Abstract
BACKGROUND: Late lumen enlargement (LLE) − a positive remodelling phenomenon − after drug-coated balloon (DCB) angioplasty for stable coronary disease contributes to a lower restenosis rate. However, lesion characteristics promoting LLE remain unclear.
AIMS: This study aimed to investigate predictive lesion characteristics for LLE using serial optical frequency domain imaging (OFDI) following DCB angioplasty for de novo coronary artery lesions.
METHODS: This retrospective, single-centre observational study included patients with angina pectoris who underwent paclitaxel-coated balloon angioplasty without stenting under OFDI guidance as well as follow-up OFDI. OFDI endpoints were lumen volume, plaque phenotype, and procedure-associated dissection. LLE was defined as a ≥10% increase in the lumen volume of the treated lesion at follow-up.
RESULTS: Between August 2016 and December 2019, among patients with successful DCB angioplasty, 108 lesions (83 patients) had available follow-up imaging after a median of 6.1 months. LLE was detected in 44 (40.7%) lesions. Fibrous/fibrocalcific and layered plaques had significantly larger lumen volumes at follow-up than immediately after the index procedure, whereas lipid plaques exhibited no significant difference. Medial dissection with an arc >90° revealed an increased lumen volume. Multivariate analysis showed that layered plaques (odds ratio [OR] 8.73, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.92-39.7; p=0.005) and medial dissection with an arc >90° (OR 4.65, 95% CI: 1.63-13.3; p=0.004) were independent LLE predictors.
CONCLUSIONS: Layered plaques and extensive medial dissection after DCB angioplasty were associated with higher LLE occurrence in de novo coronary lesions. These findings may be clinically applicable to DCB therapeutic strategies based on plaque features.
Drug-coated balloon (DCB)-only percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) for stable coronary disease is a promising treatment that eliminates stent thrombosis, as it leaves no metallic mesh and is associated with a low restenosis rate1. Very late drug-eluting stent (DES) thrombosis, caused by strut malapposition and neoatherosclerosis, results in myocardial infarction2. Although the duration of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) after PCI using second-generation DES has been shortened, a DCB-only strategy is required for the de-escalation of antiplatelet therapy, particularly in patients at high bleeding risk and with upcoming non-cardiac surgery3. DCB efficacy has been proven for in-stent restenosis of both bare metal stents and DES, and the use of DCB is supported by the European Society of Cardiology guidelines4. For diffuse coronary artery lesions, the blended approach of combining DCB with DES may be beneficial to lower the risk of stent thrombosis and restenosis owing to the advantage of an overall reduction in stent length5.
Clinical trial data using DCB in de novo coronary artery disease have demonstrated inconsistent results, although a major benefit has been demonstrated in small vessel disease6. Differences in study results have been attributed to variations in the DCB, procedural approaches, and vessel size7. However, the differences in the plaque-healing response after DCB according to the underlying pathology have not been investigated to date. Previous studies using angiography have shown late lumen enlargement (LLE) − a positive remodelling phenomenon − in 48-69% of lesions treated using DCB at 4- to 6-month follow-up89. DCB-induced LLE compensates for the adverse effects of vessel shrinkage and neointimal proliferation after balloon angioplasty and contributes to a lower restenosis rate. Identifying predictive lesion characteristics for LLE is of major interest, as this would optimise the selection of lesions for DCB intervention as well as lesion preparation before DCB delivery. Optical frequency domain imaging (OFDI; LUNAWAVE [Terumo]), a high-resolution intravascular imaging modality, permits the detailed characterisation of plaque morphology and luminal geometry during PCI procedures1011.
This study aimed to elucidate predictive lesion characteristics for LLE following a successful DCB angioplasty for de novo coronary artery disease by analysing serial OFDI images before and immediately after PCI and at post-PCI follow-up.
Methods
STUDY DESIGN AND POPULATION
This retrospective, observational study was conducted at the National Center for Global Health and Medicine in Tokyo, Japan. Patients who underwent DCB angioplasty without stenting under OFDI guidance for angina pectoris due to de novo coronary artery lesions as well as follow-up angiography and OFDI were included. DCB angioplasty was not performed in the following cases: vessel diameter ≥3 mm (not warranted by Japanese medical insurance), severe calcification, long lesions, and chronic total occlusions, particularly when acute vessel recoil was suspected. Furthermore, patients with ST- or non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, left main disease, thrombus, saphenous vein or arterial graft disease, moderate to severe renal dysfunction (estimated glomerular filtration rates <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 or serum creatinine levels >1.5 mg/dL), or unstable haemodynamics at presentation were excluded from DCB angioplasty.
This study complied with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the institutional ethics committee of our institution (NCGM-S-004507-00). All patients provided written informed consent.
PROCEDURES
The DCB-only strategy was implemented according to the recommendations of the International DCB Consensus Group12. OFDI was initiated to assess plaque morphology, vessel size, and target lesion length at the beginning of the PCI. OFDI images were acquired after intracoronary nitroglycerine administration using a near-infrared light rotational catheter (FastView [Terumo]) at a pullback speed of 40 mm/s and frame speed of 158 frames/s, in concordance with blood clearance using contrast medium, as previously described10. In cases with difficult OFDI catheter delivery, dilation with a small-diameter semicompliant balloon or rotational atherectomy (for calcified lesions) was performed. Predilation was usually performed with a cutting balloon (Boston Scientific) or a non-slip element balloon (Goodman Co.) to avoid major coronary dissection. These balloon diameters were estimated as the average of the proximal and distal references, defined as the largest lumen (usually within 10 mm of the stenosis), using OFDI. The predilation balloon was inflated at a nominal pressure for 30 seconds at least three times. The balloon pressure was further increased for additional dilation, if necessary, under OFDI observation. A thorough elastic recoil evaluation was conducted using another angiogram obtained 15 minutes after predilation. After successful lesion preparation, a paclitaxel-coated balloon (SeQuent Please [B. Braun]) was applied with the same diameter as the predilation balloon and sufficient length to completely cover the lesion without any geographical mismatch. The DCB was inflated at nominal pressure for at least 30 seconds.
After PCI, DAPT was prescribed with aspirin (100 mg/day) and either clopidogrel (75 mg/day) or prasugrel (3.75 mg/day) for 1-3 months to prevent acute thrombotic occlusion. DAPT was continued at the physician’s discretion. Subsequently, single antiplatelet therapy was administered.
Endpoints and definitions
Quantitative coronary angiography (QCA) was performed before and immediately after PCI and at follow-up using an analysis program (CAAS 7.5 [Pie Medical Imaging]). Details of the QCA analysis have been described previously13. Angiographic endpoints included lesion length, reference vessel diameter, minimum lumen diameter, diameter stenosis, late lumen loss, and binary restenosis. Target lesion revascularisation (TLR) was defined as any revascularisation, percutaneous or surgical, for restenosis at the lesion treated during index PCI14.
Offline OFDI analysis was performed by two experienced investigators, who were blinded to the QCA results, using proprietary OFDI console software (Terumo). Cases of disagreement between the investigators were resolved by consultation among the investigators to reach a consensus. The methods of quantitative measurement and morphoÂlogical assessment of OFDI have been previously described1011. The OFDI endpoints included minimum lumen area, lumen volume, plaque phenotype, and procedure-associated dissection. For quantitative measurement, cross-sectional OFDI images were analysed at 1 mm longitudinal intervals throughout the same treated length immediately after PCI and at follow-up. Lumen areas were traced by automated lumen contour detection, followed by additional manual correction if needed. Lumen volumes were calculated as the sum of the lumen areas of each cross-section multiplied by the 1 mm slice thickness over the treated segment (Simpson’s rule). The lumen volume index was calculated as the lumen volume divided by the treated length to adjust for differences in segment lengths. Qualitative assessment was conducted frame by frame to evaluate the plaque phenotype, dissection, and intramural haematomas. Plaques were classified into three groups: (1) fibrous (homogeneous high-intensity tissues with gradual signal attenuation) or fibrocalcific (fibrous tissues with calcium that appeared as a low-signal-intensity area with a sharply delineated border), (2) lipid (signal-poor regions with diffuse borders, accompanied by high signal attenuation), and (3) layered (heterogeneous tissue layers of different optical density that were clearly demarcated from the underlying plaque). For mixed lesions, the predominant plaque phenotype resulting in luminal stenosis was selected. Dissection was defined as the disruption of the vessel luminal surface after balloon angioplasty. Dissection depth into the plaque and maximum circumferential extent in degrees of an arc were visually assessed from a cross-sectional view. Dissection severity was categorised into two grades based on an increased risk of adverse events: (1) dissection limited to the intima or medial layer with a circumferential arc ≤90° or (2) dissection involving the medial layer with a circumferential arc >90°15. Intramural haematomas were defined as blood accumulations within the medial space related to dissection. Representative OFDI images of the coronary plaque phenotype and dissection are shown in Figure 1.
High accuracy and reproducibility of OFDI measurements have been reported16. The relative range of interscan reproducibility of the lumen volume measurements based on 2 standard deviations of their measurement was approximately ±10%17. Therefore, we defined LLE as a relative change in the lumen volume of ≥10% at follow-up.
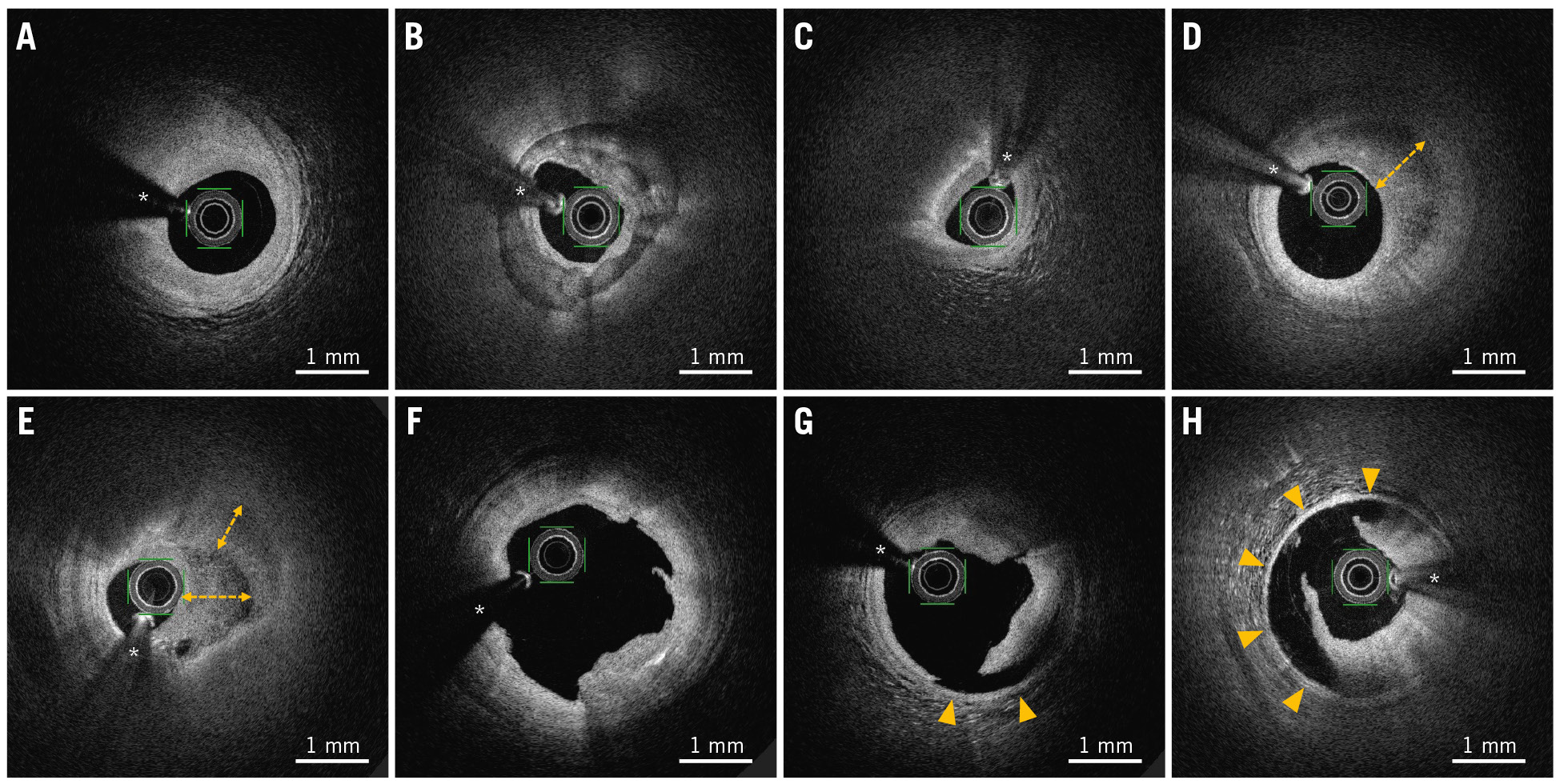
Figure 1. Representative OFDI images of coronary plaque phenotype and procedure-associated dissection. A) Fibrous plaque, defined as homogeneous high-intensity tissues with gradual signal attenuation. B) Fibrocalcific plaque, defined as fibrous tissues with calcium that appear as a low-signal-intensity area with a sharply delineated border. C) Lipid plaque, defined as signal-poor regions with diffuse borders, accompanied by high signal attenuation. D,E) Layered plaques, defined as heterogeneous tissue layers of different optical density (double-headed arrows) that were clearly demarcated from the underlying plaque. F) Intimal dissection. G) Medial dissection with a circumferential arc ≤90° (arrowheads). H) Medial dissection with a circumferential arc >90° (arrowheads). * Guidewire artefact. OFDI: optical frequency domain imaging
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Categorical variables are presented as counts (percentages) and were compared using the χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test. After assessing the data distribution using the Shapiro-Wilk test, continuous variables are presented as mean±standard deviations or medians (interquartile ranges) and were compared using the 2-sample or paired t-test, Mann-Whitney test, or Wilcoxon signed-rank test, as appropriate. Intraobserver and interobserver variabilities were assessed for plaque phenotypes and procedure-associated dissection in OFDI using the κ coefficient of agreement. Univariate logistic regression analysis was performed to evaluate the association of clinical variables, angiographic parameters, plaque phenotypes, and procedure-associated dissection with LLE. Plaque phenotypes were calculated as the odds ratio for lipid and layered plaques, with fibrous/fibrocalcific plaques as the reference group. Variables with p-values<0.100 in the univariate analysis were entered into a multivariate regression model. Statistical significance was set at p<0.050. All analyses were performed using SPSS version 25.0 (IBM).
Results
STUDY PATIENTS
Between 1 August 2016 and 31 December 2019, a total of 898 patients who underwent PCI were consecutively screened. Of these, 113 patients with 142 lesions underwent successful DCB angioplasty for de novo lesions. Ultimately, 83 patients with 108 lesions had available angiographic and OFDI follow-up examination after a median of 6.1 (5.6-6.9) months and were included in the final analysis. The selection of patients and study flowchart are shown in Supplementary Figure 1. None of the patients required bailout stenting immediately after DCB treatment.
LUMEN VOLUME CHANGES
At follow-up, the lumen volume measured using OFDI had significantly increased compared with that measured immediately after PCI (72.6 [55.8-91.8] mm3 vs 74.3 [55.3-97.8] mm3; p<0.001). Positive relative changes in the lumen volume were observed in 68 (63.0%) lesions; 44 (40.7%) lesions met the criteria for LLE (boundary for interscan reproducibility) (Supplementary Figure 2).
PATIENT AND PROCEDURAL CHARACTERISTICS
Baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. No significant differences existed in cardiovascular risk factors, comorbidities, or discharge medication between the non-LLE and LLE groups.
The angiographic and procedural details are provided in Table 2. The two groups were similar in terms of the lesion characteristics, vessel diameter, and PCI procedures. No in-hospital complications, including acute closure, myocardial infarction, or repeated PCI, occurred. Late lumen loss at follow-up was 0.01±0.37 mm. Binary restenosis was detected in 9.3% of the lesions, and TLR was required for 5.6% of the lesions. No aneurysm formation was observed in the DCB-treated lesions. Binary restenosis and TLR were more frequently observed in patients without LLE than in those with LLE (p=0.004 and p=0.043, respectively).
Table 1. Baseline characteristics.
| Characteristics | Overall (n=83 patients) |
No LLE (n=45) |
LLE (n=38) |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 67.5±12.4 | 69.5±10.3 | 65.0±14.4 | 0.109 |
| Male sex | 68 (81.9) | 37 (82.2) | 31 (81.6) | 0.940 |
| Current smoker | 16 (19.3) | 6 (13.3) | 10 (26.3) | 0.135 |
| Diabetes | 27 (32.5) | 17 (37.8) | 10 (26.3) | 0.267 |
| Hypertension | 49 (59.0) | 29 (64.4) | 20 (52.6) | 0.276 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 52 (62.7) | 26 (57.8) | 26 (68.4) | 0.318 |
| Previous myocardial infarction | 17 (20.5) | 8 (17.8) | 9 (23.7) | 0.506 |
| Previous PCI | 29 (34.9) | 15 (33.3) | 14 (36.8) | 0.738 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 36 (43.4) | 22 (48.9) | 14 (36.8) | 0.270 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 10 (12.0) | 6 (13.3) | 4 (10.5) | 0.482 |
| Clinical presentation | ||||
| Stable angina/asymptomatic | 57 (68.7) | 30 (66.7) | 27 (71.1) | 0.668 |
| Unstable angina | 26 (31.3) | 15 (33.3) | 11 (28.9) | |
| LVEF, % | 64.2 (58.9-68.2) | 65.1 (59.2-68.7) | 63.4 (58.5-68.2) | 0.374 |
| Multivessel disease | 43 (51.8) | 22 (48.9) | 21 (55.3) | 0.563 |
| Discharge medications | ||||
| Aspirin | 83 (100) | 45 (100) | 38 (100) | N/A |
| P2Y12 inhibitor | 83 (100) | 45 (100) | 38 (100) | N/A |
| ß-blocker | 29 (34.9) | 14 (31.1) | 15 (39.5) | 0.426 |
| ACE inhibitor/ARB | 37 (44.6) | 23 (51.1) | 14 (36.8) | 0.193 |
| Statin | 75 (90.4) | 41 (91.1) | 34 (89.5) | 0.544 |
| Oral anticoagulation | 9 (10.8) | 5 (11.1) | 4 (10.5) | 0.608 |
| Data are expressed as mean±standard deviations, numbers (%), or medians (25th-75th percentiles). ACE: angiotensin-converting enzyme; ARB: angiotensin receptor blocker; LLE: late lumen enlargement; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; N/A: not applicable; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention | ||||
Table 2. Angiographic and procedural characteristics.
| Characteristics | Overall (n=108 lesions) | No LLE (n=64) | LLE (n=44) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target vessel | ||||
| Left anterior descending artery | 54 (50.0) | 32 (50.0) | 22 (50.0) | 0.951 |
| Left circumflex artery | 33 (30.6) | 19 (29.7) | 14 (31.8) | |
| Right coronary artery | 21 (19.4) | 13 (20.3) | 8 (18.2) | |
| ACC/AHA lesion type B2/C | 51 (47.2) | 27 (42.2) | 24 (54.5) | 0.206 |
| Bifurcation lesion | 42 (38.9) | 25 (39.1) | 17 (38.6) | 0.964 |
| Ostial lesion | 8 (7.4) | 4 (6.3) | 4 (9.1) | 0.421 |
| Diffuse lesion (length >20 mm) | 20 (18.5) | 11 (17.2) | 9 (20.5) | 0.668 |
| Lesion preparation before DCB | ||||
| Compliant balloon used | 10 (9.3) | 7 (10.9) | 3 (6.8) | 0.356 |
| Scoring or cutting balloon used | 98 (90.7) | 57 (89.1) | 41 (93.2) | |
| Final balloon diameter, mm | 2.75 (2.50-3.00) | 2.75 (2.50-3.00) | 2.75 (2.50-3.00) | 0.486 |
| Balloon/artery ratio | 1.11±0.15 | 1.12±0.15 | 1.10±0.15 | 0.613 |
| Maximum inflation pressure, atmosphere | 10.0 (8.0-12.0) | 10.0 (8.0-12.0) | 8.5 (7.3-11.8) | 0.232 |
| Rotational atherectomy used | 2 (1.9) | 1 (1.6) | 1 (2.3) | 0.651 |
| DCB diameter, mm | 2.75 (2.50-2.75) | 2.75 (2.50-2.75) | 2.75 (2.50-2.75) | 0.977 |
| Total length of DCB, mm | 20.0 (20.0-26.0) | 20.0 (20.0-26.0) | 20.0 (20.0-26.0) | 0.555 |
| Number of DCBs per patient | 1.0 (1.0-1.0) | 1.0 (1.0-1.0) | 1.0 (1.0-1.0) | 0.372 |
| DCB inflation pressure, atmosphere | 8.0 (7.0-10.0) | 8.0 (7.0-10.0) | 7.0 (7.0-9.8) | 0.175 |
| Dissection immediately after PCI (NHLBI classification) | ||||
| Type A | 57 (52.8) | 38 (59.4) | 19 (43.2) | 0.260 |
| Type B | 34 (31.5) | 17 (26.5) | 17 (38.6) | |
| Type C | 16 (14.8) | 9 (14.1) | 7 (15.9) | |
| Type D | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.3) | |
| Type E/F | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Quantitative coronary angiography | ||||
| Before PCI | ||||
| Lesion length, mm | 12.9 (9.6-16.8) | 12.9 (10.0-16.4) | 12.9 (9.1-18.8) | 0.985 |
| Reference vessel diameter, mm | 2.46 (2.25-2.64) | 2.39 (2.19-2.66) | 2.50 (2.33-2.64) | 0.240 |
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 0.83±0.28 | 0.86±0.29 | 0.80±0.26 | 0.251 |
| Diameter stenosis, % | 66.4±10.4 | 65.3±10.1 | 68.0±10.9 | 0.200 |
| Immediately after PCI | ||||
| Reference vessel diameter, mm | 2.46 (2.24-2.67) | 2.43 (2.23-2.68) | 2.51 (2.28-2.67) | 0.584 |
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 1.76±0.34 | 1.74±0.33 | 1.79±0.35 | 0.405 |
| Diameter stenosis, % | 30.2±9.6 | 31.1±10.2 | 28.8±8.7 | 0.205 |
| Acute lumen gain, mm | 0.93±0.33 | 0.88±0.30 | 1.00±0.36 | 0.068 |
| Follow-up | ||||
| Reference vessel diameter, mm | 2.50 (2.27-2.70) | 2.43 (2.26-2.69) | 2.60 (2.41-2.85) | 0.063 |
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 1.75±0.45 | 1.62±0.41 | 1.95±0.44 | <0.001 |
| Diameter stenosis, % | 31.6±13.5 | 35.6±13.6 | 25.8±11.0 | <0.001 |
| Late lumen loss, mm | 0.01±0.37 | 0.12±0.34 | –0.15±0.36 | <0.001 |
| Binary restenosis (≥50% stenosis) | 10 (9.3) | 10 (15.6) | 0 (0.0) | 0.004 |
| Target lesion revascularisation | 6 (5.6) | 6 (9.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0.043 |
| Data are expressed as numbers (%), medians (25th-75th percentiles), or mean±standard deviations. ACC/AHA: American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association; DCB: drug-coated balloon; LLE: late lumen enlargement; NHLBI: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention | ||||
OFDI FINDINGS
Table 3 summarises the OFDI results immediately after PCI and at follow-up. No significant differences were observed in the lesion length or preprocedural reference vessel diameter among the different plaque phenotypes. While fibrous/fibrocalcific and layered plaques had a significantly larger lumen volume at follow-up than immediately after PCI (p=0.001 and p=0.002, respectively), lipid plaques exhibited no significant difference. In lipid plaques, the minimum lumen area at follow-up was reduced relative to that immediately after PCI (p<0.001). Procedure-associated medial dissection with an arc >90° revealed that the lumen volume at follow-up was significantly increased relative to that immediately after PCI (p<0.001), whereas those with intima or medial dissection with an arc ≤90° demonstrated no significant difference. Representative OFDI images of LLE following DCB angioplasty are shown in Figure 2. Irrespective of the coronary dissection severity, 10 (9.2%) lesions had residual dissection limited to the intima at follow-up. Coronary haematoma was observed in 10 lesions immediately after PCI but was resolved in all cases at follow-up. The correlation between the plaque phenotype and procedure-associated dissection is shown in Figure 3. The prevalence of medial dissection with an arc >90° was significantly higher in patients with fibrous/fibrocalcific plaques than in those with lipid and layered plaques. Intraobserver and interobserver agreements were good for fibrous/fibrocalcific plaques (κ=0.87 and κ=0.89, respectively), lipid plaques (κ=0.86 and κ=0.82, respectively), layered plaques (κ=0.82 and κ=0.80, respectively), and dissection (κ=0.88 and κ=0.86, respectively).
Table 3. OFDI findings.
| Findings (n=108 lesions) | Immediately after PCI | Follow-up | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plaque phenotype | |||
| Fibrous/fibrocalcific plaque (n=59) | |||
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 1.58±0.35 | 1.65±0.35 | 0.174 |
| Minimum lumen area, mm2 | 2.91±0.99 | 2.94±1.09 | 0.718 |
| Lumen volume, mm3 | 73.0 (52.3-96.9) | 75.8 (55.2-99.9) | 0.001 |
| Lumen volume index, mm3/mm | 3.98 (3.34-4.75) | 4.40 (3.52-5.19) | 0.001 |
| Lipid plaque (n=32) | |||
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 1.76±0.26 | 1.64±0.37 | 0.034 |
| Minimum lumen area, mm2 | 3.56±0.89 | 2.89±1.25 | <0.001 |
| Lumen volume, mm3 | 72.7 (56.0-96.3) | 67.2 (51.7-97.1) | 0.660 |
| Lumen volume index, mm3/mm | 4.63 (3.91-5.51) | 4.47 (3.68-5.29) | 0.588 |
| Layered plaque (n=17) | |||
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 1.99±0.31 | 2.12±0.34 | 0.058 |
| Minimum lumen area, mm2 | 4.24±1.11 | 4.65±1.21 | 0.046 |
| Lumen volume, mm3 | 69.3 (59.1-79.7) | 74.4 (63.8-97.3) | 0.002 |
| Lumen volume index, mm3/mm | 5.35 (4.79-6.20) | 6.33 (5.33-8.14) | 0.001 |
| Procedure-associated dissection | |||
| Intima/medial layer with an arc ≤90° (n=68) | |||
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 1.82±0.31 | 1.74±0.40 | 0.029 |
| Minimum lumen area, mm2 | 3.65±1.05 | 3.29±1.38 | 0.002 |
| Lumen volume, mm3 | 69.1 (54.4-83.6) | 68.0 (50.5-87.7) | 0.288 |
| Lumen volume index, mm3/mm | 4.64 (3.94-5.72) | 4.78 (4.04-5.88) | 0.189 |
| Medial layer with an arc >90° (n=40) | |||
| Minimum lumen diameter, mm | 1.50±0.33 | 1.69±0.38 | 0.001 |
| Minimum lumen area, mm2 | 2.73±0.91 | 3.04±1.19 | 0.035 |
| Lumen volume, mm3 | 82.8 (61.8-102.1) | 90.0 (69.8-120.6) | <0.001 |
| Lumen volume index, mm3/mm | 3.85 (3.31-4.58) | 4.25 (3.52-5.12) | <0.001 |
| Data are expressed as mean±standard deviations or medians (25th-75th percentiles). OFDI: optical frequency domain imaging; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention | |||

Figure 2. Late lumen enlargement after DCB angioplasty throughout serial OFDI images. A) Regression in the layered plaque from before PCI, immediately after PCI to follow-up, wherein a double-headed arrow denotes a layer of different optical density. B) Outward expansion of the vessel wall from before PCI, immediately after PCI to follow-up (dotted line) in the extensive medial dissection area (arrowhead). * Guidewire artefact. DCB: drug-coated balloon; OFDI: optical frequency domain imaging; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention
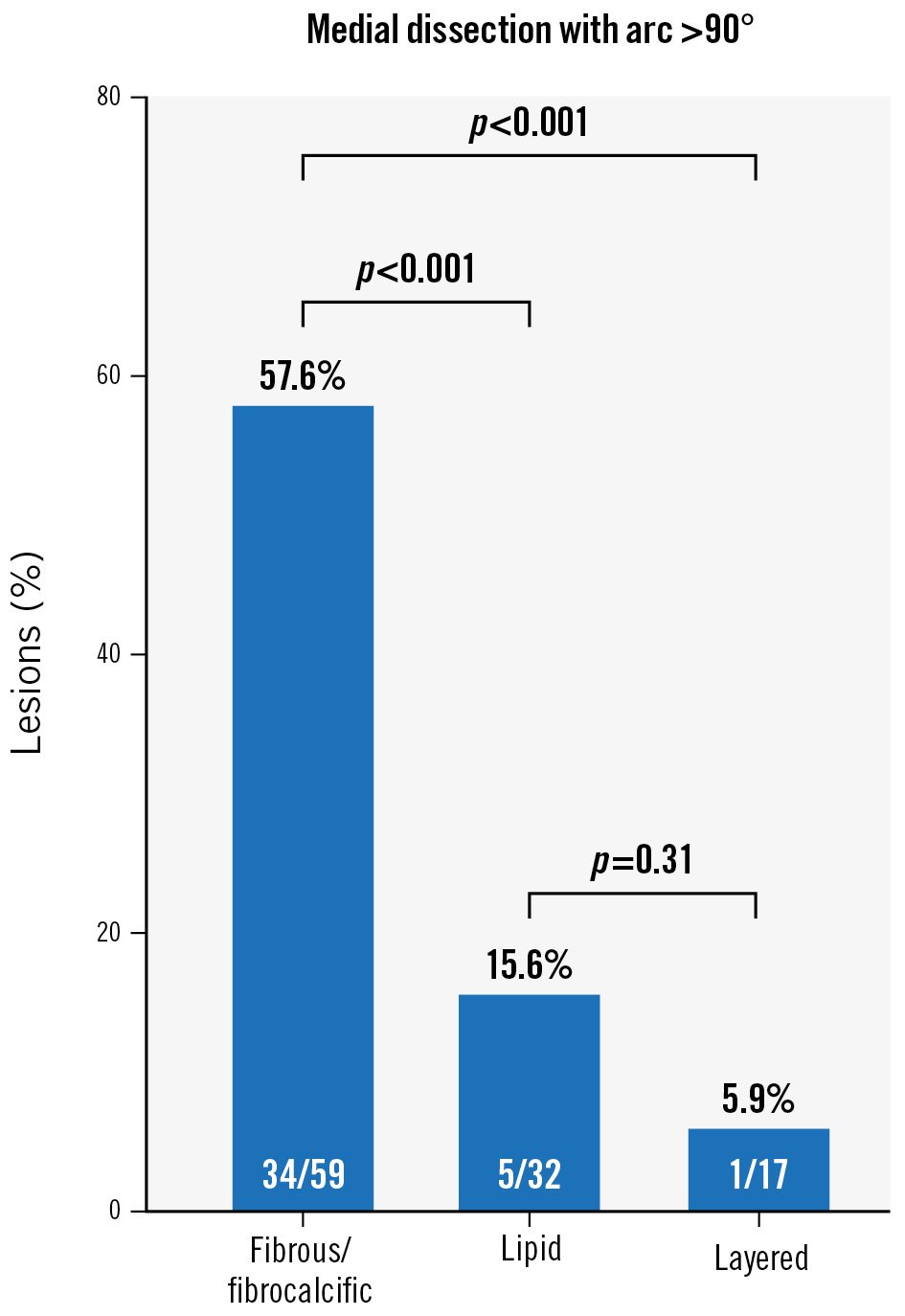
Figure 3. Correlation between plaque phenotype and procedure-associated dissection. The prevalence of medial dissection with an arc >90° is significantly higher in patients with fibrous/fibrocalcific plaques than in those with lipid and layered plaques.
LLE PREDICTORS
In the univariate logistic regression analysis, age, acute lumen gain, layered plaque, and medial dissection with an arc >90° were associated with LLE occurrence, while lipid plaques exhibited an inverse trend towards LLE. After the multivariate analysis, layered plaques (p=0.005) and medial dissection with an arc >90° (p=0.004) remained independent predictors for LLE. Neither the preprocedural reference vessel diameter nor postprocedural diameter stenosis were correlated with LLE (Table 4).
Table 4. Predictors of late lumen enlargement.
| Variables | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds ratio (95% CI) | p-value | Odds ratio (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Age, per year | 0.96 (0.94-0.99) | 0.020 | 0.97 (0.93-1.00) | 0.055 |
| Diabetes | 0.58 (0.25-1.30) | 0.183 | ||
| Preprocedural reference vessel diameter, per mm | 1.25 (0.54-2.88) | 0.598 | ||
| Postprocedural diameter stenosis, per % | 0.97 (0.94-1.02) | 0.205 | ||
| Acute lumen gain, per mm | 3.05 (0.91-10.2) | 0.071 | 2.19 (0.50-9.72) | 0.301 |
| Plaque phenotype | ||||
| Fibrous/fibrocalcific plaque | 1 [Reference] | N/A | 1 [Reference] | N/A |
| Lipid plaque | 0.41 (0.15-1.10) | 0.075 | 0.70 (0.22-2.22) | 0.544 |
| Layered plaque | 4.74 (1.38-16.3) | 0.014 | 8.73 (1.92-39.7) | 0.005 |
| Procedure-associated medial dissection with an arc >90° | 2.56 (1.14-5.71) | 0.022 | 4.65 (1.63-13.3) | 0.004 |
| CI: confidence interval; N/A: not applicable | ||||
Discussion
This study examined predictive lesion characteristics for LLE after DCB angioplasty for selected de novo lesions in coronary arteries using serial OFDI. The major findings of the study are as follows: (1) increased lumen volumes were observed in 68 (63.0%) lesions on OFDI, and 44 (40.7%) lesions met the criteria for LLE (≥10% increase in the luminal volume) at follow-up; (2) among the coronary atherosclerotic plaques, layered plaques were significantly associated with a higher LLE occurrence; and (3) in terms of procedure-related factors, extensive medial dissection on OFDI was an independent predictor for LLE (Central illustration).
Two recent studies investigated LLE predictors using intravascular ultrasound and optical coherence tomography1819; they showed that the non-flow-limiting larger dissection over the external elastic membrane or reaching the tunica media immediately after DCB angioplasty was an independent LLE predictor. Moreover, these studies revealed that LLE following DCB angioplasty was caused by both plaque burden regression and vessel enlargement. The proposed explanation for vessel enlargement is that deep dissection increases paclitaxel concentration in the adventitia, contributing to expansive vessel wall remodelling. Our finding of extensive medial dissection with an arc >90° as an LLE predictor confirmed previously reported results.
The novel finding of this study is that the presence of layered plaques predicted future LLE after DCB angioplasty. Layered plaques exhibited a significantly greater lumen volume and minimum lumen area at follow-up, compared to immediately after PCI. To the best of our knowledge, little is known about the plaque-healing response with respect to the underlying tissue substrate following DCB angioplasty. In OFDI, layered plaques appear as loose areas with lower optical signal intensities than those of dense fibrous plaques. A histological validation study demonstrated excellent agreement between layered plaques in optical coherence tomography and healed plaques based on pathology20. According to pathology studies, the healing site overlying ruptured or eroded plaques consists of an organised thrombus rich in platelets and fibrin, infiltrated inflammatory cells, proliferative smooth muscle cells, and a provisional extracellular matrix with synthesised proteoglycans and type III collagen212223. Furthermore, the ingrowth of microvessels has been identified during thrombus organisation22. These components may be easily compressed by balloon angioplasty, as 94.1% of all lesions involving layered plaques in this study remained limited to the intima or medial dissection with an arc ≤90°. Thus, LLE was attributed to layered plaque burden regression rather than vessel enlargement. However, no data fully explain the mechanisms of layered plaque regression. The highly lipophilic property of DCB-delivered paclitaxel, a microtubule-affecting drug, ensures rapid cellular uptake and a long-lasting effect in the cell, inhibiting the proliferation and migration of smooth muscle cells2425. It is reasonable to consider that paclitaxel interferes with the proliferative smooth muscle cell function in healed lesions, resulting in decreased extracellular matrix production2426.
When complete healing occurs, loose type III collagen is gradually replaced by dense type I collagen, which appears as a typical band of a high backscattering signal in OFDI2327. Fibrous or fibrocalcific plaques revealed a significant increase in the lumen volume at follow-up, whereas no significant change was observed in the minimum lumen area, which indicates that procedure-associated medial dissection did not always occur at the site of the narrowest stenosis. In this group, medial dissection with an arc >90° occurred in 57.6% of all lesions. Extensive dissection, but not the plaque phenotype, was considered to result in LLE.
In contrast, no significant differences were noted in lumen volume in lipid plaques between follow-up and post-PCI examinations. Additionally, the minimum lumen area was significantly reduced at follow-up. Statins were prescribed to 87.5% of patients immediately after PCI, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels reached a mean of 86.9 mg/dL at follow-up, with an absolute change of −28.6 mg/dL. A low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level ≤70 mg/dL was achieved in 34.4% of patients after treatment. We believe that standard lipid-lowering therapy with statins is useful in clinical practice. These observations might be explained by the fact that DCB-delivered paclitaxel does not diminish the lipid pool or necrotic core contained in lipid plaques. Another reason may be that procedure-associated extensive dissection is unlikely to occur in lipid plaques, as only 15.6% of all lesions, including lipid plaques, had medial dissection with an arc >90° in this study. Of the 10 lesions with binary restenosis, seven had lipid plaques, and three had fibrous/fibrocalcific plaques at the index procedure. Procedure-associated dissection limited to the intima or medial layer with an arc ≤90° was observed in nine lesions. All restenosis sites showed homogeneous neointimal hyperplasia on the underlying original plaques using follow-up OFDI. These results suggest that DCB angioplasty may be less favourable in cases with lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques. Intensive lipid lowering using proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor may be more effective for plaque regression than DCB in lipid-rich plaques.
Despite the small patient population, our findings have potential clinical application, as the low number of cases of binary restenosis observed in this study supports the implementation of DCB therapeutic strategies based on plaque features. DCB angioplasty may be recommended in cases with luminal stenosis, predominantly comprising layered plaques in the absence of an apparent large lipid pool on OFDI. DCB angioplasty may be the preferred option in cases with an organised thrombus overlying eroded plaques or the healing layers of the “thrombotic tail” distal to the rupture site28. In cases of dense fibrous or fibrocalcific plaques, lesion preparation through controlled dissection before DCB may be required, although bailout stenting is required for spiral or flow-limiting dissections to prevent acute vessel closure. In practice, it is difficult to control dissection with lesion preparation, and it is unclear what degree of circumferential dissection can be tolerated with intravascular imaging.
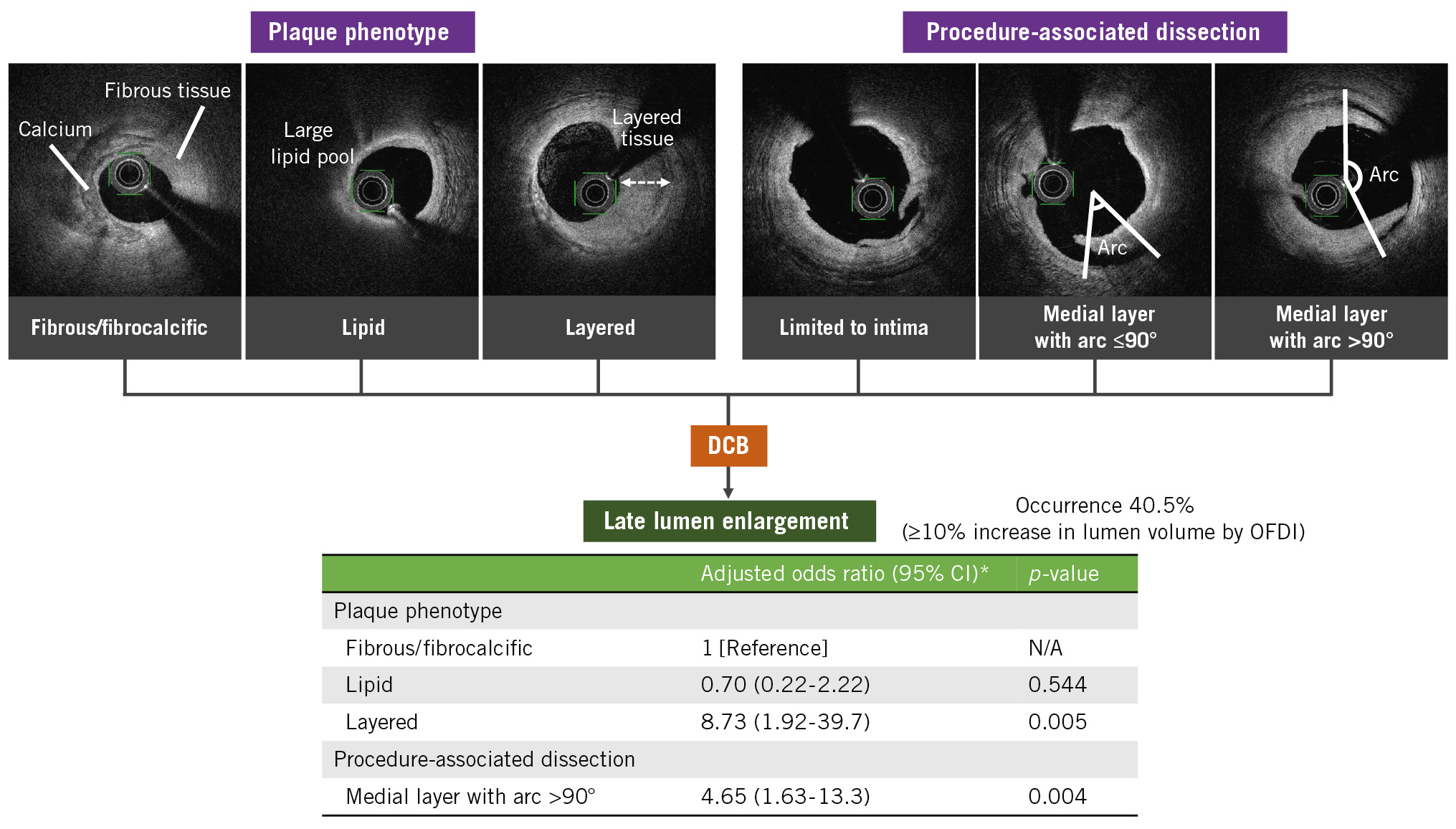
Central illustration. Predictive lesion characteristics for late lumen enlargement following DCB angioplasty. *Odds ratio adjusted for age, acute lumen gain, plaque phenotype, and procedure-associated medial dissection with an arc >90°. CI: confidence interval; DCB: drug-coated balloon; N/A: not applicable; OFDI: optical frequency domain imaging
Limitations
First, this was a retrospective single-centre study with a relatively small study population, and the results were not evaluated in an independent core laboratory. The decision to perform DCB angioplasty without stenting was at the surgeon’s discretion. Furthermore, 25.7% of the patients, who did not undergo both angiographic and OFDI follow-up, were excluded from the analysis. This may have induced a selection bias which should be considered when interpreting the results. In fact, there were fewer complex lesions in our study compared to those observed in real-world practice. Long lesions may have a more complex response after DCB angioplasty because of the mixed plaques. Conversely, the shorter and simpler lesions in this study may have allowed a more accurate assessment of the DCB response to plaques. Second, the proportion of layered plaques was smaller than that in previous studies of stable angina pectoris29. This observation may be explained by the fact that some lesions with a layered plaque overlying a large lipid pool were difficult to distinguish from lesions with a thick fibrous cap and may have been included in the lipid group. Indeed, a histopathological study showed that optical coherence tomography was able to identify all histologically defined healed lesions of fibrous plaques but only 70% of lipid plaques20. Third, the major drawback of OFDI technology is its limited tissue penetration, which precludes the determination of precise vessel dimensions in areas with a large plaque burden. Therefore, it was not possible to evaluate whether LLE was accompanied by positive remodelling of the vessels and/or plaque regression. Finally, this study did not establish a conventional balloon angioplasty arm for comparison. Non-flow-limiting dissections were described earlier as beneficial, even in conventional balloon angioplasty, probably due to compensatory arterial dilation30. Scoring or non-compliant balloon angioplasty procedures without DCB are associated with relatively greater intimal proliferation than that observed in those procedures with DCB, which may offset the effect of LLE. In fact, DCB-induced LLE occurs more frequently than compensatory arterial dilation with conventional balloon angioplasty.
Conclusions
Layered coronary plaques and extensive procedure-associated medial dissection were associated with higher LLE occurrence following DCB angioplasty for selected de novo coronary artery disease. These findings suggest potential clinical benefits of DCB therapeutic strategies based on plaque features. Furthermore, a large-scale multicentre trial is needed to verify these results and determine whether a DCB-only approach based on plaque features using intravascular imaging can result in LLE and improve clinical outcomes.
Impact on daily practice
The presence of layered coronary plaques and extensive procedure-associated medial dissection may be expected in cases of late lumen enlargement after drug-coated balloon (DCB) angioplasty for de novo coronary artery disease. These findings may apply in clinical practice to DCB therapeutic strategies based on plaque features. To improve clinical outcomes, further studies are needed to assess the DCB-only approach based on plaque features using intravascular imaging.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Yukari Uemura, Biostatistics Section, Center for Clinical Sciences, National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Tokyo, Japan, for their statistical support.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

