
Drug-eluting stent (DES) implantation is the dominant revascularisation strategy for the treatment of ischaemic heart disease. Technological improvements led to a progressive reduction of the strut thickness, moving from 130 to 140 μm of the first-generation DES to the contemporary 50 and 60 μm of the latest generations1. The importance of strut thickness was first demonstrated in ISAR-STEREO 1 and 2 (Intracoronary Stenting and Angiographic Results Strut Thickness Effect on Restenosis Outcome), showing that the use of a thinner-strut bare metal stent (BMS) was associated with significant reduction of angiographic and clinical restenosis comparing stents with both the same or with a different design2,3.
In the DES era, the use of ultra-thin struts can offer the following potential advantages (Figure 1):
– Fast endothelialisation: thinner struts will favour the process of embedment and endothelialisation, thus minimising the risk of strut uncoverage. These factors account for the low rate of acute and subacute stent thrombosis observed with novel DES even with short dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT).
– Increased deliverability: ultra-thin strut DES show excellent deliverability and flexibility.
– Lower rate of restenosis: strut thickness has been recognised to impact on the degree of vessel injury and inflammation which has been associated with the risk of restenosis. Moreover, ultra-thin struts decrease the oscillatory shear stress, favouring physiological endothelialisation with less probability of restenosis4.
– Lower rate of periprocedural myocardial infarction: the implantation of a DES with a large footprint can potentially cause small side branch occlusions with a periprocedural rise of troponin. Usually, ultra-thin DES also have reduced strut width and an open-cell design which result in a minimal risk of footprint and side branch occlusion. While the Orsiro (Biotronik, Bülach, Switzerland) has a strut width of 75 μm, its competitor XIENCE (Abbott Vascular, Santa Clara, CA, USA) has a larger footprint (104 μm) which can potentially explain the higher rate of periprocedural myocardial infarction (MI) observed in the everolimus-eluting stent group5.
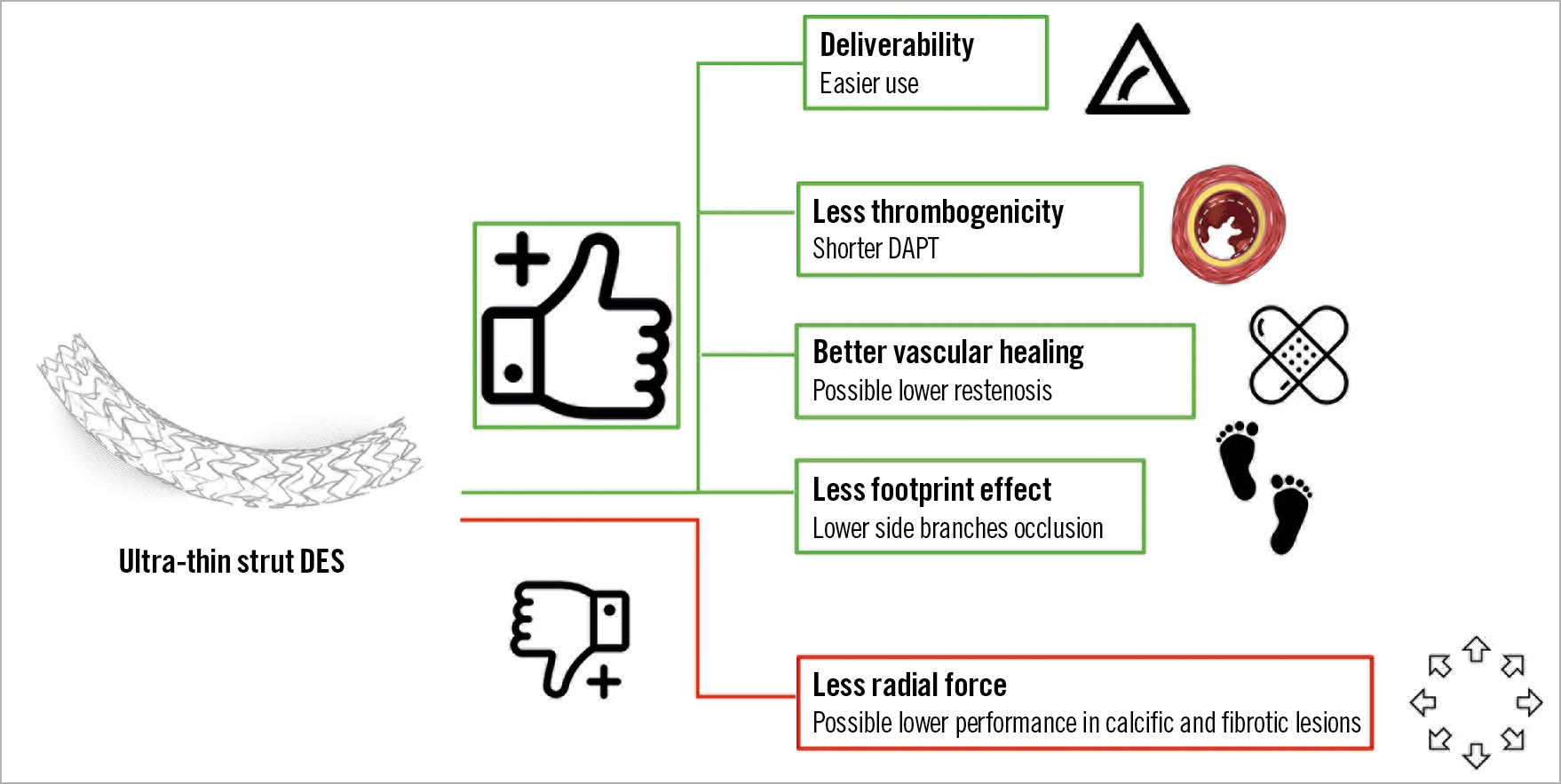
Figure 1. Possible advantages and disadvantages of ultra-thin strut DES. DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy; DES: drug-eluting stent
Nevertheless, the advantages of ultra-thin strut stents are theoretical and not always supported by consistent clinical data. The Orsiro is a metal sirolimus-eluting stent with a bioresorbable polymer (poly-L-lactic acid polymer) and a strut thickness of 60 μm for stent diameters ranging from 2.25 mm to 3.0 mm and a strut thickness of 80 μm for stent diameters of 3.5 and 4.0 mm. The stent has a silicone carbide coating and has a drug release time of 12 weeks. The superiority of the Orsiro over the everolimus-eluting XIENCE stent has been demonstrated in the Safety and Effectiveness of the Orsiro Sirolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System in Subjects With Coronary Artery Lesions (BIOFLOW V) trial. At three-year follow-up, the trial showed an ischaemia-driven revascularisation rate and a target vessel MI rate lower in the Orsiro group, even at the landmark analysis5. Notably, in the very thin strut biodegradable polymer everolimus-eluting and sirolimus-eluting stents versus durable polymer zotarolimus-eluting stents in all comers with coronary artery disease (BIO-RESORT) trial, the Orsiro reached non-inferiority but not superiority compared to its principal competitors6.
The current issue of EuroIntervention includes two studies – a large registry and a randomised study – both reporting the clinical outcome of the Orsiro stent.
The Swedish Coronary Angiography and Angioplasty Registry (SCAAR) reported the two-year outcome of 4,561 patients and 69,570 new-generation DES. Notably, the analysis was restricted to patients treated with a single stent at the index procedure. The occurrence of definite stent thrombosis was 0.67% with the Orsiro and 0.83% with other DES, target vessel revascularisation (TVR) was 1.6% with the Orsiro and 2.3% with other DES (hazard ratio [HR] 0.75, p=0.013), and the rate of MI was 6% with the Orsiro versus 5.2% with other DES7.
Even though the study was presented as a registry, it would be more appropriate to consider it as a retrospective analysis since the word registry assumes that we are dealing with unrestricted inclusion criteria. Unfortunately, the analysis excluded several patients who received different types of DES during the index procedure. The study reports a rate of stent thrombosis of less than 1% at two years and a TVR rate of less than 2%: differences favouring ultra-thin strut stents were numerically too small to have an impact on routine clinical activity.
The BIODEGRADE (Comparison of Biomatrix and Orsiro Drug Eluting Stent in AngioGraphic Result in patients with Coronary Artery DiseasE) study, from South Korea, evaluated the impact of reducing strut thickness in a randomised trial comparing the Orsiro stent in 1,175 patients to the BioMatrix™ (Biosensors, Singapore) stent (strut thickness 120 μm with a drug release time of 4 weeks) in 2,341 patients followed for 18 months8.
The study included a medium-risk population with a mean age of 63, 33% having diabetes. In 60% of cases the reason for coronary angiography was an acute coronary syndrome. The vast majority of the patients included in the trial had a single lesion treated with a mean stent length of 27 mm; 15% of the enrolled patients had a bifurcation lesion; no chronic total occlusions were included. Numerically, the results slightly favoured the Orsiro stent but failed to reach a statistically significant level for superiority with target lesion failure (TLF) of 2.9% versus 2.1%, ischaemia-driven target lesion revascularisation of 2.3% versus 2%, definite stent thrombosis of 0% versus 0.2%, and target vessel MI of 0% versus 0.3% for the BioMatrix versus the Orsiro8.
What did we learn and how should we proceed?
The reduction of strut thickness improves stent delivery and may help to reduce late lumen loss (LLL); however, even if this latter concept was largely demonstrated with BMS, in later-generation DES the presence of antiproliferative drugs mitigates the impact of strut thickness on LLL. Moreover, the ultra-thin strut design of the Orsiro stent could penalise its performance in severely calcified lesions, a subset of anatomy where stents with higher radial force could be preferable9. Nevertheless, in small vessel disease, the Orsiro seems to be better than other contemporary DES, suggesting a possible positive effect of ultra-thin struts in the treatment of lesions in vessels <2.5 mm10.
When we see so many studies reporting non-inferiority results, we understand the need to move into complex patients and lesions to set a real challenge for any new technology. The road needs to be steeper to understand who can run fast.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Mangieri has received an institutional grant from Boston Scientific and is part of the advisory board of Boston Scientific. A. Colombo has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

