Abstract
Aims: Elevated filling pressures of the left atrium (LA) are associated with poorer outcomes in patients with chronic heart failure. The V-Wave is a new percutaneously implanted device intended to decrease the LA pressure by the shunting of blood from the LA to the right atrium. This report describes the first-in-man experience with the V-Wave device.
Methods and results: A 70-year-old man with a history of heart failure of ischaemic origin, left ventricular dysfunction (LVEF: 35%, pulmonary wedge: 19 mmHg), no right heart dysfunction, NYHA Class III and orthopnoea despite optimal treatment, was accepted for V-Wave device implantation. The device consists of an ePTFE encapsulated nitinol frame that is implanted at the level of the interatrial septum and contains a trileaflet pericardium tissue valve sutured inside which allows a unidirectional LA to right atrium shunt. The procedure was performed through a transfemoral venous approach under fluoroscopic and TEE guidance. The device was successfully implanted and the patient was discharged 24 hours after the procedure with no complications. At three-month follow-up a left-to-right shunt through the device was confirmed by TEE. The patient was in NYHA Class II, without orthopnoea, the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy index was 77.6 (from 39.1 at baseline) and NT-proBNP was 322 ng/mL (from 502 ng/mL at baseline). The QP/QS was 1.17 and the pulmonary wedge was 8 mmHg, with no changes in pulmonary pressure or right ventricular function.
Conclusions: Left atrial decompression through a unidirectional left-to-right interatrial shunt represents a new concept for the treatment of patients with left ventricular failure. The present report shows the feasibility of applying this new therapy with the successful and uneventful implantation of the V-Wave device, which was associated with significant improvement in functional, quality of life and haemodynamic parameters at 90 days.
Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is a highly prevalent disease that affects 1-2% of the population. Despite recent advances in its treatment, many patients with HF continue to deteriorate while on optimal therapy leading to a decline in quality of life (QoL), a high rate of re-hospitalisations, and increased costs1. This highlights the importance of continuous progress and innovation for improving the treatment of HF.
Elevated left atrium (LA) pressure is present in most patients with chronic HF hospitalised due to HF decompensation. Strict control of LA pressure by invasive monitoring and physician-directed self-management have been associated with significant improvement in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and NYHA class, as well as with a major reduction in re-hospitalisations and mortality at midterm follow-up2. Also, the closure of congenital atrial septal defects has been associated with a rise in LA pressures and decompensated HF in some patients3-8. It has been suggested that atrial septal balloon septostomy may be useful in the setting of LV dysfunction with acute HF to permit left heart decompression and recovery of LV function9-12. Finally, several small studies in the setting of pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular dysfunction have shown that creating an interatrial shunt to decrease right atrial pressure may be associated with a significant improvement in symptoms and haemodynamics13-20. Therefore, the creation of a unidirectional left-to-right shunt in patients with left-sided HF may provide relief from acute episodes of LA pressure increase, decrease LA pressure over time and prevent re-hospitalisations and functional class deterioration.
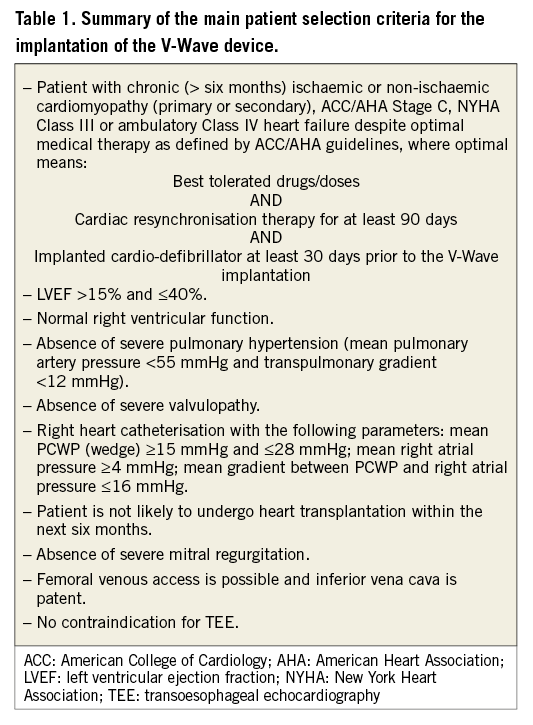
The V-Wave device (V-Wave Ltd, Or Akiva, Israel) is a new percutaneously implanted device, intended to decrease LA filling pressure by the shunting of blood volume from the LA to the right atrium (Figure 1A, Figure 1B). The device consists of an ePTFE encapsulated nitinol frame that is implanted at the level of the interatrial septum and contains a trileaflet porcine pericardial tissue valve sutured inside which allows a unidirectional flow from the LA to the right atrium if the pressure gradient exceeds 5 mmHg. The device has been evaluated in an ovine model of ischaemic HF that included a total of 21 sheep (14 with an implanted device and seven controls). The V-Wave implantation was associated with a persistent decrease in LA pressure with no increase in right atrial or pulmonary pressure. All devices showed patent interatrial shunting throughout the entire duration of the study (12 weeks), and device implantation was associated with improved LVEF and lower mortality (7% vs. 43% in controls, p=0.049). The present report describes the first-in-human experience with the V-Wave device in a patient diagnosed with HF and in NYHA Class III despite optimal medical therapy. Selection criteria for the implantation of the V-Wave device are summarised in Table 1.
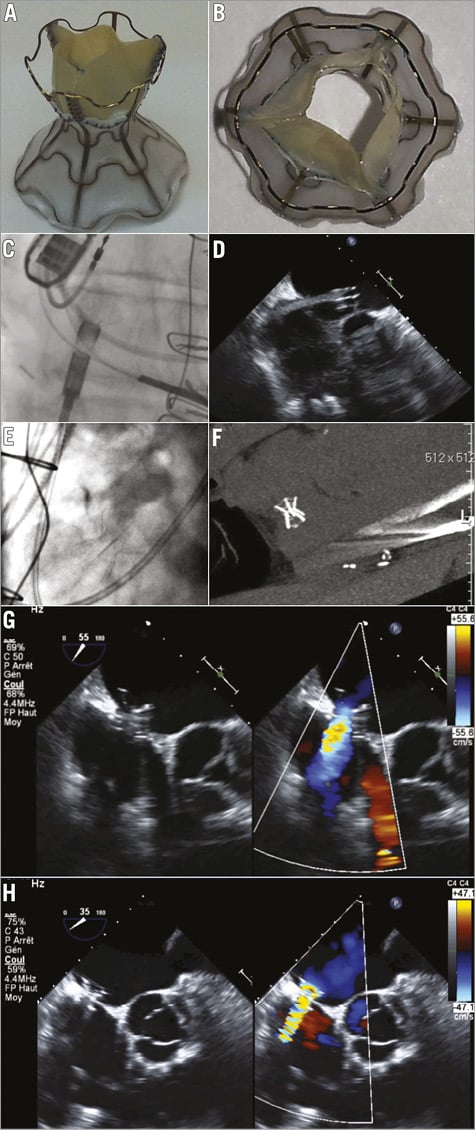
Figure 1. The V-Wave device. A) & B). Sagittal and axial views of the V-Wave device. The device consists of an hourglass-shaped nitinol frame with ePTFE encapsulation and three porcine pericardial leaflets sutured together with a prolene suture. The lumen size of the device is 5 mm at the level of the fossa. C) & D). Angiographic (left) and echocardiographic (right) images showing the deployment of the left side of the V-Wave device. E) & F). The V-Wave device located at the interatrial septum as seen by angiography (left) and computed tomography (right). G) & H). Transoesophageal echocardiography images of the V-Wave device immediately post-implantation (G) and at one-month follow-up (H) showing adequate positioning and function.
The patient was a 70-year-old man with a history of HF due to prior large anterior myocardial infarction with coronary artery bypass grafting. Other comorbidities included diabetes, dyslipidaemia, mild chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and atrial fibrillation treated with anticoagulation therapy (rivaroxaban). Echocardiography showed depression of LVEF (35%), mild mitral regurgitation, and normal right ventricular function. He presented with NYHA Class III and had orthopnoea despite optimal medical therapy including high doses of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, furosemide, spironolactone and beta-blockers. A cardiac defibrillator was implanted two years before, with no criteria for resynchronisation therapy or heart transplant. A right catheterisation showed a mean pulmonary wedge pressure of 19 mmHg, a pulmonary artery pressure of 31/14/20 mmHg, a mean right atrial pressure of 7 mmHg, and a cardiac index of 2.5 L/min/m2. The NT-proBNP values and the Duke Activity Status Index (DASI) score were 502 pg/mL and 32.2, respectively. The distance walked and maximal dyspnoea Borg scale at the six-minute walk test (6MWT) were 438 metres and 3/10, respectively. The score in the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) was 39.1. Following careful evaluation of the case by the cardiologists in charge of the Heart Failure clinic, the patient was considered a potential candidate for V-Wave device implantation. The procedure was approved by Health Canada under a Compassionate Clinical Use Program and the patient provided signed informed consent for the procedure as well as for the reporting of procedural and follow-up results.
The procedure was performed through femoral venous approach, under general anaesthesia and transoesophageal echocardiography (TEE) guidance. Following transseptal puncture at the level of the fossa ovalis, a 14 Fr Transseptal Mullins™ introducer sheath (Cook Medical, Inc., Bloomington, IN, USA) was advanced and positioned in the mid portion of the LA. The device was attached with a three latches mechanism to a delivery cable, loaded into the catheter and subsequently advanced through the catheter. After opening the left side in the mid portion of the LA (Figure 1C, Figure 1D), the system was pulled back up into the interatrial septum, where the device was detached and finally released by pulling back the delivery catheter (Figure 1E, Figure 1F, Moving image 1). The presence of a left-to-right shunt through the device was evidenced by TEE immediately after device implantation (Figure 1G), and the Qp/Qs was calculated at 1.17:1. The patient was discharged 24 hours after the intervention with no complications.
At one-month follow-up the NYHA Class had improved from III to II, and orthopnoea was no longer present. Also, furosemide could be reduced from 140 mg/day to 100 mg/day. The distance walked and the maximal Borg scale dyspnoea at the 6MWT were 480 m (increase of 42 m over baseline) and 1/10 (two points decrease from baseline), respectively. The NT-proBNP values were 413 pg/mL (decrease of 18% from baseline). TEE confirmed the correct position of the device, the patency of the interatrial shunt, and the absence of thrombus (Figure 1H). No changes were observed in left and right ventricular function and dimensions. At three-month follow-up, the patient remained in NYHA Class II, the NT-proBNP values were 322 pg/mL (decrease of 36% from baseline), the DASI score was 38.2 (increase of six points over baseline), the KCCQ was 77.6 (increase of 38 points over baseline), and a right heart catheterisation showed a pulmonary wedge pressure of 8 mmHg, a pulmonary artery pressure of 28/11/18 mmHg, a mean right atrial pressure of 5 mmHg, and a cardiac index of 2.6 L/min/m2 (Table 2).

Conclusion
In conclusion, LA decompression through unidirectional left-to-right interatrial shunt represents a new concept for the treatment of patients with HF. The present study showed the feasibility of applying this new therapy with the successful and uneventful implantation of the V-Wave device, which was indeed associated with significant improvement in functional class, QoL, and haemodynamic parameters at three-month follow-up. Future studies will have to demonstrate the efficacy of this treatment for patients diagnosed with HF. Also, a longer follow-up will be needed to ensure that the improvement in haemodynamic and functional parameters is maintained over time.
| Impact on daily practice Most patients with left heart failure hospitalised due to decompensation present elevated left atrial pressure. Decompression of the left atrium through self-regulative left-to-right shunt with the V-Wave device is a new concept for the treatment of heart failure in patients who continue to deteriorate despite maximal treatment. This report represents the first-in-man successful and uneventful implantation of a V-Wave device in a patient with symptomatic left ventricular failure despite maximal therapy. The procedure was associated with significant functional, quality of life and haemodynamic improvement at three-month follow-up. The confirmation of these results in a larger number of patients with a longer follow-up may open a new avenue for the treatment of patients with heart failure. |
Acknowledgements
We want to thank Dominque Lachance, MSc, from the Quebec Heart and Lung Institute, for her help in all the logistics related to this case.
Funding
I. Amat-Santos is supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Madrid, Spain, and Hospital Clinico de Valladolid, Spain (contrato Rio Hortega).
Conflict of interest statement
S. Verheye, G. Keren, W. Abraham, and J. Rodés-Cabau are consultants for V-Wave Ltd. M. Yaacoby and Y. Nitzan are employees of V-Wave Ltd. The other authors have no potential conflicts of interest to declare.
Online data supplement
Moving Image 1. The V-Wave device: bench test and first-in-human implantation.

