Although radial artery puncture is frequently used for arterial pressure monitoring as well as blood sampling for blood gas analysis, the radial approach has not yet gained widespread acceptance as the primary entry site for angiography and interventions, despite the well documented benefits of these procedures1,2. One reason may be that even “femoral experts” are confronted with a new learning curve. This learning curve comprises both, radial artery sheath placement as well as mastering specific difficulties of the radial artery route because of anatomic variations. The present report deals with a modified puncture technique to decrease the learning curve for radial artery sheath insertion.
Puncture technique
The presented technique can be divided into a bare needle part and a venous cannula part. The puncture set is shown in Figure 1. After preparing the arm and positioning the wrist, the radial artery is punctured using a bare needle without prior local anaesthesia (Figure 2). We use a 0.8 x 50 mm needle (emerald green; B. Braun Melsungen AG, Germany). Even without the initial local anaesthesia prior to the bare needle puncture, patient discomfort is minimal and we have not seen radial spasms immediately after the puncture. Nevertheless, local anaesthesia can also be given before puncture if desired. After successful puncture, an introducer wire (45 cm, 0.021”) is inserted into the radial artery through the needle. Leaving both in place, local anaesthesia is then given to the skin (3-5 ml) at the base of the needle. This is followed by making a small superficial skin incision with the blade of the scalpel, cutting parallel to the direction of the radial artery, in order to avoid radial artery damage. The needle should not be withdrawn before the skin incision to avoid cutting the introducer wire (Figure 3). If a hydrophilic sheath is used, skin incision is unnecessary; however, these sheaths may cause allergic reactions3,4.
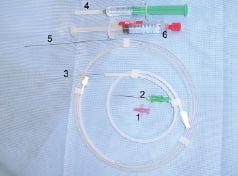
Figure 1. Puncture set comprising, venous plastic cannula (1), bare needle (2), 0.021” introducer wire (3), lidocaine syringe (4), 0.025” teflon wire, (5) syringe with 0.2 mg nitroglycerine (6).
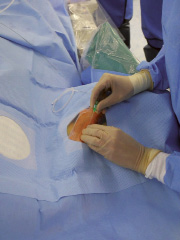
Figure 2. Radial puncture with bare needle without local anaesthesia.
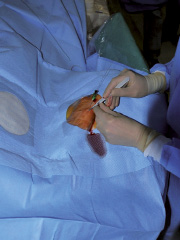
Figure 3. After successful radial puncture and introducer wire introduction, local anaesthesia is given and a skin incision is performed at the base of the needle.
After this, the needle is withdrawn and introduced into a venous cannula taken from a standard intravenous catheter (20G x1 1/4; 1.1 x 32 mm; B. Braun Melsungen AG, Germany). The needle stiffens the cannula for better penetration through the skin. It is important to note that after the introduction of the needle into the lock of the venous cannula, the tip of the needle does not reach the tip of the plastic cannula and, hence, allows for the soft insertion of the cannula (Figure 4). On the other hand, as needle and plastic cannula are inserted over the introducer wire, the plastic cannula is prevented from being sheared off by the bare needle. Finally, the bare needle and wire are both retrieved and a teflon wire (0.025”) is inserted through the venous cannula into the radial artery, the venous cannula is removed and the sheath is inserted over the teflon wire (Figure 5). The second wire (0.025”) can be used for coronary catheter steering, obviating the need for an extra J wire.
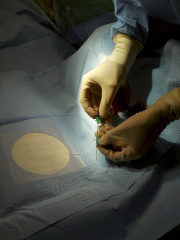
Figure 4. The withdrawn needle is introduced into the lock of a standard intravenous catheter cannula.
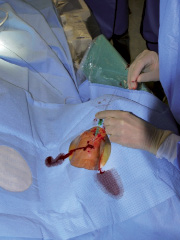
Figure 5. The connected venous cannula and needle have been successfully placed intra-arterially over the introducer wire.
These steps are shown in Figures 2-5.
Discussion
The transradial approach should be the approach of choice for a vast majority of coronary angiographies and interventions as well as non-coronary procedures1,2. Teaching hospitals worldwide should encourage radial artery puncture as safe and feasible so that interventionalists can begin taking the learning curve in stride, since radial artery puncture and the following sheath insertion sometimes do present problems5-7. To date, two techniques for radial artery punctures are used by the experts: the so called “bare needle” technique and the “intravenous cannula puncture” technique. The bare needle puncture is simple and has high success rates, even in tiny arteries6,7. The major disadvantage of this technique is the introduction of the arterial sheath especially in obese patients or in those with tough skin, due to the fact that the introducer wire may get bent or even curled making sheath insertion impossible. Moreover, spasmolytic drugs are hard to inject and angiography is impossible to perform through the bare needle. With the intravenous cannula technique, on the other hand, puncture of the radial artery itself is more difficult. The needle has to be pushed forward until blood appears and then advanced through the back wall of the artery, as a sole anterior puncture is difficult. The needle is then retracted and the plastic cannula pulled backward until free flow of blood indicates intraluminal position of the plastic cannula; importantly, no introduction wire is used for placement5,7. Moreover, the plastic cannula is not very deeply inserted in the radial artery and, hence, it is hard to avoid dislocating the inserted plastic cannula when it is necessary to inject drugs or contrast dye.
The presently suggested technique of radial artery puncture combines the advantages of both techniques, i.e., the ease of puncture of the bare needle technique and early access to the artery for angiography or drug administration before sheath insertion associated with the intravenous cannula approach, while eliminating the disadvantages of both techniques. The puncture set is commercially available by B. Braun Melsungen AG; Germany (ask for REF 5010060, Individually Pre-Assembled Kit for Angiography; Radialisset Uni Erlangen).
Limitations
The presented technique of puncture is a single-centre, multi-operator experience in over 750 patients, and its clinically value has yet to be proven world-wide.

