BIOMAG-I is a European, multicentre first-in-human study assessing the safety and performance of a third-generation sirolimus-eluting resorbable magnesium scaffold (DREAMS 3G, commercial name Freesolve [Biotronik AG]). This is a next-generation scaffold with improved radial support and stability, a reduced strut thickness, and an increased size portfolio compared to its precursor DREAMS 2G (Biotronik), while the resorption period of 12 months has been maintained1. This substudy measures drug-induced vasomotion after complete scaffold resorption at 12 months.
The study was approved by the centres’ ethics committees, and all patients provided additional informed consent for vasomotion assessments in 2 study centres. Endothelial-dependent vasomotor reactivity was estimated by selectively infusing incremental doses of acetylcholine (ACh) into the target coronary artery: ACh1 (low dose) 0.36 μg/ml, ACh2 (middle dose) 3.6 μg/ml, and ACh3 (high dose) 18 μg/ml. Each ACh concentration was infused at a speed of 2 ml/min for 3 minutes. Contrast injection and angiographic images were taken at the end of the ACh infusion for each concentration.
When the maximum tolerated ACh dose was administered, an intracoronary bolus injection of nitroglycerine (NTG, 200 μg) was selectively injected via the microcatheter to test the endothelial-independent vasomotor reaction. Repeat angiography was performed in the same 2 orthogonal views as during the baseline procedure 20 seconds after the end of the NTG bolus injection. Vasomotion was defined as a relative diameter change of at least 3%2.
The statistical analysis was performed using SAS 9.4 (SAS Institute).
BIOMAG-I enrolled 116 patients with de novo coronary lesions with 14 patients consenting to an additional angiographic vasomotion assessment at 12 months.
The baseline parameters of these 14 patients were comparable to the remaining study patients, except for statistically significant longer lesions (22.3±4.4 mm vs 17.4±6.0 mm; p=0.004), and more calcification in patients with vasomotion assessment (none, mild, and moderate calcification of 28.6%, 0%, and 71.4% vs 65.4%, 5.8% and 28.8% in the no vasomotion group; p=0.009). Type C lesions were present in 21.4%.
At 12-month follow-up, the in-scaffold mean lumen diameter decreased from 3.12±0.50 mm (95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.83-3.40) at baseline to 2.86±0.52 mm (95% CI: 2.56-3.16) after infusing the highest tolerable dose of ACh (difference −0.26 mm [95% CI: −0.33 to −0.19]) and dilated to 3.11±0.48 mm (95% CI: 2.84-3.39) after the NTG bolus injection (difference vs post-ACh infusion 0.26±0.12 mm [95% CI: 0.18-0.33]) (Figure 1). The response pattern was homogeneous across patients and similar to the in-segment sections.
BIOMAG-I is the first trial to use the third-generation sirolimus-eluting resorbable magnesium scaffold DREAMS 3G. Data from the full cohort have confirmed that this novel device has short-term outcomes that are competitive against contemporary drug-eluting stents, with a low 12-month target lesion failure rate of 2.6%, absence of any thrombotic event related to the target vessel, and late lumen loss of 0.19±0.25 mm at 6 months and 0.24±0.36 mm at 12 months1.
We evaluated the physiological consequences of the scaffold resorption by assessing endothelial-dependent and -independent coronary vasomotion. This is an essential advantage of bioresorbable scaffolds, as the ability to restore vasomotion ultimately should reduce longer-term adverse effects34.
Drug-induced vasomotion in the treated segment was documented in all 14 patients treated with DREAMS 3G, with unjailing of the vessel demonstrated at 1 year, compared to the 79% of patients that showed vasomotion after receiving its precursor, DREAMS 2G, in the BIOSOLVE-II Study13.
Furthermore, it is encouraging that there was a homogeneous response across the individual patients as well as between the in-device and proximal and distal segments.
A similar response was seen for the Absorb bioresorbable scaffold (Abbott), but at 5 years after implantation5. Specifically, at the 5-year follow-up, the mean lumen diameter was reduced by 0.26 mm after ACh infusion, and it increased by 0.31 mm after the NTG bolus injection. The response to the endothelial-dependent ACh was paradoxical (vasoconstriction) for Absorb and the DREAMS series. This might be due to the fact that the endothelial function was still abnormal or due to the high doses of ACh that can induce stimulation of vascular smooth muscle cells5.
The low patient number is attributed to patient inclusion in only 2 predefined centres and precludes the analysis of factors that impact vasomotion. In addition, the single-arm design precludes a comparison to other devices.
In conclusion, this study showed, through vasomotion testing, that after scaffold resorption the vessel can regain vasomotion comparable to the unscaffolded proximal and distal vessel segments.
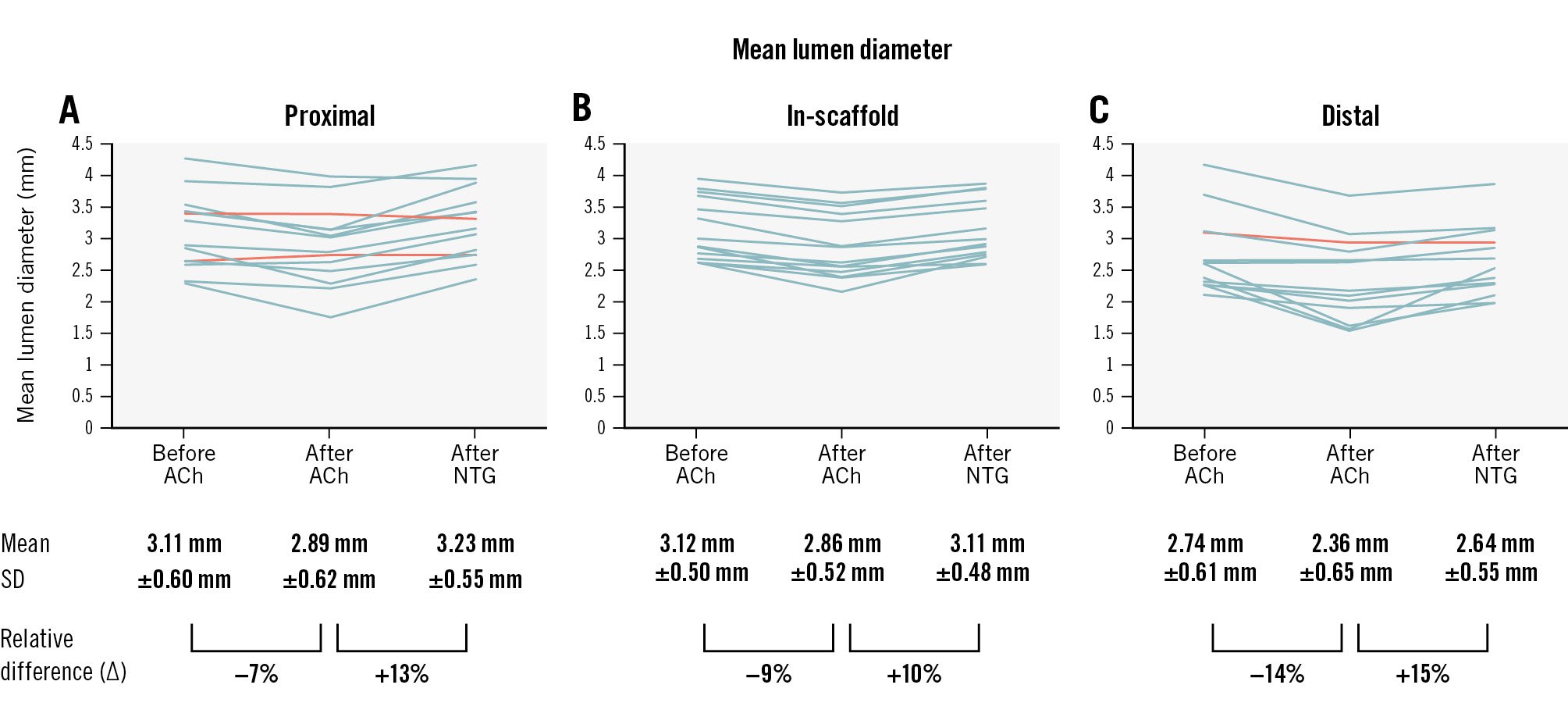
Figure 1. Vasomotion assessment at 12 months after DREAMS 3G implantation. The graphs represent the quantitative coronary angiography (QCA) core laboratory evaluation of the mean lumen diameters in 14 patients after acetylcholine (ACh) and nitroglycerine (NTG) administration in the proximal (A), scaffolded (B) and distal (C) segments. Each line represents data of 1 patient. End-diastolic images were read by the same angiographic core laboratory analyser (intraobserver concordance correlation coefficient 0.984 to 0.996; % difference −0.44% to 1.54%; the mean values of 2 readings were used for the analysis). All patients had vasomotion after either ACh or NTG in the scaffolded segment, predefined as a change in the lumen diameter of at least 3.0%, while the proximal segment in 2 patients and the distal segment in 1 patient showed no vasomotion (orange lines).
Acknowledgements
We thank Beatrix Doerr, consultant medical writer, for her help in preparing the manuscript (reimbursed by Biotronik) and Christian Knoll (Biotronik AG) for their statistical analysis.
Funding
The study was funded by Biotronik AG, Buelach, Switzerland.
Conflict of interest statement
H.M. Garcia-Garcia, G. Melaku, S. Beyene, and R. Waksman were core laboratory members, and the remaining authors were investigators of the trial. M. Haude reports grants/contracts from Biotronik, Cardiac Dimensions, OrbusNeich, and Philips; consulting fees from Biotronik, Cardiac Dimensions, Shockwave Medical, and OrbusNeich; honoraria/speaker fees from Biotronik, Cardiac Dimensions, Shockwave Medical, OrbusNeich, and Philips; support to attend meetings/travel support from Biotronik; is a steering committee member of the BIOSOLVE and BIOMAG trials; and is a Past President of EAPCI. J.F. Iglesias reports research grants to the institution from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Biosensors, Biotronik, Concept Medical, Philips, and Terumo Corp., outside the submitted work; speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Biosensors, Biotronik, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Cordis, Concept Medical, Medalliance, Medtronic, Novartis, Terumo Corp., Pfizer, Philips, and ReCor Medical, outside the submitted work; and support to attend meetings from Biotronik. H.M. Garcia-Garcia has received grants or contracts from Medtronic, Biotronik, Abbott, Neovasc, Corflow, Alucent Biomedical, Philips, and Chiesi (paid to institution); has received consulting fees from Boston Scientific and ACIST; and participates in the DSMB/advisory board of the VIVID study. S. Degrauwe reports research grants from Biotronik and Abbott; speaker fees from Medtronic, SIS Medical, Vascular Medical, Cordis, Medalliance, Shockwave Medical, OrbusNeich, Biotronik, and Boston Scientific; and meeting fees from Biotronik, OrbusNeich, Cordis, and Medtronic, all paid to her institution. R. Waksman has received grants or contracts from Amgen, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Philips IGT; has received consulting fees from Abbott, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Cordis, Medtronic, Philips IGT, Pi-Cardia, Swiss Interventional Systems/SIS Medical AG, Transmural Systems Inc, and Venus MedTech; has received honoraria from AstraZeneca; participates in DSMB/advisory boards of Abbott, Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Philips IGT, and Pi-Cardia; and is an investor in Medalliance and Transmural Systems Inc. D. Barlagiannis has no conflicts of interest to declare.

