
Abstract
Aims: The aim of this study was to investigate nationwide trends and clinical outcomes of the Impella device for cardiogenic shock (CS) and high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention (HR-PCI).
Methods and results: The IMP-IT study was a multicentre observational national registry which enrolled all patients treated with Impella 2.5, Impella CP, Impella 5.0 and Impella RP, both for CS and HR-PCI indications, across 17 Italian centres from 2004 to June 2018. A total of 406 patients were included: 229 had CS (56.4%) and 177 underwent HR-PCI (43.6%). The use of Impella increased significantly during the study period (average annual percent change 39.8%, 95% confidence interval: 30.4 to 49.9; p<0.0001) for both indications. The Impella 2.5 was the most commonly used device (N=242; 59.6%). Rates of in-hospital and one-year all-cause death in patients with CS were 46.9% and 57.0%, respectively; 18.5% underwent left ventricular assist device implantation or heart transplant at one year. Rates of in-hospital and one-year all-cause death in patients who underwent HR-PCI were 5.7% and 15.6%, respectively. Rates of device-related complications were 37.1% and 10.7% in the setting of CS and HR-PCI, respectively.
Conclusions: Use of the Impella for CS and HR-PCI is increasing substantially in Italy, despite relatively high rates of device-related complications.
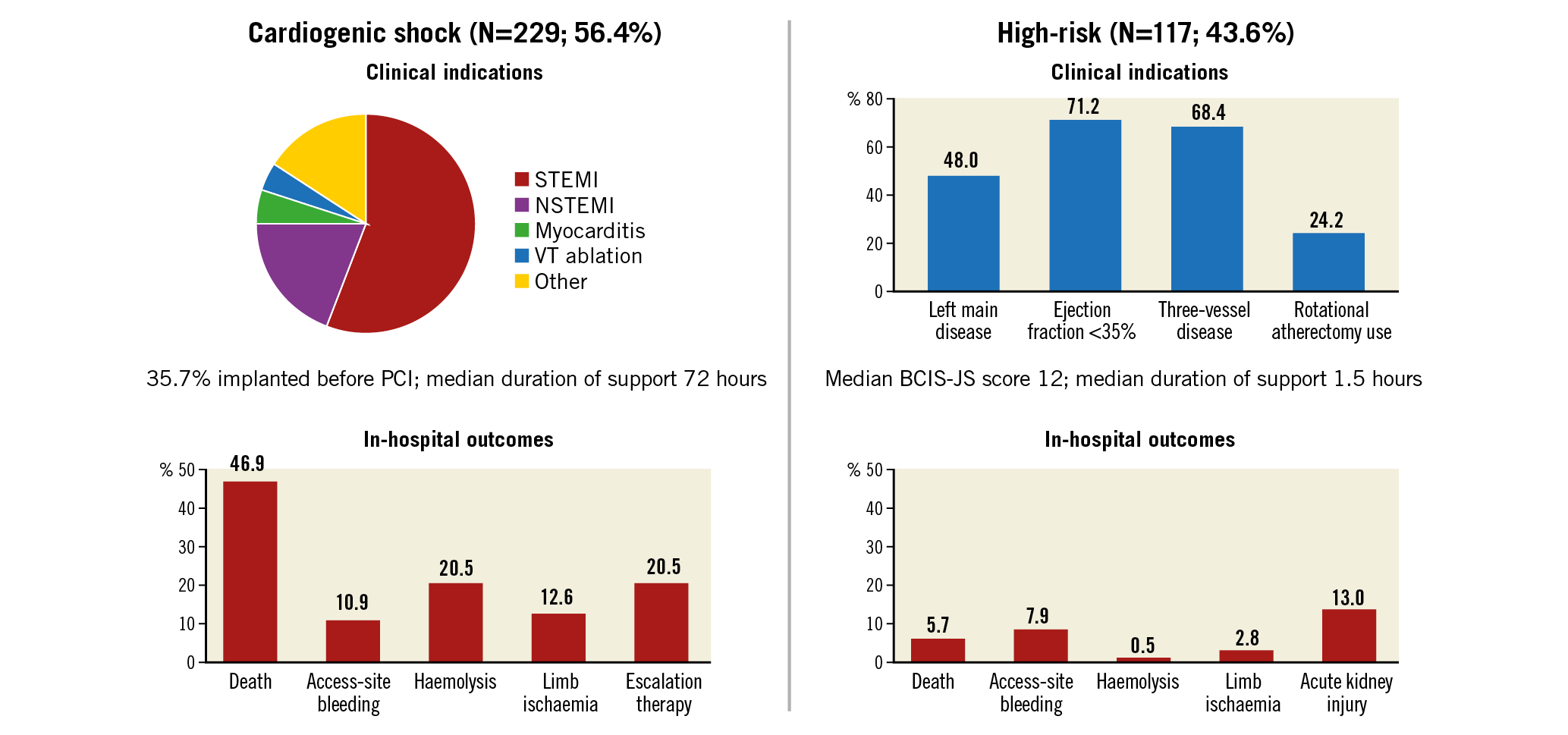
Visual summary. Impella Italian Registry (IMP-IT). 406 patients enrolled across 17 centres in Italy.
Introduction
The purpose of short-term percutaneous mechanical circulatory support (MCS) is to reduce left ventricular stroke work and myocardial oxygen demand while maintaining systemic and coronary perfusion in the setting of cardiogenic shock (CS) or to provide haemodynamic support during complex cardiac procedures such as high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention (HR-PCI)1,2. Historically, intra-aortic balloon pumps (IABP) have been used to provide haemodynamic support during CS and HR-PCI. However, evidence from randomised controlled trials does not support their use3, and their use is no longer indicated by the current European Society of Cardiology guidelines4. Over the past decade, novel percutaneous left ventricular assist devices (pLVAD) have increasingly been used in place of IABP in these clinical cases5. Currently, the most commonly used pLVAD worldwide is the microaxial Impella® pump (Abiomed, Danvers, MA, USA) which received the CE mark for the Impella 2.5 device in 20045. However, despite the widespread adoption of this technology, in both Europe and the USA, data about its efficacy and safety in a real-world population are limited to small case series and industry-sponsored registries5,6,7. Here we report the results of the IMP-IT registry (IMPella Mechanical Circulatory Support Device in Italy), an investigator-initiated, nationwide, all-comer, multicentre registry which evaluated the trends in use and clinical outcomes of the Impella in the setting of CS and HR-PCI in Italy.
Methods
STUDY POPULATION
The IMP-IT study was a multicentre retrospective observational national registry that included all consecutive patients treated with Impella 2.5, Impella CP, Impella 5.0 and Impella RP, both for CS and HR-PCI, in 17 Italian centres from 2004 to June 2018. This was an investigator-initiated study promoted by the Italian Society of Interventional Cardiology (Società Italiana di Cardiologia Interventistica – GISE). GISE is a national scientific society that hosts a prospective nationwide registry that collects yearly procedural data from catheterisation laboratories in Italy. Through the GISE registry, we identified centres that have used Impella devices for the indications of CS and HR-PCI. These centres were invited to participate in the IMP-IT registry following formal invitation from the principal investigator of the study (A. Chieffo) and the president of GISE (G. Tarantini). The participating centres which agreed to participate in the IMP-IT registry and the respective number of patients per centre enrolled in the registry are reported in Supplementary Table 1. Data related to medical history, procedural characteristics, 30-day and one-year outcomes were collected from each centre and included in a pre-specified structured data set. Clinical follow-up data were collected by in-person visits, telephone interviews, and medical notes from any hospital admission or outpatient visits. Adverse events were then adjudicated by two independent cardiologists (M. Ancona, V. Pazzanese) using source documents provided by each centre. PCI was performed according to each centre’s standard clinical practice. Collection of data at each participating site was performed according to the policies of the local institutional review board/ethics committee.
STUDY ENDPOINTS
The objectives of the study were: (i) to analyse the trends in use of Impella overall and according to its two different clinical indications (CS and HR-PCI); and (ii) to evaluate in-hospital and one-year clinical outcomes of Impella use according to the indications (CS and HR-PCI). Given the considerable differences in the clinical risk profile between patients in the CS and HR-PCI cohorts, direct comparisons between these two groups were not performed. The primary clinical endpoint of interest included in-hospital mortality, one-year mortality and the composite of death, rehospitalisation for heart failure (HF), LVAD implantation or heart transplant at one year. The full list of endpoints and study definitions is provided in Supplementary Appendix 1 and Supplementary Appendix 2.
DEVICES
The devices included in this study were the Impella 2.5, Impella CP, Impella 5.0 and Impella RP. A description of the devices used in the study is provided in Supplementary Appendix 3.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Individual patient data were pooled in a single pre-specified structured data set. Trends in the use of the Impella during the study period are reported as average annual percent change (AAPC) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Baseline characteristics are reported as number (%), mean±standard deviation, or median (interquartile range), for descriptive purposes. Event rates with 95% CIs at one year of follow-up were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method as time-to-first event. Predictors of death and the composite of death, rehospitalisation for HF, LVAD implantation or heart transplant at one year were estimated using multivariable Cox regression analysis including all variables with a p-value <0.10 at univariate analysis and using a rule of 1:8 covariates per number of events to avoid overfitting. We accounted for inter-centre heterogeneity by including the clinical centre identifier as a covariate in the multivariable models. Due to the low number of events in the HR-PCI cohort, we performed multivariable Cox regression modelling only in the CS cohort. A level of p<0.05 was set as statistically significant. Analyses were performed with Stata, version 14.0 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA) and Joinpoint software, version 4.6.0.0 (National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Results
A total of 406 patients were enrolled across 17 Italian centres. Of these, 229 patients received the Impella in the setting of CS (56.4%) and 177 patients in the setting of HR-PCI (43.6%). The study flow diagram is shown in Supplementary Figure 1. Most of the patients were treated with the Impella 2.5 in both the CS and HR-PCI groups. Trends in the use of Impella in situations of CS, HR-PCI and overall are illustrated in Figure 1A, Figure 1B and Supplementary Figure 2, respectively. Overall, the use of the Impella increased exponentially during the study period (AAPC 39.8%, 95% CI: 30.4 to 49.9; p<0.0001). The use of the Impella 2.5 increased steadily from 2004 to 2018 (AAPC 31.4%, 95% CI: 22.7-40.7; p<0.0001). Conversely, the use of Impella CP increased exponentially after its introduction (AAPC 104.3%, 95% CI: 73.1-141.2; p<0.0001). Use of the Impella 5.0 increased slightly over the study period, but this was not statistically significant (AAPC 5.1%, 95% CI: -0.8 to 11.3; p=0.10). Finally, the use of the Impella RP increased significantly after 2013 (AAPC 66.0%, 95% CI: 30.4 to 111.4; p<0.0001).
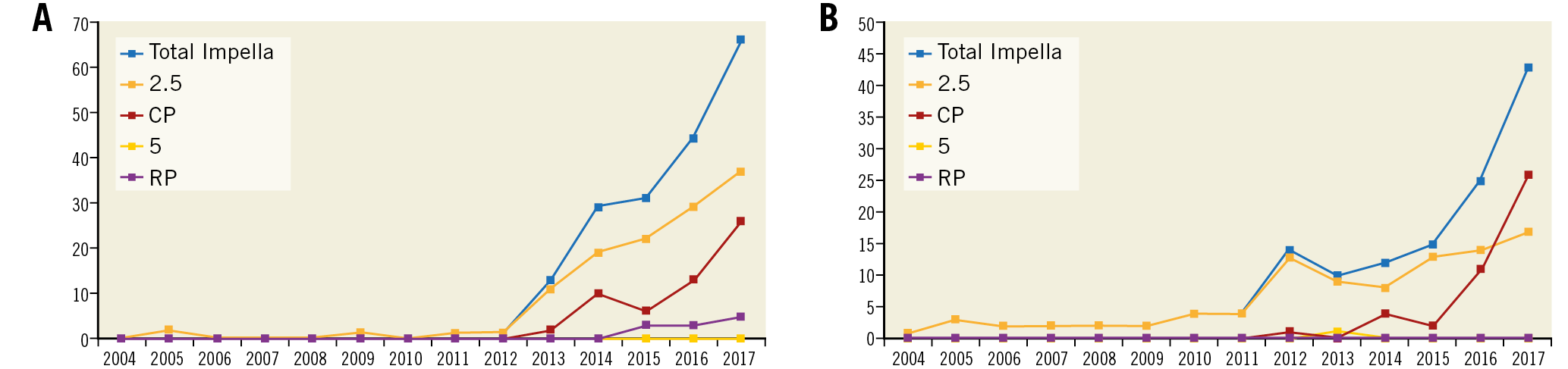
Figure 1. Trends in use of Impella in the IMP-IT registry. A) Number of Impella used during the study period in patients presenting with cardiogenic shock. B) Number of Impella used during the study period for patients undergoing high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention.
IMPELLA FOR CARDIOGENIC SHOCK
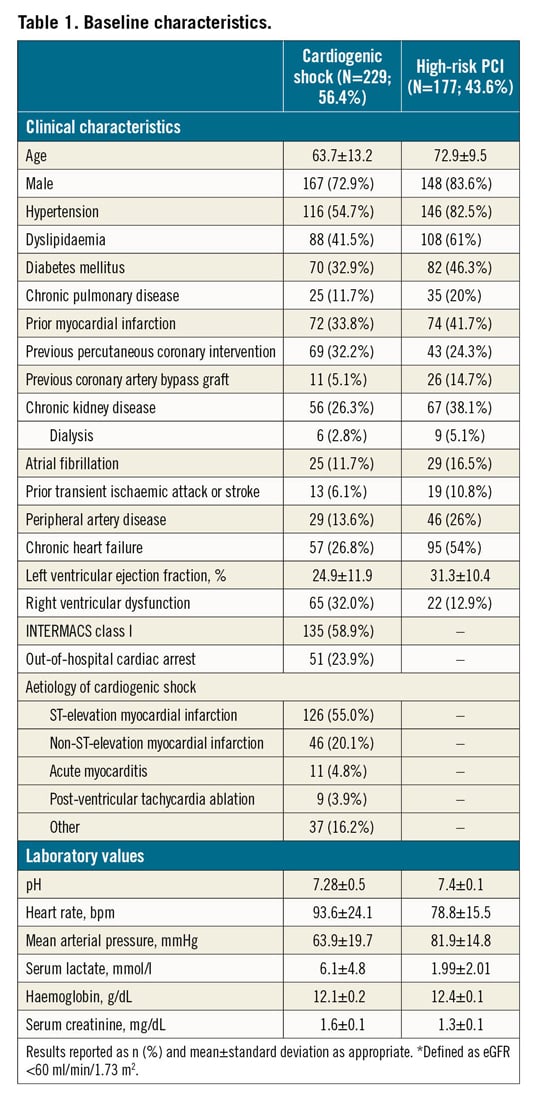
Baseline characteristics in patients with CS are reported in Table 1. In patients presenting with CS, the mean age was 63.7±13.2 years, 72.9% were male, 32.9% had diabetes mellitus and 26.8% had prior chronic heart failure (HF). The cause of CS was mostly acute myocardial infarction CS (AMICS), with ST-segment elevation and non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction accounting for 55.0% and 20.1% of cases, respectively. At the time of the index presentation, 23.9% of patients had experienced out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, 75.5% were on mechanical ventilation and 58.9% were in INTERMACS class I. The procedural characteristics of patients with CS are reported in Table 2. Most of the patients (58.5%) received an Impella 2.5, while 36.7% received an Impella CP and only a few patients received an Impella 5.0 or Impella RP. Coronary angiography was performed in the majority of patients (81.6%) and subsequent PCI in 67.2%. The Impella device was implanted before PCI in 35.7%. Among patients who underwent PCI, 12.0% of patients had three vessels treated. The median duration of Impella support was 72 hours (interquartile range [IQR]: 24-144).
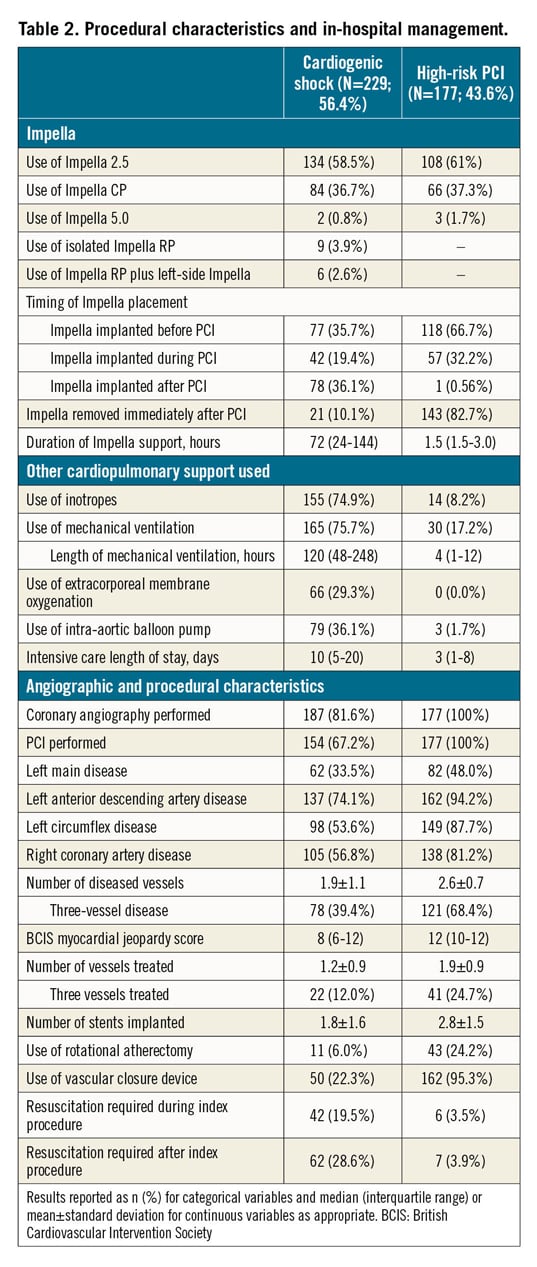
In-hospital outcomes of CS patients are reported in Table 3. Overall, the rate of in-hospital mortality was 47.2%. Median in-hospital stay was 15 days (IQR: 8-29 days). Escalation therapy to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, LVAD or transplant was required in 20.5% of patients. Life-threatening or severe bleeding occurred in 15.7% of patients; 12.6% of patients had limb ischaemia, 6.9% of which required endovascular treatment. The rates of device-related complications did not change significantly during the study period (AAPC 5.1%, 95% CI: -19.9% to 37.9%; p=0.60). One-year outcomes are reported in Table 3, Figure 2A, Figure 2B, Supplementary Figure 3A and Supplementary Figure 3B. Overall, patients who presented with CS had a one-year mortality rate of 57.0% (Figure 2A). Among those who presented with AMICS, the 30-day and one-year mortality rates were 41.1% and 54.3%, respectively. Among all CS patients, the one-year rate of LVAD or heart transplant was 18.5% and of the composite of death, hospitalisation for HF, LVAD or heart transplant 69.7% (Figure 2B). By using a smoothed hazard function, the highest risk of mortality was within 30 days, which then declined markedly beyond 90 days (Supplementary Figure 4A, Supplementary Figure 4B). Independent predictors of one-year all-cause death and the composite of death, hospitalisation for HF, LVAD or heart transplant are reported in Figure 3 and Supplementary Figure 5, respectively. There were no significant differences in all-cause mortality by type of Impella device used (Supplementary Table 2, Supplementary Figure 6).
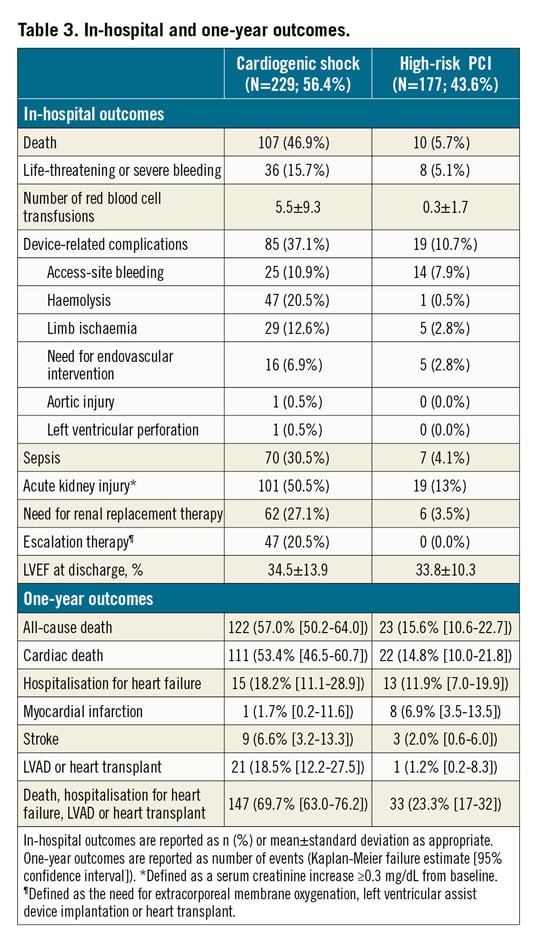
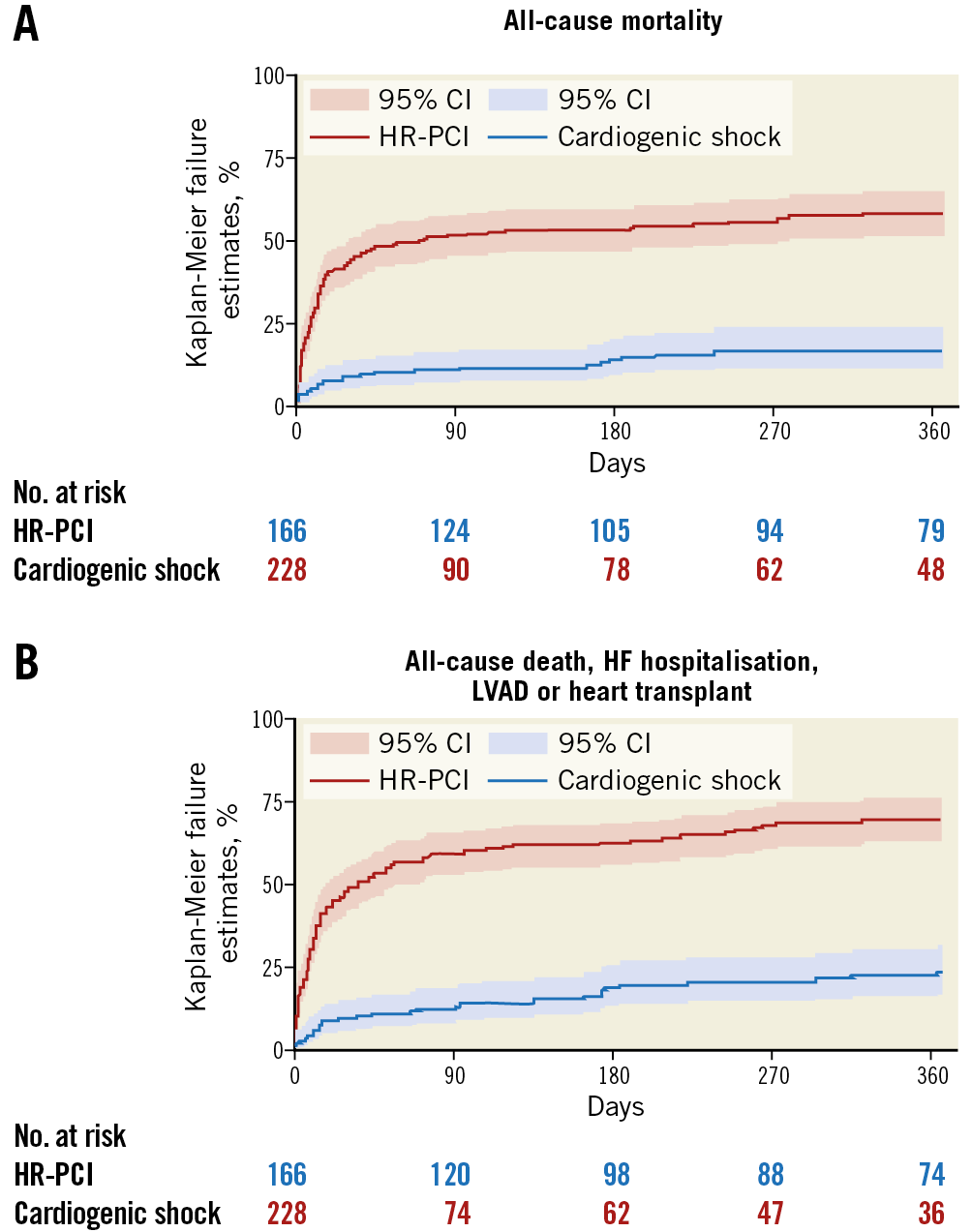
Figure 2. One-year outcomes in the IMP-IT registry. A) All-cause mortality. B) Composite of all-cause mortality, rehospitalisation for heart failure, need for left ventricular assist device or heart transplant. HF: heart failure; LVAD: left ventricular assist device
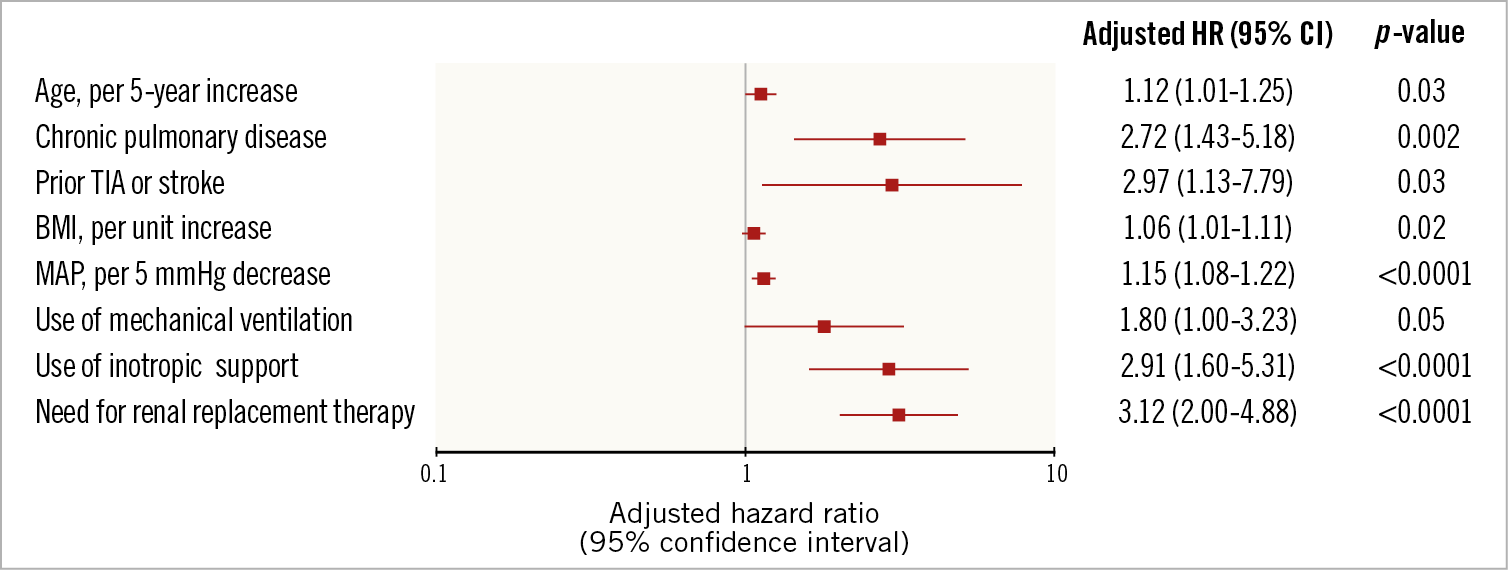
Figure 3. Predictors of all-cause mortality in patients with cardiogenic shock. A) All-cause mortality. B) Composite of all-cause mortality, heart failure hospitalisation, LVAD or heart transplant. MAP: mean arterial pressure
IMPELLA FOR HIGH-RISK PCI
Baseline characteristics in patients who underwent HR-PCI are reported in Table 1. Mean age was 72.9±9.5 years, 83.6% were male, 46.3% had diabetes mellitus and 41.7% had prior chronic HF. Mean left ventricular ejection fraction was 31.3±10.4%. The Impella 2.5 was used in 61% of patients and the Impella CP in 37.3%. The Impella device was implanted before PCI in 66.7%, during PCI in 32.2% and post PCI in 0.6% of patients. Patients had three-vessel disease in 68.4% of cases and the left main coronary artery was involved in 48.0%. Rotational atherectomy was used in 24.2% of cases and 24.7% had three-vessel PCI. The Impella device was removed immediately after PCI in 82.7% of patients. The overall duration of Impella support was 1.5 hours (IQR: 1.5-3.0).
In-hospital outcomes in patients with HR-PCI are reported in Table 3. Overall, the rate of in-hospital mortality was 5.7%. Life-threatening or severe bleeding complications occurred in 5.1% of patients. Patients had limb ischaemia in five cases (2.8%). The rates of device-related complications did not change significantly during the study period (AAPC 12.0%, 95% CI: -9.6% to 38.8%; p=0.20). The rate of all-cause mortality at one year was 15.6% (Figure 2A) and that of death, hospitalisation for HF, LVAD or heart transplant 23.3% (Figure 2B). There were no significant differences in all-cause mortality by type of Impella device used (Supplementary Table 2).
Discussion
The main findings of the IMP-IT registry, the largest European series (n=406) of patients undergoing Impella implantation in the setting of CS or HR-PCI, are the following: (i) the use of Impella devices for CS and HR-PCI has grown exponentially over the last few years; (ii) more than half of the patients (56.4%) had an Impella implanted for CS and, in the majority of CS cases, the cause was AMICS; (iii) in 43.6% of the patients the indication for Impella use was HR-PCI; as expected, more than half of the patients had impaired left ventricular ejection fraction and most of them had severe three-vessel disease with concomitant left main disease; (iv) overall, the Impella 2.5 was most commonly used for both indications; however, the Impella CP was rapidly adopted after its introduction; (v) the rates of device-related complications including access-site bleeding and limb ischaemia were relatively high and in line with prior published reports.
IMPELLA IN CS
Patients suffering from CS remain at high risk of morbidity and mortality. Since the Should We Emergently Revascularize Occluded Coronaries for Cardiogenic Shock (SHOCK) trial, conducted more than 20 years ago, demonstrated improved survival with early reperfusion of the infarct-related coronary artery by PCI in AMICS patients8, no other therapies have been proven to improve outcomes9. Percutaneous LVADs have been developed and introduced into clinical practice to overcome the limitations of IABPs by providing a greater reduction in cardiac preload and afterload, and enhance end-organ perfusion5. However, while these devices have been approved for commercial use, and their uptake worldwide is increasing10, evidence from rigorous randomised controlled trials supporting their use is lacking. In addition, these devices are associated with high costs, necessitate highly specialised care, and published data have reported high device-related complication rates. According to our data, more than half (56.4%) of the Impella devices were implanted in the setting of CS, mostly due to AMICS. Device-related complications such as life-threatening bleeding or limb ischaemia were relatively high and in line with prior reported rates. For example, in the USpella registry, among 154 consecutive patients with AMICS who underwent Impella 2.5 support and PCI, the rate of vascular complications requiring surgical repair was 9.7%, the rate of bleeding requiring transfusion was 17.5% and that of haemolysis was 10.3%11. More recently, in a large propensity-matched analysis comparing IABP versus Impella in the setting of AMICS, the rates of life-threatening or severe bleeding and peripheral ischaemic complications with the Impella were 8.5% and 9.8%, respectively12. In the setting of AMICS, the rate of 30-day mortality in our registry was 41.1%, which compares relatively favourably with other prior reports11. Finally, we investigated factors associated with increased mortality at one year in CS. Independent predictors of one-year mortality, such as inotropic support, mechanical ventilation use and need for renal replacement therapy have been described previously, and correlate with the severity of clinical presentation.
IMPELLA IN HR-PCI
Patients with complex multivessel or unprotected left main coronary artery disease and ischaemic cardiomyopathy are a challenging subset of patients with poor prognosis and few treatment options. Within this setting, prophylactic MCS during PCI is used with the rationale of providing haemodynamic stability during the procedure and allowing complete revascularisation1,2. The uptake of Impella for this clinical indication is also increasing worldwide6, despite the lack of randomised trials establishing the role of MCS-supported PCI versus unprotected PCI. In our series, HR-PCI was an indication for Impella use in 43.6% of the study cohort. As expected, most of these patients had low left ventricular ejection fraction and high-risk anatomical features including three-vessel disease, left main disease and/or left anterior descending coronary artery disease. Similar patient characteristics were observed in the USpella (N=175) and German (N=154) HR-PCI registries13,14. The rates of life-threatening bleeding and vascular complications in our registry were comparable to prior reports13,14. For example, in the HR-PCI cohort of the USpella registry, the rates of bleeding requiring transfusion and major vascular complications were 9.7% and 4.0%, respectively. In the Prospective, Multicenter, Randomized Controlled Trial of the IMPELLA RECOVER LP 2.5 System Versus Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump in Patients Undergoing Non Emergent High Risk PCI (PROTECT II) trial15, Impella-supported PCI was associated with lower rates of major adverse cardiac events at three months compared with IABP-supported PCI in the per protocol population (but not in the intention-to-treat population). No randomised trials have compared Impella-supported PCI versus unprotected PCI in case of equipoise as to whether or not haemodynamic support is required. Therefore, evidence from appropriately designed randomised trials is needed to guide the application of this technology in non-CS indications further.
Limitations
This study has several limitations that need to be disclosed. Given its observational, non-randomised design, our findings remain hypothesis-generating. However, they may be used to inform further studies in this field. Data collection was retrospective and therefore subject to recall and ascertainment bias. In addition, in view of its retrospective design, event monitoring was not standardised across clinical centres which could have led to underreporting of adverse events; however, the rates of adverse events in our study were largely in line with other studies in comparable patient populations.
Conclusions
The use of Impella devices for both CS and HR-PCI indications is growing exponentially in Italy; however, the rates of device-related complications remain high, especially in CS patients. Considering their increasing uptake in clinical practice without clear guidance from scientific societies, adequately powered randomised clinical trials and large national/multinational registries are warranted in order to define better the patients who may benefit from Impella implantation, especially for AMICS indications.
|
Impact on daily practice The IMP-IT study was a multicentre nationwide registry that enrolled 406 patients from 17 centres in Italy. Rates of in-hospital and one-year all-cause death in patients with CS (N=229) were 46.9% and 57.0%, respectively. Rates of in-hospital and one-year all-cause death in patients who underwent HR-PCI (N=177) were 5.7% and 15.6%, respectively. Rates of device-related complications were 37.1% and 10.7% in the setting of CS and HR-PCI, respectively. Randomised clinical trials are needed in order to define better those patients who may benefit from Impella implantation. |
Appendix. Study collaborators
Roberto Garbo, MD, Interventional Cardiology, Ospedale San Giovanni Bosco, Turin, Italy; Gerlando Preti, MD, Interventional Cardiology Unit, Ospedale di Conegliano, Italy; Elisa Nicolini, MD, Interventional Cardiology Unit, Ospedali Riuniti di Ancona, Ancona, Italy; Rocco Sclafani, MD, Interventional Cardiology Unit, Azienda Ospedaliera di Perugia, Italy; Giuseppe Colonna, MD, Interventional Cardiology Unit, Vito Fazzi Hospital, Lecce, Italy; Marco Mojoli, MD, SS Emodinamica Interventistica, AAS5, Ospedale di Pordenone, Italy; Massimo Siviglia, MD, Interventional Cardiology Unit, A.O. Bianchi Melacrino Morelli, Reggio Calabria, Italy; Cristiana Denurra, MD, Interventional Cardiology Unit, Ospedale SS Annunziata, Sassari, Italy; Francesco -Caprioglio, MD, Interventional Cardiology Unit, Mestre General Hospital, Mestre, Italy.
Funding
This was an investigator-driven study promoted by the Italian Society of Interventional Cardiology (GISE). No specific funding was allocated for this study.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Chieffo and G. Tarantini have received speakers’ fees from Abiomed and GADA. M.B. Ancona has received speaker’s fees from Cordis. F. Burzotta and C. Trani have received speakers’ fees from Abiomed, Abbott and Medtronic. P. Pagnotta has received speaker’s fees from Boston Scientific and Cardia. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. The study collaborators have no conflicts of interest to declare.

