
In the last decade, transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) has become an important alternative to surgical aortic valve replacement (sAVR) for those at intermediate and high surgical risk. The efficacy and safety of TAVI have been demonstrated in several randomised trials1-3. As a result there has been rapid growth in TAVI with more than 300,000 procedures performed worldwide. Patient selection and evaluation is best achieved by a Heart Team approach4. This shared decision making includes assessment of symptom severity and comorbidities4. Observational data suggest that coronary artery disease (CAD) co-exists in up to 60% of cases5. This high prevalence can be attributed to overlapping causative factors. CAD is an independent predictor of adverse outcomes in the surgical population and revascularisation is recommended in patients undergoing sAVR6. However, the management of CAD in patients undergoing TAVI is less clear. There are no randomised data, and outcomes from observational studies of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in TAVI are conflicting. This is probably attributable to a combination of heterogeneous risk factors and reliance on retrospective data.
In this issue of EuroIntervention, D’Ascenzo et al report the findings of a large meta-analysis of more than 8,000 patients from 13 studies7.
They evaluated the impact of the complexity of CAD (assessed using the SYNTAX score [SS]) on clinical outcomes in patients undergoing TAVI, and then determined the association between CAD, baseline and residual SS on 30-day and one-year outcomes. In this meta-analysis, complex CAD with a high baseline SS was associated with increased mortality at one year. Conversely, low residual SS was associated with improved one-year mortality.
Previous studies have also shown an increased risk of mortality associated with increasing SS8. The mortality risk associated with increased complexity and burden of concomitant CAD could be related to haemodynamic instability during the procedure9. Furthermore, incomplete revascularisation can lead to impaired contractile function following TAVI10. However, it is often difficult to determine the significance of CAD in patients with severe aortic stenosis (AS). Conventional indices of coronary physiology are of limited use in this cohort and underestimate the haemodynamic significance of individual lesions11. Symptom differentiation is further complicated by the clinical overlap between the two pathologies. Decreased coronary blood flow, increased microvascular resistance and increased afterload can manifest as supply-demand mismatch in severe AS in the absence of significant CAD12.
The role of PCI and optimal timing in TAVI patients
The findings of this meta-analysis highlight the importance of determining the role and optimal timing of PCI in TAVI patients. Although it is technically feasible to perform PCI post TAVI, coronary access and stent delivery may be more challenging. This is particularly relevant as TAVI expands into the lower-risk and younger population. PCI is not a low-risk procedure in haemodynamically significant AS and may cause acute decompensation13. Furthermore, each additional procedure adds further risk of adverse events, particularly in the presence of heavily calcified disease14. This becomes increasingly relevant in a higher-risk cohort where patients are frequently frail with multiple comorbidities.
This meta-analysis adds to the growing body of observational data on PCI in TAVI patients. However, the absence of randomisation in these studies introduces bias and the findings should be interpreted with caution. It is not possible to derive causality from observational data due to unknown confounders. This includes confounding by indication, whereby clinicians may withhold PCI in patients thought to be too high risk to undergo a prolonged PCI procedure. Few would question performing PCI in patients with unstable angina and treatable CAD (Figure 1)15. However, in the absence of randomised data, performing complex PCI in the context of severe AS and stable symptoms is difficult to justify. Determining which patients benefit from which strategy remains a challenge, particularly in patients with CCS class II angina. Results of the percutAneous Coronary inTervention prIor to transcatheter aortic VAlve implantaTION (ACTIVATION) trial (ISRCTN75836930), which aims to address this question, are widely anticipated and will facilitate the Heart Team decision-making process16.
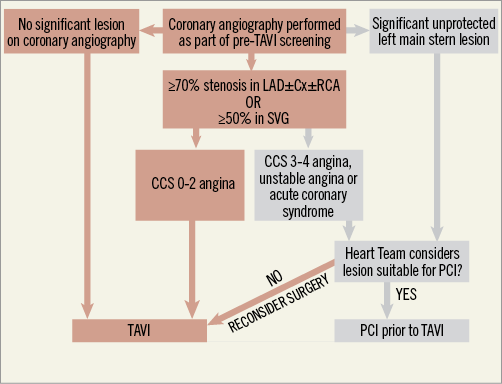
Figure 1. Percutaneous coronary intervention prior to TAVI. This flow diagram demonstrates identification and management of coronary disease. In the absence of randomised data, revascularisation should be reserved for patients with unstable angina or those presenting with an acute coronary syndrome (Figure adapted with permission from Khawaja et al)15.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

