
Abstract
Aims: The aim of this study was to compare the periprocedural and late clinical outcomes of left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) with AMPLATZER devices by access through transseptal puncture (TSP) versus a patent foramen ovale (PFO) or an atrial septal defect (ASD).
Methods and results: Between 2009 and 2018, 578 consecutive patients underwent LAAC via TSP or PFO/ASD access in three centres. After a 3:1 propensity score matching, 246 (TSP) versus 91 (PFO/ASD) patients were compared using the primary efficacy endpoint of all-cause stroke, systemic embolism and cardiovascular/unexplained death and the primary safety endpoint of major periprocedural complications and major bleedings at follow-up. Mean age was 75.2±8.7 (TSP) vs 74.4±10.9 (PFO/ASD) years, CHA2DS2-VASc score 4.5±1.6 vs 4.3±1.4 and HAS-BLED score 3.3±1.0 vs 3.3±0.9. Device success (97.6% vs 97.8%, p=0.90) was similar. After 2.5±1.4 vs 2.6±1.6 years, clinical efficacy (46/603, 7.6% [TSP] vs 21/233, 9.0% [PFO/ASD], hazard ratio [HR] 1.2; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.69-0.85, p=0.54) and safety (24/603, 4.0% vs 11/233, 4.7%; HR 1.4; 95% CI: 0.52-3.6, p=0.49) did not differ.
Conclusions: Use of a PFO/ASD access for LAAC with AMPLATZER devices offers similar periprocedural and late clinical outcomes to TSP. Simultaneous PFO/ASD closure for an additional protective benefit does not increase risk.
Introduction
Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) is a validated, non-pharmacological treatment for stroke prevention in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF) and contraindications to oral anticoagulation (OAC)1,2,3,4,5. The WATCHMAN™ (Boston Scientific, Marlborough, MA, USA) and the AMPLATZER™ (Abbott, St Paul, MN, USA) are the most commonly used systems. The latter’s first- and second-generation AMPLATZER™ Cardiac Plug (ACP) and Amulet™ have shown high device success, an acceptable rate of periprocedural adverse events, and a low annual rate of ischaemic events in large multicentre registries1,2,3. A transseptal puncture (TSP) in an infero-posterior portion of the fossa ovalis is generally recommended for optimal implantation results. This approach facilitates coaxial alignment of the delivery sheath to the left atrial appendage (LAA)4. To simplify the procedure and potentially avoid TSP-related complications in patients with a patent foramen ovale (PFO) or an atrial septal defect (ASD), access to the left atrium (LA) through the PFO/ASD has been practised in selected centres for over 15 years6. In a first retrospective analysis, the feasibility and safety of such an approach was reported in 51 patients6. The PFO/ASD can be closed at the end of the procedure in a matter of minutes, reloading the gear used for LAAC with a respective occluder. However, left atrial access via PFO/ASD remains shunned by most operators due to the typically more anterior or superior entrance into the LA and therefore more challenging or suboptimal positioning of the delivery sheath. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the periprocedural and late clinical outcomes of TSP versus PFO/ASD access for LAAC with AMPLATZER devices.
Methods
PATIENT POPULATION
A total of 578 consecutive patients underwent LAAC with the first-generation ACP and the second-generation AMPLATZER Amulet between 2009 and 2015 at Coburg Hospital, Germany, and Bern and Zurich University Hospitals, Switzerland. Indications for LAAC were based on current guidelines and expert recommendations4,7. Exclusion criteria included active infection, reasons for OAC other than AF, and pregnancy. All patients gave written informed consent. Data were captured in a dedicated database according to the respective regulations of the responsible ethics committees. Late clinical outcomes were collected from follow-up visits, telephone calls and hospitalisations. All adverse events underwent adjudication by a clinical events committee comprising two independent physicians and, in case of disagreement, by a third acting as adjudicator.
LAAC PROCEDURE AND FOLLOW-UP
LAAC with AMPLATZER occluders has been described in detail previously8. Transoesophageal echocardiography (TEE) guidance was performed depending on operator routine. Most devices were implanted conventionally via TSP, preferably in the infero-posterior portion of the fossa ovalis. In case of a known PFO/ASD, access to the LA was attained through them by some operators6. Most such cases were performed without TEE guidance and, in the majority, PFO/ASD closure was performed at the end of the procedure. After deployment of the occluder in the LAA, the delivery sheath was kept in the LA. A properly sized AMPLATZER™ PFO/ASD occluder (Abbott) was attached to the LAAC pusher cable and deployed to the PFO/ASD (Figure 1). Post-procedural antithrombotic therapy consisted of a dual antiplatelet regimen with aspirin and clopidogrel for one to six months8. A follow-up TEE was performed in a time frame from six weeks to four months post LAAC.
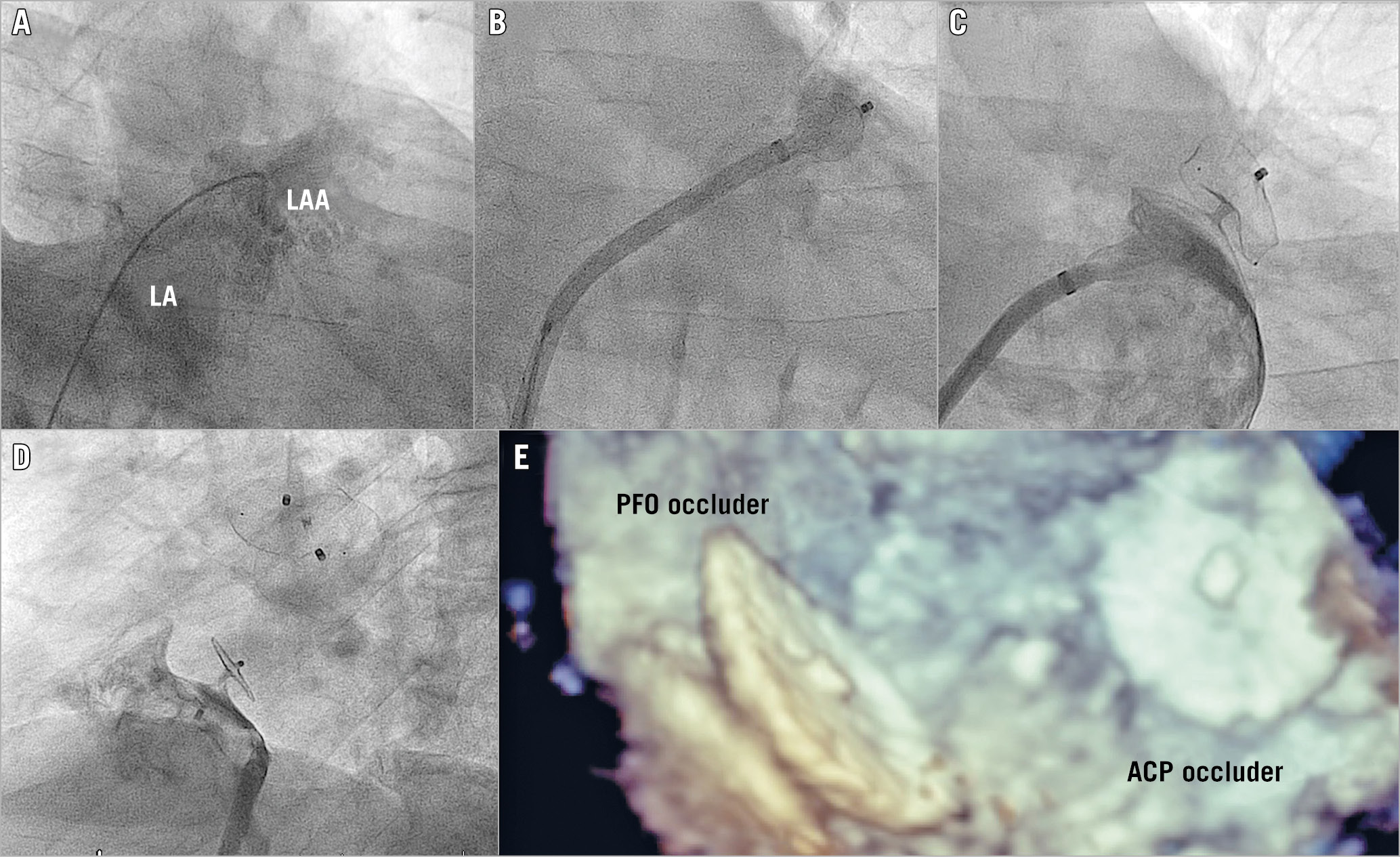
Figure 1. Combined left atrial appendage and PFO closure. A) Access to the left atrium through a PFO. B) Implantation of an ACP. C) Left atrial angiography after LAAC. D) Right atrial angiography after PFO occlusion. E) 3D TEE after five months.
DEFINITIONS AND CLINICAL ENDPOINTS
Demographic, clinical, and procedural characteristics as well as adverse events and endpoints were assessed according to the current recommendations of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) and the European Association of Percutaneous Coronary Interventions (EAPCI)4, the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC)9, the Valve Academic Research Consortium criteria (VARC-2)10, and the 2017 Cardiovascular and Stroke Endpoint Definitions for Clinical Trials11. Device success was defined as correct deployment of the occluder. Major periprocedural complications included death, any stroke, major bleeding, device embolisation, major access vessel complication, need for cardiovascular surgery or cardiopulmonary resuscitation, cardiac tamponade, and other relevant complications leading to prolonged hospital stay. The primary efficacy endpoint was a composite of all-cause stroke, systemic embolism, and cardiovascular/unexplained death. The primary safety endpoint was a composite of major periprocedural complications and major bleeding events at follow-up.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Continuous variables are presented as mean±standard deviation (SD) and were compared using the unpaired t-test. Categorical variables are presented as frequency and percentage and were compared using the chi-square test. The Kaplan-Meier method was used for graphical assessment of time-dependent events. For comparison of event curves, the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used. For determination of the hazard ratio (HR), the Mantel-Haenszel method was applied. Analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism, version 7.0 (GraphPad, La Jolla, CA, USA).
A propensity score matching was performed using the R software12. With a calliper value of 0.05 and ratio of 3:1, there were no significant differences in the covariables among the two groups using a univariate logistic regression.
Results
STUDY POPULATION
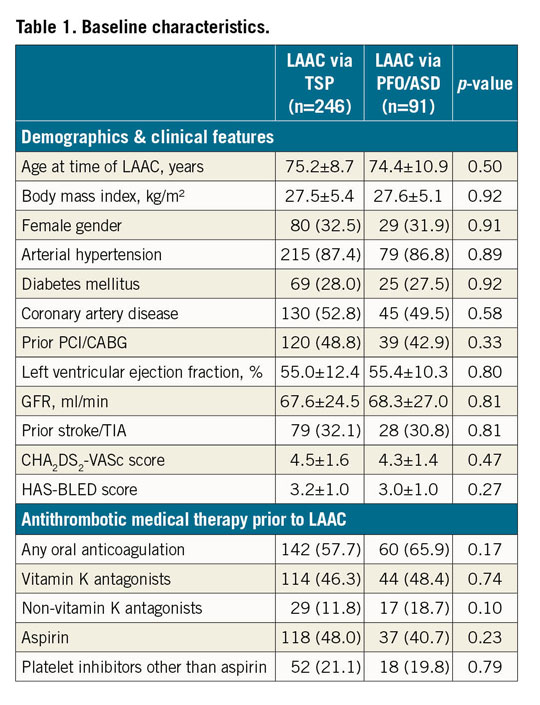
Of 578 consecutive patients who underwent LAAC with AMPLATZER devices, 462 interventions were performed via TSP access and 116 via PFO/ASD. After the 3:1 propensity score matching, a cohort of 246 patients with TSP and 91 patients with PFO/ASD access remained and showed good comparability with similar baseline characteristics (Table 1). This analysis comprises a total of 836 patient-years with a mean follow-up of 2.5±1.4 years (TSP) and 2.6±1.6 years (PFO/ASD).
PROCEDURAL CHARACTERISTICS AND TEE FOLLOW-UP
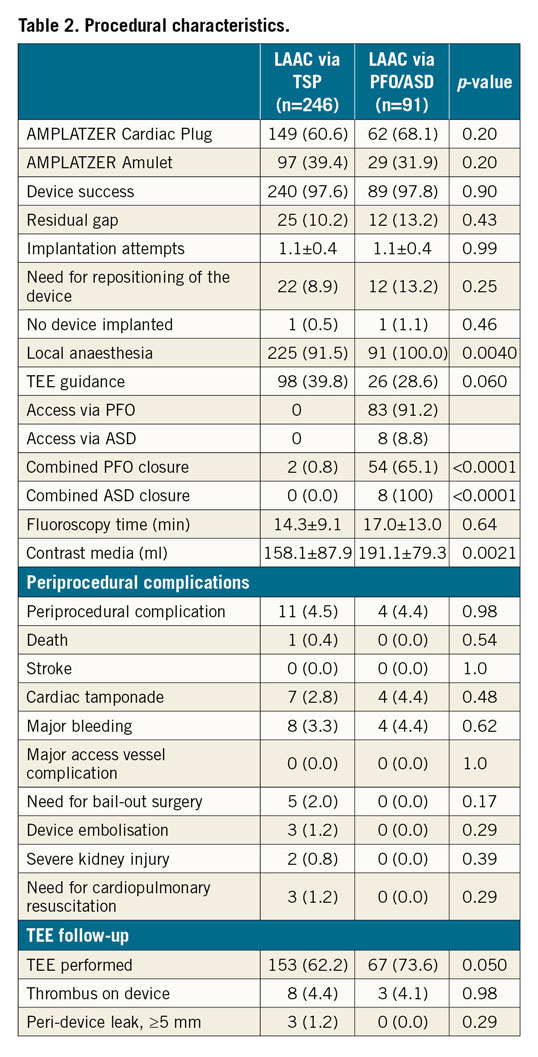
Procedural characteristics and TEE follow-up are summarised in Table 2. In the PFO/ASD group, 54 of 83 (65.1%) patients received a simultaneous PFO closure, and 8 of 8 (100.0%) patients a simultaneous ASD closure. This resulted in higher amounts of contrast volume in the PFO/ASD group (158.1±87.9 [TSP] vs 191.1±79.3 [PFO/ASD] ml, p=0.0021), but did not significantly prolong fluoroscopy time (14.3±9.1 vs 17.0±13.0 min, p=0.64). Overall device success was high and similar for both groups (240/246, 97.6% vs 89/91, 97.8%, p=0.90). The device contour in fluoroscopy, which reflects the degree of undersizing or oversizing, was determined in 138/246 (56.1%) (TSP) and 60/91 (56.9%) (PFO/ASD) patients, respectively; no difference between the groups was observed. A “tyre shape” indicates optimal compression of the lobe and was documented in 72/138 (33.2%) (TSP) versus 27/60 (31.4%) (PFO/ASD), p=0.35, individuals. The “square-shaped” lobe, which is a sign of undersizing, occurred in 28/138 (12.9%) versus 13/60 (15.1%), p=0.83, patients. Oversizing or deep implantation is indicated by a “strawberry” compression of the lobe. It was seen in 38/138 (17.5%) versus 20/60 (23.3%), p=0.41, cases.
Major periprocedural complications (11/246, 4.5% [TSP] vs 4/91, 4.4% [PFO/ASD], p=0.98) did not differ. The most common complication was cardiac tamponade (7/246, 2.8% vs 4/91, 4.4%, p=0.48). Three device embolisations occurred in the TSP group (1.2%); no device embolisation was observed in the PFO/ASD group.
TEE at follow-up was available in 153 of 246 patients (62.2%) in the TSP group and in 67 of 91 patients (73.6%) in the PFO/ASD group, p=0.050. Due to the lack of a controlled design, patient frailty and logistic reasons, the TEE follow-up rate is incomplete. The rate of device-related thrombus (DRT) was similar (8/246 [4.4%] [TSP] vs 3/91 [4.1%] [PFO/ASD], p=0.98). In the TSP group, one patient with DRT suffered a transient ischaemic attack (TIA), and one patient each a non-disabling ischaemic stroke and a disabling ischaemic stroke. In the PFO/ASD group, DRT was not associated with thromboembolic events during follow-up. The rates of major peri-device leaks (3/246 [1.2%] vs 0/91, p=0.29) were low and did not differ. Major peri-device leaks were not associated with ischaemic events at follow-up. In concomitant PFO and ASD closure, transthoracic echocardiography (TTE)/TEE follow-up was performed in 48/54 (88.9%) and 6/8 (75.0%) cases, respectively. A residual shunt after PFO and ASD closure was detected in 7/48 (2.1%) and 1/6 (16.7%) patients. Residual shunts after PFO closure were considered as clinically non-relevant and patients were treated with antiplatelet therapy. None of the patients was switched to (N)OAC. No ischaemic event was documented at follow-up. One patient with residual shunt after ASD closure underwent reintervention with implantation of a second ASD occluder. A residual shunt after TSP was detected in 19/182 (10.4%) patients, in whom TTE or TEE was performed at follow-up. Three of those 19 patients (15.8%) suffered from two disabling strokes and one TIA, of which one disabling stroke and one TIA occurred in the presence of a DRT.
CLINICAL OUTCOMES
Late clinical outcome is shown in Table 3. All events are reported per 100 patient-years. The cumulative incidence of the primary endpoints is shown in Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier curves of its components are shown in Figure 3. Antithrombotic therapy at follow-up was similar for both groups and consisted predominantly of aspirin. At follow-up, the number of anticoagulated patients had increased from 4/246 (1.6%) (TSP) vs 2/91 (2.2%) (PFO/ASD) to 17/246 (6.9%) (TSP) vs 9/91 (9.9%) (PFO/ASD). Reasons for initiation of (N)OAC during follow-up were stroke/TIA/thromboembolism (3/17 [17.6%] [TSP] vs 2/9 [22.2%] [PFO/ASD]), DRT, dense smoke in the LA (1/17 [5.9%] vs 3/9 [33.3%]), peri-device leak ≥5 mm (2/17 [11.8%] vs 0/9 [0.0%]), pulmonary embolism or deep venous thrombosis (5/17 [29.4%] vs 2/9 [22.2%]), OAC mistakenly given by general practitioners (1/17 [5.9%] vs 1/9 [11.1%]), and unknown reasons (5/17 [29.4%] vs 1/9 [11.1%]).
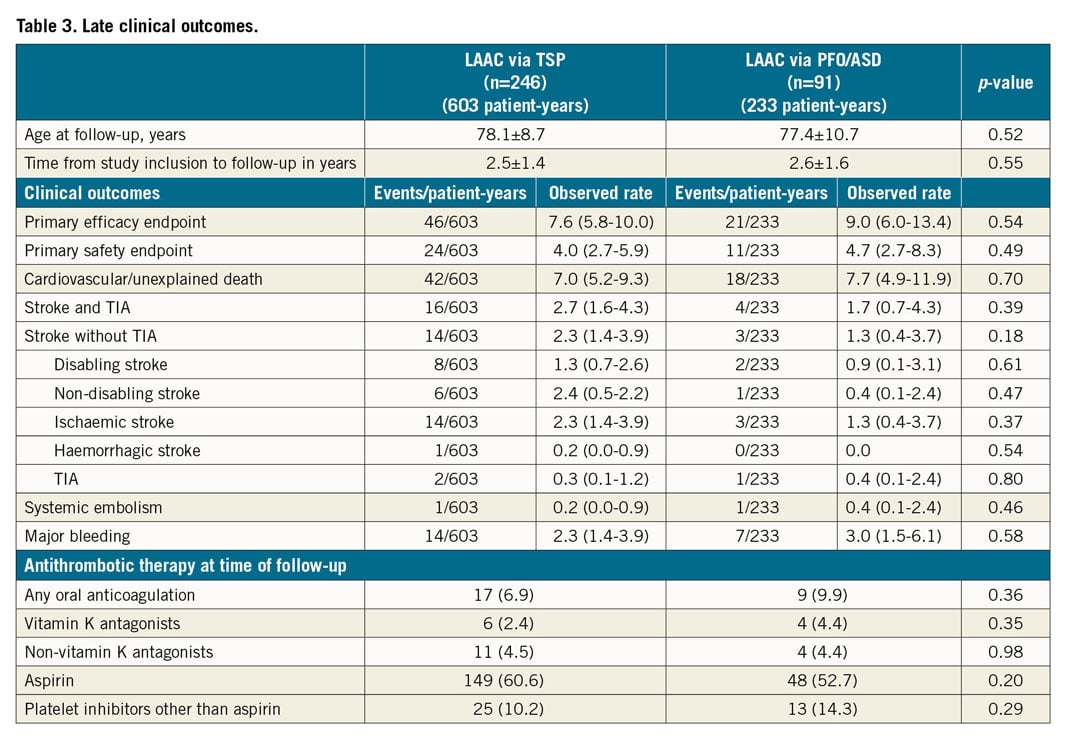
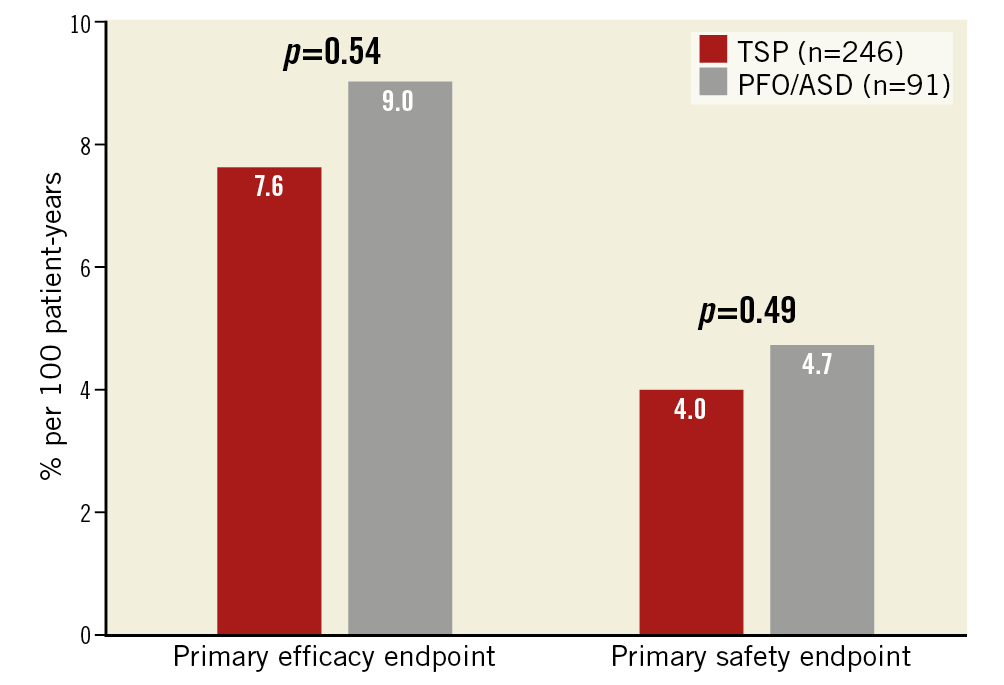
Figure 2. Cumulative incidence of the primary endpoints in % per 100 patient-years.
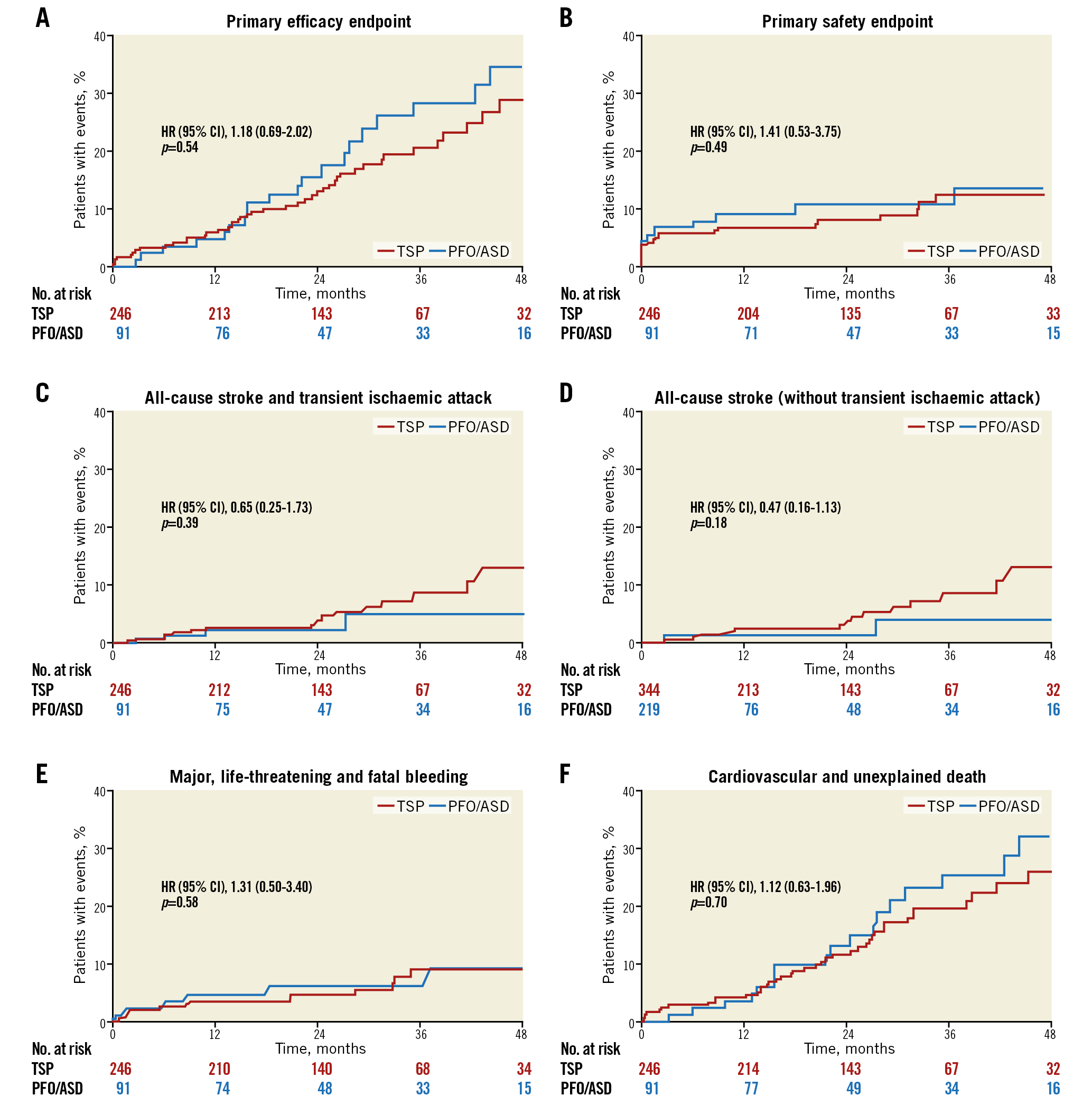
Figure 3. Kaplan-Meier curves of clinical events up to 48 months. A) Primary efficacy endpoint. B) Primary safety endpoint. C) All-cause stroke and transient ischaemic attack. D) All-cause stroke (without transient ischaemic attack). E) Major, life-threatening and fatal bleeding. F) Cardiovascular and unexplained death.
The primary efficacy endpoint of all-cause stroke, systemic embolism, and cardiovascular/unexplained death was comparable for both groups (46/603, 7.6% [TSP] vs 21/233, 9.0% [PFO/ASD], HR 1.2; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.69-0.85, p=0.54). None of the components of the primary efficacy endpoint was different between the two groups. All-cause stroke occurred in 16/603, 2.7% in the TSP group vs 4/233, 1.7% in the PFO/ASD group (HR 0.65; 95% CI: 0.25-1.73, p=0.39). Cardiovascular and unexplained death were documented for the TSP group in 42/60, 7.0% vs 18/233, 7.7% in the ASD/PFO group (HR 1.12; 95% CI: 0.63-1.97, p=0.70). Also, the primary safety endpoint of major periprocedural complications and major bleeding events occurred with a comparable frequency in the TSP and PFO/ASD groups (24/603, 4.0% vs 11/23, 4.7%; HR 1.31; 95% CI: 0.50-3.40, p=0.49). Likewise, the rate of major bleedings was similar in both groups (14/603, 2.3% vs 7/233, 3.0%; HR 1.31; 95% CI: 0.50-3.40, p=0.58).
Discussion
In the present study, we compared periprocedural and late clinical outcomes of LAAC through a TSP versus through a PFO or an ASD. Device success was high in both groups and similar rates of major periprocedural complications were documented. In the long term, left atrial access through a PFO or an ASD provided similar efficacy with regard to all-cause stroke, systemic embolism, and cardiovascular/unexplained death compared to the TSP access. In terms of safety, the rate of major bleeding events was also similar.
The AMPLATZER devices feature a two-part plug-and-disc system with closure of the LAA according to the “pacifier” principle. To provide a full coverage of the LAA orifice without leaving a peri-device leak as potential space for tissue filling and DRT, optimal deployment of the AMPLATZER system is the goal. This is assumed to be facilitated by a recommended access to the LA via a TSP in the infero-posterior portion of the fossa ovalis, directly opposite the LAA. Not using a PFO tunnel is based on the concern that they are located too cranio-anteriorly for proper coaxial LAA intubation with the delivery sheath (Figure 4). Nevertheless, a previous study has demonstrated the technical feasibility of LAAC with AMPLATZER devices via a PFO/ASD6. The present study confirms those early findings of feasibility for the PFO/ASD access with the same rate of implantation attempts and need for repositioning of the device as in the case of TSP. Concomitant PFO/ASD closure resulted in higher amounts of contrast volume, but did not prolong fluoroscopy time. An additional amount of 33 ml contrast volume was used for a final right atrial angiographic check of the implantation result after ASD or PFO closure.
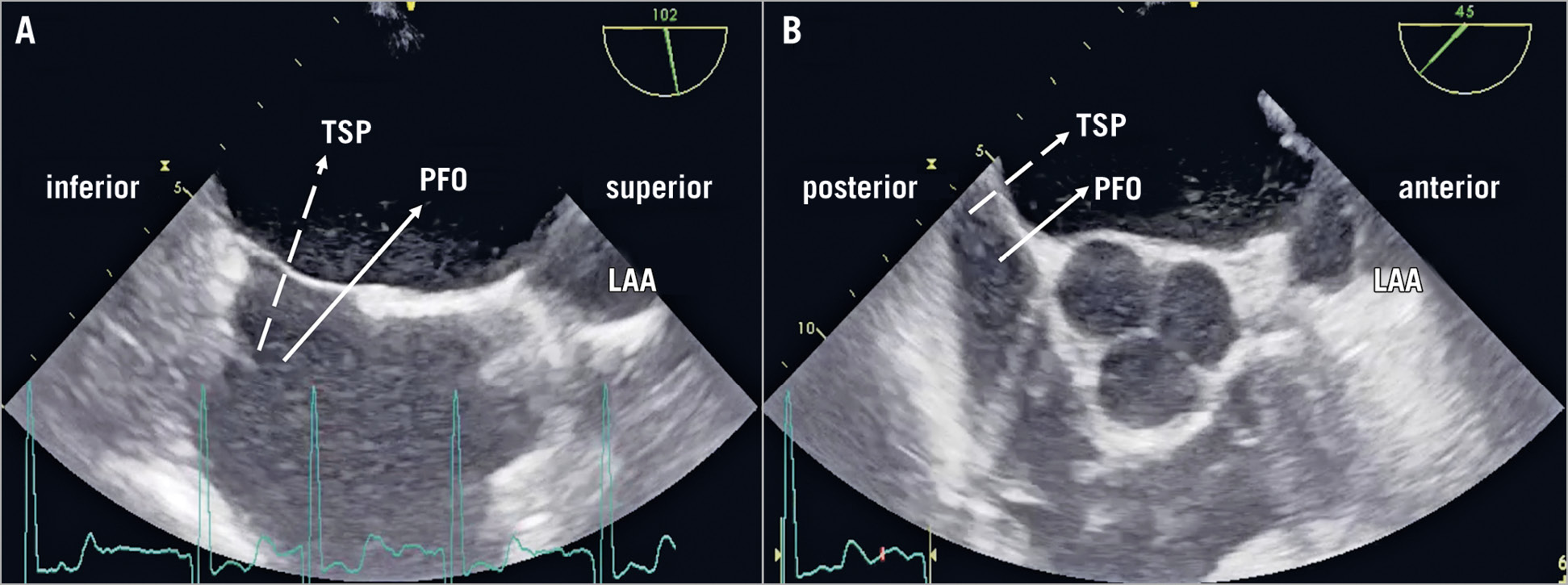
Figure 4. Schematic illustration of TSP versus PFO access on TEE. A) Bicaval view. B) Short-axis view.
Major procedural complications consisted mainly of cardiac tamponade. Most recent studies have reported low rates of cardiac tamponade – 1.24%1, 1.2%2, 1.02%13 and 0.2%14. The relatively high rate of cardiac tamponade in the present study may be attributable to the low rate of periprocedural TEE guidance (TSP vs PFO/ASD: 39.8% vs 28.6%, p=0.06), especially in the early phase of recruiting, reflecting the learning curve of the operators. Nowadays, TEE guidance is strongly recommended to avoid such complications. Hypothetically, passage via a PFO or ASD simplifies LA access and avoids potential complications of TSP such as perforation of the left atrial free wall or the aortic root.
However, in our study a higher number of cases of cardiac tamponade (4 [4.4%]) was documented in the PFO/ASD group. In two of four patients, multiple implantation attempts were needed for proper deployment of the device, which may have been related to a more challenging positioning of the delivery sheath and the occluder in these cases. From this one can conclude that the PFO/ASD access may be demanding and is instead an option for advanced operators.
The rate of device embolisation in the TSP group (1.2%) was slightly higher than documented in other registries at 0.76%1, 0.1%2, 0.24%13 and 0.20%14. It is most likely a chance finding reflecting the learning curves. Nonetheless, overall adverse event rates are in line with the large multicentre registries for the ACP (5.0%)1 and for the Amulet (3.2%)2.
TEE at follow-up revealed a low rate of major peri-device leaks, comparable to those reported in the ACP1 and Amulet2 multicentre trials (1.9% and 1.6%, respectively). Also, the rate of DRT was comparable for TSP and PFO/ASD access. In current registries the incidence of DRT varies notably, which may be attributable to a missing consensus on the definition of DRT, different sample sizes of those series and reporting bias related to inconsistency in TEE follow-up1,2,15.
Implantation results for the TSP and PFO/ASD access led to similar late clinical outcomes. The rate of all-cause stroke, TIA, and systemic embolism is comparable with other AMPLATZER registries (2.3% for the ACP1, 2.9% for the Amulet3). In the PFO/ASD group, the rate of stroke and TIA was numerically lower. This may be attributable to combined PFO/ASD closure in this group; however, the present study was not powered to detect such differences. A meta-analysis of six randomised trials, including 3,560 patients with a mean follow-up of 4.6 (2.0-5.9) years yielding about 25,000 patient-years, confirmed that stroke risk was significantly lower after transcatheter PFO closure than under antithrombotic therapy alone16. Despite an elderly patient cohort, major bleeding events during follow-up were rare and did not differ between the groups. The five-year follow-up of the PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL studies reported a major bleeding rate of 1.7%5. Of note, these populations were eligible for OAC, significantly younger, and at lower risk for stroke and bleedings. Consequently, our data show higher rates of all-cause and cardiovascular death in comparison to the above-mentioned trials.
Limitations
Although data were prospectively collected, this study has several limitations attributable to its non-randomised, observational, and retrospective design. It was not powered to detect differences in thromboembolic and bleeding events, as well as cardiovascular mortality. Despite adequate matching of the two groups, unmeasured confounders probably persist. TEE guidance was performed depending on the operator’s routine and preferences and varied among the three centres. Also, TEE follow-up was not available for all patients and was not assessed in a standardised manner by a core lab. This may have led to an underreporting of DRT and peri-device leaks for both groups.
Conclusions
In patients undergoing left atrial appendage closure with AMPLATZER systems, the use of a PFO or ASD for LA access is equally feasible and safe and offers similar late clinical outcomes in comparison to a TSP. Additional PFO or ASD closure does not increase risk and may yield further protection against systemic embolism.
|
Impact on daily practice LAAC is an established treatment option for stroke prevention in patients with AF as an alternative to OAC. While TSP is the standard access to the LA for LAAC with AMPLATZER devices, the technical feasibility of LAAC through a PFO/ASD has been shown for AMPLATZER devices. However, PFO/ASD access may be demanding and is therefore an option for advanced operators. |
Acknowledgements
C. Kleinecke, M. Fuerholz, E. Buffle, S. Gloekler, and B. Meier took part in the data evaluation and in the planning, writing, revising, and reviewing of the final draft of this manuscript. All co-authors contributed fully in terms of the design of the study, the evaluation of data, the actual manuscript preparation, and the revision and approval of the final submitted manuscript. As the corresponding author, S. Gloekler confirms that all authors have seen and approved the final text.
Funding
This study was supported by the Swiss Heart Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
J. Brachmann reports consulting fees from Abbott, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, LivaNova and Biotronik. F. Nietlispach is a consultant to Abbott, Edwards Lifesciences, and Medtronic. S. Windecker reports grants to the institution from Abbott, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Edwards Lifesciences. B. Meier is a consultant to Abbott. S. Gloekler reports grants to the institution from Abbott and a grant from the Swiss Heart Foundation. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

