
Challenges still remain in borderline indications for transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), such as paravalvular aortic regurgitations and procedure-related failure, in particular with balloon-expandable devices. TAVR has not been performed in unicuspid aortic valves, with the exception of a few compassionate cases.
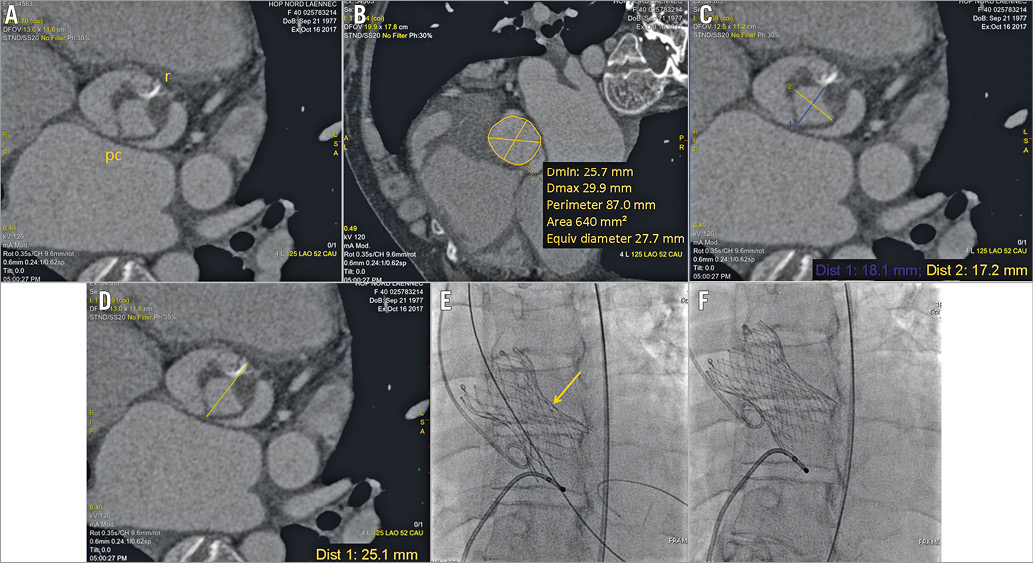
We present the case of a 40-year-old woman with cardiogenic shock in the context of severe chronic aortic regurgitation complicating the unicuspid valve. Clinical presentation was severe because of critical biventricular dysfunction failure despite inotropic support (Moving image 1, Moving image 2), associated with moderate kidney failure and liver dysfunction. Conventional valve surgery was contraindicated because of a prohibitive operative risk. Heart transplantation was not an option as the patient presented extreme alloimmunisation. Computed tomography demonstrated favourable transfemoral access for TAVR and a suitable valvular anatomy (Panel A, Panel B). The sizing relied on a compromise between a large aortic annulus (640 mm2) and a small distance between the pseudocommissure and the raphe (18 mm) (Panel C, Panel D), as previously described in bicuspid morphology1. In the context of clinical instability despite inotropic support, the Heart Team decided to proceed with implantation of a 29 mm CoreValve® Evolut™ R (Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, USA) under local anaesthesia.
A standard transfemoral procedure was performed. Optimal positioning of the prosthesis required three manoeuvres of recapture (Moving image 5-Moving image 7). The fourth delivery attempt, performed 5 mm below the aortic annulus (Moving image 8, Moving image 9), allowed complete release of the prosthesis. A suboptimal deployment in the transverse plane near the raphe (Panel E) was corrected after a post-dilatation (Panel F, Moving image 10, Moving image 11).
The clinical evolution was favourable, allowing discharge from the hospital 30 days after TAVR, under medical treatment including ramipril, bisoprolol, and spironolactone. Postoperative echocardiography demonstrated improvement in LVEF (about 25%), normal cardiac output, and satisfactory bioprosthesis haemodynamic performance (Moving image 3, Moving image 4).
Here we report the first successful implantation of a self-expanding bioprosthesis for the treatment of severe aortic regurgitation complicating the unicuspid aortic valve. TAVR following a minimalist approach seems to be an attractive treatment approach even in patients presenting with unfavourable clinical and anatomic conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
Part 1. Moving transthoracic echographic data
Moving image 1. Severe aortic regurgitation visualised in long-axis view.
Moving image 2. Preoperative LV dysfunction despite inotropic support.
Moving image 3. Improvement of LVEF 25 days after TAVR procedure.
Moving image 4. Echocardiographic result 25 days after TAVR implantation.
Part 2. Angiographic procedural data
Moving image 5. Preoperative aortography showing severe aortic regurgitation.
Moving image 6. Incorrect positioning of the prosthesis above the annulus plane requiring recapture.
Moving image 7. Incorrect positioning of the prosthesis below the annulus plane requiring recapture.
Moving image 8. Correct positioning of the prosthesis 5 mm below the annulus plane.
Moving image 9. Aortography after prosthesis deployment showing moderate residual aortic regurgitation.
Moving image 10. Final post-dilatation of the deployed prosthesis.
Moving image 11. Final aortography after post-dilatation.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.
Moving image 1. Severe aortic regurgitation visualised in longaxis view.
Moving image 10. Final post-dilatation of the deployed prosthesis.
Moving image 11. Final aortography after post-dilatation.
Moving image 2. Preoperative LV dysfunction despite inotropic support.
Moving image 3. Improvement of LVEF 25 days after TAVR procedure.
Moving image 4. Echocardiographic result 25 days after TAVR implantation.
Moving image 5. Preoperative aortography showing severe aortic regurgitation.
Moving image 6. Incorrect positioning of the prosthesis above the annulus plane requiring recapture.
Moving image 7. Incorrect positioning of the prosthesis below the annulus plane requiring recapture.
Moving image 8. Correct positioning of the prosthesis 5 mm below the annulus plane.
Moving image 9. Aortography after prosthesis deployment showing moderate residual aortic regurgitation.

