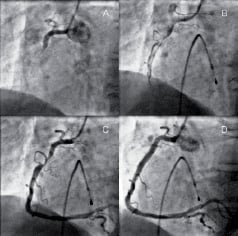
A 67 year old man with a one-hour history of chest pain due to acute inferior ST elevation myocardial infarction underwent coronary angiography after treatment with aspirin 300 mg, clopidogrel 600 mg, and a weight-adjusted abciximab bolus. The culprit lesion was a proximal occlusion of the right coronary artery (panel A). Passage of a 0.014” angioplasty wire through the occlusion restored TIMI I antegrade flow, which revealed a severe stenosis in the proximal right coronary artery (RCA) in association with a large thrombus extending to the acute margin (panel B). Angiographically visible thrombus was completely removed by the use of an aspiration catheter (Export Catheter, Medtronic, USA) (panel C). The stenosis was then stented with a 5.0 x 20 mm Liberte™ (Boston Scientific, USA) stent with no angiographic evidence of distal embolisation or no-reflow (panel D). The patient was discharged 48 hours later.
A large thrombus burden in the infarct-related artery poses technical and therapeutic challenges during percutaneous coronary intervention. Furthermore, its presence is associated with adverse angiographic and clinical outcomes. Conventional management employs combination antiplatelet therapy that includes an infusion of a glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitor, but the role of mechanical thrombectomy devices remains contentious. These images demonstrate that the use of an aspiration catheter can dramatically reduce thrombus load in these patients. This facilitates the procedure through better visualisation of the lesion, allowing appropriate stent selection, and it may reduce the propensity to no-reflow. Whether or not there is a clinical advantage from the use of such devices, however, remains to be determined.