Abstract
Background: Antithrombotic treatment (ATT) post-left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) remains controversial. Furthermore, most of the patients undergoing LAAO are at a very high bleeding risk.
Aims: This study aimed to compare a simplified versus conventional ATT after LAAO in very high bleeding risk patients.
Methods: This is a multicentre, retrospective study including very high bleeding risk patients, according to the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) definition, who underwent LAAO. These included patients at >4% risk of BARC 3 to 5 bleeding or >1% risk of intracranial bleeding after the procedure. Two groups were established based on the discharge ATT. The simplified group included single antiplatelet treatment or no treatment, and the conventional group comprised dual antiplatelet treatment or anticoagulation (combined or not with antiplatelet therapy).
Results: A total of 1,135 patients were included. The mean CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores were 4.5±1.5 and 3.7±1.0, respectively. There were no differences in the composite endpoint (death, stroke, transient ischaemic attack, device-related thrombus or major bleeding) between the 2 groups (hazard ratio [HR] 0.81, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.59-1.11; p=0.188). Although the rate of major bleeding during the first year was numerically lower in the simplified group, it did not reach statistical significance (HR 0.67, 95% CI: 0.41-1.10; p=0.104). Nonetheless, patients with previous major bleeding presented a significantly lower rate of major bleeding when using the simplified treatment (HR 0.61, 95% CI: 0.36-0.99; p=0.049).
Conclusions: In patients with very high bleeding risk, a simplified ATT after LAAO seems to be as effective as conventional protocols. Furthermore, patients with a history of major bleeding experienced a lower risk of major bleeding with the simplified ATT.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most frequent arrhythmia worldwide, and its prevalence continues to increase, secondary to the higher life expectancy. In fact, it is expected that more than one-third of the European population over 55 years will experience this condition1. Moreover, AF is associated not only with higher mortality but also higher morbidity, including heart failure or stroke. AF is linked to a 5-fold increased stroke risk2, and up to 15-20% of ischaemic strokes are secondary to AF. Moreover, these strokes caused by AF are associated with a poorer prognosis3.
Permanent anticoagulation has been established as the gold standard treatment for preventing AF-related cardioembolic events in patients with a CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥2 (in males or ≥3 in females)14. However, due to their elderly condition and the presence of multiple comorbidities, a high percentage of patients also present a high bleeding risk, defined by a high HAS-BLED score5. Percutaneous left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) has emerged as an alternative to oral anticoagulation (OAC) for thromboembolic prevention678. Currently, European guidelines recommend LAAO in patients with previous history of major bleeding1; however, there are other scenarios in which performing LAAO has been suggested. For example, it could be recommended for patients with contraindications to OAC or those at high risk of bleeding, as well as individuals experiencing ischaemic stroke while on OAC therapy, or even patients who are unwilling to take OAC medication910.
It is worth noting that after LAAO, OAC can be stopped immediately. However, some antithrombotic treatments (ATT) should ideally be maintained during the first months to prevent device-related thrombosis (DRT). Previous studies evaluating the feasibility and safety of LAAO have proposed heterogeneous ATT6711121314151617. Indeed, OAC for a minimum of 45 days following LAAO is recommended in certain instances according to manufacturer recommendations. However, variations exist among different institutions and countries; OAC is more commonly continued in the USA, whereas in European countries, it is typically discontinued immediately after the procedure.
Furthermore, the most frequent indication for LAAO is previous severe bleeding18. Therefore, a high stroke risk and very high bleeding risk are present in many patients undergoing LAAO. The implementation of a less aggressive ATT post-LAAO might be useful in this setting. Nevertheless, although a less aggressive ATT should translate into a lower rate of bleeding events, it is not clear whether it provides enough protection against thromboembolic events and DRT. The objective of our study was to compare a simplified versus a conventional ATT post-LAAO in a multicentre large-scale registry.
Methods
This is a retrospective and multicentre study including 1,135 patients at a very high risk of bleeding, according to the Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) definition, undergoing LAAO. These patients presented a >4% risk of BARC type 3-5 bleeding and/or a >1% risk of intracranial bleeding after the procedure. The patients who were included met at least 1 major or 2 minor BARC criteria19. Major criteria included severe or end-stage chronic kidney disease, anaemia (haemoglobin <11 g/dL), thrombocytopaenia (platelet count <100x109/L), recent or recurrent major spontaneous bleeding, chronic bleeding diathesis, liver cirrhosis with portal hypertension, active malignancy, previous spontaneous or recent traumatic intracranial bleeding, recent moderate or severe ischaemic stroke, and non-deferrable or recent major surgery. Minor criteria included older age (over 75 years old), moderate chronic kidney disease, mild anaemia (haemoglobin 11-12.9 g/dL for males, and 11-11.9 g/dL for females), spontaneous bleeding not meeting the major criterion, long-term use of oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or steroids, and any ischaemic stroke not meeting the major criterion. We intended to include not only patients at a very high risk of bleeding but also those at high risk of presenting bleeding with important clinical implications, such as intracranial bleeding. All cases were performed in 12 different centres in Europe between July 2009 and December 2022. Patients were divided into 2 groups depending on the discharge ATT after LAAO.
The simplified treatment after LAAO was defined as single antiplatelet therapy (SAPT) or no treatment at all at discharge. In contrast, patients receiving dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT), oral or subcutaneous anticoagulation, or any combination of SAPT and anticoagulation were allocated to the conventional group, according to the protocols established in previous studies. The ATT was decided according to local criteria and operator experience. No specific approach was used, and each patient received individualised treatment based on the inherent risks.
Clinical and imaging follow-up were performed at each centre following local protocols. Clinical assessment and antithrombotic management during follow-up were carried out according to the physicians' criteria. However, all patients were maintained with long-term SAPT, to be started, if possible, after the first 3-6 months. DRT and peridevice leak were assessed by either transoesophageal echocardiography (TOE) or cardiac computed tomography (CT) according to each institution’s protocol. Therefore, at least 1 of these diagnostic tools was performed during the first 3 to 6 months after the procedure, especially aiming to dismiss DRT. However, neither TOE nor CT beyond 12 months were performed in any of the patients.
The primary efficacy endpoint was a combination of death, stroke, transient ischaemic attack (TIA), peripheral embolisms, DRT or major bleeding. For the safety evaluation, we considered any major bleeding as the safety endpoint. All centres stratified BARC bleeding during follow-up using the BARC classification previously described20. We identified minor bleeding in patients with a type 1 or 2 BARC bleeding classification. Conversely, those with a type 3-5 BARC bleeding classification were considered to have major bleeding. Global bleeding was defined as any clinically relevant bleeding, including both minor and major. A combined endpoint of death, stroke, TIA, peripheral embolism and DRT was also evaluated.
Both ischaemic and bleeding adverse events were recorded during the first year after LAAO to compare these different ATT regimens. However, follow-up was extended beyond the first year to dismiss further events, especially DRT.
There is no consensus on the exact definition of DRT in the previous literature. In this study, no standard definition was used, and each centre determined the presence of DRT according to their own criteria. Therefore, not only due to different definitions but also due to different follow-up regimes, there may be a potential bias between different centres that participated in this registry when ruling out DRT after LAAO.
Technical success was defined as the successful implantation of the device. Procedural success was defined as technical success without major procedure-related complications. Complete occlusion was defined as successful device implantation with no peridevice leak greater than 1 mm after deployment. A significant peridevice leak was defined as gaps greater than 5 mm between the device and the left atrial appendage (LAA) wall after deployment, measured by TOE or CT depending on local availability.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are expressed as mean±standard deviation or median and interquartile range, and normality was assessed with the Shapiro-Wilk test. Variables with a normal distribution were compared with Student’s t-test. On the other hand, variables without a normal distribution were analysed with the Mann-Whitney U test. Qualitative variables are expressed as percentages and were compared with the chi-squared test.
The chi-squared test was also used to compare the incidence of the composite event and the individual events. In addition, the Cox regression model was used to assess the impact of the outpatient program versus the standard conventional protocol on survival rates or adverse events during or after the procedure.
Survival analysis was also performed; the results were expressed as hazard ratios, and they were analysed with Kaplan-Meier survival curves at 1 year after the procedure. Verification of the proportional hazard ratio assumption was performed, with the 95% confidence interval (CI). In addition, the incidences of ischaemic and bleeding complications were recorded inside the hospital and in the long-term follow-up and were analysed independently. DRT and the annual rate of cardioembolic events or major bleeding were evaluated during the complete follow-up for each patient and compared with their expected rates.
Cox multivariable regression analysis was performed to identify the independent predictors for the primary endpoint. The multivariable model was built by backward stepwise (likelihood ratio) selection. For the univariable analysis, all variables considered potential clinical predictors for events were analysed. The variables included in the multivariable model were those with p≤0.05 in the univariable analysis. Age, smoking, previous ischaemic stroke, previous heart failure, estimated glomerular filtration rate, previous major bleeding, previous intracranial bleeding, previous gastrointestinal bleeding and labile international normalised ratio (INR) were included in the model.
A bilateral p-value<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed using Stata, version 15.1 (StataCorp).
Ethical aspects of the study
Data were anonymised and collected retrospectively from each local dataset. This study fulfils the Declaration of Helsinki of 1964, and it was approved by a local ethical committee (Comité de Ética en la Investigación con medicamentos de las Áreas de León y del Bierzo) with the validation code number 22146.
Results
A total of 1,135 patients were included in the analysis. Among them, 738 patients were included in the conventional protocol and 397 cases in the simplified ATT group. The median age of the entire cohort was 77.47±8.06 years old, and most of the patients were male (63.08%). As shown in Table 1, there were no significant differences between groups in age, CHA2DS2-VASc or HAS-BLED scores, baseline haemoglobin or platelet levels, nor in the rate of hypertension or diabetes. Conversely, in the group receiving simplified treatment, there were fewer males and significantly higher rates of prior major bleeding or intracranial bleeding.
The most frequent indication for LAAO was previous bleeding, followed by high bleeding risk without prior bleeding. Indications for LAAO are shown in Figure 1.
Technical success was achieved in almost all cases (99.38%), and the most common devices used were the Amplatzer Amulet (Abbott) in 52.1% and the WATCHMAN 2.5 and FLX (both Boston Scientific) in 27.4%. Other devices like the Amplatzer Cardiac Plug (ACP [Abbott]), the LAmbre (LifeTech Scientific) and the Omega (Eclipse Medical) were also used. There were no differences in the rate of efficacy and safety events between devices or their iterations over the course of the study. Indeed, no significant differences were found between distinct devices in the rate of peridevice leaks. Periprocedural complications were 2.77% in the simplified group and 3.93% in the conventional group (p=0.313) (Table 2). Moreover, the rate of pericardial effusion did not differ between groups (1.26% vs 1.76%; p=0.518). Discharge treatment and 6-month follow-up treatment after LAAO are summarised in Table 3 and Table 4. No ATT was chosen in 13.85% of the patients at discharge. On the other hand, ATT was continued beyond 6 months after LAAO in 21.94%.
As there were significant differences in the rates of previous major bleeding between the 2 groups, a multivariable analysis was conducted to identify independent predictors of the composite primary endpoint. The results, outlined in Table 5, underscore that prior major bleeding emerged as a robust independent predictor. Moreover, this predictive model demonstrated commendable accuracy, as evidenced by a robust area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, registering at 0.725.
At 1 year, the primary composite endpoint (death, ischaemic stroke, TIA, peripheral embolism, DRT or major bleeding) occurred in 58 patients (14.61%) and 129 (17.48%) in the simplified and conventional groups, respectively (Figure 2). When survival analysis was performed, although the rate was numerically lower in the simplified group, no significant differences were found (HR 0.81, 95% CI: 0.59-1.11; p=0.188) (Central illustration).
There were also no differences in the individual components of the primary endpoint between the 2 groups. Mortality rates were 10.58% and 10.30% (p=0.882) in the simplified and conventional groups, respectively. Rates of ischaemic stroke were 0.76% vs 0.81% (p=0.917), and rates of TIA were 0.25% vs 0.27% (p=0.952), in the simplified and conventional groups, respectively. No systemic embolism was found during the follow-up in any group. Major bleeding rates were slightly but not significantly lower in the simplified group (5.54% vs 7.99%; p=0.126).
Similarly, when only those with a history of major bleeding were selected, there were no significant differences in the primary endpoint (HR 0.77, 95% CI: 0.56-1.08; p=0.124) (Figure 3A).
Only 45 (3.96%) patients presented with DRT during an extended median follow-up of 22.38 months (interquartile range [IQR] 10.30-39.28). TOE and CT were used to diagnose DRT in 95.74% and 4.26% of the cases, respectively. Indeed, no significant differences were observed between the 2 groups, with rates of 3.78% and 4.07% for the less aggressive and the conventional groups, respectively (p=0.813).
The composite endpoint including all thromboembolic events and DRT occurred in 15 (3.78%) patients in the simplified group and 26 (3.52%) in the conventional group during the first year. When survival analysis was performed, no differences were found (HR 1.09, 95% CI: 0.56-2.10; p=0.806) (Figure 3C). In those patients with prior major bleeding, the results of the efficacy of a simplified treatment after LAAO remained similar (HR 1.05, 95% CI: 0.51-2.16; p=0.900) (Figure 3D).
The rates of major bleeding during the first year of follow-up were 5.54% and 7.99% in the simplified and conventional groups, respectively. Despite this reduction, no significant differences were observed (HR 0.67, 95% CI: 0.41-1.10; p=0.104) (Figure 3B). However, when patients with prior major bleeding were selected, the reduction in major bleeding during follow-up was found to be significant (HR 0.61, 95% CI: 0.36-0.99; p=0.049) (Central illustration).
During the entire follow-up period, the observed annual rate of the combined ischaemic endpoint was 0.8% in the simplified group and 0.7% in the conventional group, compared to an expected 5.6% according to the CHA2DS2-VASc score. In addition, the annual rate of observed major bleeding was 1.7% in the simplified group (vs 2.4% in the conventional group), compared to an expected annual bleeding risk of 7.6% based on a mean HAS-BLED score of 3.7. However, only 70.00% and 45.85% of the patients completed 1 and 2 years of follow-up, respectively.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics.
| Variable | Simplified treatment (N=397) | Conventional protocol (N=738) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 77.67±8.36 | 77.23±7.83 | 0.373 |
| Male sex | 232/397 (58.44) | 484/738 (65.58) | 0.017 |
| Hypertension | 339/397 (85.39) | 649/738 (87.94) | 0.222 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 150/397 (37.78) | 279/738 (37.80) | 0.994 |
| AF type | 0.276 | ||
| Paroxysmal | 103/324 (31.79) | 170/617 (27.55) | |
| Persistent/permanent | 195/324 (60.19) | 404/617 (65.48) | |
| CHA2DS2-VASc | 4.50±1.49 | 4.57±1.45 | 0.448 |
| HAS-BLED | 3.73±0.96 | 3.77±1.03 | 0.557 |
| HAS-BLED ≥4 | 231/397 (58.19) | 445/738 (60.30) | 0.489 |
| High bleeding risk (BARC criteria) | 397/397 (100) | 738/738 (100) | 1.000 |
| Prior ischaemic stroke | 126/397 (31.74) | 216/738 (29.27) | 0.387 |
| Prior TIA | 26/395 (6.58) | 58/738 (7.86) | 0.434 |
| Prior bleeding | 355/396 (89.65) | 623/737 (84.53) | 0.017 |
| Prior major bleeding | 361/395 (91.39) | 595/735 (80.95) | <0.001 |
| Prior intracranial bleeding | 148/397 (37.28) | 203/736 (27.58) | 0.001 |
| Prior GI bleeding | 196/397 (49.37) | 382/735 (51.97) | 0.403 |
| Prior intravitreal bleeding | 2/248 (0.81) | 4/429 (0.93) | 0.866 |
| Prior cerebral amyloid angiopathy | 8/239 (3.35) | 11/403 (2.73) | 0.655 |
| Prior labile INR | 42/396 (10.61) | 86/731 (11.76) | 0.558 |
| Prior heart failure | 102/396 (25.76) | 222/738 (30.08) | 0.124 |
| Prior LVEF <40% | 34/397 (8.56) | 70/736 (9.51) | 0.599 |
| Prior peripheral artery disease | 54/397 (13.60) | 132/738 (17.89) | 0.063 |
| Prior CAD | 83/394 (21.07) | 213/735 (28.98) | 0.004 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 62.00 (40.00-80.11) | 60.01 (41.00-80.78) | 0.912 |
| Prior dialysis | 21/395 (5.32) | 67/738 (9.08) | 0.024 |
| Prior cirrhosis | 34/395 (8.61) | 43/738 (5.83) | 0.076 |
| Active malignancy | 8/135 (4.32) | 13/330 (3.94) | 0.832 |
| Baseline haemoglobin, g/dL | 11.8 (9.9-13.4) | 11.9 (10.2-13.5) | 0.273 |
| Baseline platelets, x109 | 186 (145-234) | 193 (155-239) | 0.209 |
| Categorical variables are expressed as n/N (%). Continuous variables are shown as mean±SD for those with normal distribution and median (Q1-Q3) for those not fulfilling a normal distribution. P-values in bold indicate statistical significance. AF: atrial fibrillation; BARC: Bleeding Academic Research Consortium; CAD: coronary artery disease; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; GI: gastrointestinal; INR: international normalised ratio; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; SD: standard deviation; TIA: transient ischaemic attack | |||
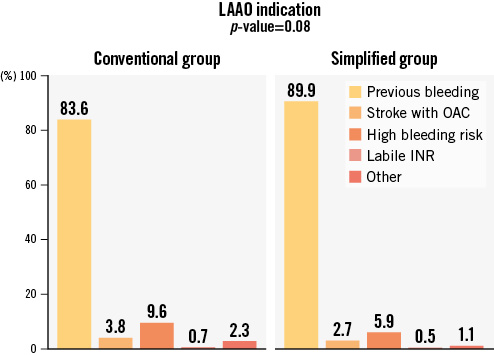
Figure 1. Primary indication for LAAO. Representation of the most frequent indications for LAAO. High bleeding risk included patients with a need for anticoagulation and any comorbidity that increased the risk of bleeding. INR: international normalised ratio; LAAO: left atrial appendage occlusion; OAC: oral anticoagulation
Table 2. Procedural characteristics and complications.
| Variable | Simplified treatment (N=397) | Conventional protocol (N=738) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technical success | 394 (99.24) | 734 (99.46) | 0.661 |
| Complete occlusion | 381 (95.97) | 693 (93.90) | 0.141 |
| Peridevice leak (significant) | 4 (1.01) | 17 (2.30) | 0.214 |
| Procedural complications (any) | 11 (2.77) | 29 (3.93) | 0.313 |
| Procedural pericardial effusion | 5 (1.26) | 13 (1.76) | 0.518 |
| Device embolisation | 0 (0.00) | 2 (0.27) | 0.299 |
| Vascular complications | 5 (1.26) | 9 (1.22) | 0.954 |
| Procedural major bleeding | 3 (0.76) | 4 (0.54) | 0.661 |
| Procedural stroke | 1 (0.25) | 4 (0.54) | 0.482 |
| Categorical variables are expressed as n (%). | |||
Table 3. Treatment at discharge.
| Treatment at discharge after LAAO (N=1,135) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified group (n=397) | Conventional group (n=738) | ||
| No treatment | 55 (13.85) | DAPT | 522 (70.73) |
| Warfarin | 21 (2.85) | ||
| DOAC | 111 (15.08) | ||
| SAPT | 342 (86.15) | LMWH | 55 (8.65) |
| OAC+SAPT | 29 (3.42) | ||
| Categorical variables are expressed as n (%). DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy; DOAC: direct oral anticoagulants; LAAO: left atrial appendage occlusion; LMWH: low-molecular-weight heparin; OAC: oral anticoagulation; SAPT: single antiplatelet therapy | |||
Table 4. Antithrombotic treatment at 6 months after LAAO.
| Antithrombotic treatment | Simplified treatment | Conventional protocol | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| No treatment | 79/360 (21.94) | 63/670(9.40) | <0.001 |
| SAPT | 272/388 (70.10) | 429/709 (60.51) | 0.002 |
| DAPT | 7/388(1.80) | 127/709 (17.91) | <0.001 |
| Warfarin | 0/388(0) | 13/708(1.84) | 0.007 |
| DOAC | 0/338(0) | 11/412(2.67) | 0.011 |
| LMWH | 1/388(0.26) | 9/704(1.28) | 0.090 |
| OAC+SAPT | 1/388(0.26) | 21/709(2.96) | 0.002 |
| Categorical variables are expressed as n/N (%). DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy; DOAC: direct oral anticoagulants; LAAO: left atrial appendage occlusion; LMWH: low-molecular-weight heparin; OAC: oral anticoagulation; SAPT: single antiplatelet therapy | |||
Table 5. Univariable and multivariable analysis of potential independent predictors of the composite primary endpoint.
| Variable | p-value univariable | p-value multivariable | OR 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.03(0.01 to 0.06) |
| Sex | 0.982 | ||
| Hypertension | 0.080 | ||
| Dyslipidaemia | 0.256 | ||
| Diabetes | 0.932 | ||
| Smoking | 0.037 | 0.207 | |
| AF type | 0.253 | ||
| Previous ischaemic stroke | <0.001 | 0.022 | –0.61 (–1.14 to –0.09) |
| Previous heart failure | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.77(0.38 to 1.16) |
| Previous peripheral artery disease | 0.274 | ||
| Previous coronary artery disease | 0.382 | ||
| Previous LV dysfunction (<40%) | 0.548 | ||
| CHA2DS2-VASc | 0.192 | ||
| HAS-BLED | 0.052 | ||
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | <0.001 | 0.060 | |
| Prior dialysis | 0.061 | ||
| Previous cirrhosis | 0.613 | ||
| Previous recent major surgery | 0.131 | ||
| Prior major bleeding | 0.009 | 0.021 | 0.86(0.13 to 1.60) |
| Previous intracranial bleeding | <0.001 | 0.004 | –1.00 (–1.68 to –0.31) |
| Previous gastrointestinal bleeding | <0.001 | 0.246 | |
| Previous spontaneous haematoma | 0.390 | ||
| Previous intravitreal bleeding | 0.748 | ||
| Prior labile INR | 0.026 | 0.123 | |
| LAAO indication | 0.414 | ||
| P-values in bold represent statistical significance. AF: atrial fibrillation; CI: confidence interval; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; INR: international normalised ratio; LAAO: left atrial appendage occlusion; LV: left ventricular; OR: odds ratio | |||
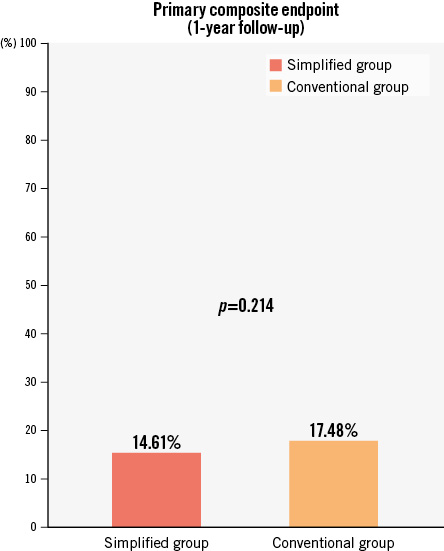
Figure 2. Event rates for the primary composite endpoint of stroke, TIA, peripheral embolism, DRT or major bleeding events. The conventional group and the simplified treatment groups are compared in the global cohort of very high bleeding risk patients according to the BARC criteria.BARC: Bleeding Academic Research Consortium; DRT: device-related thrombus; TIA: transient ischaemic attack
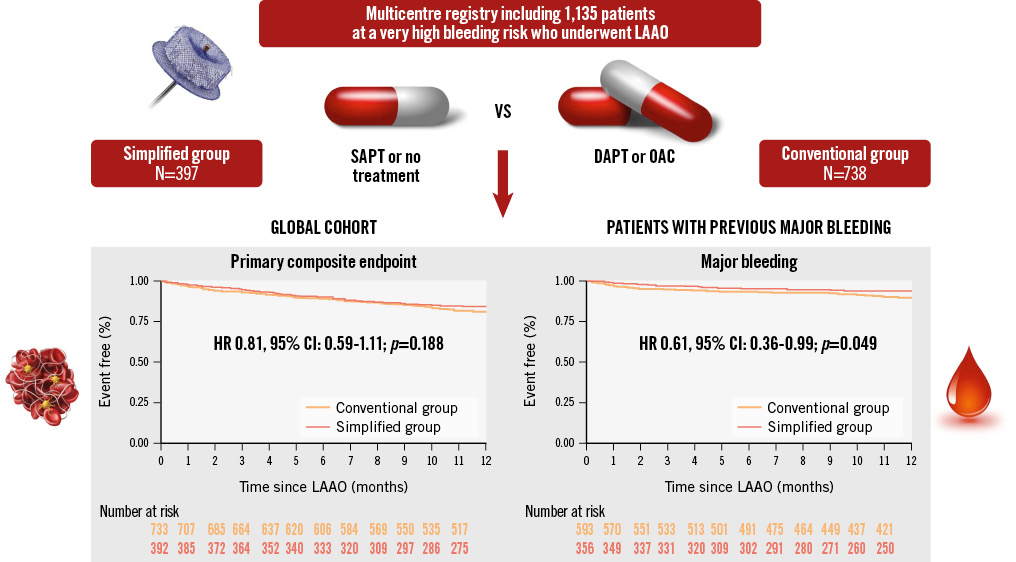
Central illustration. Main findings of a simplified versus conventional treatment after LAAO in very high bleeding risk patients. No differences were found in the composite endpoint during the first year of follow-up. Moreover, in patients with previous major bleeding, the simplified group presented a lower rate of new major bleeding during the first year post-LAAO. CI: confidence interval; DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy; HR: hazard ratio; LAAO: left atrial appendage occlusion; OAC: oral anticoagulation; SAPT: single antiplatelet therapy
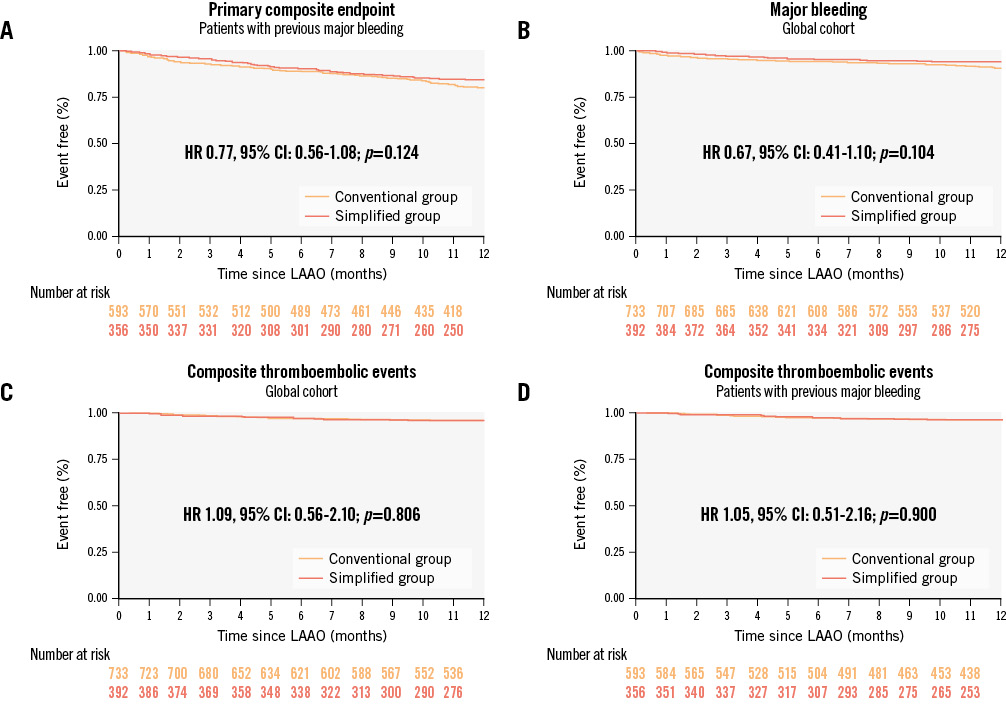
Figure 3. Event-free survival analyses. Event-free survival analyses for the primary composite endpoint of stroke, TIA, peripheral embolism, DRT or major bleeding events (A); major bleeding events (B) and secondary endpoints, a composite of stroke, TIA, peripheral embolism, or DRT (C and D). The conventional and the simplified treatment groups are compared in this global cohort of very high bleeding risk patients according to the BARC criteria (B and C) and in the subgroup of subjects with previous major bleeding prior to LAAO (A and D). BARC: Bleeding Academic Research Consortium; CI: confidence interval; DRT: device-related thrombus; HR: hazard ratio; LAAO: left atrial appendage occlusion; TIA: transient ischaemic attack
Discussion
In this study, our primary objective was to juxtapose a simplified ATT regimen post-LAAO, involving SAPT or no treatment, against conventional protocols within a cohort of patients at an elevated risk of bleeding. Given that a substantial proportion of patients undergoing LAAO are predisposed to a high bleeding risk, optimising ATT assumes paramount importance1819.
In our study, we found no differences between this less aggressive ATT and the conventional protocols when evaluating the efficacy of LAAO. We compared the primary efficacy composite endpoint of stroke, TIA, peripheral embolism, and DRT in both groups. No significant differences were observed in the survival analysis during the first year of follow-up after LAAO (HR 0.81, 95% CI: 0.59-1.11; p=0.188). These findings underscore the global effectiveness of a simplified therapy as a viable treatment option for high bleeding risk patients. This conclusion was further validated when subgroup analysis considered patients with a history of relevant major bleeding, revealing comparable efficacy between simplified therapy and conventional protocols incorporating oral anticoagulation or DAPT (HR 0.77, 95% CI: 0.56-1.08; p=0.124).
However, different analyses were also performed to determine whether there were differences in the prevention of thromboembolic events and to assess whether this therapy could reduce the risk of major bleeding during follow-up.
The incidence of the composite endpoint of thromboembolic events including stroke, TIA, peripheral embolism, and DRT remained low in both groups. There were no differences in the survival analysis (HR 1.09, 95% CI: 0.56-2.10). In contrast with these findings, Carvalho et al21 did find in their new meta-analysis a reduced rate of thromboembolic events in patients with DAPT after LAAO compared with SAPT. It is of note that thromboembolic events showed a relative risk reduction of 85.7% compared to the risk predicted by the CHA2DS2-VASc score. These findings are similar to those of Korsholm et al15. However, theirs was a single-centre study without comparison to the conventional protocol.
Moreover, antithrombotic treatment after LAAO was not found to predict the risk of DRT22. These findings may create uncertainties about the best post-LAAO regimens. In this sense, Merella et al18 also previously evaluated the efficacy of SAPT after LAAO in a high bleeding risk cohort like ours, without evidence of an increased rate of DRT.
All these findings suggest that SAPT or no treatment after LAAO can be used to prevent ischaemic events without increasing the rate of DRT in subjects with a very high bleeding risk.
Addressing safety endpoints, our multicentre study hinted at numerically lower major bleeding events in the simplified treatment group, though statistical significance was not achieved. It is imperative to note that certain bleeding risk factors were more prevalent in the simplified group. On the other hand, significant differences in antithrombotic treatment persisted at 6 months after LAAO, with almost one-quarter of patients in the conventional group still on DAPT or OAC. These differences between the two groups introduce a potential bias. Subsequent analysis, focusing exclusively on patients with prior major bleeding, substantiated a significant reduction in new major bleeding events within the simplified group during the first year of follow-up (HR 0.61, 95% CI: 0.36-0.99; p=0.049).
These findings are consistent with those of Patti et al23. They compared SAPT with DAPT and showed the same efficacy but with a lower incidence of major bleeding during the follow-up. However, this cohort seems to be at lower risk compared to ours, with a lower HAS-BLED score (3.3) and a lower rate of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) including death during the first year (7.8% and 7.4%, respectively) in both groups. On the other hand, Carvalho et al21 found no differences in the bleeding rate in their study. However, this meta-analysis included all types of patients undergoing LAAO, not only those at a very high bleeding risk, like our patients. It is likely that this less aggressive treatment should be preferred in subjects with a higher risk of bleeding.
Other studies have evaluated a simplified therapy after LAAO. Paitazoglou et al16 evaluated the safety and efficacy of single or no antithrombotic therapy switched at 3 to 6 months after LAAO in 766 patients in the EWOLUTION registry. However, initial therapy with DAPT or anticoagulation was suggested during these first months. Moreover, although the rates of ischaemic and bleeding events were low (1.4 and 1.3 per 100 patient-years, respectively), these patients were not at a very high risk of bleeding, as the mean HAS-BLED score was 2.2±1.2.
Regarding DRT, previous studies have failed to find a particular postprocedural treatment as a predictor of DRT242526. In our cohort, the rate of DRT remained low (3.96%), similar to those previously described in other registries2527. In fact, no differences were found between the 2 groups with different discharge treatments. These findings are consistent with those reported by Merella et al18. They also found that DRT was not increased in the high bleeding risk subgroup receiving SAPT after LAAO. However, DRT ranged from 0.00% to 10.71% between different centres, because each centre had their own protocol to treat DRT during follow-up.
In our study, we used the BARC definition to select patients with a high bleeding risk. Despite having been intended to assess the bleeding risk in percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) procedures19, the BARC definition has also been used in previous LAAO studies2829 and ongoing trials such as SAFE LAAC CKD (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT05660811) and CLOSURE-AF (NCT03463317). Its relevance in procedures such as LAAO is still unknown, although post-LAAO treatment in most of the patients also consists of OAC or DAPT, as is the case after PCI.
The discourse surrounding the optimal antithrombotic approach after LAAO has perennially been controversial. The diversity in protocols utilised in previous studies evaluating LAAO has compounded the lack of consensus on the most efficacious postprocedural strategy91112. This extends not only to the choice of treatment but also the optimal treatment duration. Various options have been explored to prevent DRT, such as prolonged anticoagulation with or without SAPT during the initial 6 months7 and a 1-3 month duration of DAPT after LAAO1314. Heterogeneous registries have reported the efficacy and safety of less aggressive treatments151630. Nonetheless, there is no consensus on the best strategy. In view of this heterogeneity, some ongoing trials are trying to elucidate the best ATT: the ADALA (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT05632445)17 and ANDES (NCT03568890) trials are trying to determine whether DAPT versus low-dose direct oral anticoagulants is superior not only in preventing thromboembolic events but also in reducing the risk of bleeding. The ADALA study was presented at EuroPCR 202317. It was stopped prematurely due to an advantage for low-dose DOAC being demonstrated after 90 of the planned 160 patients were randomised. The composite endpoint of thromboembolic events, DRT, and major bleeding up to 3 months was reduced with low-dose apixaban (Eliquis [Bristol-Myers Squibb]) compared to DAPT with aspirin and clopidogrel. In addition, SAFE-LAAC (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT03445949) will compare short versus extended DAPT after LAAO and, furthermore, the continuation of antithrombotic therapy beyond the first 6 months. On the other hand, the STROKECLOSE trial (NCT02830152) will give us a better understanding about LAAO in patients at high risk of bleeding, like those with a history of intracranial haemorrhage. In that trial, the group with LAAO will receive single antithrombotic therapy for at least 6 months, with or without clopidogrel during the first 45 days.
Finally, the antiplatelet treatment after LAAO must be individualised, considering the patient’s comorbidities. All these observations may help to promote a more precise and personalised medicine. Selecting those patients who could benefit from a simplified antithrombotic treatment could lead to a lower rate of complications during follow-up.
Limitations
The retrospective nature of our study introduces inherent biases, and the operator-driven selection of antithrombotic treatment might influence outcomes. The absence of a standardised post-LAAO treatment management, which varies according to operator criteria across centres, poses challenges. Moreover, follow-up protocol (both clinical and imaging with TOE or CT) differed between centres, and in some patients imaging follow-up beyond 12 months was not performed, so DRT may be underestimated. Significant differences in post-LAAO treatment persisted after 6 months of follow-up. This may be another source of bias. In addition, another limitation is the high success and low complication rates of the registry, which are difficult to achieve in randomised clinical trials. Finally, one last limitation could be the selection of patients using the BARC definition, which was created for PCI and not procedures such as LAAO.
Despite these limitations, our multicentre study, the largest of its kind in very high-risk patients undergoing LAAO, suggests the efficacy and safety of a simplified treatment. This underscores the need for continued exploration of personalised antithrombotic approaches in post-LAAO care, striving for precision medicine tailored to individual patient characteristics. In addition, different ongoing trials like ADALA17, ANDES and SAFE-LAAC will try to elucidate the best antithrombotic therapy after LAAO.
Conclusions
A simplified treatment with SAPT or no treatment after LAAO in patients at a very high risk of bleeding seemed to be as effective as a conventional treatment regimen. Additionally, it hints at a potentially safer profile, with a lower rate of major bleeding, especially notable in those patients with a history of major bleeding prior to the LAAO procedure. Further validation through randomised trials is warranted to solidify these observations.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, P. Antúnez-Muiños.
Ethics approval statement
Data were collected from a Spanish registry of left atrial appendage occlusion, which was approved by the local ethical committee (Comité de Ética en la Investigación con medicamentos de las Áreas de León y del Bierzo) with the validation code number 22146. All data were anonymised when included for the analysis, so no further informed consent was necessary for the study. Nevertheless, informed consent was obtained for each procedure.
Impact on daily practice
Patients undergoing left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) are generally patients at a higher risk of bleeding, and postprocedural antithrombotic therapy after LAAO is still controversial. In this study we found that a simplified treatment with a single antiplatelet regimen or even no treatment may be useful in patients at a higher risk of bleeding, such as those with a history of major bleeding prior to LAAO. Randomised trials may be needed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of this simplified treatment in this cohort of very high-risk patients undergoing LAAO.
Conflict of interest statement
I. Cruz-González has been a proctor of Abbott, Boston Scientific, Lifetech, and Eclipse Medical. R. Estévez-Loureiro has received speaker fees from Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Venus Medtech, Lifetech, and Jenscare. X. Freixa-Rofastes reports support from Abbott, Boston Scientific, and Lifetech. I.J. Amat-Santos has been a proctor of Boston Scientific. L. Nombela-Franco has been a proctor of Abbott. D. Martí Sánchez has received speaker and consulting fees from Boston Scientific and SMT. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.

