A 73-year-old man presented with one month of extensional chest pain. Physical examination, CXR, ECG and cardiac enzymes were all within normal limits. Thallium SPECT showed a moderate inferolateral and anterolateral reversible perfusion defect. Coronary angiography revealed a normal looking left main coronary artery (LMCA) leading only to small diagonal and septal branches (Moving image 1). The left anterior descending (LAD) artery and the circumflex (CX) artery each originate from a separate ostium from the right aortic sinus of Valsalva. The right coronary artery (RCA) had a normal independent origin (Moving image 2). A severe proximal narrowing of the proximal CX artery was uneventfully dilated with a drug-eluting stent. Cardiac computed tomography angiography demonstrated that the course of the LAD is anterior to the right ventricle (Figure 1).
The independent origin of the LAD and CX arteries from two separate ostia in the right aortic sinus of Valsalva is an extremely rare anomaly1,2. Myocardial ischaemia and sudden death could be the result of LAD compression if it crosses between the aorta and the pulmonary artery1. A LAD course anterior to the right ventricle or behind the aorta is of low risk for an adverse event.
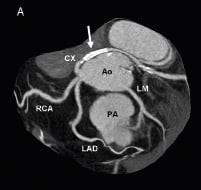
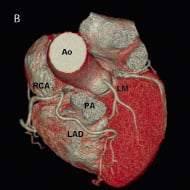
Figure 1. Cardiac computed tomography (CT) with three-dimensional view of the heart showing the anomalous coronary abnormality. The LAD, the CX and the RCA originate separately from the right coronary sinus. The LAD passes anterior to the pulmonary artery (PA), while the CX passes behind the aorta (Ao). The LMCA is the sole coronary branch to originate from the left coronary sinus. Note a stent in the proximal CX (arrow). A: maximal intensity projection (MIP); B: volume rendered reconstruction. RCA: right coronary artery; LAD: left anterior descending coronary artery; CX: circumflex coronary artery; LM: left main coronary artery; Ao: aorta; PA: pulmonary artery
Online data supplement
Moving image 1. A cranial right anterior oblique (RAO) view showing the left main coronary artery attributing only small diagonal and septal branches. The LAD and CX arteries are absent.
Moving image 2. A flat left anterior oblique (LAO) view of a non-selective right aortic sinus of Valsalva injection showing the LAD and CX arteries each originating from a separate ostium while the RCA has a normal independent origin.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. A cranial right anterior oblique (RAO) view showing the left main coronary artery attributing only small diagonal and septal branches. The LAD and CX arteeries are absent.
Moving image 2. A flat left anterior oblique (LAO) view of a non-selective right aortic sinus of Valsalva injection showing the LAD and CX arteries each originating from a separate ostium while th RCA has a normal independent origin.

