross-sections with post-mortem histopathology specimens. A1) & B1) Angiography of the LAD and RCA, respectively. A2) & B2) NIRS chemogram of the LAD and RCA, respectively. The red line indicates where lipid accumulation was maximal according to the NIRS-derived chemogram within the maxLCBI4mm segment and where matching with OCT and post-mortem histology was performed. A3) & B3) Matched IVUS-NIRS, OCT and post-mortem histology cross-sections. The asterisk marks the lipid pool. The arrow points to the calcium to confirm appropriate matching. Histopathology specimen confirmed NIRS-detected lipid behind the calcium, which could not be detected by OCT (hashtag). B3) Histopathology cross-section. The calcific tissue is not clearly demarcated by histology and can only vaguely be discerned (arrow). The fibrous cap is ruptured during the fixation process, suggesting a much bigger plaque burden than in IVUS and OCT, and the lumen contour remains elusive.
A 67-year-old female presented with an acute anterior ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) of the mid-left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery. Following successful implantation of two drug-eluting stents with Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) grade 3 flow, multimodality imaging using near-infrared spectroscopy with intravascular ultrasound (NIRS-IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT) was performed in the LAD and right coronary artery (RCA) in the setting of an imaging study (Figure 1A1, Figure 1B1).
The NIRS chemogram of the LAD and RCA showed two lipid-rich plaques (LRPs). The 4 mm segment with the maximum amount of lipid (maxLCBI4mm) was 488 in the LAD and 309 in the RCA (Figure 1A2, Figure 1B2). Matched OCT and IVUS of the NIRS-detected LRPs of the LAD and RCA showed a fibroatheroma with a fibrous cap thickness of approximately 300 μm and a plaque burden of 76% in the LAD, and a fibroatheroma with a fibrous cap thickness of approximately 350 μm and a plaque burden of 40% in the RCA (Figure 1A3, Figure 1B3). Of note, the calcification challenges the lipid detection by OCT and should not be misinterpreted as lipid (arrow).
The further course was uneventful until day 5 when the patient suffered from pulseless electrical activity. Immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation was unsuccessful; an autopsy was performed confirming a ventricular myocardial rupture with cardiac tamponade as the immediate cause of death. The previously imaged vessels were further examined by histology (Verhoeff-van Gieson stain). Matched post-mortem histology cross-sections showed two LRPs, confirming the previous assessment by in vivo intracoronary imaging (Figure 1A3, Figure 1B3).
This cardiovascular flashlight uniquely confirms the good concordance between NIRS, OCT and post-mortem histopathology for lipid detection but also illustrates challenges in the differentiation between lipid and calcium.
Conflict of interest statement
L. Räber has received research grants by Abbott and Infraredx and speaker fees by Abbott. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

