Abstract
Aims: The aim of the Titan PORI Registry was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a stainless steel stent coated with titanium nitride oxide (Titan®, Hexacath, France) in routine clinical practice.
Methods and results: We report a prospective single-centre experience in treating patients with the Titan® stent. All consecutive patients receiving Titan® stent(s) were enrolled. The choice of a stent was at the discretion of the operator with no exclusion criteria. The primary end point of the registry was Major Adverse Cardiac Events (MACE) at 6 and 9 months. A total of 210 lesions were treated in 193 enrolled patients (mean age 67±10; men 71%; diabetes 17%). Lesions were of type B in 64% and type C in 23%. The indications for PCI were unstable angina or non-Q-wave MI in 36% and acute STEMI in 30% of the patients. Mean reference diameter was 2.9±0.3 mm and mean lesion length 12.9±3.0 mm. Mean stent size was 2.98 mm (range 2-3.5 mm) and length 15.5 mm (range 7-28 mm). Stent delivery was successful in all cases (23% direct stenting). Complete follow-up of all 193 patients was obtained up to 9 months. There were no in-hospital or 30-day MACE observed. At 270 days, the MACE rate was 10.4% (MI 4.1%, cardiac death 0%, TVR 8.3%). There were no cases with stent thrombosis.
Conclusion: These medium term data confirm good safety profile of Titan® stent even in high risk patients and complex coronary lesions in routine clinical use.
Introduction
The implantation of bare metal coronary stents reduces the risk of periprocedural complications and restenosis compared to plain balloon angioplasty1,2. Despite the use of coronary stents, the frequency of restenosis may be up to 30 percent in several subgroups of patients, including diabetics and patients with small coronary vessels or long lesions3,4. Modifications in stent geometry5, strut thickness6, and surface material7 have been shown to influence the restenosis rate after bare metal stent implantation. Recently, patients with nickel allergy have been reported to be at an increased risk for restenosis after bare metal stent implantation8. Attempts to reduce restenosis after angioplasty with the use of various stent coatings have been largely unsuccessful9,10. Titanium features superior biocompatibility compared with stainless steel, gold, or other surface coatings11,12. In vitro examination titanium nitride oxide showed diminished platelet adhesion and fibrinogen binding compared with stainless steel13. Titan® stent (Hexacath, France) is a thin strut balloon expandable stent made of stainless steel and coated with titanium nitride oxide.
Stent coating with titanium nitride oxide reduced angiographic and ultrasonic measures of restenosis compared with stainless steel control stents in a prospective, randomised, multicentre trial (The TiNOX Trial)14. However, there is only limited data available on unrestricted use of Titan® stents in unselected populations15,16. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a stainless steel stent coated with titanium nitride oxide (Titan®) in unrestricted routine clinical practice.
Methods
Study design and patient population
The Titan PORI Registry is a prospective single centre registry with the main purpose of evaluating the safety and efficacy of Titan® stent implantation for consecutive unselected patients treated in daily practice. Between June, 2003 and November, 2004, all consecutive patients with symptoms or signs of myocardial ischaemia and de novo coronary lesion(s) scheduled for stent implantation were considered for study enrolment. The choice of a stent was at the discretion of the operator with no exclusion criteria.
During the study period a total of 193 patients were treated with the Titan® stent(s) comprising 32% of all patients with de novo disease who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in our centre.
Stents
A commercially available stainless steel stent with the unique helicoidal design was used in this study. Titan® stent is a thin strut (0.07-0.09 mm) balloon expandable stent made of stainless steel and coated with titanium nitride oxide which completely prevents discharge of nickel, chromium and molybdenum. Coating of stainless steel stents is performed by plasma enhanced vapour deposition of titanium in a pre-specified gas mixture of nitrogen and oxygen in a vacuum chamber. Stents were available in lengths of 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, 22 and 28 mm and in diameters of 2, 2.25, 2.50, 2.75, 3.0 and 3.5 mm.
Coronary-stent procedure
All patients were pre-treated with aspirin (100 mg daily) and received intravenous enoxaparine (1 mg/kg) during the procedure. Oral clopidogrel was administered as a loading dose of 300 mg before or immediately after the procedure and clopidogrel was continued at a daily dose of 75 mg for at least 3 months. Lesions were treated according to current standard interventional techniques, with the final strategy (including direct stenting, post-dilatation, periprocedural glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor, and the use of intravascular ultrasound) left entirely up to the operator’s discretion. Angiographic success was defined as a residual stenosis < 30% by visual analysis in the presence of Thrombolysis In Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) flow grade 3. The medical treatment of coronary artery disease was optimised according to the contemporary guidelines.
End point definitions and clinical follow-up
The primary end point of the Titan PORI registry was major adverse cardiac events (MACE), defined as the occurrence of any of the following within 270 days after the index procedure: death from cardiac causes, Q-wave or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction, or revascularisation of the target vessel (emergency or elective coronary-artery bypass grafting or repeated coronary angioplasty).
Q-wave myocardial infarction was defined as either (1) the presence of chest pain or other acute symptoms consistent with myocardial ischaemia and new pathologic Q waves in > 2 continuous electrocardiographic leads, or (2) elevated cardiac enzyme levels > 2 times the upper limit of normal associated with any elevation above the upper limit of normal in creatine kinase-MB levels in the presence of new pathologic Q waves. Non-Q-wave myocardial infarction was defined as an elevated creatine kinase > 2 times the upper limit of normal associated with any elevation above the upper limit of normal in creatine kinase-MB levels.
Target lesion revascularisation (TLR) was defined as a repeat intervention to treat a stenosis within the stent or in the segments 5 mm distal or proximal to the stent. Target vessel revascularisation (TVR) was defined as a reintervention driven by any lesion located in the stented vessel. Stent thrombosis was diagnosed in the presence of an acute coronary syndrome with angiographic evidence of either vessel occlusion or thrombus within the study stent. All MACE were reviewed by two of the cardiologists. All patients underwent clinical follow-up. Adverse events were monitored at hospital discharge and by office visits or telephone interviews by the cardiologist at 6 months and after a follow-up of at least 9 months. All data available from hospital records, the institutional electronic clinical database, or the referring physicians were entered into a computer database. Follow-up coronary angiography was clinically driven by symptoms or signs suggestive of myocardial ischaemia. Indication for repeat revascularisation was a significant luminal stenosis (> 50% diameter stenosis) in the presence of anginal symptoms and/or proven myocardial ischaemia in the target vessel territory.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are presented as mean±standard deviation and categorical variables as counts and percentages. The event free survival curve was calculated according to the Kaplan-Meier method. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify independent predictors of MACE. All data were analysed with the use of SPSS version 1117.
Results
Baseline and procedural characteristics
A total of 193 patients who received > 1 Titan® stent(s) during the index PCI were included in the Titan PORI Registry. The baseline clinical characteristics of the population are shown in Table 1.
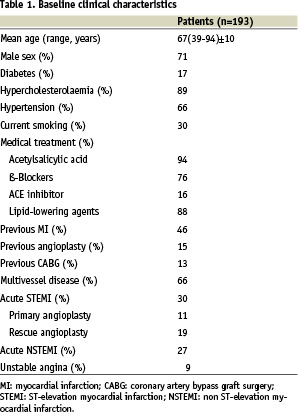
Most of the patients (66%) were treated for acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction, non-Q-wave myocardial infarction or unstable angina. Diabetes was present in 17% of the patients. The angiographic and procedural characteristics are summarised in Table 2.
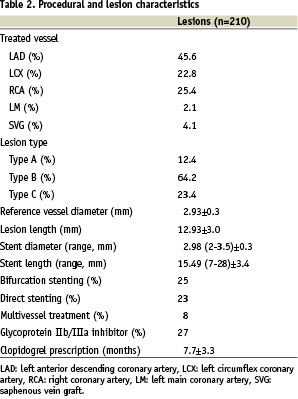
A total of 212 stents were implanted in 210 lesions in 193 patients. Lesions were of type B in 64% and type C in 23%, and 25% were bifurcation lesions and 4% chronic total occlusions. Direct stenting was performed in 48 lesions (23%). A glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor was used in 52 patients (27%). Procedural success was reached in all cases.
Clinical outcome
Complete follow-up was obtained in all 193 (100%) patients. The mean duration of the clopidogrel treatment was 7.7±3.3 months. The coronary angiography was done in 37 (19%) patients. Clinical events during 6 and 9 months follow-up are shown in Table 3.
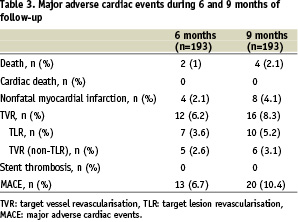
There were no in-hospital MACE observed. At 270 days follow-up, there were no cardiac deaths. Four patients died during the follow-up: two patients from malignant tumours, one patient from progressive renal failure and one patient from an infection after an orthopaedic operation. Seven patients had new non-Q-wave myocardial infarction and one patient had Q-wave myocardial infarction. The incidence of Target Vessel Revascularisation (TVR) and Target Lesion Revascularisation (TLR) were 8.3% and 5.2%, respectively. The overall MACE rate at 9 months was 10.4%. The event free survival curve is illustrated in Figure 1.
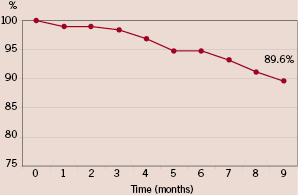
Figure 1. Event free survival at 9 months.
Multivariate analysis revealed no independent predictors for MACE. There were no cases of subacute or late stent thrombosis.
Discussion
Currently, drug-eluting stents (DES) are considered to be the most effective tool to prevent restenosis. However, there is no evidence that DES could influence mortality or prevent myocardial infarction after stent implantation. A pressing question concerns the potential risk of stent thrombosis in clinical practice18,19. In this prospective, single-centre study, unrestricted use of Titan® stent was safe and effective even in high risk patients with complex coronary lesions. Of note, no cases of stent thrombosis were observed.
Our results are in agreement with earlier small registry studies on Titan® stents15,16 extending their results to a more complex patient population. The TIBET registry demonstrated an acceptable rate of angiographic restenosis in diabetic patients treated with Titan® stent compared to bare metal stent15. Similarly, the Titan Israeli Registry reported a good safety profile and a low clinical TLR rate16. Recent registries on bare metal stents have also demonstrated comparable low rates of MACE and TLR20,21. In both of these registries, however, the included patients had stable angina and the stented vessels were larger than in our study.
The relatively low incidence of MACE in the present registry is comparable to recently published randomised DES trials22,23 and DES registries24,25. Most randomised DES trials have been performed in patient populations with comprehensive lists of exclusion criteria, including recent myocardial infarction, left main coronary artery, ostial or bifurcated lesions, chronic total occlusions, visible thrombus, depressed left ventricular function or saphenous vein grafts22,23. In our study, there were no exclusion criteria and all the above patient and lesion characteristics were allowed and were common.
One strength of our study is the fact that Satakunta Central Hospital is the only centre with coronary angiography capacity in the referral area. In this rural area, the population is stationary enabling a complete and sufficiently long-term follow-up of an all-inclusive unrestricted PCI population reflecting daily clinical practice. Our study carries with it all the general problems related to registry based observational studies with non-blinded outcome assessment. The fact that this is a single-centre, low patient number registry may give rise to an unrecognised selection and performance bias. The surprisingly low rate of mortality may be attributable to a play of chance in a relatively small patient population with single vessel PCI. Angiographic control was performed on clinical grounds, and only in a minority of patients. So, our results probably underestimate the incidence of angiographic restenosis. On the other hand, by relying on clinical follow-up alone, we avoided the chance of unnecessary TVRs due to the occulo-stenotic reflex or patient’s unjustified anxiety.
In a recent meta-analysis of PCI trials with a follow-up > 6 months, the incidence of clinical restenosis and need for revascularisation increased with the duration of follow-up26. Our data support the view that we need a follow-up longer then 6 months to disclose all the angioplasty related clinical events, since one-third of the MACE occurred after 6 months, even though we had no cases of late thrombosis.
Conclusions
These medium-term data confirm good safety profile of titanium nitride oxide coated stent (Titan®) even in high-risk patients and complex coronary lesions in routine clinical use. The clinical restenosis rate was low and so the Titan® stent may be an attractive alternative to DES especially in patients with high-risk features for stent thrombosis. Further investigation is however warranted to randomly compare the Titan® stent to other passive and active coated stents as an alternative to current drug-eluting stents in various subsets of patients.