Abstract
Background: Anatomical vessel location affects post-percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) physiology.
Aims: We aimed to compare the post-PCI instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR) in left anterior descending (LAD) versus non-LAD vessels and to identify the factors associated with a suboptimal post-PCI iFR.
Methods: DEFINE PCI was a multicentre, prospective, observational study in which a blinded post-PCI iFR pullback was used to assess residual ischaemia following angiographically successful PCI.
Results: Pre- and post-PCI iFR recordings of 311 LAD and 195 non-LAD vessels were compared. Though pre-PCI iFR in the LAD vessels (median 0.82 [0.63, 0.86]) were higher compared with those in non-LAD vessels (median 0.72 [0.49, 0.84]; p<0.0001), post-PCI iFR were lower in the LAD vessels (median 0.92 [0.88, 0.94] vs 0.98 [0.95, 1.00]; p<0.0001). The prevalence of a suboptimal post-PCI iFR of <0.95 was higher in the LAD vessels (77.8% vs 22.6%; p<0.0001). While the overall frequency of residual physiological diffuse disease (31.4% vs 38.6%; p=0.26) and residual focal disease in the non-stented segment (49.6% vs 50.0%; p=0.99) were similar in both groups, residual focal disease within the stented segment was more common in LAD versus non-LAD vessels (53.7% vs 27.3%; p=0.0009). Improvement in iFR from pre- to post-PCI was associated with angina relief regardless of vessel location.
Conclusions: After angiographically successful PCI, post-PCI iFR is lower in the LAD compared with non-LAD vessels, resulting in a higher prevalence of suboptimal post-PCI iFR in LAD vessels. This difference is, in part, due to a greater frequency of a residual focal pressure gradient within the stented segment which may be amenable to more aggressive PCI.
Introduction
The instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR) has been validated as a useful diagnostic tool to assess the haemodynamic significance of a coronary artery lesion without pharmacological induction of hyperaemia12, allowing a rapid assessment of lesion severity with clinical outcomes comparable to those of fractional flow reserve (FFR)123. Although the use of coronary physiology for lesion assessment prior to percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has been widely adopted and endorsed by clinical guidelines4, it is not presently recommended for post-PCI assessment of the adequacy of revascularisation. Prior studies have shown that despite an angiographically successful procedure, many vessels continue to demonstrate suboptimal physiological results, with ~20% of FFR values in the ischaemic range56. Additionally, a suboptimal physiological post-PCI result has been associated with an increased risk of major adverse cardiovascular events567. Lesions located in the left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery have been identified as a major predictor of a suboptimal post-PCI FFR result789.
In the Physiologic Assessment of Coronary Stenosis Following PCI study (DEFINE PCI), 24.0% of 467 patients demonstrated residual ischaemia (iFR ≤0.89) after angiographically successful PCI, and in 81.6% this was attributable to focal lesions10. At 1-year follow-up, a post-PCI iFR ≥0.95 was associated with a significant reduction in cardiac death, spontaneous myocardial infarction (MI), or clinically driven target vessel revascularisation (TVR) compared with a post-PCI iFR <0.9511. Herein, we aim to evaluate post-PCI iFR in LAD versus non-LAD vessels, comparing the prevalence and predictors of post-PCI iFR, patterns of residual disease (focal vs diffuse), as well as angina and clinical outcomes at 1 year.
Methods
PATIENT POPULATION
The study design and protocol of DEFINE PCI have been published previously10. In brief, DEFINE PCI was a prospective, single-arm, blinded, multicentre study designed to assess the incidence and mechanisms of an abnormal iFR after angiographically successful PCI. A total of 28 sites from the USA and Europe participated in the study. The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board or ethics committee at each participating site. The original study was supported by funding from Philips/Volcano; the current analysis was conducted independently by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation, New York, NY, USA.
STUDY PROCEDURES
A distal spot iFR assessment (Verrata and Verrata Plus guide wire [Philips/Volcano]) was performed in all vessels in which a lesion of at least 40% angiographic severity was identified and deemed suitable for PCI. The wire was positioned in the distal third of the vessel, at least 10 mm distal to the most distal stenosis (pre-PCI) or treated segment (post-PCI) with angiographic documentation. Patients with a pre-PCI iFR of ≤0.89 in at least 1 vessel were formally enrolled. An iFR pullback with interrogation of individual lesions was not allowed before PCI. PCI was performed according to the standard of care based on angiographic guidance. Intravascular imaging was allowed and used per operator discretion. Once PCI was successfully completed, a blinded post-PCI iFR measurement was taken in the distal vessel, and an iFR pullback was performed along the length of the vessel until the pressure sensor reached the tip of the guiding catheter at the coronary ostium under resting conditions to determine residual transstenotic pressure gradients. Bookmarks were inserted 5 mm distal and proximal to the implanted stent as well as at the coronary ostium for core laboratory analysis. A final drift check was performed and recorded with the pressure wire located in the coronary ostium.
CORE LABORATORY ANALYSIS
All pressure tracings and angiograms were sent to the physiology and angiographic core laboratories at the Cardiovascular Research Foundation (New York, NY, USA) for centralised independent review. All physiology tracings were reviewed on a Volcano s5 imaging system (Philips/Volcano), and all angiograms were analysed on QAngio XA 7.3.92.0 (Medis Medical Imaging). The physiology core laboratory assessed each individual tracing for quality based on prespecified criteria that included evaluation of the aortic and coronary pressure signals for waveform distortion or loss, aortic pressure ventricularisation, and arrhythmias, as previously outlined12. A range of 0.98-1.02 for mean wire pressure/aortic pressure in the coronary ostium was considered acceptable.
The blinded post-PCI iFR pullback was analysed for transstenotic pressure gradients, which were categorised according to their location (distal to the stent; in-stent including 5 mm proximal and distal margins; and proximal to the stent) and classified as focal lesions or diffuse disease. Transstenotic pressure gradients of ≥0.03 were categorised as focal lesions if their length was ≤15 mm and as diffuse disease if their length exceeded 15 mm. Focal lesions and diffuse disease could be present in the same vessel.
FOLLOW-UP ASSESSMENT
The 1-year outcomes included target vessel failure (TVF), a composite of target vessel MI, clinically driven TVR, or cardiac death. Each of these clinical events were adjudicated by an independent committee whose members were blinded to the angiographic and physiology data. The Seattle Angina Questionnaire (SAQ) Angina Frequency (AF) scale was assessed at baseline and 12 months using standard questionnaires by trained personnel.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Categorical variables are presented as numbers and frequencies and were compared with the chi-square test. Continuous variables are presented as means and standard deviations or medians with first and third quartiles and were compared using the Student’s t-test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test based on the distribution. For post-iFR and follow-up SAQ-AF scores, least squares mean differences were compared between LAD versus non-LAD groups in an analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) model adjusted for baseline values. Multivariable linear regression models were used to evaluate 1) the association between the clinical and lesion-related characteristics and post-PCI iFR, and 2) the association between the change in iFR from pre- to post-PCI and change in SAQ-AF score from baseline to 1-year follow-up. Time-to-first event rates are shown as Kaplan-Meier estimates and were compared with the log-rank test. All probability values were 2-sided, and p-values<0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS
Two vessels with a target lesion in the left main coronary artery were excluded from the present substudy. Among the remaining cases, 459 patients with 506 vessels with qualified pre- and post-PCI iFR were included. iFR was compared in 311 LAD and 195 non-LAD vessels (99 right coronary artery [RCA] and 96 left circumflex [LCx]). The prevalence of a proximal lesion location was similar between LAD versus non-LAD vessels (32.2% vs 31.8%). Baseline patient and angiographic procedural characteristics stratified by LAD versus non-LAD vessels are shown in Table 1 and Supplementary Table 1. Compared with non-LAD vessels, the pre-PCI minimum lumen diameter was larger, the pre-PCI diameter stenosis was smaller, and there was greater lesion calcification in LAD vessels. Post-dilatation was performed more frequently in LAD vessels compared with non-LAD vessels.
Table 1. Angiographic and procedural characteristics per vessel.
| All vessels (N=506) |
LAD (N=311) |
Non-LAD (N=195) |
p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bifurcation lesion | 4.0 (20/505) | 4.8 (15) | 2.6 (5/194) | 0.21 |
| Calcification (moderate/severe) | 38.2 (192/503) | 43.4 (135) | 29.7 (57/192) | 0.002 |
| Lesion length, mm | 21.2 (13.8, 30.2) | 21.9 (14.7, 31.5) | 19.9 (12.5, 28.7) | 0.051 |
| Reference vessel diameter, mm | 2.76 (2.45, 3.07) | 2.73 (2.45, 3.01) | 2.84 (2.45, 3.13) | 0.09 |
| Pre-PCI minimum lumen diameter, mm | 0.86 (0.65, 1.12) | 0.96 (0.72, 1.19) | 0.74 (0.60, 0.96) | <0.0001 |
| Pre-PCI DS, % | 68.0 (59.5, 76.0) | 64.2 (57.0, 65.6) | 72.5 (65.6, 78.9) | <0.0001 |
| Post-PCI worst DS in the target vessel, % | 19.8 (12.7, 33.5) | 19.9 (13.0, 32.3) | 19.3 (12.2, 35.1) | 0.75 |
| Post-PCI worst DS ≥50% | 7.1 (36/504) | 7.4 (23/309) | 6.7 (13) | 0.74 |
| Proximal | 22.2 (8) | 21.7 (5) | 23.1 (3) | 0.99 |
| In-stent | 5.6 (2) | 4.3 (1) | 7.7 (1) | 0.99 |
| Distal | 72.2 (26) | 73.9 (17) | 69.2 (9) | 0.99 |
| Total stent length, mm | 29 (20, 38) | 30 (21, 38) | 28 (18, 38) | 0.07 |
| Maximum device size, mm | 3.0 (3.0, 3.5) | 3.0 (3.0, 3.5) | 3.0 (3.0, 3.5) | 0.89 |
| Maximum balloon pressure, atm | 18 (16, 20) | 17 (16, 20) | 18 (16, 20) | 0.25 |
| Post-dilatation performed | 59.0 (294/498) | 63.8 (194/304) | 51.5 (100/194) | 0.007 |
| Values are % (n), % (n/N), or median (first quartile, third quartile). DS: diameter stenosis; LAD: left anterior descending; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention | ||||
PRE- AND POST-PCI PHYSIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT
Pre-PCI iFR in the LAD vessels (median 0.82 [0.63, 0.86]) was higher compared with the non-LAD vessels (median 0.72 [0.49, 0.84]; p<0.0001) (Table 2, Figure 1). Despite this, post-PCI iFR was lower in the LAD (median 0.92 [0.88, 0.94]) compared with the non-LAD vessels (median 0.98 [0.95, 1.00]; p<0.0001). Accordingly, ΔiFR (post-PCI iFR − pre-PCI iFR) was lower in the LAD vessels (median 0.09 [0.06, 0.28]) vs 0.26 [0.14, 0.51]; p<0.0001) (Table 2, Figure 2). Almost half the patients undergoing LAD-PCI had a change in iFR of less than 0.10. Similarly, iFR gain ([Δ iFR/pre-PCI iFR]*100) was lower in LAD compared with non-LAD vessels (median 11.5% [6.9, 45.0] vs 35.7% [16.7, 105.1]; p<0.0001).
Despite similar residual post-PCI angiographic diameter stenosis in both groups (median 19.9% [13.0, 32.3] vs 19.3% [12.2, 35.1]; p=0.75) (Table 1), the prevalence of post-PCI iFR ≤0.89 (30.9% vs 6.7%; p<0.0001) and <0.95 (77.8% vs 22.6%; p<0.0001) were higher in LAD compared with non-LAD vessels (Central illustration).
Table 2. Physiology findings per vessel.
| All vessels (N=506) |
LAD (N=311) |
Non-LAD (N=195) |
p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-PCI iFR | 0.79 (0.55, 0.86) | 0.82 (0.63, 0.86) | 0.72 (0.49, 0.84) | <0.0001 |
| Post-PCI iFR | 0.94 (0.90, 0.97) | 0.92 (0.88, 0.94) | 0.98 (0.95, 1.00) | <0.0001 |
| LSM±SE - ANCOVA model* | - | 0.90±0.005 | 0.98±0.007 | <0.0001 |
| Post-PCI iFR <0.95 | 56.6 (286) | 77.8 (242) | 22.6 (44) | <0.0001 |
| Post-PCI iFR ≤0.89 | 21.5 (109) | 30.9 (96) | 6.7 (13) | <0.0001 |
| ∆ iFR (post-iFR–pre-iFR) | 0.15 (0.07, 0.39) | 0.09 (0.06, 0.28) | 0.26 (0.14, 0.51) | <0.0001 |
| LSM±SE - ANCOVA model | - | 0.22±0.005 | 0.29±0.007 | <0.0001 |
| Percentage ∆ iFR, % | 18.8 (8.6, 72.8) | 11.5 (6.9, 45.0) | 35.7 (16.7, 105.1) | <0.0001 |
| Post-PCI iFR pullback assessment in 286 vessels with post-PCI iFR <0.95 | ||||
| All vessels (N=286) |
LAD (N=242) |
Non-LAD (N=44) |
p-value | |
| iFR gradient from distal to aorta | 0.09 (0.07, 0.13) | 0.10 (0.07, 0.13) | 0.08 (0.06, 0.11) | 0.056 |
| Diffuse lesion | 32.5 (93) | 31.4 (76) | 38.6 (17) | 0.26 |
| Any focal lesion | 67.5 (193) | 68.6 (166) | 61.4 (27) | 0.26 |
| Any focal lesion proximal to the stent | 30.1 (86) | 28.9 (70) | 36.4 (16) | 0.37 |
| Any focal lesion in-stent | 49.7 (142) | 53.7 (130) | 27.3 (12) | 0.0009 |
| Any focal lesion distal to the stent | 29.7 (85) | 30.2 (73) | 27.3 (12) | 0.64 |
| Values are % (n) or median (first quartile, third quartile). *Least squares mean (LSM) difference tested between groups in an analysis of covariance model (ANCOVA) adjusted for baseline values. iFR: instantaneous wave-free ratio; LAD: left anterior descending; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; SE: standard error | ||||
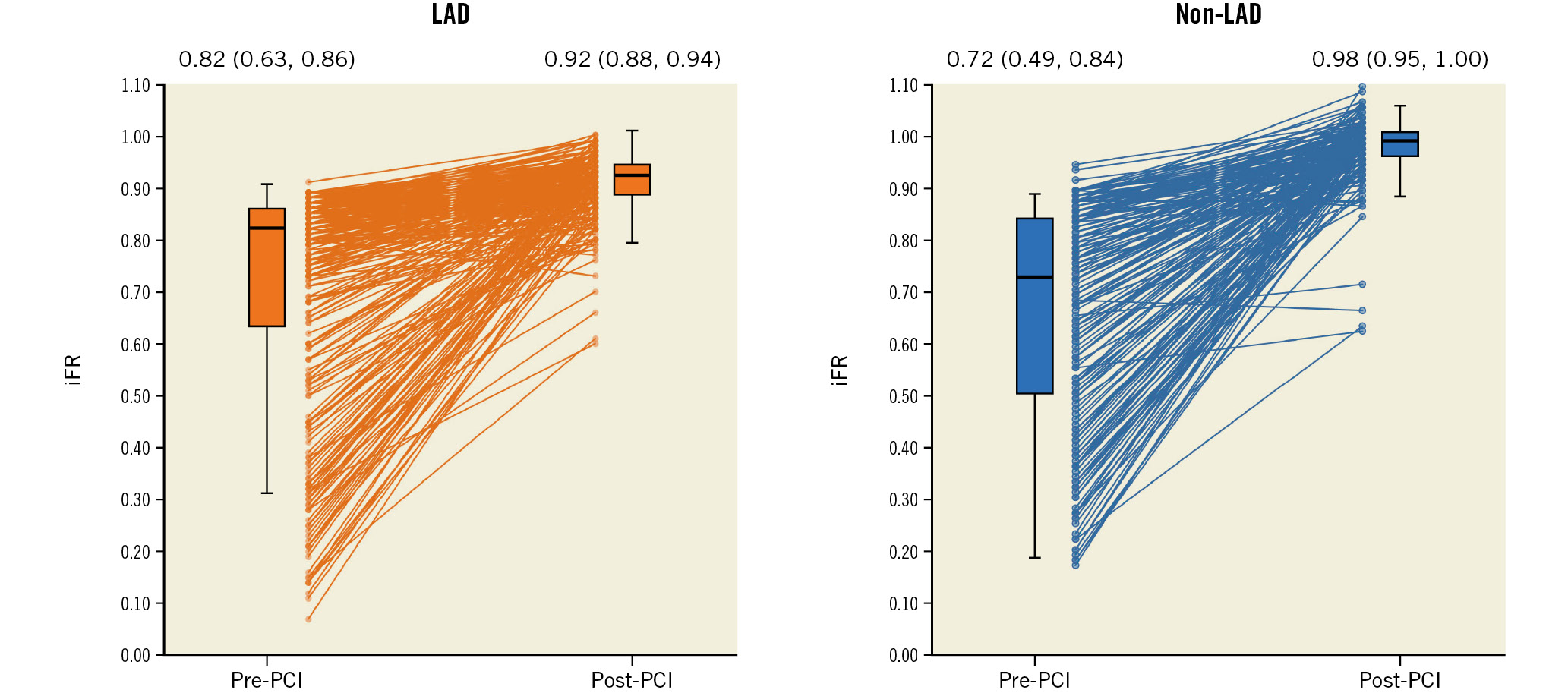
Figure 1. Comparison of individual pre- and post-PCI iFR in LAD versus non-LAD vessels. Median (first quartile, third quartile) pre-PCI and post-PCI iFR were 0.82 (0.63, 0.86) and 0.92 (0.88, 0.94) in LAD vessels and 0.72 (0.49, 0.84) and 0.98 (0.95, 1.00) in non-LAD vessels, respectively. Pre- to post-PCI iFR gain was less in LAD versus non-LAD vessels. iFR: instantaneous wave-free ratio; LAD: left anterior descending artery; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
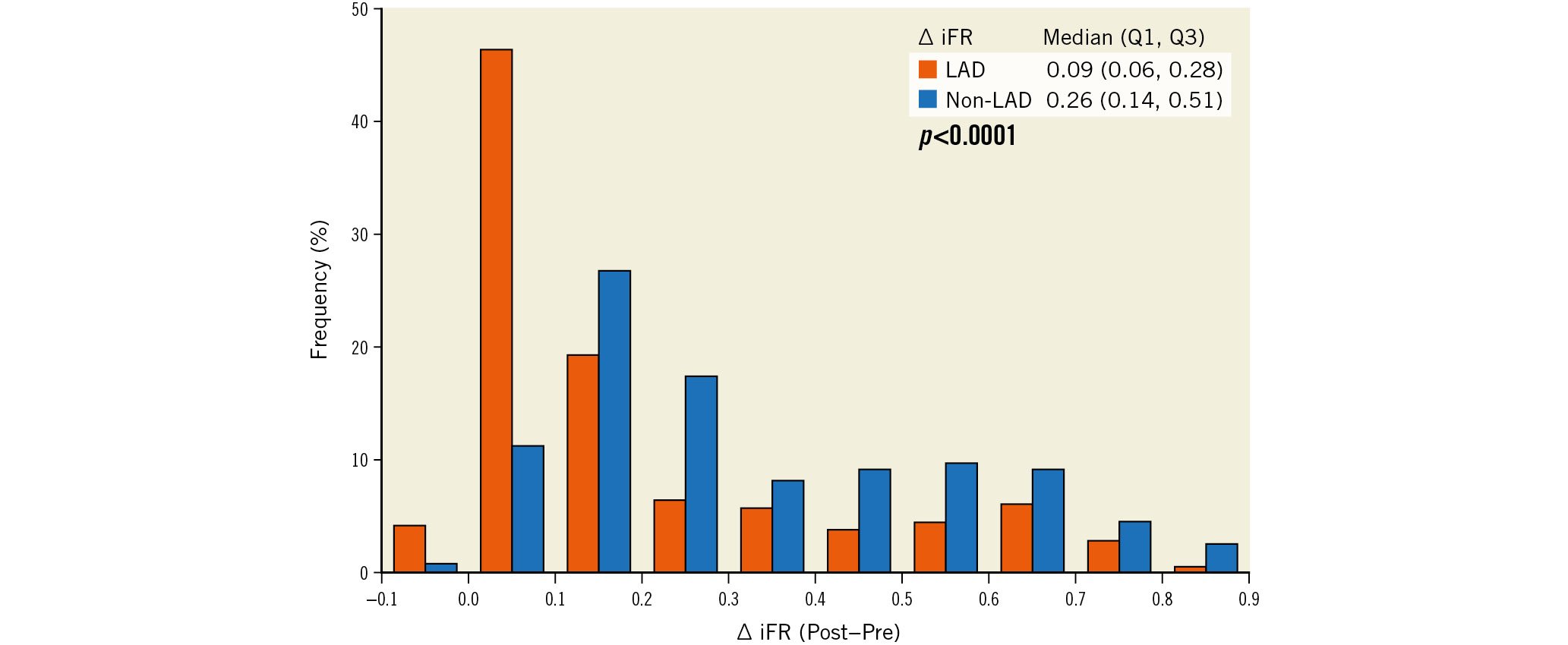
Figure 2. Distribution of iFR gain in LAD versus non-LAD vessels. iFR gain (defined as post-PCI iFR minus pre-PCI iFR) was significantly less in LAD vessels compared with non-LAD vessels. iFR: instantaneous wave-free ratio; LAD: left anterior descending artery; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; Q: quartile
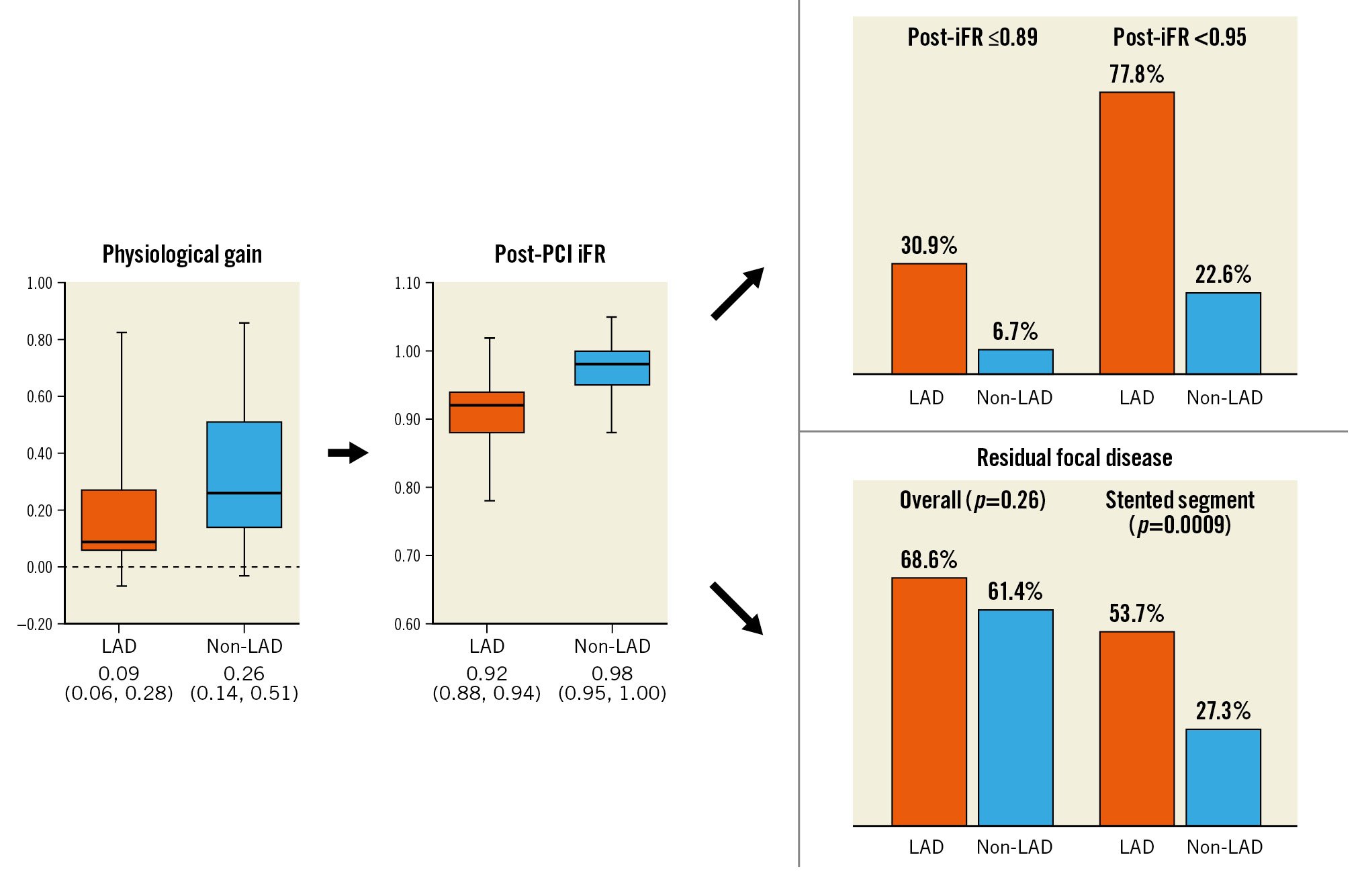
Central illustration. Comparison of physiological assessment in the LAD versus non-LAD vessels. iFR: instantaneous wave-free ratio; LAD: left anterior descending; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
PATTERNS OF RESIDUAL DISEASE
Among the 286 vessels with a suboptimal post-PCI iFR of <0.95, there was a larger translesion gradient in LAD compared with non-LAD vessels (median 0.10 [0.07, 0.13] vs 0.08 [0.06, 0.11]; p=0.056) (Table 2). However, the frequency of residual focal disease (68.6% vs 61.4%; p=0.26), and diffuse disease (31.4% vs 38.6%; p=0.26) were similar in both groups. While there was no difference between the groups in residual focal disease proximal to the stent (28.9% vs 36.4%; p=0.37), distal to the stent (30.2% vs 27.3%; p=0.64) or in the combined non-stented segment (49.6% vs 50.0%; p=0.99), the prevalence of residual focal disease within the stented segment was greater in LAD versus non-LAD vessels (53.7% vs 27.3%; p=0.0009) (Supplementary Figure 1).
FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH POST-PCI IFR
By multivariable linear regression, the factors independently associated with a lower post-PCI iFR were different in LAD and non-LAD vessels. In the LAD vessels, a larger body surface area (BSA; p=0.03), older age (p=0.006), lower pre-PCI iFR (p=0.01), and a smaller reference vessel diameter (RVD; p=0.0002) were all associated with lower post-PCI iFR, whereas in non-LAD vessels, lesion calcification (p=0.03) and a smaller RVD (p=0.01) were the only predictors of lower post-PCI iFR (Table 3).
Table 3. Patient or pre-PCI lesion characteristics associated with post-PCI iFR by multivariable linear regression.
| Dependent variablePost-PCI iFR per 0.01 | All vessel (N=506) |
LAD (N=311) |
Non-LAD (N=195) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression coefficient (95% CI) |
p-value | Regression coefficient (95% CI) |
p-value | Regression coefficient (95% CI) |
p-value | |
| Age, per 10 years | −0.40 (−0.97, 0.16) | 0.16 | −0.84 (−1.43, −0.24) | 0.006 | −0.04 (−0.98, 0.90) | 0.93 |
| Body surface area, m2 | −2.53 (−4.96, −0.09) | 0.04 | −2.54 (−4.88, −0.19) | 0.03 | −1.56 (−6.28, 3.16) | 0.52 |
| Diabetes mellitus | −0.41 (−1.70, 0.88) | 0.53 | −0.17 (−1.43, 1.08) | 0.79 | −1.26 (−3.18, 0.66) | 0.20 |
| Pre-PCI RVD, mm | 3.47 (2.02, 1.91) | <0.0001 | 2.95 (1.41, 4.49) | 0.0002 | 2.65 (0.63, 4.67) | 0.01 |
| Lesion length, mm | 0.01 (−0.03, 0.04) | 0.75 | 0.02 (−0.02, 0.06) | 0.35 | 0.01 (−0.04, 0.05) | 0.68 |
| Calcification (moderate/severe) | −2.16 (−3.32, -1.01) | 0.0002 | −0.59 (−1.72, 0.54) | 0.30 | −2.44 (−4.68, −0.20) | 0.03 |
| Pre-PCI iFR | 1.07 (−1.99, 4.13) | 0.49 | 4.62 (1.05, 8.18) | 0.01 | 1.24 (−3.14, 5.62) | 0.58 |
| CI: confidence interval; iFR: instantaneous wave-free ratio; LAD: left anterior descending; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; RVD: reference vessel diameter | ||||||
SAQ-AF SCORES AT ONE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP
As shown in Supplementary Table 2, SAQ-AF scores at baseline and at 1 year were similar in patients with LAD and non-LAD disease. Compared with patients with an iFR gain ≥median had a higher mean SAQ-AF score at 1 year (97.2±8.0 vs 91.7±15.7; p=0.0002) and greater improvement in mean SAQ-AF score (26.9±21.0 vs 16.9±25.7; p=0.0006), although the SAQ-AF scores at baseline were similar. By multivariable linear regression, lower baseline SAQ-AF scores (p<0.0001) and greater ΔiFR (p=0.007), but not target lesion location in LAD (p=0.74), were associated with greater improvement of SAQ-AF scores from baseline to 1 year (Table 4).
Table 4. Factors associated with absolute change of SAQ-AF score from baseline to 1-year follow-up in multivariate linear regression model.
| Regression coefficient (95%CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|
| ∆ iFR (pre-iFR–post-iFR) | 7.86 (2.15, 13.58) | 0.007 |
| LAD versus non-LAD | −0.48 (−3.32, 2.36) | 0.74 |
| Baseline SAQ-AF score | −0.87 (−0.93, −0.81) | <0.0001 |
| AF: angina frequency; CI: confidence interval; iFR: instantaneous wave-free ratio; LAD: left anterior descending artery; SAQ: Seattle Angina Questionnaire | ||
CLINICAL OUTCOMES
The 1-year incidence of target vessel failure (TVF) and its components were similar in patients with LAD target vessel disease and non-LAD target vessel disease (Supplementary Table 3, Figure 3).
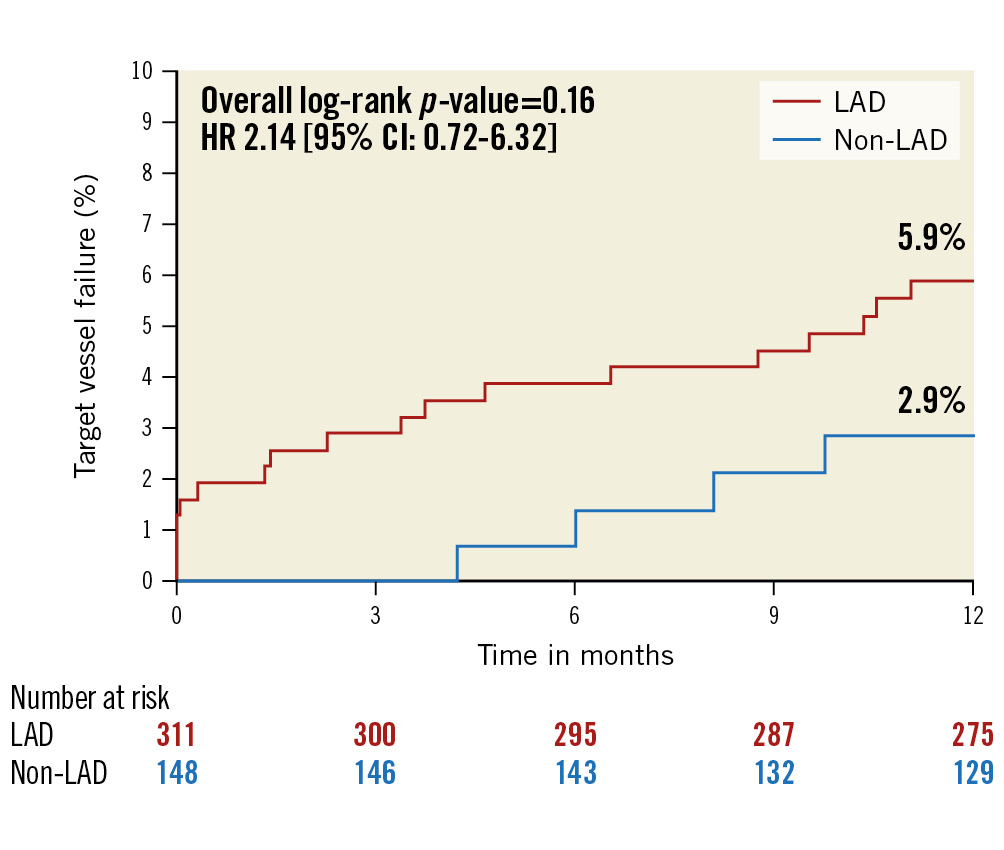
Figure 3. One-year target vessel failure between LAD versus non-LAD vessels. Patient-level Kaplan-Meier curves for target vessel failure. There was no significant difference in clinical events at 1 year between LAD versus non-LAD target vessels. CI: confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; LAD: left anterior descending artery
Discussion
As shown in the Central illustration, the main findings of this substudy from the multicentre, prospective DEFINE PCI registry are as follows: compared with PCI in non-LAD vessels, PCI in LAD vessels showed 1) lower absolute post-PCI iFR; 2) greater residual focal pressure gradient within the treated segment; 3) different clinical and anatomical factors predicting post-PCI iFR, though smaller RVD was associated with lower post-PCI iFR both in LAD and non-LAD vessels; and 4) improvement in iFR from pre- to post-PCI was associated with an improvement of angina, regardless of vessel location.
IMPAIRED POST-PCI PHYSIOLOGY IN LAD COMPARED WITH NON-LAD VESSELS
Lesion location in the LAD was a predictor of a lower post-PCI iFR10. This finding in DEFINE PCI is consistent with prior studies demonstrating that LAD lesion location is an independent predictor of an abnormal post-PCI FFR789. In the current study, though pre-PCI iFR in LAD vessels was higher compared with those in non-LAD vessels, lower post-PCI iFR in LAD compared with non-LAD vessels was observed. Specifically, iFR pullback analysis demonstrated that iFR focal lesions within the stented segment were more frequent in LAD compared with non-LAD vessels, whereas no significant differences were observed outside the treated segment or in the prevalence of diffuse disease. Of note, the lesion and stent length were similar between the 2 groups, indicating that worse PCI results may, in part, be responsible for the overall smaller iFR improvement in the LAD group. This is an important finding since suboptimal PCI is potentially modifiable with additional stent optimisation13. A recently published paper demonstrated that segmental non-hyperaemic pressure ratios (distal coronary pressure-to-aortic pressure ratio and diastolic pressure ratio gradients) had moderate ability to identify intravascular ultrasound-detected focal residual lesions and stent underexpansion14. Whether PCI guidance with iFR pullback and stent optimisation leads to improved clinical outcomes is currently being tested in the large-scale randomised Distal Evaluation of Functional Performance With Intravascular Sensors to Assess the Narrowing Effect: Guided Physiologic Stenting (DEFINE GPS) trial (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04451044).
DIFFUSE ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN THE LAD COMPARED WITH NON-LAD VESSELS
Smaller angiographic RVD was an independent predictor of lower post-PCI iFR in both LAD and non-LAD vessels, and RVD tended to be smaller in the LAD compared with non-LAD vessels (2.73 mm vs 2.84 mm). Smaller RVD in the LAD may indicate diffuse atherosclerosis, although no statistical difference was observed when compared with non-LAD vessels. Prior intravascular ultrasound studies have shown that angiographically “normal” segments are rarely normal15, and plaque burden is greater in LAD compared with non-LAD vessels16. Coronary artery calcification has also been shown to be greater in LAD compared with non-LAD vessels in patients with mild to moderate levels of overall coronary artery calcium17. Warisawa et al reported that an iFR-derived diffuse pattern was more frequent in LAD compared with non-LAD vessels (53.8% in 520 LAD vessels vs 18.5% in 151 non-LAD vessels)18. A similar trend was observed using the hyperaemic pullback pressure gradient19. These factors may all contribute to smaller minimum stent areas in LAD lesions, potentially explaining the higher prevalence of residual in-stent pressure gradients in the LAD.
PRESSURE LOSS IN THE LAD ANATOMY INDEPENDENT OF STENOSIS
Vessel curvature, the presence of branches, and vessel tapering affect pressure loss even in relatively normal coronary arteries2021. In addition, compared with the ground truth, wire-based invasive physiology measurements in the supine position may reveal lower values in the LAD and higher values in the LCx because of hydrostatic pressure22. Using computed tomography, a prior study showed that the mid- to distal LAD is located higher than the ostium of the left main coronary artery, and the LCx is located lower than the ostium. Thus, compared with the position of the ostium, where equalisation between the aortic pressure and pressure sensor on the wire is performed, the hydrostatic pressure is negative in the mid- to distal LAD (i.e., invasive physiology measurements may reveal lower numbers than the ground truth) and positive in the LCx (i.e., invasive physiology measurements may reveal higher values than the ground truth). Fukunaga et al reported that in 26 angiographically normal LAD vessels, FFR values gradually decreased from proximal to distal, measuring 0.85±0.06 at 12 cm distal to the ostium. In 6 swine with normal coronary arteries, the FFR was 0.95±0.01 at 10 cm distal to the ostium in the LAD, compared with a value of 1.0 at 10 cm distal to the ostium in all RCA and LCx arteries23. Finally, the larger myocardial mass that is typically subtended by the LAD may lead to a greater pressure loss and consequently smaller post-PCI physiological gain24. Kang et al showed that a larger BSA or greater left ventricular mass were independently associated with lower FFR values after adjustment for intravascular ultrasound minimum lumen area25. In this study, the RVD among the different vessels was similar, with the LAD being the longest vessel. Consequently, the normalised arterial volume to left ventricular mass ratio is much smaller in the LAD than in the other arteries.
Ultimately, a combination of more advanced disease, worse acute PCI results with larger in-stent pressure gradients, greater subtended myocardium, and the LAD anatomy itself may explain the lesser iFR gain from pre- to post-PCI in LAD compared with non-LAD vessels. In this regard, Hwang et al reported that the cutoff value of post-PCI FFR to predict TVF was different for LAD (≤0.82) and non-LAD vessels (≤0.88)8.
CORRELATION BETWEEN IMPROVEMENT IN SAQ-AF SCORE AND LESION LOCATION
There is a strong correlation between invasive physiology measurements and stress echocardiography-detected ischaemia, as well as with the efficacy of PCI in reducing ischaemia and angina frequency26. Symptomatic patients with ischaemia treated with revascularisation are more likely to be free from angina at follow-up compared with patients managed with medical therapy only27, especially those with greater degrees of ischaemia as assessed by stress echocardiography or with invasive physiology2628. In the present study, greater improvements of iFR were associated with greater reductions in angina, independent of the target vessel location. Similarly, larger relative improvements in FFR have been associated with a reduced burden of patient-reported angina at 3-month follow-up29.
Limitations
First, the present analysis only included patients with pre- and post-PCI iFR measurements and excluded left main lesions, therefore, some degree of selection bias cannot be excluded. The current study included only patients with abnormal pre-PCI iFR. Prior studies have shown that a reverse mismatch (angiographically mild stenosis, but physiologically significant) occurs more frequently in the LAD compared with non-LAD30. Given that the current study included only patients with abnormal pre-PCI iFR assessment, lesion severity was greater in non-LAD vessels. Second, intravascular imaging was only performed in a small proportion of patients and was not made available to the core laboratory. As such, we cannot correlate the physiology findings with the severity of residual atherosclerosis. Third, the optimal post-PCI iFR target value of 0.95 was identified post hoc and requires prospective validation before being adopted into clinical practice. Finally, there were a relatively small number of clinical events at 1 year, limiting our ability to determine differences in vessel-based angina-related and clinical outcomes.
Conclusions
In a large cohort of patients undergoing angiographically successful PCI, post-PCI iFR values were lower in LAD vessels compared with non-LAD vessels. Larger residual in-stent pressure gradients were observed in LAD vessels, the treatment of which may result in improved acute physiological gain and clinical outcomes; this hypothesis is currently being tested in the pivotal DEFINE GPS trial.
Impact on daily practice
The current study demonstrates that LAD vessels have a smaller improvement of iFR from pre-PCI to post-PCI with a greater frequency of residual focal pressure gradients within the stented segment compared with non-LAD vessels; this directly contributes to a lower absolute post-PCI iFR and higher prevalence of post-PCI iFR ≤0.89 and <0.95. The clinical and anatomical factors associated with lower post-PCI iFR were different between LAD and non-LAD vessels.
Funding
This study was supported by funding from Philips/Volcano Corporation (San Diego, CA, USA). The funding source was uninvolved with the design of the protocol, the analysis and interpretation of the study results.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Matsumura is a consultant for Terumo and Boston Scientific. A. Maehara is a consultant for Boston Scientific; receives honoraria from Nipro and Boston Scientific; and is on the advisory board of SpectraWave. J. Davies has patents pertaining to the iFR technology; and is a consultant for Philips. A. Sharp is a consultant for Philips, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, ReCor Medical, and Penumbra; and receives honoraria from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Philips, Recor Medical, and Penumbra. H. Samady is on the advisory board of Philips; co-founder and equity holder in Covanos; and a holder of four patents in the computational physiology space. A. Seto receives research grants from Philips; and is part of the leadership of SCAI. D. Cohen receives institutional grant support from Philips; is a consultant for Abbott, Edwards Lifesciences, and HeartBeam; and is on the advisory board of Medtronic. M. Patel receives research grants from Philips; and is a consultant for Bayer, Janssen, and Novartis. Z.A. Ali receives institutional grant support from Abbott, Abiomed, Acist, Amgen, Boston Scientific, Cathworks, Canon, Conavi, HeartFlow, Inari, Medtronic Inc, National Institute of Health, Nipro, Opsens Medical, Medis, Philips, Shockwave Medical, Siemens, Spectrawave, and Teleflex; is a consultant for Abiomed, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Cathworks, OpSens, Philips, and Shockwave Medical; receives a honoraria from Abiomed, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, Cathworks, OpSens, Philips, and Shockwave Medical; and has equity/options from Elucid, Lifelink, SpectraWave, Shockwave Medical, and VitalConnect. G.W. Stone has received institutional grant support from Abbott, Abiomed, Bioventrix, Cardiovascular Systems Inc, Philips, Biosense-Webster, Shockwave Medical, Vascular Dynamics, Pulnovo, and V-Wave; is a consultant for Abbott, Daiichi Sankyo, Ablative Solutions, CorFlow, Cardiomech, Robocath, Miracor, Vectorious, Apollo Therapeutics, Valfix, TherOx, HeartFlow, Neovasc, Ancora, Elucid Bio, Occlutech, Impulse Dynamics, Adona Medical, Millennia Biopharma, Oxitope, Cardiac Success, and HighLife; received honoraria from Medtronic, Pulnovo, Infraredx, Abiomed, Amgen, and Boehringer Ingelheim; and has equity/options from Ancora, Cagent, Applied Therapeutics, Biostar family of funds, SpectraWave, Orchestra Biomed, Aria, Cardiac Success, Valfix, and Xenter. A. Jeremias receives institutional grant support from Philips; is a consultant for Philips, Abbott Vascular, ACIST Medical, Shockwave Medical, and Cathworks; and is on the advisory board of Philips. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

