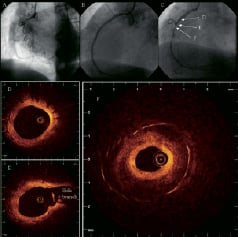
A 73-year-old woman with hypertension, hyperlipidemia and positive familial history of coronary artery disease presented with Canadian Cardiovascular Society class III angina and underwent coronary angiography, which showed a chronic occluded right coronary artery (Panel A). The vessel was recanalized and treated with three paclitaxel-eluting stents (TAXUS®, Boston Scientific: 3.5 x 32 mm distally, 3.5 x 28 mm in the middle part, 3.5 x 12 mm proximally). Postintervention coronary angiography showed a good result (Panel B). Twelve-month follow-up angiography revealed focal in-stent restenosis (Panel C). Intracoronary optical coherence tomography (OCT: LightLabImaging™, Boston, MA, USA) pullback displayed well-expanded stents covered with a thin, homogenous, highly reflective neointimal layer (Panel D, E). In contrast, the narrowest lesion site (minimal lumen area 1.1 mm2; stent area 9.0 mm2) showed a three-layer appearance of the neointima (Panel F). The inner luminal layer appeared concentric, homogenous and signal-rich (maximal thickness 0.27 mm). A second layer consisting of a low-reflective area with poorly delineated borders followed. The third layer was in direct contact with the stent struts and revealed only minimal signal intensity. These signal-poor areas (maximal thickness 1.18 mm) might represent acellular fibrinoid deposition that has been well described in experimental studies. The patient was re-treated with repeat paclitaxel-eluting stent implantation.
OCT is an analogue of intravascular ultrasound with an ultra-high resolution (10 µm) superior to any current available imaging modalities. This imaging device may be useful in visualizing neointimal growth in drug-eluting stents and improve our understanding of its underlying physiopathology in the future.