Introduction
Recent European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Guidelines have extensively investigated antithrombotic therapy during percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI)1-3. However, based on their complexity and partial difference from existing ACC/AHA guidelines, it is sometimes difficult to follow them in individual decisions. Moreover, most of the recommendations are based on prospective randomised trials, which only partially reflect the “real world” situation. Meta-analyses and guideline-based registries might help to guide daily practice. With respect to cardiovascular interventions the combination of both anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapies is mandatory to prevent thrombosis, because activation of both platelets and the coagulation system contribute to thrombus formation. The choice, initiation and duration of antithrombotic strategies is based on the clinical setting (elective, acute or urgent intervention). To optimise efficacy of therapy and reduce the potential bleeding hazard both, ischaemic and bleeding risks, have to be evaluated on an individual basis. The present report aims to give practical solutions to handle antithrombotic therapy for patients undergoing PCI in various clinical conditions.
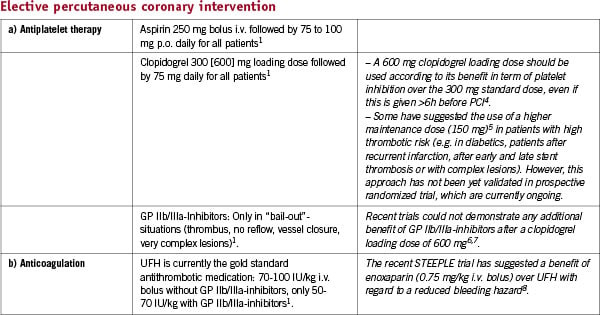
Non ST elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS)
See also: Algorithm of NSTE ACS management (Figure 1)
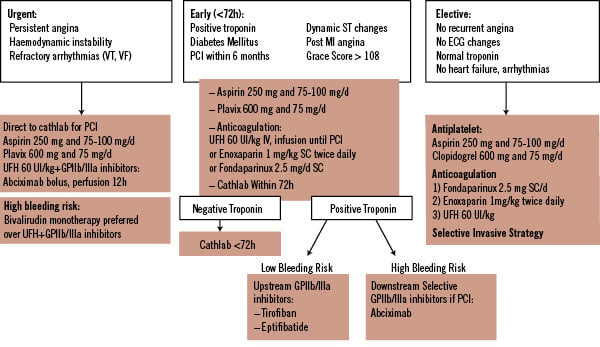
Figure 1. NSTE Acute Coronary Syndrome.
To find the optimal strategy the risk of ischaemic events and the bleeding risk of an individual patient have to be weighed against each other. Thereby, easy to use variables or scores should be preferred.
Assessment of patient risk:
– Higher ischaemic risk:
ST-segment changes, elevated troponin, diabetes, GRACE score >1089
– Higher bleeding risk:
Female, >75 years, bleeding history, GFR<30ml/min, femoral access
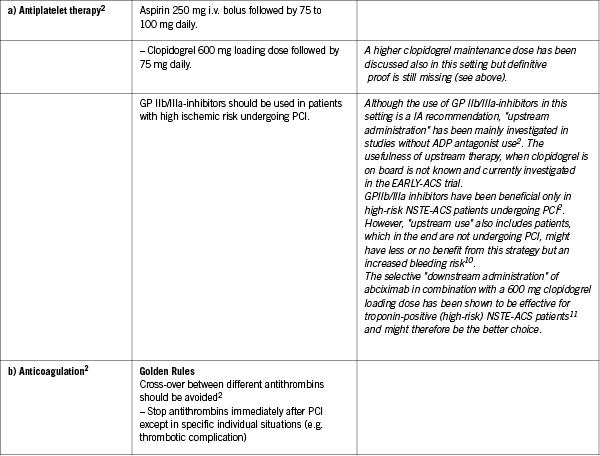
Pre-cath management
1. In very high risk patients
(e.g. Persistent Angina, Haemodynamic Instability, Refractory Arrhythmias)
Patients are immediately referred to the cathlab:
UFH 60 IU/kg i.v. bolus, then infusion until PCI with GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors (abciximab)
In patients with high bleeding risk: monotherapy with bivalirudin, 0.1 mg/kg i.v. bolus followed by an infusion of 0.25 mg/kg/hr
2. In medium-to-high risk patients (e.g. troponin-positive, recurrent angina, dynamic ST changes)
Primarily invasive strategy is planned <72h:
In patients <75 years
UFH 60 IU/kg i.v. bolus, then infusion (aPTT-controlled) until PCI
or enoxaparin 1 mg/kg s.c. twice daily until PCI
or fondaparinux 2.5 mg daily s.c. until PCI
In patients > 75 years
UFH 60 IU/kg i.v. bolus, then infusion (aPTT-controlled) until PCI
Fondaparinux 2.5 mg daily s.c.
In case of renal failure (GFR<30 ml/min)
UFH 60 IU/kg i.v. bolus, then infusion (aPTT-controlled) until PCI
3. In low-risk patients
Primarily conservative strategy is planned:
Fondaparinux 2.5 mg s.c. daily
or enoxaparin 1 mg/kg s.c. twice daily
or UFH 60 IU/kg i.v. bolus, then infusion (aPTT-controlled) until PCI
Management in the cathlab
Golden Rule:
Continue the initial therapy! (Don’t switch except after fondaparinux)
If under UFH: Continue perfusion, ACT measurement might be useful
Target range:
- 200-250 sec with GP IIb/IIIa-inhibitors
- 250-350 sec without GP IIb/IIIa-inhibitors
If under enoxaparin:
< 8h of last s.c. application: no additional bolus
within 8-12h of last s.c. application: add 0.30 mg/kg i.v. bolus
>12h of last s.c. application: 0.75 mg/kg i.v. bolus
If under bivalirudin: An additional i.v. bolus of 0.5 mg/kg and an increase of the infusion to 1.75 mg/kg/hour before PCI is performed
If under fondaparinux: UFH 50-100 IU/kg when angiography and PCI is performed
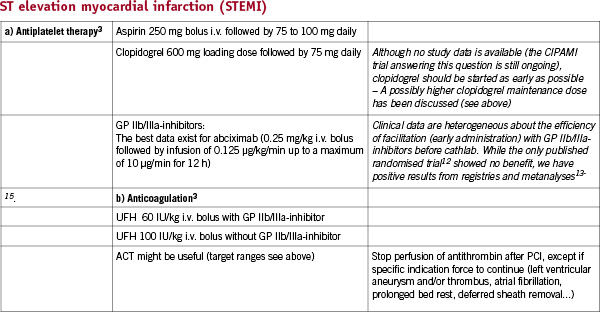
Specific points of interest
Prevention of bleeding
– Assessment of bleeding risk
– No crossover of antithrombotic therapy
– No overdosing of antithrombotic therapy
– Radial access should be the preferred option in high bleeding risk
– Stop anticoagulation after PCI unless a specific indication exists
– Selective downstream use of GP IIb/IIIa-inhibitors in NSTE ACS might be better than unselective upstream use
– A consensual bleeding risk score is highly warranted
Duration of dual antiplatelet therapy
– After bare metal stent (BMS) implantation in stable angina: one month
– After drug eluting stent (DES) implantation (all patients): one year
– After ACS (all patients independent of therapeutic strategy): one year
Golden rules to avoid premature discontinuation of antiplatelet therapy
– Avoid DES in patients not expected to comply with therapy
– Avoid DES if surgery is planned within 12 months
– Detailed information and education of the patient might prevent premature cessation of antiplatelet therapy
– Most surgical procedures can be performed under dual antiplatelet therapy with acceptable rate of bleeding: a multidisciplinary approach is required (cardiologist, anaesthesiologist, surgeon).
In surgical procedures with high bleeding risk:
– Stop clopidogrel five days before surgery and stay on ASA, unless high bleeding risk surgery
– The substitution of combined antiplatelet therapy with LMWH is ineffective and useless
– Restart clopidogrel as soon as possible with loading dose
– In very high risk patients (e.g. multivessel DES<1 years, left main stenting...), in whom cessation of antiplatelet therapy before surgery seems to be dangerous, it has been suggested to switch from clopidogrel five days before surgery to a short half-life antiplatelet agent, e.g. the GP IIb/IIIa-inhibitors tirofiban or eptifibatide and stop infusion of these agents four hours before surgery.
Patient under chronic anticoagulation
To avoid long-term triple antithrombotic therapy, BMS implantation or the use of pure balloon dilatation is preferred over the use of DES.
Antiplatelet therapy monitoring
– No consensual test system available
– No consensual definition of “non”– or “low” – response
– No large clinical evidence that tailored antiplatelet therapy improves clinical outcomes
– Monitoring of antiplatelet response by platelet function assays is used at present only in clinical research. Data are not strong enough to support the common use of the available assay systems in daily clinical practice.
Patients with aspirin hypersensitivity
If aspirin is highly required a “rapid desensitisation procedure” should be performed17
Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
In patient with a history of HIT, neither UFH nor LMWH should not be used (cross reactivity). Bivalirudin is the best option in this case for elective PCI and ACS. Others options are argatroban, lepirudin and danaparoid.

