A 50-year-old female was referred for cardiac screening because of the sudden cardiac death of her 48 year-old brother. She had no cardiopulmonary complaints and her physical examination was unremarkable.
Electrocardiography demonstrated sinus rhythm and normal QRS duration without any repolarisation abnormality.
A 24-hours Holter monitoring revealed sinus rhythm and no ventricular arrhythmias. Echocardiography disclosed a moderately diminished, diffuse left ventricular dysfunction with suspected hypertrophy of apical, mid-posterior end mid-inferior ventricular walls.
Patient subsequently underwent left heart catheterisation to exclude ischaemic cardiomyopathy. Coronary angiography showed normal coronary arteries. Left ventricular angiogram (LV) in right anterior oblique projection (figure 1 and movie 1) showed an excessively prominent trabecular zone with a spongy appearance of the myocardium in apical, inferior and anterior and to a lesser extent the posterolateral segment. These findings were highly suspicious of a left ventricular noncompaction or noncompaction cardiomyopathy (NCCM), which was confirmed by subsequent contrast echocardiography (figure 2), multislice CT-scan (figure 3) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the heart (figure 4 and movie 2).
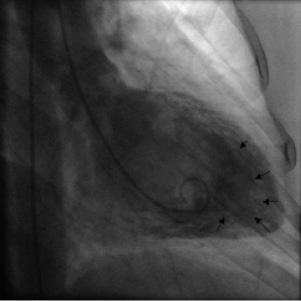
Figure 1. Left ventricular angiogram of this patient showing extensive hypertrabeculation, mostly of the apical segments.
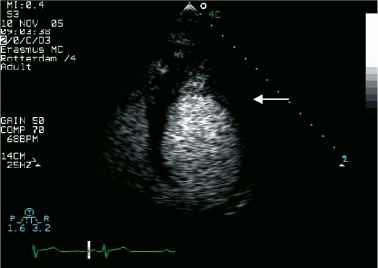
Figure 2. Two-dimensional contrast echocardiography of the apical four-chamber view: excessive and prominent trabeculation of the left ventricle apical segments is visible. Communication between the recesses and ventricular cavity is clearly demonstrated with a contrast agent.
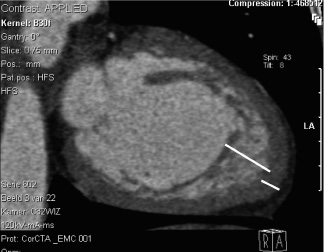
Figure 3. Multislice CT-scan of the LV ventricle showing excessive and prominent trabeculations; the short line delineates the compacted area, and the longer line, the noncompacted area.
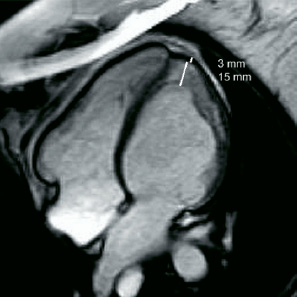
Figure 4. Four chamber MRI view of the heart, demonstrating the hypertrabeculation of apical and lateral walls of the left ventricle; the ratio of noncompacted to compacted myocardium is here a maximum of five.
NCCM is as yet a rare, unclassified form of cardiomyopathy.1 Incidence of this unique cardiomyopathy is estimated to be 0.05% in adults. It is characterised by excessively thickened, irregular endocardial surfaces with prominent trabeculations and intertrabecular recesses. Patients with NCCM can be either asymptomatic develop systolic dysfunction with heart failure, supra-ventricular and / or (lethal) ventricular arrhythmias or systemic thrombo-emboli.2
As this disease is not widely known, its diagnosis is frequently missed or misclassified.
The standard diagnostic procedure for NCCM is two-dimensional echocardiography with colour Doppler studies. In case of a planned diagnostic heart catheterisation or impaired echocardiographic imaging quality, an LV angiogram can be helpful in further diagnostic process.
References

