Description
XTENT® Custom NX™ DES Systems (XTENT, Inc.) are designed to enable the treatment of single lesions, long lesions and multiple lesions of varying lengths and diameters, in one or more arteries with a single device. The stent is a proprietary modular design and consists of multiple 6 mm cobalt chromium segments that are interdigitated as shown in Figure 1.
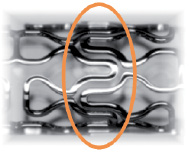
Figure 1. Interdigitated segments.
The delivery system as shown in Figure 2 incorporates a protective sheath and a mechanism to control the length of stent deployed.
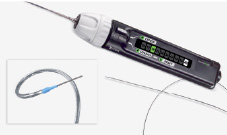
Figure 2. Custom NX delivery system.
The stents are coated with a coating formulation specifically designed for endovascular use and is made of a biodegradable polymer and a new rapamycin derivative, Biolimus A9® (Biosensors International), with enhanced lipophilicity enabling increased uptake in local target tissues and reduced presence in the systemic circulation1.
History
Although significant advances have been made with drug eluting stents, current stent designs and methods of delivery can limit their effectiveness and efficiency and can result in increased costs for healthcare providers. Current fixed-length stent systems are not customisable, and require a separate device and a separate exchange for each stent or balloon used, which increases procedural complexity, time and cost. Treatment of longer lesions with current fixed-length stents can require placement of overlapping stents, which has been identified as a possible cause for incidence of sub acute thrombosis (SAT)2, non Q-Wave myocardial infarction3,4, non-focal restenosis5, delayed endothelialisation6, and greater potential for stent fracture7,8. During delivery of non-sheath protected drug eluting stents to the target lesion, coating damage may occur, which might impact drug elution or the ability to prevent restenosis9. Due to the difficulty of accurately pre-selecting the necessary stent length and diameter, geographic miss, or inaccurate placement of stents, may occur, which results in portions of a lesion remaining exposed. In the STLLR trial, longitudinal geographic miss was observed in 47.6% of procedures, and resulted in higher rates of thrombosis and TLR10. In addition, the longitudinal straightening effect of current stent designs can contribute significantly to the occurrence of MACE and angiographic restenosis11.
Technical specifications
The XTENT® Custom NX™ 36 DES System consists of 36 mm of total stent length configured in six 6 mm stent segments. The XTENT® Custom NX™ 60 DES System consists of 60 mm of total stent length configured in ten 6mm stent segments. The number of stent segments can be adjusted in situ to deliver up to 36 mm or 60mm of stent length. The stent segments are pre-mounted on an adjustable balloon catheter and are protected by an outer sheath. Each stent segment is coated with a formulation consisting of Biolimus A9® and a biodegradable drug carrier, PolyLacticAcid (PLA).
Following the placement of a guidewire, the Custom NX DES System is delivered to the site of the target lesion. Opaque markers on the balloon inflation lumen and the protective sheath allow for accurate position of the catheter. Features of the device handle enable the operator to control the number of stent segments to be deployed and to also separate the exposed stent segments from those remaining protected in the sheath of the catheter. After separation, the balloon is inflated to deploy the custom length stent. If desired, by adjusting the integrated balloon, the operator can shorten, reposition and re-inflate the balloon in situ, for post-dilatation. After the lesion is covered with the desired stent length the Custom NX DES system can be reset and used to treat an additional lesion with any remaining stent segments. The deployment sequence of the device is illustrated in Figures 3-9.
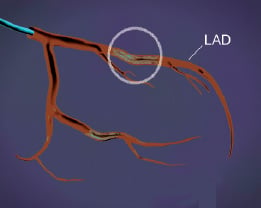
Figure 3. First target lesion.
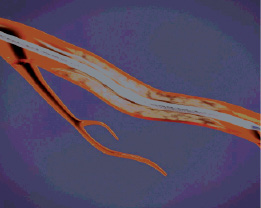
Figure 4. Device is advanced across the first lesion over conventional guidewire.
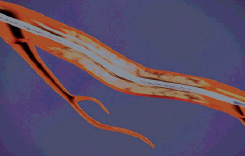
Figure 5. The sheath is retracted to expose the amount of stent needed.

Figure 6. Once the correct length of stent is exposed, the exposed stent is separated from the stent remaining in the device.
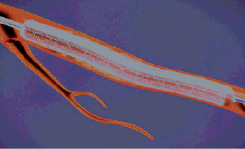
Figure 7. The exposed stent is deployed using standard technique.
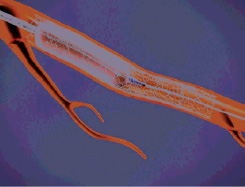
Figure 8. If desired, the balloon can be shortened for post dilatation at higher pressure within the boundaries of the stented segment.
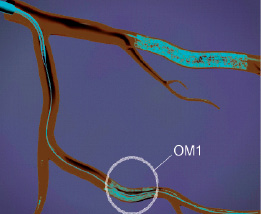
Figure 9. The system can be reset within the blood vessel, the wire can be redirected to another lesion and the remaining stent can be used for an additional customised stent deployment.
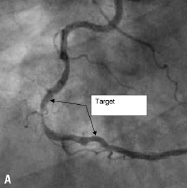
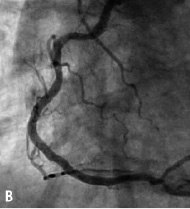
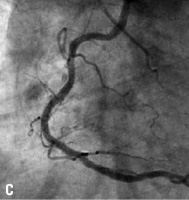
Figure 10. A: Right coronary artery; B: Final result; C: 6 month follow-up.
Indications for use
XTENT® Custom NX™ DES Systems have not been approved for sale by any regulatory authority. The Custom NX 36 and NX 60 DES Systems enable the user to place, using a single delivery catheter, up to two drug eluting stents of in situ customisable length of respective cumulative length of 36 and 60 mm, for improving coronary luminal diameter in patients with symptomatic ischaemic disease due to de novo lesions in native coronary arteries. The Custom NX 36 Catheter System will allow for treatment of lesions < 30 mm in length and the Custom NX 60 Catheter System will allow for treatment of lesions up to 52 mm in length. Custom NX 36 and Custom NX 60 DES System configurations are 2.5 mm, 3.0 mm, and 3.5 mm diameter and can be used in vessels of reference diameters of 2.25 to 3.75 mm.
Clinical experience
The CUSTOM I clinical trial was designed to evaluate the preliminary safety and efficacy of in situ customisation using the Custom NX 36 DES System. Enrolment of 30 patients was completed in July 2005. To date patients have been reassessed at 30 days, four months, eight months and 12 months. This trial will continue to follow patients annually through five years.
The CUSTOM II clinical trial was designed to evaluate the safety of in situ customisation for long lesions and multiple lesions using the XTENT Custom NX 60 DES System. Enrolment of 100 patients was completed in October 2006 at 10 cardiology centres in Europe. Patients will be reassessed at 30 days, six months and 12 months. Patients will be followed annually for five years. Figure 10 shows a long right coronary artery treated as part of the CUSTOM II trial.
The CUSTOM III clinical trial is designed to evaluate in situ customisation for long lesions and multiple lesions using an expanded range of diameters of XTENT Custom NX DES Systems. Enrolment of 90 patients at up to 15 European centers is ongoing. Patients will be reassessed at 30 days, six months, 12 months, and annually up to five years. Upon completion of CUSTOM I, II, and III, XTENT intends to initiate CUSTOM IV, V and VI pivotal trials.

