
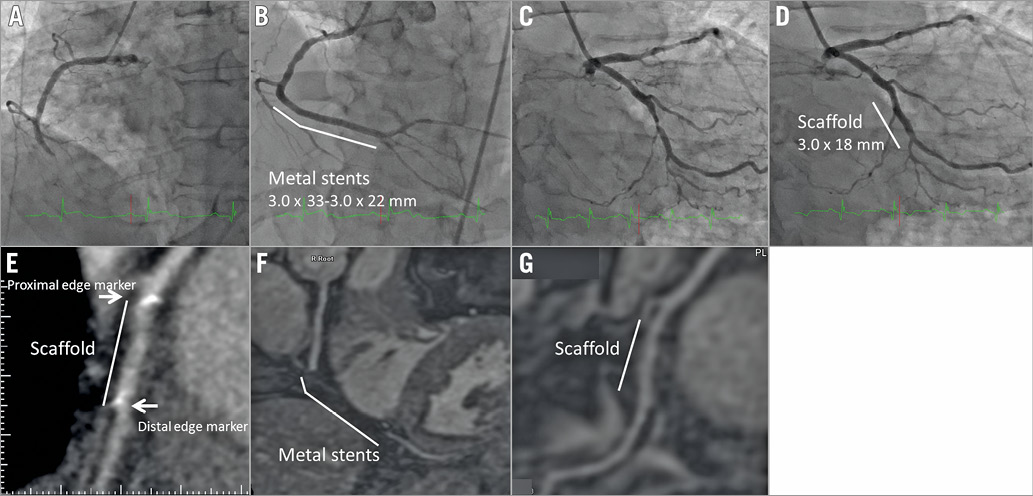
A 48-year-old man was referred to our hospital for acute coronary syndrome. Coronary metal stents were implanted at the distal right coronary artery as the culprit lesion (pre-treatment: Panel A; post-treatment: Panel B). After one month, he was readmitted to our hospital in order to treat the remaining coronary artery stenosis. He was enrolled in the ABSORB EXTEND study, and a fully bioresorbable polymeric everolimus-eluting scaffold (Absorb; Abbott Vascular, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was implanted at the mid left circumflex coronary artery (pre-treatment: Panel C; post-treatment: Panel D). Follow-up coronary computed tomographic angiography was performed at eight months after the scaffold implantation. Mild stenosis and small platinum markers at scaffold edges were depicted at the mid left circumflex coronary artery (Panel E). At three years following the scaffold implantation, coronary magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) was performed to check his coronary artery. A coronary luminal image was not obtained at the metal stent site due to metal artefact (Panel F). However, a coronary luminal image was clearly obtained at the scaffold site (Panel G). No restenosis was observed, and the small platinum markers did not hamper lumen visibility. The patient is currently doing well without symptoms. Coronary MRA does not require radiation exposure and a contrast agent. Coronary MRA might be a useful modality to follow patients treated with fully bioresorbable polymeric scaffolds.
Conflict of interest statement
K. Tanabe is a member of the Advisory Board of Abbott Vascular Japan and receives lecture honoraria from Abbott Vascular Japan. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

