A mandatory period of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) consisting of aspirin plus a P2Y12 inhibitor is recommended after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and/or acute coronary syndrome (ACS). However, the optimal DAPT duration, minimising bleeding risk while preserving efficacy, is still debated. Shortening DAPT by dropping the aspirin or the P2Y12 inhibitor and continuing with an indefinite maintenance of antiplatelet monotherapy is among the main strategies to reduce bleeding. Indeed, the introduction of newer drug-eluting stents (DES) with improved safety has allowed for the testing of increasingly abbreviated periods of DAPT. One month is the shortest DAPT duration after implantation of a DES, assessed in trials which include those comparing the clinical performance of different DES followed by 1-month DAPT in patients at high bleeding risk (HBR), and those comparing 1-month DAPT followed by aspirin or P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy versus longer DAPT durations1. In these latter randomised trials, shown in Figure 1, the monotherapy that followed 1-month DAPT was exclusively only aspirin in the One-Month DAPT trial, while it was one of the P2Y12 inhibitors or either aspirin or a P2Y12 inhibitor in the remaining trials2345. Overall, 1-month DAPT was associated with a neutral or favourable effect on bleeding without an increase in ischaemic events in all the aforementioned trials, except in the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial, which enrolled only ACS patients in whom the short (1-2 months) versus standard DAPT was associated with a higher risk of ischaemic events5. Therefore, this latter trial suggested that very short DAPT might not be sufficient in ACS, prompting the need for additional data exploring the safety and efficacy of 1-month DAPT according to clinical presentation with chronic coronary syndrome (CCS) or ACS.
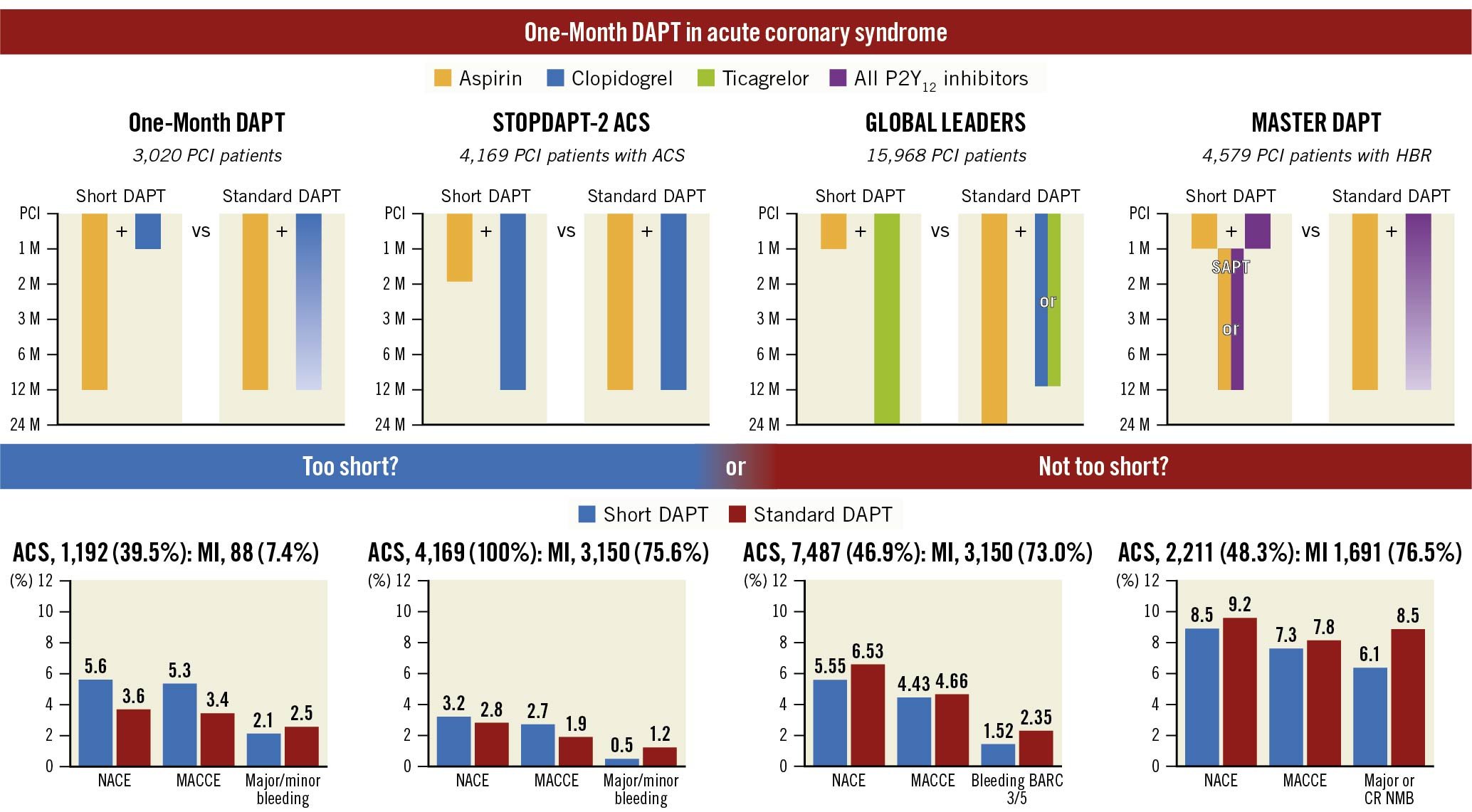
Figure 1. Outcomes of 1-month versus standard dual antiplatelet therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome from randomised studies. MACCE included cardiac or all-cause death, myocardial infarction, and stroke in all trials. In addition to those individual endpoints, target vessel revascularisation was included in the One-Month DAPT trial and definite stent thrombosis was included in the STOPDAPT-2 ACS. NACE included MACCE and bleeding. ACS: acute coronary syndrome; BARC: Bleeding Academic Research Consortium; CRNMB: clinically relevant non-major bleeding; DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy; HBR: high bleeding risk; MACCE: major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events; MI: myocardial infarction; NACE: net adverse clinical events; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; SAPT: single antiplatelet therapy
In this issue of EuroIntervention, Lee et al6 report the results of a post hoc subgroup analysis from the One-Month DAPT open-label, randomised trial. They explore outcomes among patients (n=3,020) assigned to 1-month DAPT followed by aspirin after polymer-free drug-coated stent (PF-DCS) implantation or to 6–12-month DAPT followed by aspirin after the implantation of a biodegradable polymer (BP)-DES, stratified according to CCS (n=1,828) or ACS (n=1,192). The One-Month DAPT trial showed that short DAPT after PF-DCS implantation was non-inferior to 6-12-month DAPT after BP-DES implantation with regard to a 1-year net clinical composite of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE, including cardiac death, non-fatal myocardial infarction [MI], target vessel revascularisation [TVR], and stroke), and major bleeding (5.9% vs 6.5%, p<0.001). These results were not consistent across the CCS and ACS subgroups. Among CCS patients, those randomised to short DAPT (n=933), compared with those assigned to standard DAPT (n=895), had a significantly lower net clinical endpoint (3.9% vs 6.5%, hazard ratio [HR] 0.59, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.39-0.90). This difference was driven by reductions in both components of the net clinical endpoint, including MACCE and major bleeding. Conversely, among patients with ACS, the net clinical endpoint was not significantly different but numerically higher in the short (n=574) versus standard (n=618) DAPT group (5.6% vs 3.6%, HR 1.57, 95% CI: 0.91-2.70) because of a numerical increase in MACCE and no differences in major bleeding. These opposite trends in the net clinical endpoint with short versus standard DAPT among CCS and ACS led to a significant interaction between treatment strategy and clinical presentation (p=0.005).
This subanalysis provides novel insights on the importance of patient selection when considering a short-DAPT strategy, questioning the safety of 1-month DAPT followed by aspirin monotherapy in ACS patients. However, due to the inherent limitations of subgroup analyses, these results should be interpreted with caution, taking into consideration the specific design of the One-Month DAPT trial. This was a strategy-based study, as different stent platforms with different DAPT regimens were compared, and thus it is challenging to establish the relative impact of the therapy or stent on outcomes. For instance, among ACS patients, the increase in MACCE with short DAPT was evident after 6 months and mostly driven by higher TVR, while no differences in cardiac death, MI or stent thrombosis were observed between the 2 compared DES-DAPT groups, suggesting the potential impact of stent-related factors. However, excluding TVR, the net clinical endpoint would remain in favour of short DAPT among CCS patients, while it would tend to be neutral in ACS patients. Therefore, the main finding on the differential effect of short DAPT according to clinical presentation remains unchanged, with no evidence of benefit or possible harm in ACS patients.
The unfavourable net clinical endpoint observed in the 1-Month DAPT trial among ACS patients is consistent with the results of the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial. This trial included only ACS patients, in whom the strategy of short DAPT (1-2 months) followed by clopidogrel monotherapy failed to attest noninferiority to standard DAPT for the net clinical benefit because, despite a slight reduction in bleeding, it was associated with an increase in MI5. Thus, these 2 studies suggested that 1-month DAPT, followed by aspirin or clopidogrel monotherapy, could be risky in ACS patients. On the other hand, these latter results differ from those of the subgroup analyses from the GLOBAL LEADERS and MASTER DAPT trials, in which 1-month versus standard DAPT reduced bleeding without increasing composite ischaemic events in ACS patients (Figure 1). However, the discordant results should be interpreted considering key differences across the trials. Indeed, in the GLOBAL LEADERS trial, ticagrelor, instead of aspirin or clopidogrel, was adopted as monotherapy after short DAPT, while in the MASTER DAPT trial mostly clopidogrel was used as monotherapy, but, in contrast with previous trials, only patients with HBR were included23. Despite the fact that the subgroup analyses should be interpreted with caution, the overall data cast a great deal of uncertainty on the effect of shortening DAPT to 1 month in ACS patients, and suggest the importance of the monotherapy type and patient selection. In this regard, in patients with HBR, the benefit of short DAPT, derived from the reduction of bleeding and related events, could be such to balance a possible intrinsic risk of ischaemic events. Patient selection may explain the opposite effects of short DAPT on bleeding observed among CCS and ACS patients in the 1-Month DAPT trial. Indeed, it is possible that in ACS patients the ischaemic risk prevailed over the very low bleeding risk, such that the standard versus short DAPT provided higher protection without increasing bleeding. Conversely, among CCS patients, the low ischaemic risk made longer DAPT unnecessary and even excessive, leading to an increased risk of overall events.
In conclusion, the 1-Month DAPT clinical presentation subanalysis, which was consistent with the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial, raised important concerns about the safety of 1-month DAPT followed by aspirin or clopidogrel monotherapy in unselected ACS patients. One-month DAPT may not be too short for ACS if it is followed by more potent P2Y12 inhibitors or given to selected ACS patients with HBR. However, additional data are needed to evaluate these possibilities and solve the dilemma of whether 1-month DAPT is too short or not too short in ACS patients.
Conflict of interest statement
P. Capranzano reports personal fees from Bayer, Daiichi Sankyo, Boehringer-Ingelheim and Chiesi, outside the submitted work.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

