Abstract
Background: Previous studies have reported the value of quantitative flow ratio (QFR) to assess the physiological significance of non-culprit lesions (NCLs) in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients and of optical coherence tomography (OCT)-defined thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA) to identify non-culprit vulnerable plaques.
Aims: We sought to systematically compare long-term NCL-related clinical prognosis in an AMI population utilising acute Murray fractal law-based QFR (μQFR) values and OCT-defined TCFA.
Methods: Three-vessel OCT imaging and μQFR assessment were conducted in 645 AMI patients, identifying 1,320 intermediate NCLs in non-infarct-related arteries. The primary endpoint was a composite of cardiac death, NCL-related non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), and NCL-related unplanned coronary revascularisation, with follow-up lasting up to 5 years.
Results: The primary endpoint occurred in 59 patients (11.1%). OCT-defined TCFA independently predicted patient-level (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 3.05, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.80-5.19) and NCL-specific primary endpoints (adjusted HR 4.46, 95% CI: 2.33-8.56). The highest event rate of 29.6% was observed in patients with NCLs that were TCFA (+) with μQFR ≤0.80, compared to 16.3% in those that were also TCFA (+) but with μQFR>0.80, 6.0% in those that were TCFA (–) with μQFR ≤0.80, and 6.6% in those that were TCFA (–) with μQFR>0.80 (log-rank p<0.001). TCFA was an independent predictor for the primary endpoint in ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI; adjusted HR 3.27, 95% CI: 1.67-6.41) and non-STEMI (adjusted HR 3.26, 95% CI: 1.24-8.54) patients, whereas μQFR ≤0.80 was not.
Conclusions: When assessing NCLs during the index procedure in AMI patients, OCT-defined TCFA serves as the dominant prognostic predictor for long-term clinical outcomes, rather than μQFR-determined physiological significance.
Non-culprit lesions (NCLs) in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) may be associated with an increased risk of future adverse cardiac events123. In addition to coronary angiography, coronary physiology and plaque morphology are two ways to evaluate these lesions4.
Although invasive physiological assessment for intermediate coronary stenosis is the standard care in stable patients, its superiority for achieving complete revascularisation in AMI patients remains controversial. Previous studies have suggested that fractional flow reserve (FFR) may underestimate lesion severity during the acute phase, while the instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR) might overestimate it56, raising concerns about their reliability for evaluating NCLs, especially at the time of primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)78. So far, head-to-head comparisons between FFR-guided and conventional angiography-guided strategies for evaluating NCLs have produced inconsistent results910, and a recent study indicated that FFR-guided complete revascularisation during the index hospitalisation did not yield better outcomes compared to a culprit-only strategy11. Quantitative flow ratio (QFR), enabling estimation of FFR from coronary angiography12131415, may be superior to guidewire-based coronary physiology when assessing NCLs in an AMI population161718. Murray fractal law-based QFR (μQFR), the latest generation of QFR, enables rapid FFR calculation from a single angiographic view, with high diagnostic accuracy for functionally significant coronary stenosis19.
Intravascular optical coherence tomography (OCT)-defined thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA) has been shown to be efficacious when assessing intermediate NCLs in stable as well as AMI patients, including those who were FFR-negative202122.
This study aimed to systematically investigate the association of acute μQFR values and OCT-defined TCFA with long-term NCL-related clinical prognosis during the index procedure of patients presenting with an AMI at both the patient and lesion levels.
Methods
Study population
Patients qualified for inclusion if they were aged 18 years or older, had successfully undergone primary or urgent PCI of the culprit lesion for AMI (ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction [STEMI] or non-STEMI [NSTEMI]), and had undergone OCT examination of all three major epicardial coronary arteries. The main exclusion criteria were cardiogenic shock, end-stage renal disease, severe liver dysfunction, and contrast allergy. Patients with left main disease, chronic total occlusion, extreme tortuosity, or severe calcification were also excluded because of potential difficulties in performing OCT. This was a retrospective study of 1,118 eligible AMI patients who underwent three-vessel OCT imaging at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University (Harbin, China) between January 2017 and May 2019. Among them, 235 patients were excluded from the analysis for the following reasons: (i) suboptimal OCT imaging (i.e., massive thrombus) or short OCT pullback less than two-thirds of the artery length (n=164); (ii) previous PCI or coronary artery bypass grafting (n=62); (iii) coronary spasm due to the OCT procedure (n=2); and (iv) in-hospital death (n=7). We further excluded 151 patients without intermediate NCLs on coronary angiography (i.e., 30-90% visible diameter stenosis), 61 patients exhibiting NCLs solely in infarct-related arteries (IRAs), 20 patients with poor angiographic quality, and 6 patients with severe vessel overlap or tortuosity. Ultimately, 645 patients with evaluable three-vessel OCT imaging and μQFR data were included in the study and received scheduled clinical follow-up after discharge (Figure 1).
The study was approved by the ethics committee of our institution, and all patients provided written informed consent. The diagnostic criteria for AMI, means of identification of the culprit lesion at baseline, and detailed definitions of traditional coronary risk factors are presented in Supplementary Appendix 1.
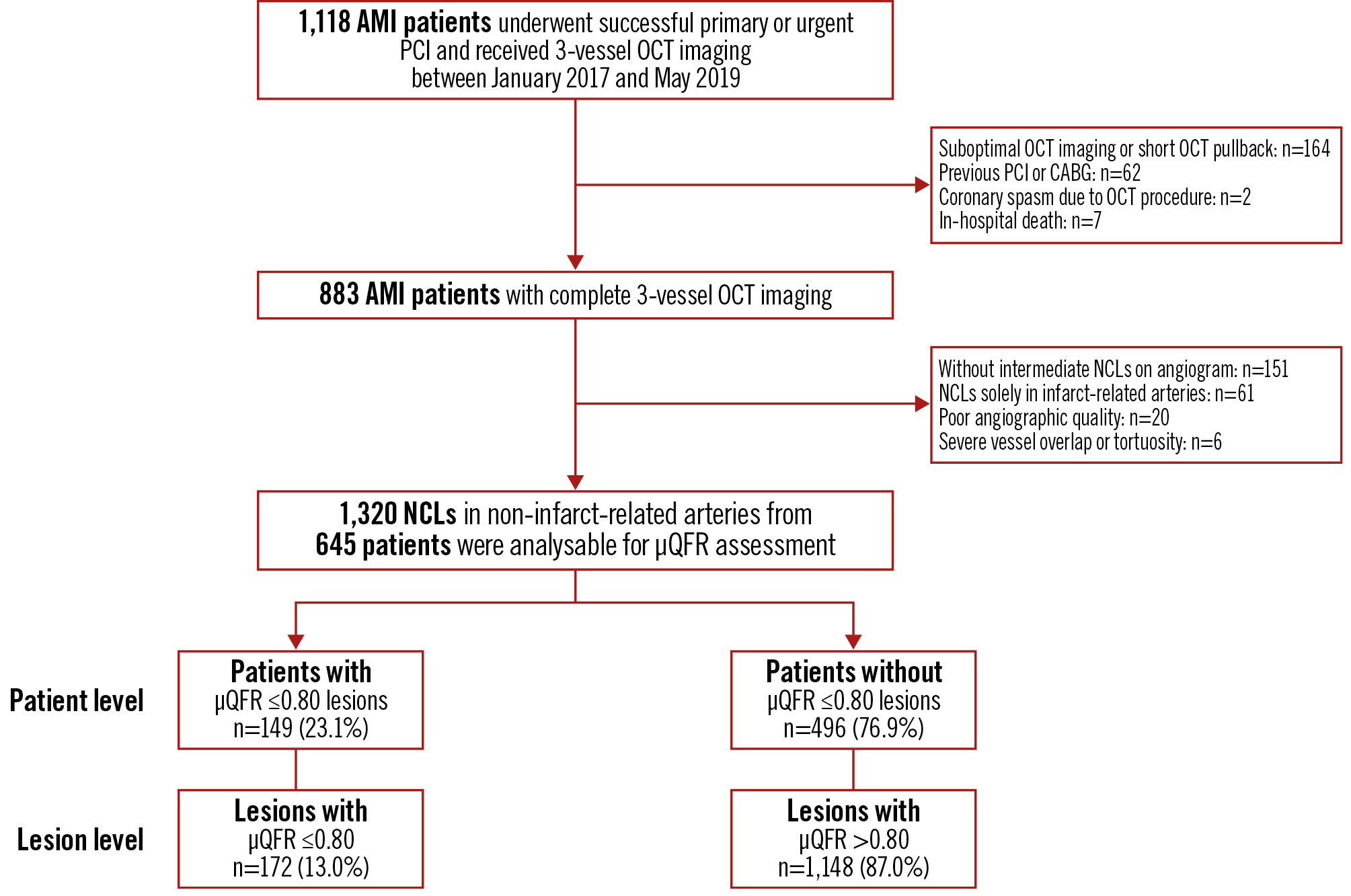
Figure 1. Study flowchart. In this study, the full analysis set included 645 AMI patients, encompassing a total of 1,320 NCLs. Among these, 149 patients (23.1%) were identified, with 172 NCLs between them (13.0%) having a μQFR ≤0.80, and the remaining 496 patients (76.9%) presented with NCLs all exhibiting a μQFR >0.80. μQFR: Murray fractal law-based quantitative flow ratio; AMI: acute myocardial infarction; CABG: coronary artery bypass grafting; NCL: non-culprit lesion; OCT: optical coherence tomography; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
Angiography acquisition and analysis
Coronary angiography was performed using standard techniques. Quantitative coronary angiographic analyses were performed for eligible NCLs (i.e., 30-90% visible diameter stenosis) using the Cardiovascular Angiography Analysis System (CAAS) version 5.10.1 (Pie Medical Imaging). After selection of end-diastolic frames and calibration using the catheter tip, the reference vessel diameter, minimal lumen diameter, diameter stenosis, and lesion length were measured.
µQFR computation and analysis
Offline μQFR analysis of NCLs in non-IRAs was conducted using AngioPlus Core 2.0 (Pulse Medical Technology), based on angiograms from the index procedure, by investigators blinded to OCT data and clinical outcomes. In this study, a new generation of artificial intelligence (AI)-powered μQFR was used for calculation19. The detailed methodology for μQFR computation has been reported previously19 and is described in Supplementary Appendix 1. Briefly, from a single angiographic projection with optimal visualisation (minimal foreshortening and vessel overlap), hyperaemic flow velocity was calculated by dividing the length of the centreline by the contrast dye filling time of the artery. A key frame with a sharp luminal contour on a major epicardial coronary artery containing the evaluable NCL was selected for subsequent analysis. Luminal contours of scanned vessels and major side branches were automatically delineated and manually corrected as needed. AI algorithms based on Murray’s fractal law were used to reconstruct the reference diameter function. Finally, pressure drop was calculated using fluid dynamic equations with hyperaemic flow velocity as a boundary condition, and μQFR was available for each NCL. In this study, we analysed 1,320 intermediate NCLs from 952 vessels in 645 patients with AMI, demonstrating an average of 1.39 NCLs per vessel, which is a relatively reasonable number. However, there is currently no clear consensus on how to address the effects of tandem lesions on μQFR measurements. To minimise the impact of tandem lesions on μQFR calculations, our study estimated μQFR for each individual lesion. We referenced the work by Guan et al23, which utilised the “virtual stent technique”, a built-in function of the μQFR system. In this method, a “virtually implanted stent” is marked using stent length markers at the precise location of the implantation site, with proximal and distal markers specified to obtain ΔμQFR. The system then calculates the μQFR of the target NCL as 1.0 minus ΔμQFR. An NCL was considered flow-limiting if the μQFR was ≤0.80, a threshold that has been widely utilised in recent studies1517181924. Patients with at least one NCL with μQFR ≤0.80 are termed the μQFR-positive group, while patients with exclusively μQFR>0.80 lesions are termed the μQFR-negative group.
OCT imaging acquisition and analysis
OCT imaging was acquired using a commercially available frequency domain system (OPTIS [Abbott]), first, in the treated infarct-related artery and, then, in the non-infarct-related arteries. All OCT images were analysed in the Intravascular Imaging and Physiology Core Lab of our centre by analysts who were blinded to patient outcomes. Coregistration of the angiograms and OCT was performed automatically or using fiduciary points (i.e., side branches) when online angiographic coregistration was not successful.
The OCT analyses have been detailed in Supplementary Appendix 12526. Briefly, NCLs identified by OCT were untreated coronary segments with luminal narrowing and a loss of the normal vessel wall architecture (i.e., intima, media, and adventitia)27. After successful intervention of the culprit lesion, NCLs that were deemed to be clearly severe (i.e., >90% angiographic diameter stenosis) and/or had a Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction flow <3 were also eligible for revascularisation. Management was left to the discretion of the interventional cardiologist, and lesions scheduled for staged revascularisation were also excluded from the study. To be considered as two separate NCLs in the same vessel, the intervening reference segment had to be at least 5 mm in length on the longitudinal OCT view. TCFA was defined as lipidic plaque with the thinnest fibrous cap thickness <65 μm and a maximum lipid arc >180°202122.
Clinical follow-up
Follow-up information was obtained at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after discharge and annually thereafter by clinical visit or telephone contact. Patients were censored at 5 years (with a 30-day window) or at the last known contact. For the patient-level analysis, the primary endpoint was a composite of adverse cardiac events, including cardiac death, NCL-related non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), and NCL-related unplanned coronary revascularisation. For the lesion-level analysis, cardiac death without an angiogram at the time of the event was not included. All clinical outcomes were defined according to the Academic Research Consortium guidelines, and detailed definitions of adverse cardiac events are provided in Supplementary Appendix 128. An independent clinical endpoint committee consisting of three experienced interventional cardiologists (T. Chen, J. Tan, and X. Liu), who were blinded to the OCT and μQFR data, reviewed and adjudicated all events. When possible, each new MI or revascularisation was assigned to a specific coronary lesion by comparison of baseline and event angiograms, and an NCL-related event was adjudicated as occurring in initially untreated coronary segments.
Statistical analysis
Categorical variables have been presented as n (%) and were compared using the Pearson’s chi-squared test or the Fisher’s exact test, depending on the size of the category cell. Normality of continuous data was assessed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Continuous variables are presented as mean±standard deviation (SD) or median (interquartile range [IQR]) and were compared using the Student’s t-test or the Mann-Whitney U test, respectively. Data were analysed on a per-patient basis for clinical characteristics and on a per-lesion basis for comparison of lesion characteristics and physiological indices. To account for the potential clustering effects of multiple NCLs within a single patient, we used generalised estimating equations to compare characteristics of NCLs with μQFR ≤0.80 and μQFR>0.80. Estimated means±SD are presented as summary statistics. Independent predictors of μQFR ≤0.80 were determined by a binary logistic regression model which included independent variables demonstrating a significant association in the univariate analyses (p<0.05). Prior to this, variance inflation factors (VIF) were calculated through linear regression analysis to assess the presence of multicollinearity among the independent variables, with a VIF value of less than 10 often considered an acceptable threshold, indicating that multicollinearity is not a major concern. The Kaplan-Meier estimator was used to calculate time-to-first event rates, and a log-rank test was performed to assess the differences in event-time distributions among groups. A univariate Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to estimate the hazard ratio (HR) and its corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI). A multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to identify adjusted prognostic factors. The patient-level multivariate model included clinically relevant baseline variables (age, sex, coronary risk factors, and clinical presentation). The lesion-level multivariate model was adjusted for other OCT characteristics with significant effects on clinical outcomes in the univariable analysis assessed within the same NCL (p<0.05). Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 26.0 (IBM), with a 2-tailed p-value <0.05 considered statistically significant.
Results
Baseline clinical characteristics
Baseline clinical characteristics are summarised in Table 1. The average age of the 645 patients was 58.1±11.1 years, with 25.7% being female and 69.9% presenting with STEMI. Offline μQFR assessment indicated that 149 (23.1%) patients had at least one NCL with a μQFR ≤0.80, while 496 (76.9%) patients had no NCL with a μQFR ≤0.80. Patients with at least one lesion with a μQFR ≤0.80 were characterised by older age, higher female representation, and STEMI on admission. Medication use at discharge was comparable among groups regardless of μQFR stratification.
Table 1. Baseline clinical characteristics.
| Overall patients (N=645) | μQFR-positive group (n=149, 23.1%) | μQFR-negative group (n=496, 76.9%) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 58.1±11.1 | 59.7±10.4 | 57.6±11.3 | 0.043 |
| Female | 166 (25.7) | 48 (32.2) | 118 (23.8) | 0.039 |
| Coronary risk factors | ||||
| Hypertension | 289 (44.8) | 72 (48.3) | 217 (43.8) | 0.325 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 379 (58.8) | 88 (59.1) | 291 (58.7) | 0.932 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 157 (24.3) | 33 (22.1) | 124 (25.0) | 0.477 |
| Current smoker | 326 (50.5) | 69 (46.3) | 257 (51.8) | 0.238 |
| CKD: eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 66 (10.2) | 20 (13.4) | 46 (9.3) | 0.143 |
| Clinical presentation | 0.046 | |||
| STEMI | 451 (69.9) | 114 (76.5) | 337 (67.9) | |
| Non-STEMI | 194 (30.1) | 35 (23.5) | 159 (32.1) | |
| Laboratory data | ||||
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 175.0±51.5 | 168.4±52.6 | 177.0±51.1 | 0.083 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 116.1 [79.7-174.5] | 123.2 [90.3-169.3] | 115.6 [77.3-180.3] | 0.289 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 108.9±40.4 | 104.0±39.5 | 110.4±40.6 | 0.093 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 48.7±15.9 | 47.4±14.5 | 49.0±16.3 | 0.291 |
| hs-CRP, mg/L | 4.5 [2.1-9.3] | 4.5 [1.9-10.2] | 4.5 [2.1-9.2] | 0.759 |
| HbA1c, % | 6.2±1.3 | 6.3±1.3 | 6.2±1.4 | 0.763 |
| Medication at discharge | ||||
| Aspirin | 640 (99.2) | 147 (98.7) | 493 (99.4) | 0.713 |
| P2Y12 inhibitor | 639 (99.1) | 147 (98.7) | 492 (99.2) | 0.912 |
| Ticagrelor | 380 (58.9) | 86 (57.7) | 294 (59.3) | 0.735 |
| Clopidogrel | 271 (42.0) | 62 (41.6) | 209 (42.1) | 0.909 |
| Dual antiplatelet therapy | 635 (98.4) | 146 (98.0) | 489 (98.6) | 0.602 |
| Statins | 641 (99.4) | 146 (98.0) | 495 (99.8) | 0.061 |
| Values are n (%), mean±SD, or median [IQR]. μQFR: Murray fractal law-based quantitative flow ratio; CKD: chronic kidney disease; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c: glycated haemoglobin c; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; hs-CRP: high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; IQR: interquartile range; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; SD: standard deviation; STEMI: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction | ||||
Different lesion characteristics between µQFR ≤0.80 versus µQFR >0.80
A total of 1,320 untreated intermediate NCLs (median 2.0 [IQR 1.0-3.0] per patient) were identified. The mean diameter stenosis of these lesions was 42.4±10.1%, and the mean μQFR was 0.90±0.10 (Table 2). Specifically, μQFR was positive (≤0.80) in 172 lesions (13.0%) and negative (>0.80) in 1,148 lesions (87.0%). Lesions with μQFR ≤0.80 were more frequently located in the left anterior descending artery (LAD), exhibited greater angiographic diameter stenosis, and had a higher prevalence of TCFA (26.2% vs 18.8%; p=0.025) compared to those with μQFR>0.80 (Table 2). Additionally, the presence of cholesterol crystals (32.6% vs 21.8%; p=0.004) and layered tissue (63.4% vs 46.9%; p<0.001) were more common in μQFR-positive lesions.
In the multivariable analysis, only LAD location (odds ratio [OR] 2.23, 95% CI: 1.51-3.27; p<0.001), lipid core length (OR 1.04, 95% CI: 1.02-1.05; p<0.001), and minimal lumen area (OR 0.41, 95% CI: 0.34-0.51; p<0.001) were independently associated with μQFR ≤0.80 (Supplementary Table 1). The VIF calculated using linear regression indicated no evidence of multicollinearity among the independent variables (Supplementary Table 2).
Table 2. Comparative analysis of NCL characteristics between those with μQFR ≤0.80 and μQFR >0.80.
| Lesion characteristics | Overall lesions (N=1,320) | Lesions with μQFR ≤0.80 (n=172, 13.0%) | Lesions with μQFR >0.80 (n=1,148, 87.0%) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coronary physiology index | ||||
| μQFR | 0.90±0.10 | 0.68±0.12 | 0.93±0.04 | <0.001 |
| Angiographic characteristics | ||||
| Lesion location | <0.001 | |||
| LAD | 445 (33.7) | 92 (53.5) | 353 (30.7) | <0.001 |
| LCx | 428 (32.4) | 53 (30.8) | 375 (32.7) | 0.574 |
| RCA | 447 (33.9) | 27 (15.7) | 420 (36.6) | <0.001 |
| Reference vessel diameter, mm | 3.1±1.4 | 2.8±0.5 | 3.1±1.5 | 0.003 |
| Minimal lumen diameter, mm | 1.8±0.8 | 1.3±0.4 | 1.8±0.8 | <0.001 |
| Diameter stenosis, % | 42.4±10.1 | 54.3±11.4 | 40.7±8.6 | <0.001 |
| Lesion length, mm | 17.4±9.1 | 22.1±11.7 | 16.7±8.4 | <0.001 |
| OCT characteristics | ||||
| Distance from coronary ostium to MLA site, mm | 32.0±28.7 | 30.2±16.9 | 32.3±30.1 | 0.383 |
| Minimal fibrous cap thickness, μm | 105.7±56.2 | 102.2±58.7 | 106.3±55.8 | 0.399 |
| Mean lipid arc, ° | 170.9±49.6 | 179.6±52.4 | 169.4±48.9 | 0.018 |
| Lipid core length, mm | 12.8±10.0 | 17.0±12.0 | 12.1±9.5 | <0.001 |
| TCFA | 261 (19.8) | 45 (26.2) | 216 (18.8) | 0.025 |
| MLA, mm2 | 3.3±1.9 | 1.8±1.1 | 3.5±1.9 | <0.001 |
| Lumen area stenosis, % | 59.1±15.0 | 70.7±14.2 | 57.4±14.3 | <0.001 |
| Other qualitative characteristics | ||||
| Non-culprit plaque rupture | 100 (7.6) | 17 (9.9) | 83 (7.2) | 0.165 |
| Thrombus | 47 (3.6) | 7 (4.1) | 40 (3.5) | 0.675 |
| Calcification | 592 (44.8) | 85 (49.4) | 507 (44.2) | 0.162 |
| Macrophage | 1,206 (91.4) | 164 (95.3) | 1,042 (90.8) | 0.064 |
| Microchannel | 749 (56.7) | 93 (54.1) | 656 (57.1) | 0.529 |
| Cholesterol crystals | 306 (23.2) | 56 (32.6) | 250 (21.8) | 0.004 |
| Layered tissue | 647 (49.0) | 109 (63.4) | 538 (46.9) | <0.001 |
| Values are n (%) or mean±SD. μQFR: Murray fractal law-based quantitative flow ratio; LAD: left anterior descending artery; LCx: left circumflex artery; MLA: minimal lumen area; NCL: non-culprit lesion; OCT: optical coherence tomography; RCA: right coronary artery; TCFA: thin-cap fibroatheroma | ||||
Clinical outcomes during follow-up
Patients were followed for up to 5 years (median of 4.1 [IQR 3.7-4.7] years), with 17 patients (2.6%) either lost to follow-up or refusing to provide follow-up information. Among the 645 patients, 76 experienced adverse cardiac events (cumulative rate 13.9%): 22 had culprit lesion-related events (cumulative rate 3.6%), 39 had NCL-related events (cumulative rate 7.6%), and 20 had cardiac deaths without angiograms at the time of events, rendering the responsible lesions indeterminate (cumulative rate 3.7%) (Figure 2).
The primary endpoint occurred in 59 patients (cumulative rate 11.1%), including 20 cardiac deaths, 10 patients with NCL-related non-fatal MIs, and 36 patients with NCL-related unplanned coronary revascularisations (Supplementary Table 3). In the lesion-level analysis, 42 NCLs were identified with event angiography and matching baseline OCT, including 11 lesions with a non-fatal MI and 39 lesions with an unplanned coronary revascularisation. Angiographic diameter stenosis of NCLs leading to events increased significantly from 47.9±10.2% at baseline to 63.4±16.6% at the time of event (p<0.001). The same was true when limited to lesions leading to an unplanned coronary revascularisation (48.3±10.5% at baseline vs 63.9±16.9% at the time of event; p<0.001).
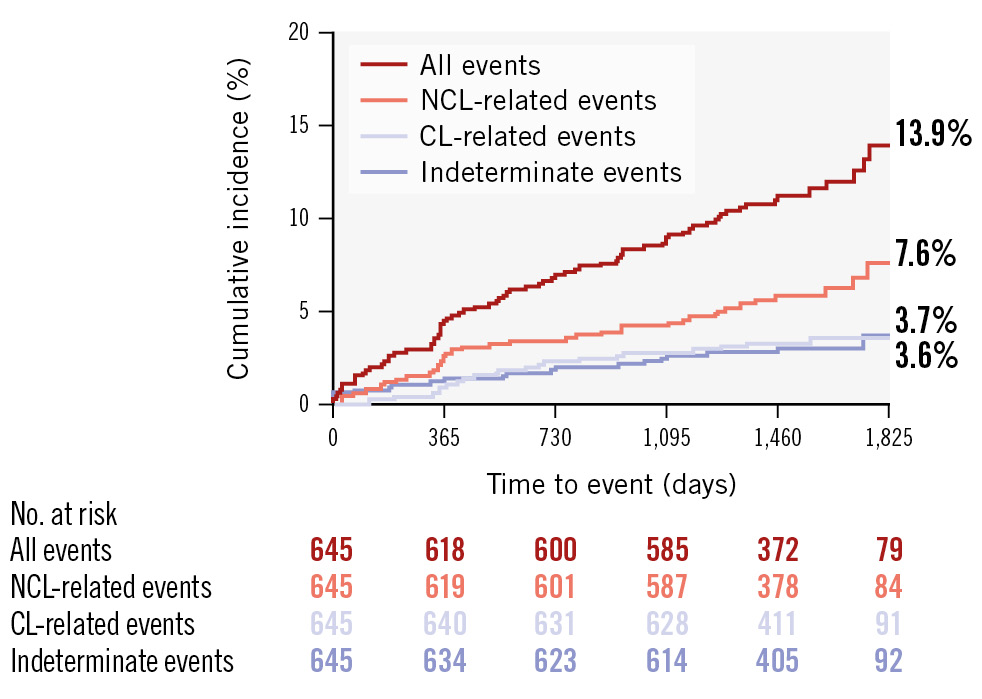
Figure 2. Longitudinal Kaplan-Meier curves for adverse cardiac events incidence. Among the 645 patients, the Kaplan-Meier curves indicate that the highest cumulative incidence of adverse cardiac events was observed for NCL-related events (7.6%). This was followed by indeterminate events (3.7%) and CL-related events (3.6%). CL: culprit lesion; NCL: non-culprit lesion
Prognostic implications of µQFR and OCT-defined TCFA
In Figure 3, Kaplan-Meier curves illustrate the composite clinical outcomes categorised by μQFR and TCFA at the patient and lesion levels. The risk of the primary endpoint was consistently higher in patients with at least one NCL with a μQFR ≤0.80 (16.2% vs 9.6%, HR 1.92, 95% CI: 1.13-3.28) (Figure 3A) or TCFA (20.5% vs 6.5%, HR 3.28, 95% CI: 1.95-5.51) (Figure 3B) compared to their counterparts, with a more pronounced difference in the divergence of the survival curves for patients stratified by TCFA. These properties generally held for the lesion-level analysis (for μQFR ≤0.80: HR 2.77, 95% CI: 1.42-5.41; for TCFA: HR 4.65, 95% CI: 2.54-8.52) (Figure 3C, Figure 3D). Complete patient-level and lesion-level multivariable models are presented in Supplementary Table 4 and Supplementary Table 5. In the multivariate analysis, OCT-defined TCFA (adjusted HR 3.05, 95% CI: 1.80-5.19) was independently associated with the primary endpoint, and the hazard proportionality remained consistent in the multivariable analysis at the lesion level (adjusted HR 4.46, 95% CI: 2.33-8.56) (Table 3). Conversely, the presence of an NCL with a μQFR ≤0.80 was not significantly associated with the occurrence of the primary endpoint (adjusted HR 1.37, 95% CI: 0.79-2.40).
Patients and lesions were divided into 4 groups based on μQFR values and the presence or absence of TCFA (Figure 4). In the patient-level analysis, the highest event rate of 29.6% was observed in patients with NCLs that were TCFA (+) with μQFR ≤0.80, compared to 16.3% in those that were also TCFA (+) but with μQFR>0.80, 6.0% in those that were TCFA (–) with μQFR ≤0.80, and 6.6% in those that were TCFA (–) with μQFR>0.80 (log-rank p<0.001) (Figure 4A). Similar results were obtained at the lesion level, with event rates of 17.4%, 9.7%, 4.3%, and 2.1%, respectively (log-rank p<0.001) (Figure 4B). The subgroup analysis indicated that the presence of TCFA, regardless of μQFR values, had significant prognostic value for future adverse clinical outcomes (Supplementary Figure 1, Supplementary Figure 2). Table 4 showed that OCT-defined TCFA was independently associated with the risk of the primary endpoint in both STEMI (adjusted HR 3.27, 95% CI: 1.67-6.41) and NSTEMI patients (adjusted HR 3.26, 95% CI: 1.24-8.54). In contrast, μQFR ≤0.80 did not demonstrate a significant predictive value in either group. Detailed results of other covariates have been provided in Supplementary Table 6.
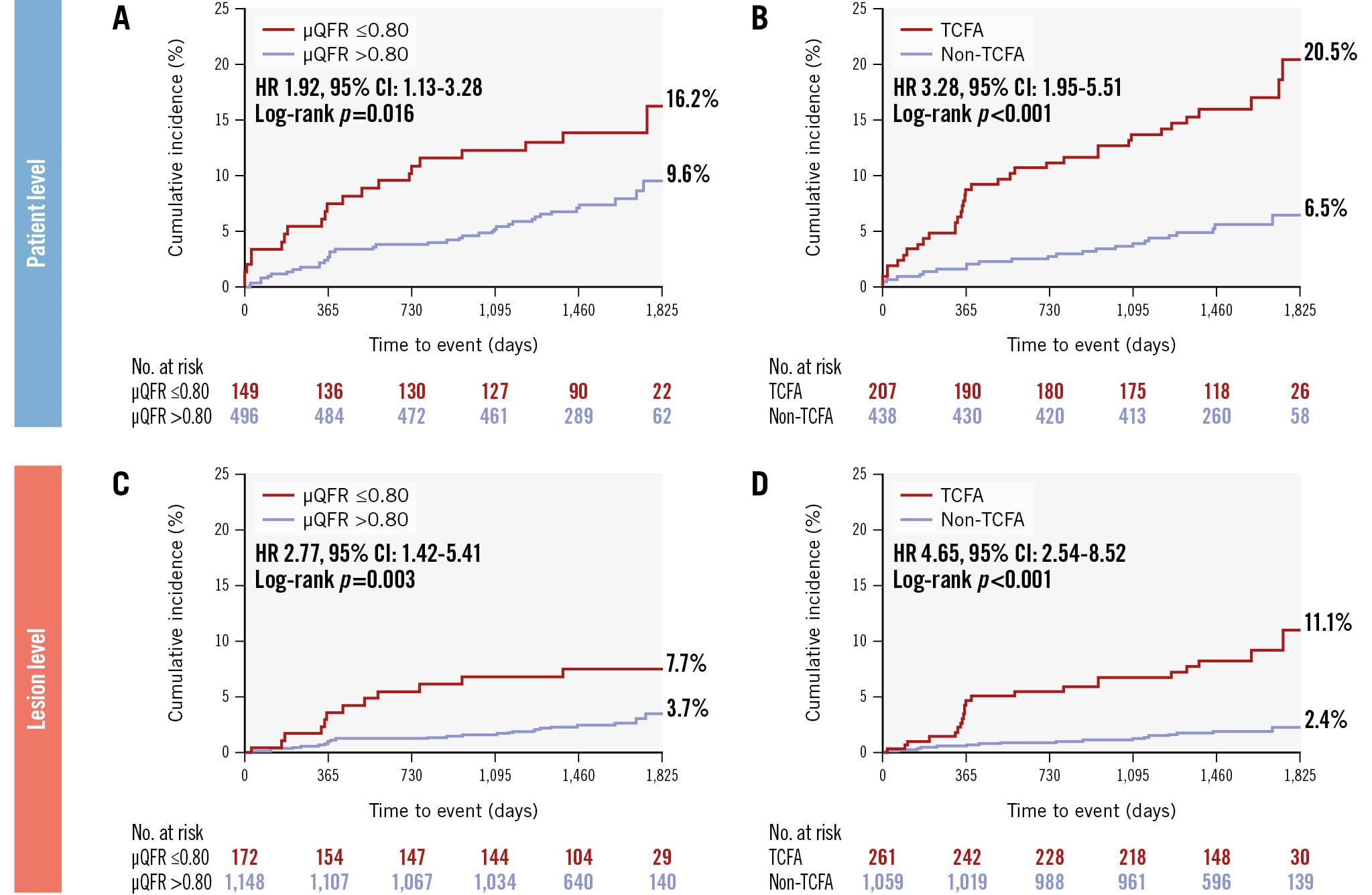
Figure 3. Individual prognostic value of μQFR and OCT-defined TCFA in patient-level and lesion-level analyses. The risk of NCL-related clinical events was significantly higher in patients with (A) μQFR ≤0.80 or (B) TCFA, compared to their counterparts. These properties generally held at the lesion level for NCLs with (C) μQFR ≤0.80 or (D) TCFA. μQFR: Murray fractal law-based quantitative flow ratio; CI: confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; OCT: optical coherence tomography; TCFA: thin-cap fibroatheroma
Table 3. Multivariable analysis for NCL-related clinical events at the patient and lesion levels.
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|
| Patient-level modela | ||
| μQFR (≤0.80 vs >0.80) | 1.37 (0.79-2.40) | 0.266 |
| TCFA | 3.05 (1.80-5.19) | <0.001 |
| Lesion-level modelb | ||
| μQFR (≤0.80 vs >0.80) | 1.46 (0.71-3.01) | 0.304 |
| TCFA | 4.46 (2.33-8.56) | <0.001 |
| aIn the patient-level analysis, the primary endpoint occurred in 59 patients, comprising 20 patients with cardiac death and 39 patients with NCL-related events (10 patients with non-fatal myocardial infarctions and 36 patients with unplanned coronary revascularisations). The baseline variables that were considered clinically relevant (age, sex, coronary risk factors and clinical presentation) were entered in the patient-level model. bIn the lesion-level analysis, 42 evaluable NCLs (11 NCLs with a non-fatal myocardial infarction and 39 NCLs with an unplanned coronary revascularisation) with angiography at the time of event and matched baseline OCT were determined in 39 patients. Cardiac deaths were not included in the lesion-level analysis. The other OCT characteristics with significant effects on clinical outcomes in the univariable analysis (MLA and non-culprit plaque rupture) that were identified within the same lesion were entered in the lesion-level model. μQFR: Murray fractal law-based quantitative flow ratio; CI: confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; MLA: minimal lumen area; NCL: non-culprit lesion; OCT: optical coherence tomography; TCFA: thin-cap fibroatheroma | ||
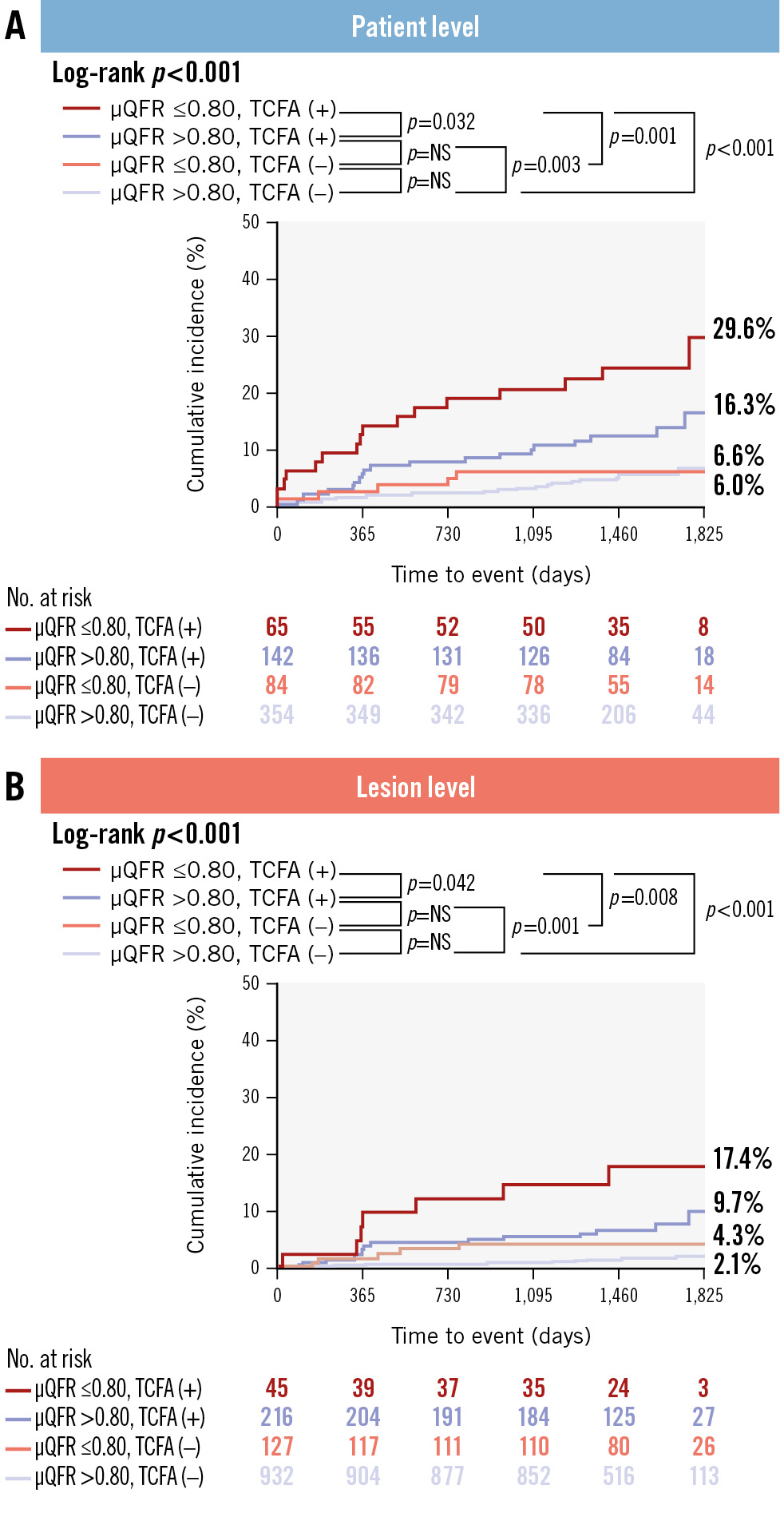
Figure 4. Combined prognostic value of μQFR and OCT-defined TCFA in patient-level and lesion-level analyses. A significant difference in the risk of NCL-related clinical events was observed when categorising (A) patients and (B) lesions into four groups based on μQFR values and the presence or absence of TCFA. μQFR: Murray fractal law-based quantitative flow ratio; NS: non-significant; OCT: optical coherence tomography; TCFA: thin-cap fibroatheroma
Table 4. Adjusted risk for μQFR ≤0.80 and OCT-defined TCFA in STEMI and non-STEMI patients.
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|
| STEMI | ||
| μQFR (≤0.80 vs >0.80) | 1.75 (0.89-3.45) | 0.104 |
| TCFA | 3.27 (1.67-6.41) | 0.001 |
| Non-STEMI | ||
| μQFR (≤0.80 vs >0.80) | 0.69 (0.21-2.27) | 0.542 |
| TCFA | 3.26 (1.24-8.54) | 0.016 |
| Model adjustments are consistent with those applied in Table 3. μQFR: Murray fractal law-based quantitative flow ratio; CI: confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; OCT: optical coherence tomography; STEMI: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; TCFA: thin-cap fibroatheroma | ||
Discussion
This large-scale observational analysis integrated μQFR values with OCT-defined TCFA at the time of primary PCI to evaluate the long-term prognostic implications of NCLs in patients presenting with an AMI. Our findings revealed that an OCT-defined TCFA was more prevalent in NCLs with a μQFR ≤0.80; however, no independent association between these parameters was identified. The highest risk of adverse events was observed in patients and lesions with μQFR ≤0.80 combined with OCT-defined TCFA. Importantly, OCT-defined TCFA provided a significant incremental prognostic value, irrespective of μQFR values or the clinical presentation of AMI at admission. Conversely, the prognostic relevance of a μQFR ≤0.80 was relatively limited and primarily evident only when TCFA was also present. These insights have underscored the critical prognostic significance of OCT-identified NCL TCFA during the index procedure, demonstrating greater clinical relevance than μQFR for long-term clinical outcomes in an AMI population (Central illustration).
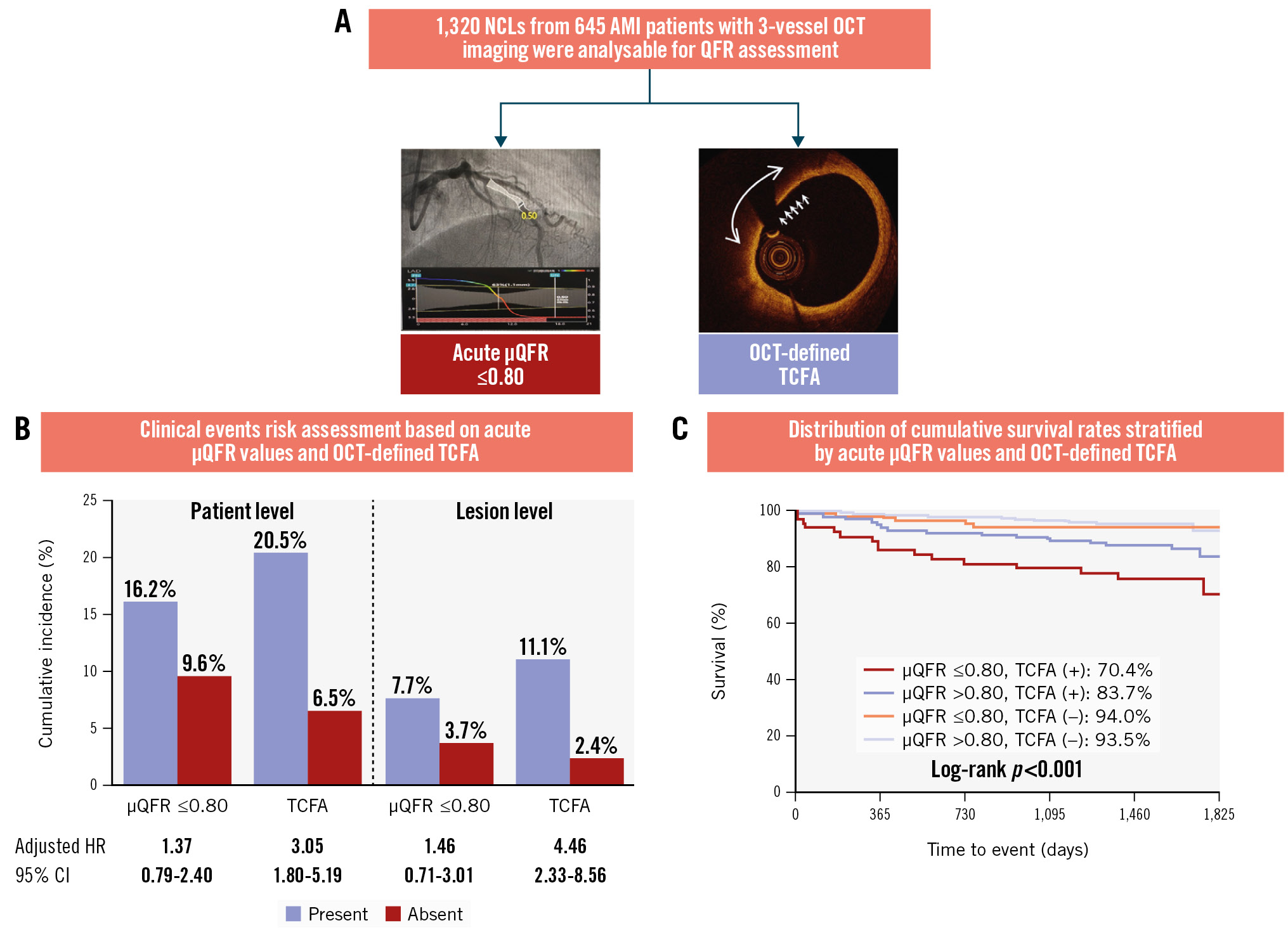
Central illustration. OCT-defined NCL TCFA demonstrates superior prognostic value compared to μQFR-determined functional significance A) Optical coherence tomography (OCT) examination and Murray fractal law-based quantitative flow ratio (μQFR) assessment were systematically conducted on a total of 1,320 non-culprit lesions (NCLs) from 645 patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI), with a median follow-up period of 4.1 years (IQR 3.7-4.7). During the index procedure, OCT-defined thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA) demonstrated a dominant prognostic value for patient-level and lesion-specific adverse clinical events related to NCLs, whereas the μQFR-determined functional significance was insignificant. B) Clinical events risk assessment and (C) the cumulative survival rates. CI: confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio; IQR: interquartile range
Assessment of NCLs based on µQFR and OCT-defined TCFA
Coronary physiology and plaque morphology are two dimensions for assessing NCLs, and a pathophysiological interplay exists between these factors429. Multiple investigations conducted on mixed populations comprising both stable coronary artery disease (CAD) and acute coronary syndrome patients have suggested an independent association between pressure wire-based haemodynamic significance and the presence of OCT-defined TCFA303132. In contrast to these studies, our study recognised that OCT-defined TCFA was not an independent determinant of physiological severity as assessed by μQFR. The reason for this discrepancy may be that, although several studies using FFR19 and three-dimensional (3D)-QFR33 as references have demonstrated that the computation of μQFR from a single angiographic view has high feasibility and excellent diagnostic accuracy in identifying haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis, the existing evidence is still insufficient to support μQFR as a complete substitute for pressure wire-based FFR methods in accurately reflecting the true physiological status of plaques during the index procedure for AMI. This limitation might partly explain the lack of association observed in our study. In the present study, although the analysis of OCT imaging and offline μQFR calculations were performed retrospectively, both the OCT pullback and the angiograms used for μQFR were obtained at the time of the index procedure. This methodology allowed for a comprehensive assessment of NCLs in AMI patients undergoing primary or urgent PCI, providing greater convenience and minimising additional procedural risks, thus offering a distinct advantage over previous studies that primarily utilised FFR for similar evaluations. To summarise, our findings suggest that the impact of TCFA on clinical outcomes is independent of its interplay with coronary physiological characteristics, particularly in the context of AMI.
Risk stratification according to µQFR and OCT-defined TCFA
The evaluation of clinical outcomes based on μQFR assessment and OCT examination has not been comprehensively reported. In the present study, the risk of clinical events was highest in patients with acute μQFR ≤0.80 and OCT-defined TCFA (29.6%), followed by those with μQFR>0.80 and OCT-defined TCFA (16.3%); in both of these patient groups, the risk of clinical events was higher than in those without TCFA, where the predictive value of a μQFR ≤0.80 was insignificant. Similar trends were observed in the lesion-specific analysis. These findings align with the multivariate regression model, demonstrating an independent association between TCFA and clinical events, rather than μQFR values. Our study also demonstrated that TCFA provided significant prognostic information in both STEMI and NSTEMI patients, indicating that it is not influenced by the clinical environment, thus proving to be a more robust predictor compared to μQFR. Recently, Seike et al demonstrated that lesion-specific intravascular ultrasound (IVUS)-derived FFR ≤0.95 was an independent predictor of non-culprit clinical endpoints, alongside IVUS-defined plaque morphological characteristics34. Similarly, Safi et al found that a low but normal QFR (>0.80 to <0.97) provided additional prognostic information beyond plaque morphology for predicting clinical endpoints up to 5 years35. However, these findings do not conflict with our results. Our study aimed to demonstrate that OCT-defined TCFA offered significant prognostic value compared to μQFR-determined functional significance (defined as ≤0.80). In future research, we plan to investigate the optimal μQFR threshold for diagnosing lesion-specific clinical events and explore its clinical significance in comparison to OCT-defined TCFA. Furthermore, we found that in NCLs with μQFR>0.80, OCT-defined TCFA was significantly associated with a higher risk of clinical endpoints; contrastingly, the remaining μQFR-negative lesions without TCFA had a truly low risk of future adverse events. Numerous studies have previously reported the impact of high-risk plaque on clinical outcomes in non-ischaemic lesions. However, the present study differs substantially from previous reports in several ways. In the COMBINE OCT-FFR (Optical Coherence Tomography Morphologic and Fractional Flow Reserve Assessment in Diabetes Mellitus Patients) study21, OCT imaging was performed on 445 FFR-negative lesions in 390 patients with diabetes mellitus, 74.9% of whom had stable CAD, and follow-up was limited to 1.5 years. In the PECTUS-obs (Identification of Risk Factors for Acute Coronary Events by OCT After STEMI and NSTEMI in Patients With Residual Non-flow Limiting Lesions) study36, 420 patients with MI underwent FFR assessment either during the index procedure or within 6 weeks in a staged approach, with subsequent OCT examination focused on specific lesions that were FFR-negative, and the follow-up was 2 years. Notably, a recent study reported that FFR values obtained during the acute phase of AMI decreased significantly over time, leading to false-negative results, while QFR remained relatively constant16. Therefore, the present study used μQFR instead of FFR to determine the functional significance of NCLs, and OCT imaging covered the non-IRAs to avoid missing high-risk NCLs. Based on these findings, the present study suggests that during the acute phase, OCT-defined TCFA may serve as a more critical prognostic predictor than acute μQFR assessment for long-term clinical outcomes related to NCLs in an AMI population. However, given the retrospective nature of this study, further prospective research is needed to confirm the superiority of OCT-defined plaque vulnerability, especially TCFA, over μQFR-derived coronary physiology in risk stratification and, potentially, in tailoring treatment.
Limitations
Several limitations should be considered when interpreting the results of this study. First, the single-centre and retrospective design of the present study may have introduced some selection bias. Additionally, as this study represents an initial exploratory analysis, it was not registered in a public registry, which may limit transparency and increase potential bias. Future studies will address this limitation by ensuring proper registration to enhance reproducibility and alignment with established research standards. Second, our findings pertain only to patients with AMI, and thus may not be generalisable to patients with stable CAD. However, similar results have been documented previously for the latter patient category2137. Third, although OCT was performed on all three main coronary arteries, some distal small segments and branches were not examined. Moreover, a total of 468 NCLs in IRAs were excluded from the study due to issues with interpretation of acute μQFR IRA computation during the index procedure of AMI patients. Fourth, it was difficult to determine the origin of cardiac death without follow-up angiography. Consistent with previous studies2021, cardiac deaths that could not be clearly attributed to culprit lesions were classified as NCL-related in the patient-level analysis, which is probable given the treatment of the culprit lesion with contemporary PCI3. Fifth, given the presence of coronary microcirculatory dysfunction in patients with AMI, the reduced diagnostic performance of μQFR cannot be fully excluded38. Sixth, the findings of the present study are specific to μQFR and may not necessarily extend to other modalities such as QFR, OCT-based FFR, or pressure wire-based FFR and non-hyperaemic diastolic pressure ratios. Further research is required to determine whether similar results can be replicated using these alternative physiological assessment tools. Seventh, although we utilised the virtual stent technique embedded within the μQFR system to calculate each target NCL independently, thereby reducing the impact of tandem lesions, this influence cannot be completely ruled out. Further studies are needed to better understand the effect of tandem lesions on μQFR calculations, their potential prognostic implications, and their relationship with plaque phenotype. Finally, a small number of patients were evaluated at the 5-year follow-up. However, the Kaplan-Meier curves continued to diverge at both the patient and lesion levels, indicating a potentially higher HR for future clinical events if all patients completed the 5-year follow-up.
Conclusions
During the index procedure in an AMI population, OCT-identified NCL TCFA serves as a more dominant and independent prognostic indicator for long-term clinical outcomes than μQFR-determined physiological significance, emphasising the critical role of OCT as a powerful tool for identifying high-risk patients and its potential for tailoring treatment.
Impact on daily practice
The present large-scale observational analysis suggests that optical coherence tomography (OCT)-defined thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA) is significantly predictive of both patient-level and lesion-specific non-culprit lesion (NCL)-related clinical outcomes, irrespective of Murray fractal law-based quantitative flow ratio (μQFR) values and acute myocardial infarction (AMI) presentation at admission, whereas the prognostic implication of a μQFR ≤0.80 was insignificant in this analysis. These insights provide robust evidence that OCT-identified NCL TCFA during the index procedure for AMI has greater clinical relevance than μQFR-determined coronary physiology for long-term clinical outcomes, emphasising the critical value of OCT in assessing NCL in patients with AMI.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank all the participating patients for their contributions to the study.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant no. 82322036 (to Dr Dai), 82072091 (to Dr Dai), 62135002 (to Dr Yu), 82202286 (to Dr Fang), and the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province, grant no. YQ2023H014 (to Dr Fang).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

