
Abstract
Aims: The aim of the study was to establish the value of new-generation mechanical circulatory support (MCS) devices such as HeartMate PHP, Impella CP and PulseCath iVAC2.
Methods and results: We retrospectively analysed all consecutive elective high-risk PCI procedures performed in the Erasmus Medical Center (2011-2018) in order to compare MCS protected and unprotected patients. The primary endpoint was a composite of procedure-related adverse events including death (<24 hours), cardiac arrest, need for vasopressors, rescue MCS, endotracheal intubation and limb ischaemia with need for surgery. Secondary endpoints included 30-day survival. A total of 198 elective high-risk PCI patients were included (69 [35%] MCS protected, 129 [65%] MCS unprotected). When compared with unprotected patients, MCS protected patients had a significantly worse left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (25±10 vs 33±8%, p<0.01) and higher SYNTAX I score (33±11 vs 24±8, p<0.01). The primary endpoint occurred in 26 (20%) of the unprotected patients and in 6 (9%) of the MCS protected patients (OR 0.38, 95% CI: 0.15-0.97, p=0.04). Patients under 75 years of age, with a SYNTAX I score above 32 and with an LVEF below 30% showed most potential benefit from MCS. Survival during the first 24 hours after the procedure and at 30 days was significantly higher in MCS protected patients (100% vs 95%, p=0.04 at 24 hours, and 98% vs 87%, OR 10.32, 95% CI: 1.34-79.31, p=0.006 at 30 days).
Conclusions: In a consecutive real-world cohort of high-risk PCI patients, protection with new-generation MCS resulted in better procedural outcomes despite worse EF and more complex coronary artery disease at baseline. Larger prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings.
Introduction
Coronary artery bypass is the gold standard of care to treat patients with complex multivessel coronary artery disease1,2,3. Nevertheless, a significant number of patients are denied surgery because of frailty, poor left ventricular (LV) function and comorbidities. Percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) in vulnerable patients with complex coronary artery disease (CAD) may comprise atherectomy, repetitive and prolonged balloon inflations, complex stenting and high contrast load. The cumulative ischaemia that results from these repetitive coronary manipulations may trigger the deathly cardiogenic shock cascade with hypotension leading to reduced coronary perfusion and further reduction in cardiac output or ventricular arrhythmias. Pre-emptive mechanical circulatory support (MCS) can facilitate high-risk PCI4. Nevertheless, two randomised trials failed to show a benefit of the use of either an intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) or the Impella® 2.5L (Abiomed, Danvers, MA, USA) as compared to unprotected high-risk PCI5,6. Apart from possible methodological flaws in these trials, the overall performance of the IABP and the Impella 2.5L may be insufficient to provide adequate haemodynamic support. New-generation MCS devices were developed to generate either a higher or a pulsatile output and may be more effective. The Impella® CP (Abiomed) is a 14 Fr axial flow pump able to deliver 3.5 L/min continuous flow. The HeartMate™ percutaneous heart pump (PHP) (Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL, USA) is a 13 Fr-compatible device that is unsheathed across the aortic valve to a 24 Fr pump, generating flow up to 5.0 L/min, depending on the haemodynamic state7. The iVAC2L (PulseCath BV, Amsterdam, the Netherlands) is a 17 Fr bi-directional flow catheter which produces pulsatile support up to 2.0 L/min8,9,10 (Figure 1). The clinical value of these new MCS devices in high-risk PCI remains unclear. We therefore aimed to compare retrospectively the procedural outcome of high-risk PCI with or without protection with new-generation MCS.
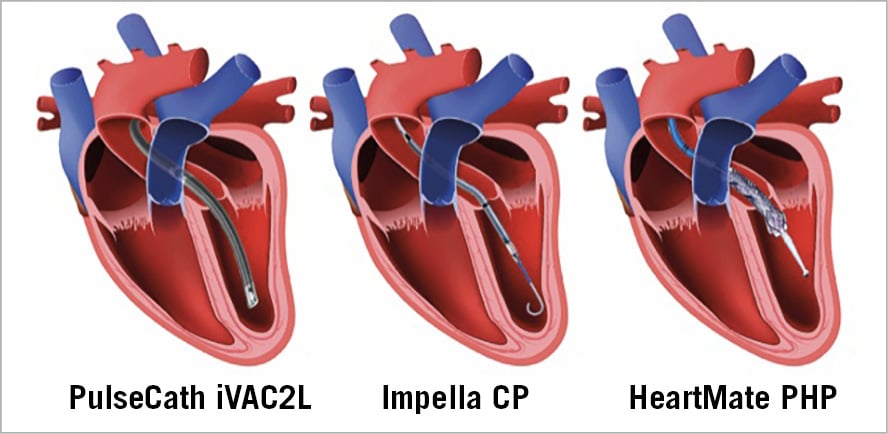
Figure 1. New-generation MCS devices: PulseCath iVAC2L, Impella CP and HeartMate PHP.
Methods
STUDY DESIGN
This is a retrospective cross-sectional study including all consecutive elective high-risk PCI conducted at the Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, between January 2011 and March 2018. We performed an automatic search of our local cath lab database in order to identify high-risk PCI patients having either a PCI of the unprotected left main or PCI of a single remaining vessel or PCI of the proximal LAD in patients with two- or three-vessel disease. Additionally, to be included patients had to have at least a moderately reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF <45%). Patients with indication for primary PCI (ST-elevation myocardial infarction [STEMI], non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction [nSTEMI] with persisting pain) and patients in shock, on inotropes or on mechanical ventilator support were excluded from the present analysis. The indication for high-risk PCI was based on Heart Team consensus, consisting of at least one cardiac surgeon and one interventional cardiologist. The decision to use MCS was at the operator’s discretion. The study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Since this is a purely observational and retrospective study, the need for ethics committee approval was waived. However, all patients signed informed consent including authorisation for anonymous data analysis for scientific purposes before the procedure.
DATA ANALYSIS
Baseline and procedural characteristics of the study patients were collected from our dedicated prospective database. Continuous variables are described as means±standard deviation and categorical variables as numbers and percentages. MCS protected and unprotected patients were compared using two-sided t-tests (continuous variables assuming normal distribution based on visual inspection of histograms, Q-Q plots and box plots) or χ2 tests (categorical variables) with calculation of odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals. The primary endpoint was a composite of procedure-related adverse events including death (up to 24 hours), cardiac arrest requiring resuscitation, hypotension with need for vasopressor support, need for rescue MCS, limb ischaemia with need for surgery and need for endotracheal intubation. To assess the interaction between candidate variables and potential benefit of MCS, a forest plot was constructed. Univariate logistic regression was used to identify all factors associated with the occurrence of the primary endpoint and a backward multivariate logistic regression model was constructed using all univariate candidate variables with a p-value below 0.10. The current status of the study patients (dead/alive) was collected using municipal civil registry data. Follow-up data were censored at 1,000 days. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were constructed and compared using the log-rank test. Logistic Cox regression analysis was used to calculate the hazard ratio for long-term survival taking unprotected patients as a reference1. Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS software, Version 24 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). A p-value below 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
STUDY PATIENTS
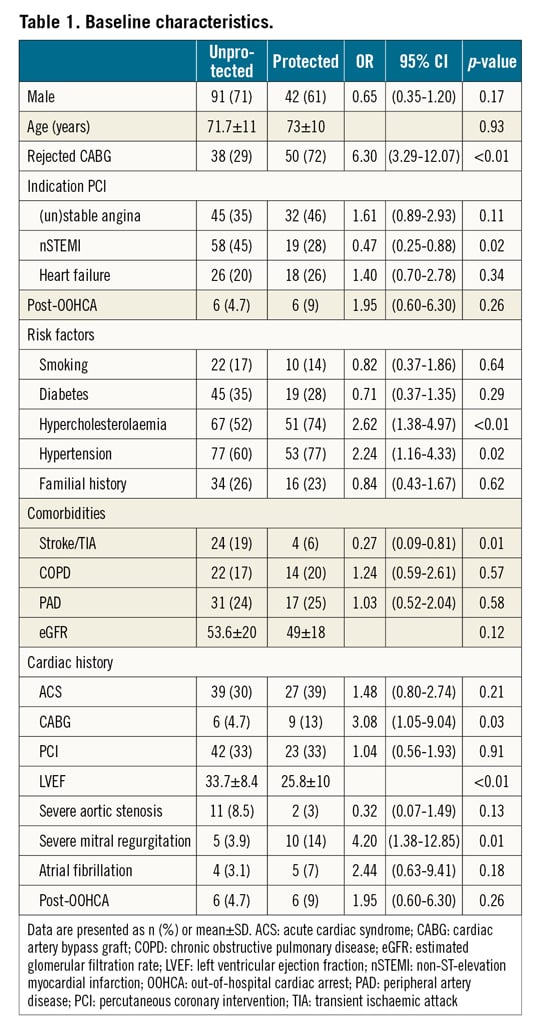
A total of 198 elective high-risk PCI patients were included. MCS protected PCI was performed in 69 (35%) patients. PulseCath iVAC2L was used in 26 patients (38%), HeartMate PHP in 25 patients (36%) and Impella CP in 18 patients (26%). In the remaining 129 (65%) patients, PCI was performed without MCS protection. One patient in whom the MCS device could not be positioned across the aortic valve due to severe aortic arch calcifications was not included in the present analysis. The baseline characteristics of the study patients are summarised in Table 1. When compared with unprotected patients, MCS protected patients were more often considered inoperable by Heart Team discussion, had a significantly worse LVEF (25±10 vs 33±8%, p<0.01) and more often had severe mitral regurgitation before the procedure.
PROCEDURAL CHARACTERISTICS
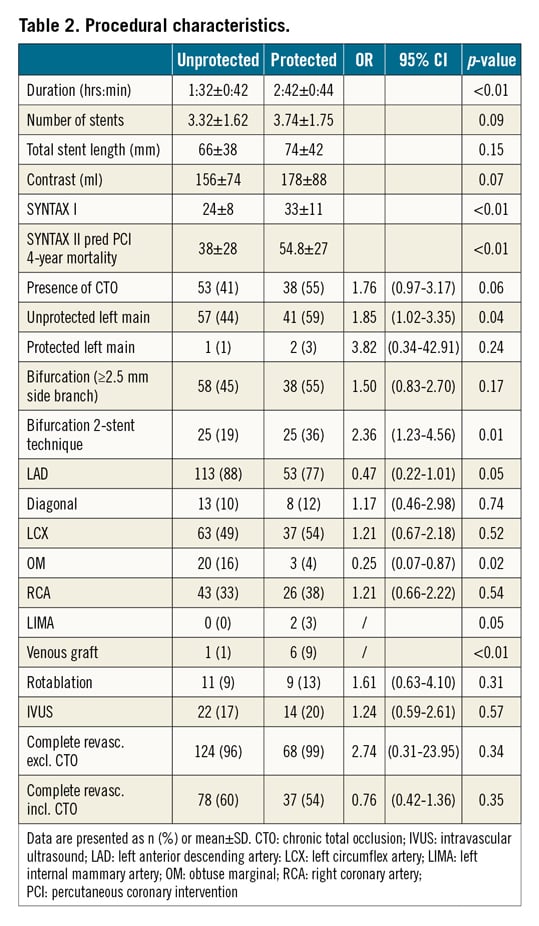
Procedural characteristics are summarised in Table 2. When compared with unprotected patients, MCS protected patients had a higher SYNTAX I score (33±11 vs 24±8, p<0.01), a higher SYNTAX II predicted four-year mortality (54±27 vs 38±28%, p<0.01), were more often treated for unprotected left main disease (59 vs 44%, p=0.04) and were more often treated with two-stent bifurcation strategies (36 vs 19%, p=0.01). The duration of the procedure was significantly longer in MCS protected patients (2:42±0:44 vs 1:32±0:42 hours, p<0.01). The completeness of revascularisation was comparable between the groups. Dedicated closure devices were used in MCS supported patients: ProGlide® (Abbott) in 39 patients (57%), MANTA™ (Teleflex, Morrisville, NC, USA) in 24 patients (35%) and Prostar® (Abbott) in 6 patients (9%).
SEVERE PROCEDURAL ADVERSE EVENTS
Severe procedural adverse events are summarised in Figure 2. The primary endpoint occurred in 26 (20%) of the unprotected patients and in 6 (9%) of the MCS protected patients (OR 0.38, 95% CI: 0.15-0.97, p=0.04). The primary endpoint occurred in one patient with Impella CP, two patients with HeartMate PHP and three patients with PulseCath iVAC2L. Regarding the components of the primary endpoint, MCS protected patients had significantly lower rates of death, cardiac arrest, cardioversion, chest compressions and need for endotracheal intubation. One MCS protected patient needed surgery for a major vascular complication. Additionally, three patients needed a one-unit blood transfusion (BARC type 3a bleeding), one patient with a tamponade needed pericardiocentesis (BARC type 3b bleeding) and one patient underwent percutaneous treatment of a femoral pseudoaneurysm. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression identified age and history of CABG to be associated with a higher incidence and the use of MCS to be independently associated with a lower incidence of severe procedural adverse events (Table 3, Table 4). Both SYNTAX I and II scores did not predict severe procedural adverse events. The forest plot is shown in Figure 3. The potential benefit of MCS seemed largest in patients under 75 years of age, with a SYNTAX I score above 32 and with a left ventricular ejection fraction below 30%.
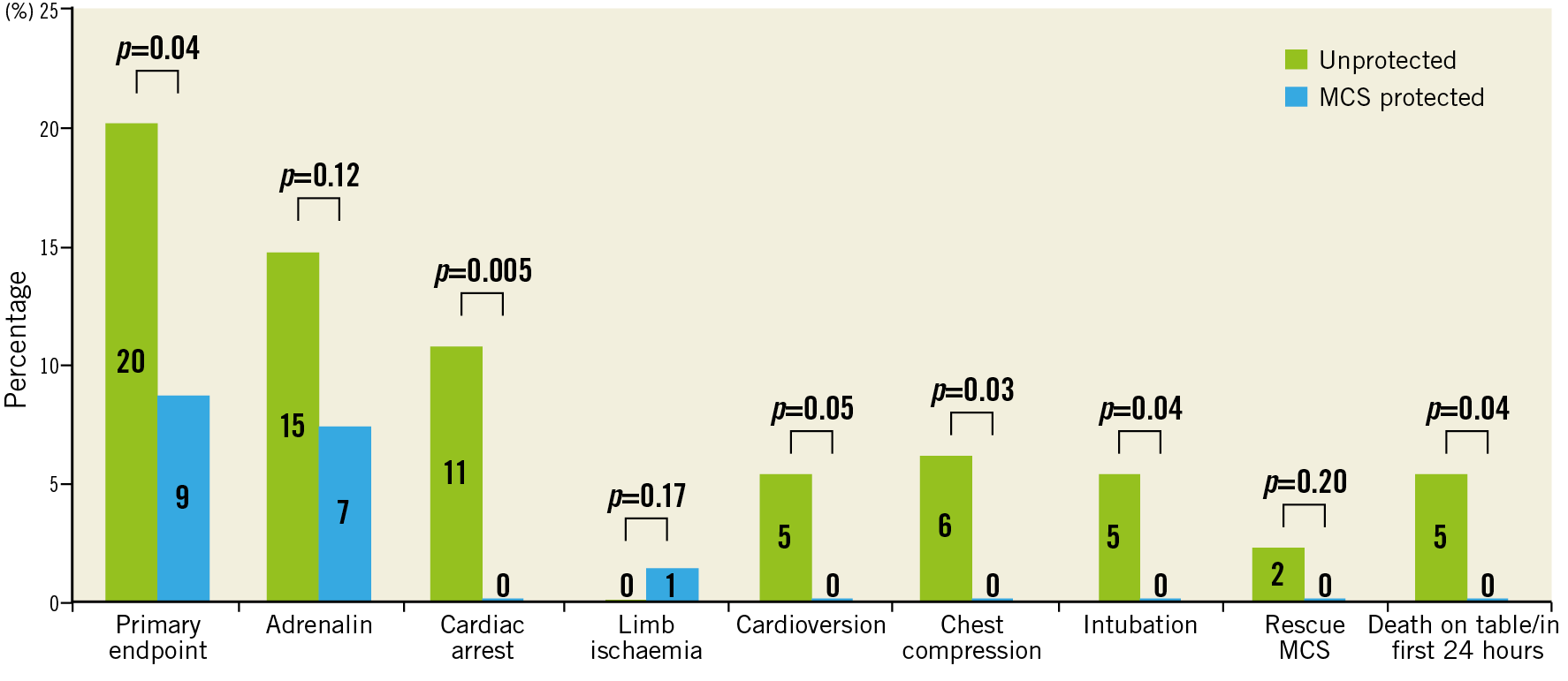
Figure 2. Components of the primary endpoint.
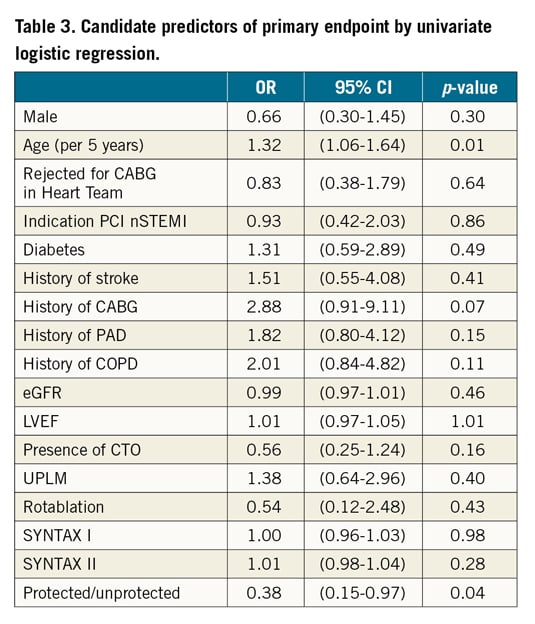
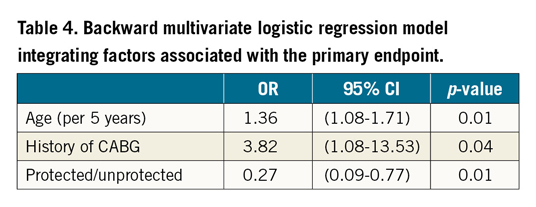
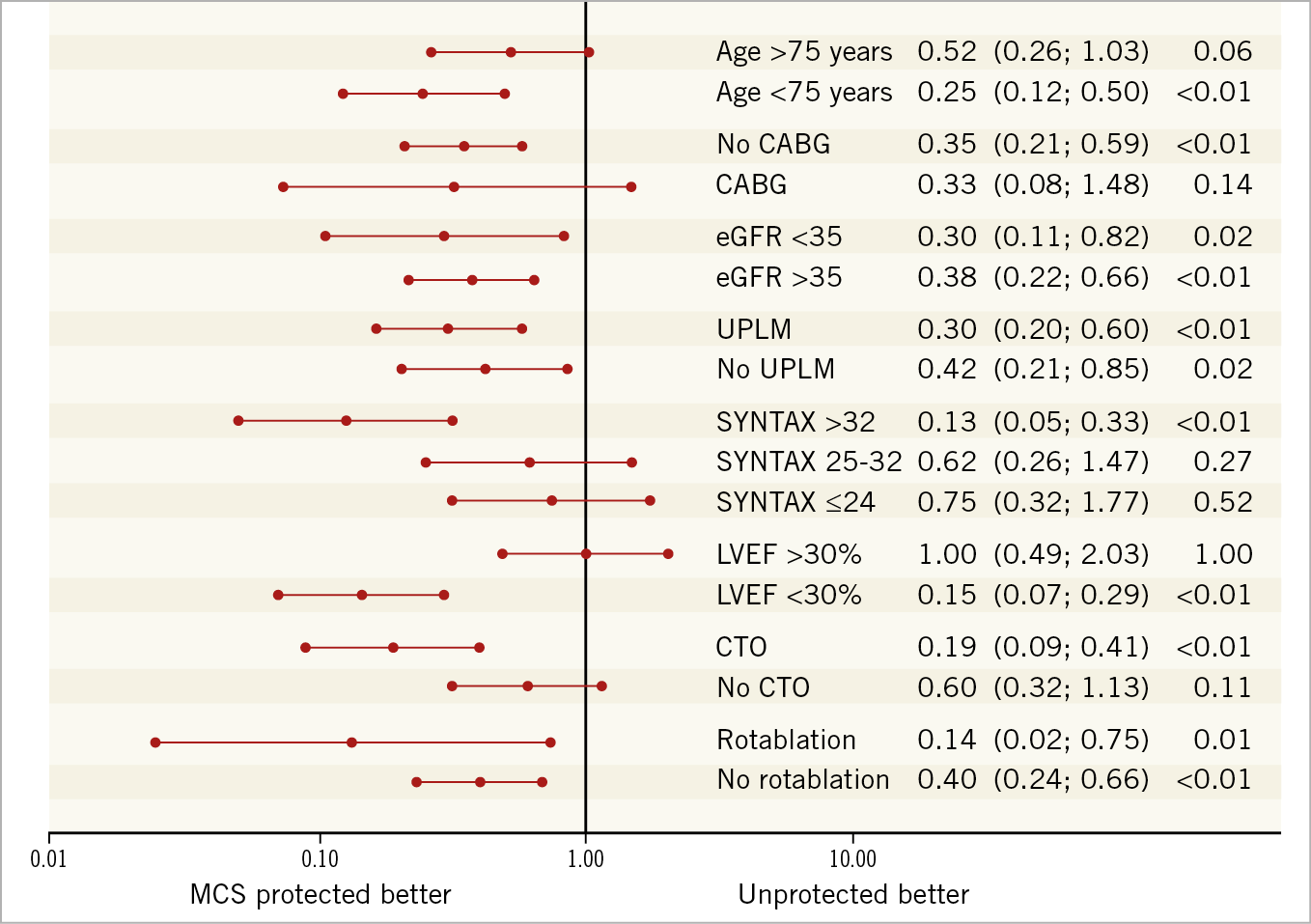
Figure 3. Forest plot.
SURVIVAL
No patients were lost to follow-up. Survival during the first 24 hours after the procedure and at 30 days was significantly higher in MCS protected patients (100% vs 95%, p=0.04 at 24 hours, and 98% vs 87%, OR 10.32, 95% CI: 1.34-79.31, p=0.006 at 30 days). One MCS protected patient died at day 16 due to refractory heart failure. Reasons for 30-day mortality in unprotected patients included death on the table due to technical complications such as dissection or perforation (n=6), refractory cardiogenic shock post PCI (n=6), and acute stent thrombosis (n=3). The cause of death could not be determined retrospectively in two patients. In MCS protected patients, after a mean follow-up of 591±500 days, survival was 81% (56/69 patients). In unprotected patients, after a mean follow-up of 631±714 days, survival was 73% (94/129 patients). Kaplan-Meier survival curves show an early separation with progressive increase during follow-up (Figure 4). Although there was a trend towards better survival in MCS protected patients, the log-rank test did not show statistical significance (p=0.12). The hazard ratio was 1.70 (95% CI: 0.85-3.40).
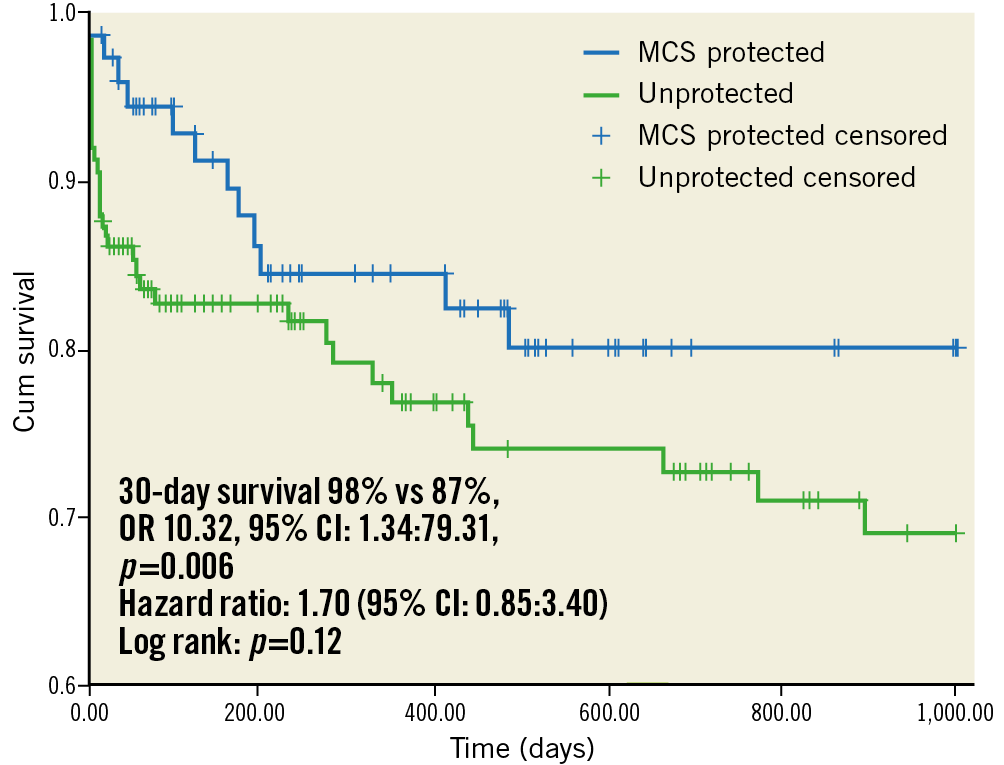
Figure 4. Kaplan-Meier survival curves.
Discussion
The key findings of this cross-sectional study on elective high-risk PCI are: 1) new-generation MCS devices increased procedural safety and were associated with improved 30-day survival; 2) MCS benefit was more pronounced in the setting of high SYNTAX I score (>32) and poor LVEF (<30%); and 3) access-site complications related to large-bore MCS were low.
Our data support the use of new-generation MCS devices in high-risk PCI and suggest a substantial additive procedural value not present with first-generation MCS devices. The Balloon Pump Assisted Coronary Intervention Study (BCIS-1) failed to show benefit in reducing major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events at 28 days associated with the use of pre-emptive IABP in high-risk PCI patients5. Additionally, the PROTECT II study also failed to show a reduction of a composite of major adverse events at 30 days associated with the use of the Impella 2.5L as compared with IABP6. The new-generation MCS devices analysed in the present report provide more powerful left ventricular support. While IABP (0.5 L/min) and Impella 2.5L generate only modest support, the Impella CP (+3.5 L/min) and HeartMate PHP (+5 L/min) are clearly more potent MCS devices4,7,8,9,10. Also, pulsatile displacement of 2 L/min by the iVAC2L may potentially be superior to continuous displacement of 2.5 L/min by an Impella device. While asynchronous pumps may increase left ventricular afterload by ejecting blood on top of the native systole, the counterpulsation strategy applied by the iVAC2L may lower afterload and may optimise ventricular arterial coupling, thereby aiming to reduce myocardial oxygen consumption and to promote native cardiac output. Second, the risk profile of the patients included in these trials with previous-generation MCS may not have been high enough to benefit fully from MCS. In our study, pre-emptive MCS benefit was limited to patients with SYNTAX I score >32 or LVEF <30%. This is in accordance with a pre-specified subgroup analysis of the PROTECT II trial showing that patients with three-vessel disease and the highest Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) score benefited most from MCS during high-risk PCI6. Patients in the PROTECT II trial had a lower SYNTAX score when compared with our MCS protected cohort (33.3±11.1 vs 29.8±13.3, p=0.05)6. Also, 30-day mortality in our unprotected cohort (13%) seemed to be higher when compared with other contemporary revascularisation studies on left main or multivessel PCI such as NOBLE, EXCEL, FREEDOM and SYNTAX reporting a 30-day mortality of between 0.8 and 1.3%11,12,13,14. The majority of our patients would not be eligible for these trials as they were turned down for CABG by Heart Team consensus. Furthermore, the EF of patients included in these revascularisation trials seemed more preserved, which may further explain differences in 30-day mortality. The number needed to treat to prevent one major adverse event in the present study was nine. Given the costs of MCS devices, fine-tuning of risk scores will be paramount to define the patient group that benefits most from MCS. Third, effects of MCS may only appear during longer-term follow-up. A post hoc analysis of the BCIS-1 trial showed reduced all-cause mortality in the IABP arm at a median follow-up of 51 months and a pre-specified analysis in the PROTECT II study showed a reduction of the primary endpoint with Impella 2.5L at 90 days6,15. Similar to both trials, Kaplan-Meier survival curves in our study continued to diverge during follow-up, suggesting an early treatment effect that is subsequently reinforced. Hypothetically, adequate MCS may allow optimal PCI conditions, complex stent techniques and increase the likelihood of complete revascularisation. Furthermore, MCS effects on periprocedural ischaemia and type 2 myocardial infarctions may only manifest later and result in better long-term outcome because of a lower risk of fatal arrhythmias and adverse ventricular remodelling. Fourth, in line with our results, rates of procedural complications such as ventricular arrhythmias requiring chest compressions and severe hypotension requiring vasopressors were significantly lower with IABP in the BCIS-1 trial5. Finally, the crossover rate in the BCIS-1 trial was 18%, and the PROTECT II trial was prematurely stopped after inclusion of 69% of the target population of patients, rendering both trials underpowered5,6.
Further adequately powered research should focus on refined patient selection and might need to target patients with high SYNTAX I scores and LVEF <30% to establish the use of pre-emptive MCS placement in high-risk PCI. Also, haemodynamic and clinical studies comparing different MCS platforms (including continuous vs pulsatile flow) may help to unravel device-specific mechanisms of LV support and potentially develop a more patient-tailored MCS selection. A few smaller trials are currently underway. The PULSE trial (NCT03200990) is addressing the haemodynamic effects with iVAC2L and Impella CP in 40 high-risk PCI patients in order to establish the difference between continuous and pulsatile flow devices. SHIELD II, a randomised trial comparing PHP with Impella CP in high-risk PCI (NCT02468778), was stopped because of selected device malfunctioning. Other MCS trials are focusing mainly on cardiogenic shock and STEMI patients. Previously, the IABP-SHOCK II trial failed to show 30-day survival benefit of IABP in STEMI patients with cardiogenic shock16 and the IMPRESS trial did not show 30-day survival benefit of Impella CP versus IABP in cardiogenic shock patients17. The Danish cardiogenic shock trial (NCT01633502) is currently randomising 360 patients with severe cardiogenic shock to optimal medical therapy (+/- IABP) and Impella CP. The Door to Unloading (DTU) trial (NCT03000270) aims to investigate whether unloading the ventricle with Impella CP prior to primary PCI may reduce infarct size in anterior STEMI patients. The EURO SHOCK heart attack study aims to investigate whether early insertion of veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) in shocked STEMI patients may improve survival.
Pre-emptive use of large-bore MCS mandates a scrutinised access-site management. In our study vascular complications were rare. Preprocedural planning included comprehensive evaluation of the peripheral arterial tree by multislice computed tomography (MSCT) in selected cases. Ultrasound-guided femoral artery access was routinely performed in all patients. Additionally, operators involved in the MCS programme were highly experienced with suture-based and plug-based closure devices such as ProGlide, Prostar and MANTA.
Limitations
This single-centre retrospective study with a modest sample size has inherent limitations of selection and operator bias. Our findings seem limited to institutions with ample experience of large-bore arteriotomies. Because MCS protected patients had much higher SYNTAX scores and worse LVEF than unprotected patients, propensity matching seemed less relevant. Nevertheless, despite worse baseline characteristics, MCS protected patients fared better, and one might assume that differences in procedural adverse events and survival might have been even more pronounced in a properly matched cohort or in a randomised clinical trial. Finally, the three types of assist device used are clearly different in terms of mechanism and level of support, and our results should be regarded as hypothesis-generating.
Conclusions
In a consecutive cohort of high-risk PCI patients, protection with new-generation MCS devices resulted in better procedural outcomes despite worse EF and more complex coronary artery disease at baseline. Larger prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings.
|
Impact on daily practice Interventional cardiologists should consider pre-emptive MCS when revascularising patients with complex coronary artery disease (SYNTAX score >32) and poor LVEF (<30%). |
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

