Abstract
BACKGROUND: Cardiac fibrosis plays a major pathophysiological role in any form of chronic heart disease, and high levels are associated with poor outcome. Diffuse and focal cardiac fibrosis are different subtypes, which have different pathomechanisms and prognostic implications. The total fibrosis burden in endomyocardial biopsy tissue was recently proved to play an independent prognostic role in aortic stenosis patients after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI).
AIMS: Here, for the first time, we aim to assess the specific impact of different fibrosis subtypes on sudden cardiac death (SCD) as a primary reason for cardiovascular mortality after TAVI.
METHODS: The fibrosis pattern was assessed histologically in the left ventricular biopsies obtained during TAVI interventions in 161 patients, who received a structured follow-up thereafter.
RESULTS: Receiver operating characteristic analyses, performed 6, 12, 24 and 48 months after TAVI, showed diffuse, but not focal, fibrosis as a significant predictor for SCD at all timepoints, with the highest area under the curve at the first time point and a decrease in its SCD predictivity over time. In both multivariate Cox proportional hazards and Fine-Gray competing risk models, including both fibrosis subtypes, as well as age, sex and ejection fraction, high diffuse fibrosis remained statistically significant. Accordingly, it represents an independent SCD predictor, most importantly for the occurrence of early events.
CONCLUSIONS: The burden of diffuse cardiac fibrosis plays an important and independent prognostic role regarding SCD early after TAVI. Therefore, the histological evaluation of fibrosis topography has value as a prognostic tool for TAVI patients and may help to tailor individualised approaches to optimise their postinterventional management.
Cardiac fibrosis, assessed histologically, was recently found to be an independent predictor of cardiovascular mortality after transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) in a previous study from our centre1. Sudden cardiac death (SCD) accounted for the largest proportion of cardiovascular mortality in that study. The number of patients requiring TAVI is steadily increasing in our ageing population, whose risk of dying from SCD must still be considered, even after addressing the problem of each patient’s narrowed valve2.
Despite advances in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques, endomyocardial biopsy remains the gold standard for evaluating the fibrotic process in the heart3. Histologically, cardiac fibrosis can be broadly classified into two subtypes: reactive diffuse fibrosis, including perivascular and interstitial fibrosis, and reparative (also named replacement, scar or focal) fibrosis34. These fibrosis subtypes may be present simultaneously, with either a static or dynamic nature35. However, they reflect fundamentally different pathophysiological processes. Focal fibrosis can be seen as an inevitable accumulation of extracellular matrix replacing dead cardiomyocytes after acute injuries, while diffuse fibrosis is probably due to chronic progressive pathological signalling during the process of cardiac remodelling3.
Accordingly, it is of great importance to obtain a comprehensive understanding of the histological fibrotic changes in each cardiac disease, in both a quantitative and a qualitative way, in order to establish a specific antifibrotic approach. Both major subtypes of cardiac fibrosis were previously linked to SCD in several – mostly MRI-based – studies dealing with different heart diseases6789101112. However, to date, there remains unclarity as to whether one fibrosis subtype may be more relevant than the other regarding the occurrence of SCD in the context of all cardiac pathologies.
Therefore, we aim in this study to evaluate the prognostic impact of diffuse and focal fibrosis with respect to SCD after TAVI. The findings here may yield valuable insights on how to plan personalised treatment strategies to optimise the prognosis of these patients, and possibly of patients with aortic stenosis in general.
Methods
Between 2017 and 2022, all patients who were scheduled for TAVI at the University Medical Centre Göttingen and who consented for study participation (including biopsy extraction) were prospectively enrolled into our trial (N=172). The indication for TAVI was based on a Heart Team consensus according to the 2017 European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines13. Except for two transapical cases, a transfemoral approach was chosen using standard techniques. The majority of patients received either a SAPIEN 3 valve (Edwards Lifesciences) or an Evolut PRO bioprosthesis (Medtronic). Transthoracic echocardiography was recorded at baseline14.
A structured follow-up for all patients was performed in May 2022. In the event of death, medical reports were obtained. In case of missing medical reports due to at home or unwitnessed deaths, we collected death certificates and contacted primary physicians or relatives. Causes of death were classified into all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality (defined according to Valve Academic Research Consortium [VARC]-2 criteria15) and SCD (according to the current guidelines16) by a committee blinded to patient characteristics. This committee consisted of a medical intern, a senior physician and the Head of the Department of Electrophysiology. This study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. The local ethics committee in Göttingen approved this study (registration number: 1934); and it is listed in the German Clinical Trials Register (registration number: DRKS00024479). Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
Echocardiography was performed on either a GE Vivid E9 (GE HealthCare) or an EPIQ7 (Philips) system, routinely recorded in a picture archiving and communication system (PACS) and re-evaluated by a single physician using Q-Station 3.8.5 (Philips). All measurements were taken as recommended17.
ASSESSMENT OF CARDIAC FIBROSIS IN ENDOMYOCARDIAL BIOPSIES
Left ventricular (LV) biopsies were harvested from the basal anteroseptum using a biopsy forceps after deployment of the transcatheter valve. The biopsies were thereafter fixed in paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 3 μm and stained using Masson’s trichrome staining18. The evaluation of fibrotic topography was performed by two independent observers blinded to patient data using quantitative morphometry (Olympus cellSens 1.6 software [Evident]) as previously described1. The total burden of cardiac fibrosis was quantified as the total area stained in blue as a percentage of the total tissue area. Focal fibrosis burden was calculated as the sum of confluent blue areas, irrespective of localisation, as a percentage of the total tissue area (including peri-infarct zones)3457819. The remaining area stained in blue (including perivascular fibrotic strands and fibrosis in the interstitial space between cardiomyocytes), as a percentage of the total tissue area, determined (mathematically) the burden of diffuse fibrosis. An independent pathologist validated our methodology and confirmed the fibrosis quantification and classification in all questionable biopsies and in case of interobserver discrepancy.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Data were presented as median (25th-75th percentiles) or total number (percentage), as appropriate. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for two-group comparisons of fibrosis subtypes depending on the status of other baseline variables; the significance level (alpha) was set to 0.05. The discrimination ability to identify the patients with SCD events was evaluated using the area under the curve (AUC) of standard receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses at different timepoints after TAVI720. For the analysis of time from procedure (TAVI) to event (SCD), Kaplan-Meier plots were generated, and significance was assessed with log-rank and Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon tests. Cox proportional hazards models (univariate or multivariate), logistic regression analyses and Fine-Gray competing risk models were computed as indicated in the results section. All calculations were conducted using GraphPad Prism, version 8 (GraphPad Software), SPSS, version 26 (IBM), or R software, version 4.2.3 with its lme4 package (R Foundation for Statistical Computing), and these calculations were confirmed by an independent statistician.
Results
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS
Among 172 enrolled patients, a valid quantitative assessment of fibrosis subtypes was not possible in 11 patients, who were thus excluded from further analysis. Our final study cohort (161 patients in total) was characterised by an advanced age (median 80 years) and a high burden of comorbidities (Table 1). In this cohort, 46 patients had an implanted cardiac device upon discharge, only 6 of whom had an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD).
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients in the study cohort.
| Baseline cohort characteristics (n=161 patients) | |
|---|---|
| Female | 61 (37.9) |
| Age, years | 80 [77-84] |
| CAD | 102 (63.3) |
| Prior myocardial infarction* | 21 (13.1) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 74 (46.0) |
| Prior CVA | 27 (16.8) |
| PAD | 19 (11.8) |
| Chronic lung disease | 39 (24.2) |
| eGFR†, ml/min/1.73 m2 | 58.1 [45.0-75.5] |
| Diabetes | 64 (39.8) |
| Arterial hypertension | 144 (89.4) |
| EF‡, % | 53.9 [41.7-60.0] |
| LVEDD, mm | 45 [41-51] |
| LVMI, g/m² | 138.7 [117.8-167.3] |
| LAVI#, ml/m² | 47.5 [36.9-58.1] |
| E/e’ ratio$ | 15.2 [11.4-19.7] |
| BMI, kg/m² | 26.8 [24.0-30.6] |
| NT-proBNP§, pg/ml | 2,183.8 [864.6-4,825.5] |
| Implanted cardiac device|| | 46 (28.6) |
| NYHA Class IV‡ | 17 (10.6) |
| Values are presented as n (%) or median [25th-75th percentiles]. *160 patients with valid data. †Calculated using MDRD formula upon admission. ‡Upon admission. #149 patients with valid data. $62 patients with valid data. §146 patients with valid data. ||Upon discharge (30 patients upon admission). BMI: body mass index; CAD: coronary artery disease; CVA: cerebrovascular accident; EF: ejection fraction; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; LAVI: left atrial volume index; LVEDD: left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; LVMI: left ventricular mass index; MDRD: Modification of Diet in Renal Disease; NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; NYHA: New York Heart Association; PAD: peripheral artery disease | |
HISTOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT OF HEART FIBROSIS AND ASSOCIATION WITH OTHER VARIABLES
Consistent with the results of our previous publication1, the median total fibrosis burden amounted to 11.8%. Focal fibrosis was dominant (median 6.6%) in comparison with diffuse fibrosis (median 3.5%) as displayed in Figure 1. Interestingly, we could not find any significant associations between fibrosis subtypes and the variables of age, sex, coronary artery disease (CAD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), atrial fibrillation, or diabetes, when the Mann-Whitney U test was used. However, hypertensive patients exhibited a significantly lower burden of diffuse fibrosis (p=0.007). Patients with severe CAD (defined as CAD with a history of myocardial infarction or coronary artery bypass grafts1, n=29 patients) showed a clear trend towards higher levels of focal fibrosis (p=0.087). The results of the Mann-Whitney U analyses for all variables are displayed in Supplementary Table 1.
Furthermore, we investigated the correlations of the echocardiographic parameters: ejection fraction (EF; as a measure for LV systolic function), E/e’ and left atrial volume index (LAVI; as surrogates for diastolic function), as well as LV mass index (LVMI) and LV end-diastolic diameter (LVEDD; as parameters for remodelling changes in the LV), with the status of high diffuse or focal fibrosis burden (above the median) depending on logistic regression analyses. Lower EF values, and higher values of LVEDD and LVMI were significantly predictive here for the pattern of high focal fibrosis (p=0.004; p<0.001; and p=0.017, respectively) (Table 2); no significant associations were found with high diffuse fibrosis. Data for detailed strain analysis are unfortunately not available for our cohort.
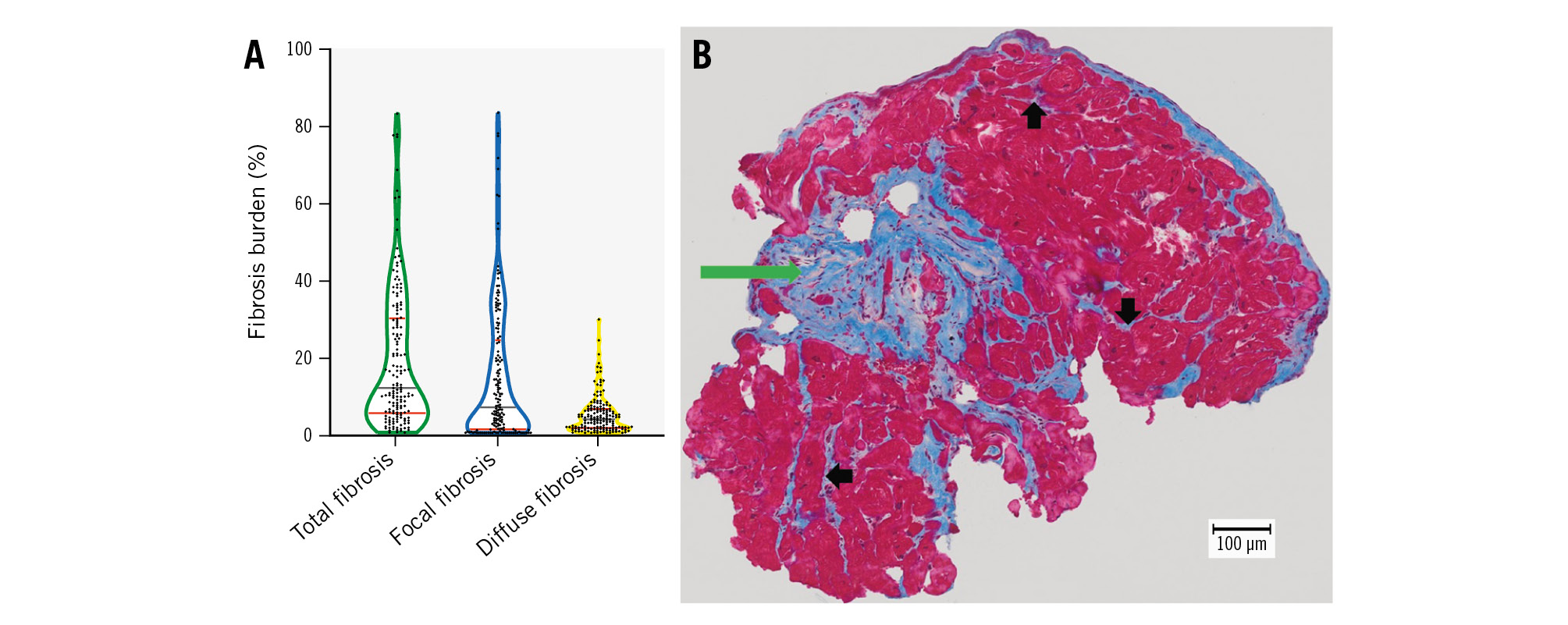
Figure 1. The statistical distribution of histological fibrosis parameters with a representative example. A) The median and quartiles of statistical distribution for total, focal and diffuse fibrosis in our cohort are shown, represented by grey and red lines, respectively. B) MTS of an endomyocardial biopsy obtained during TAVI from a patient with aortic stenosis. The total burden of cardiac fibrosis equalled 16.4% in this example: focal scar fibrosis was dominant (green arrow) compared to the diffuse subtype (black arrows); these amounted to 13.8% and 2.6%, respectively. MTS: Masson’s trichrome staining; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation
Table 2. Results of logistic regression analysis for correlation between fibrosis subtypes and echo parameters in our cohort.
| Focal fibrosis | Diffuse fibrosis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-value | HR | 95% CI | p-value | HR | 95% CI | |
| EF, % | 0.004 | 0.965 | 0.942-0.989 | 0.152 | 0.983 | 0.961-1.006 |
| LVEDD, mm | 0.000 | 1.103 | 1.053-1.155 | 0.057 | 1.039 | 0.999-1.081 |
| LVMI, g/m² | 0.017 | 1.011 | 1.002-1.020 | 0.194 | 1.006 | 0.997-1.015 |
| LAVI, ml/m² | 0.106 | 1.015 | 0.997-1.035 | 0.314 | 1.009 | 0.991-1.028 |
| E/e’ ratio | 0.058 | 1.078 | 0.997-1.166 | 0.469 | 1.028 | 0.955-1.106 |
| P-values in bold are statistically significant. CI: confidence interval; EF: ejection fraction; HR: hazard ratio; LAVI: left atrial volume index; LVEDD: left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; LVMI: left ventricular mass index | ||||||
OVERALL AND CARDIOVASCULAR MORTALITY AND SCD DURING FOLLOW-UP
The median follow-up period was 847 days (interquartile range 1,122 days). A total of 71 deaths were documented during this time. According to VARC-2 criteria, 45 deaths were attributed to cardiovascular reasons. Out of these deaths, 21 events were classified as SCD, representing 46.7% of the cardiovascular mortality (median event time was 332 days; 11 cases occurred in the first year after TAVI) (Figure 2).
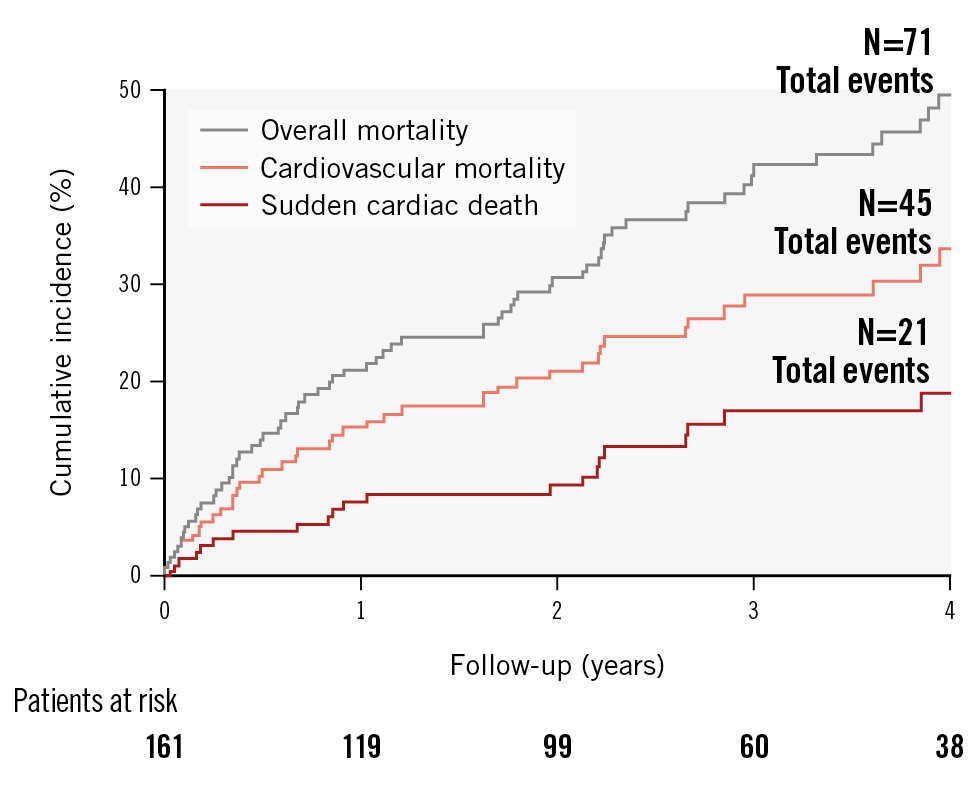
Figure 2. Event curves for overall and cardiovascular mortality, and sudden cardiac death. The cumulative incidence for overall and cardiovascular mortality, and sudden cardiac death during the first 4 years of follow-up after TAVI in our cohort are depicted with grey, orange and red lines, respectively. A total of 71 deaths were observed, of which 45 events were due to cardiovascular reasons. Sudden cardiac death was the dominant form of cardiovascular death (accounting for 46.7% of all cardiovascular deaths). TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation
ANALYSIS OF HISTOLOGICAL FIBROSIS SUBTYPES AS PREDICTORS OF SCD
We aimed to determine the prognostic impact of focal and diffuse fibrosis on the clinical endpoint, SCD, over time. Therefore, we performed standard ROC analyses for both fibrosis subtypes, as well as for all other quantitative variables in our study, at 4 different timepoints after TAVI (6, 12, 24 and 48 months); we then calculated the corresponding AUC values to assess their discrimination ability regarding SCD in our cohort (Table 3). This statistical approach was planned to enable us to compare the prognostic importance of all these variables, head-to-head, at each time point. The burden of diffuse fibrosis, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) values and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels were the only variables that emerged in this analysis as significant predictors of SCD at all timepoints (AUC on average 0.75, 0.79 and 0.75, respectively), whereas focal fibrosis gained its significance only at the latest two timepoints (AUC on average 0.67). Interestingly, diffuse fibrosis showed a progressive decrease in its SCD predictivity as time increased (AUC of 0.810, 0.763, 0.736 and 0.689 at 6, 12, 24 and 48 months after TAVI, respectively), which was not observed for any other tested variable; it was the best SCD predictor at the first time point (6 months after TAVI).
Additionally, we generated Kaplan-Meier plots for SCD-free survival (using the median values of fibrosis subtypes as cutoff points) to visualise the stratification and progress of SCD events in our cohort (Figure 3). It was visually clear that the stratification power of diffuse fibrosis regarding SCD was not stable over time. The survival curves for patients above or below the median stopped diverging almost at the end of the first year of follow-up. A Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test comparing the curves showed statistical significance, whereas a log-rank test showed near-significance (p=0.0627), probably reflecting that early events are weighted more in the former test21. These results suggested an interaction between the prognostic effect of diffuse fibrosis regarding SCD and follow-up time after TAVI. For focal fibrosis, the survival curves for patients with high or low fibrosis burden diverged in a constant manner towards the end of the follow-up period, providing evidence against any interaction with time for its stratification effect. Both Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon and log-rank tests here were statistically significant.
Furthermore, univariate Cox proportional hazards models for the prediction of SCD events were computed for fibrosis subtypes and all other baseline variables, with and without a covariate for interaction with time22 (Supplementary Table 2). The variable of time interaction showed statistical significance for the categorical variable of diffuse fibrosis (median as the cutoff point) with a hazard ratio (Exp[B]-value) of 0.219 (time in years), indicating that more than 75% of its stratification effect could no longer be detected after 1 year of follow-up and, thus, confirming our previous findings. The other variables that emerged as significant SCD predictors in this analysis were high focal fibrosis (above median), atrial fibrillation, New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class IV upon admission and the baseline values of EF, eGFR, body mass index (BMI) and NT-proBNP level (without evidence for any significant interaction with time).
Interestingly, the presence of an implanted cardiac device upon discharge after TAVI was not associated with a favourable outcome regarding SCD risk in the previous analysis. This argues against the possibility that the progression of advanced conduction block is (relevantly) responsible for SCD events after TAVI in our cohort223. Furthermore, we performed a survival analysis for our patients which was classified depending on the presence of an implanted cardiac device upon discharge (with or without an ICD). No statistical significance was found in this analysis using either Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon or log-rank tests (Supplementary Figure 1). One of the 6 patients discharged with an ICD received an appropriate ICD shock about 100 days after TAVI, which could be evaluated as an aborted SCD event. The burden of diffuse fibrosis in this patient was markedly high (29.2%), in accordance with our previous results.
Because of the reported high prevalence of cardiac amyloidosis in patients with aortic stenosis (estimated to be 4-16% in patients over 65 years old24), we investigated this association depending on the presence of morphological manifestations of amyloidosis in the heart MRIs of our patients. MRI analysis was performed in 76 patients in our cohort; three of them (4%) showed clear signs of amyloidosis on MRI, but none of these patients suffered an SCD event during the follow-up period after TAVI.
Finally, in order to investigate the independence of fibrosis parameters as SCD predictors in our cohort, a multivariate Cox proportional hazards model was computed. Because of the limited number of documented SCD events, this analysis was restricted to the most important clinical variables: age, sex and EF, in addition to the fibrosis subtypes (all in categorical form), with a time covariate for diffuse fibrosis. The only variable that kept its significance here was high diffuse fibrosis with its time interaction variable, probably representing an independent SCD predictor (Figure 4A). Diffuse fibrosis also remained significant as an SCD predictor in a multivariate Cox proportional hazards model including the previous variates as continuous variables (Supplementary Table 3). Fine-Gray competing risk models were additionally computed in order to assess the subdistribution hazards and showed similar results (p=0.002 and p=0.028 for diffuse fibrosis as a categorical and continuous variable, respectively) (Figure 4B, Supplementary Table 4). The results of (complex) multivariate Cox proportional hazards and Fine-Gray competing risk models, including all significant variables in univariate analyses in categorical or continuous form, are shown in Supplementary Table 5-Supplementary Table 8, where diffuse fibrosis also consistently showed statistical significance as an SCD predictor.
Table 3. Results of ROC analyses for predicting SCD events in our study cohort.
| 6 months | 12 months | 24 months | 48 months | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | p-value | AUC | p-value | AUC | p-value | AUC | p-value | |
| Focal fibrosis | 0.608 | 0.338 | 0.652 | 0.095 | 0.706 | 0.016 | 0.698 | 0.012 |
| Diffuse fibrosis | 0.810 | 0.006 | 0.763 | 0.004 | 0.736 | 0.006 | 0.689 | 0.017 |
| Age | 0.620 | 0.287 | 0.476 | 0.789 | 0.491 | 0.917 | 0.536 | 0.652 |
| eGFR* | 0.762 | 0.020 | 0.778 | 0.002 | 0.812 | 0.000 | 0.805 | 0.000 |
| EF* | 0.646 | 0.195 | 0.612 | 0.219 | 0.615 | 0.180 | 0.736 | 0.003 |
| LVEDD | 0.670 | 0.131 | 0.620 | 0.188 | 0.627 | 0.139 | 0.710 | 0.008 |
| LVMI | 0.560 | 0.591 | 0.519 | 0.838 | 0.520 | 0.813 | 0.643 | 0.070 |
| LAVI | 0.541 | 0.713 | 0.514 | 0.882 | 0.535 | 0.695 | 0.651 | 0.071 |
| E/e’ ratio* | n.a. | 0.860 | 0.087 | 0.844 | 0.102 | 0.618 | 0.465 | |
| BMI | 0.636 | 0.227 | 0.663 | 0.074 | 0.622 | 0.155 | 0.663 | 0.040 |
| NT-proBNP | 0.759 | 0.033 | 0.726 | 0.018 | 0.705 | 0.022 | 0.811 | 0.000 |
| NYHA Class | 0.539 | 0.729 | 0.602 | 0.266 | 0.648 | 0.083 | 0.716 | 0.006 |
| *Lower values predict positive events; for all other variables, higher values predict positive events. P-values in bold are statistically significant. AUC: area under the curve; BMI: body mass index; EF: ejection fraction; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; LAVI: left atrial volume index; LVEDD: left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; LVMI: left ventricular mass index; MDRD: Modification of Diet in Renal Disease; n.a.: not applicable; NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; NYHA: New York Heart Association; ROC: receiver operating characteristic; SCD: sudden cardiac death; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation | ||||||||
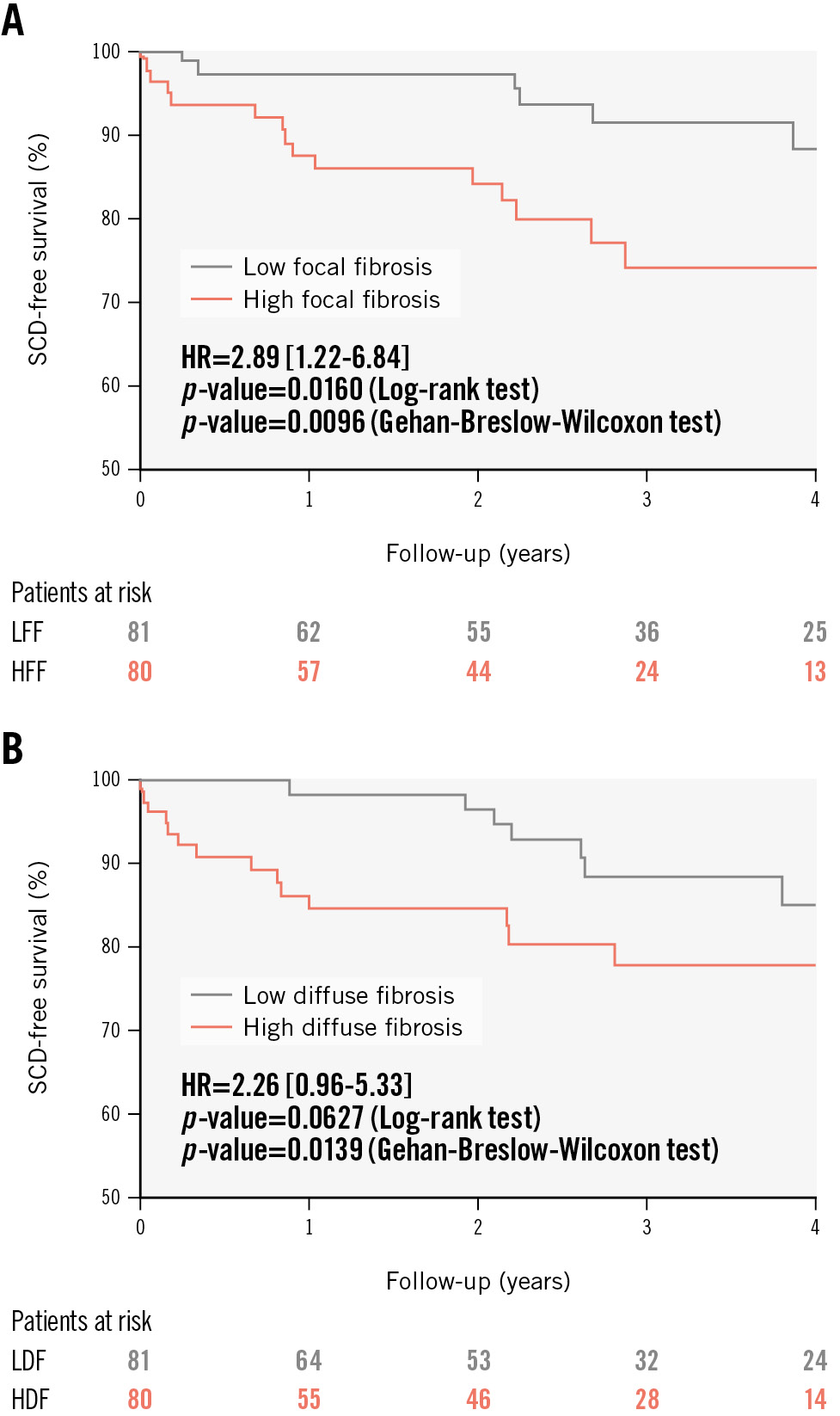
Figure 3. SCD-free survival curves according to the burden of the fibrosis subtypes. Kaplan-Meier plots of SCD-free survival are presented for patients with high or low burden (median as the cutoff point) of focal (A) and diffuse (B) fibrosis. Both patterns of high focal and high diffuse fibrosis subtype were associated with a worse prognosis regarding SCD risk after TAVI. HDF: high diffuse fibrosis; HFF: high focal fibrosis; HR: hazard ratio; LDF: low diffuse fibrosis; LFF: low focal fibrosis; SCD: sudden cardiac death; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation
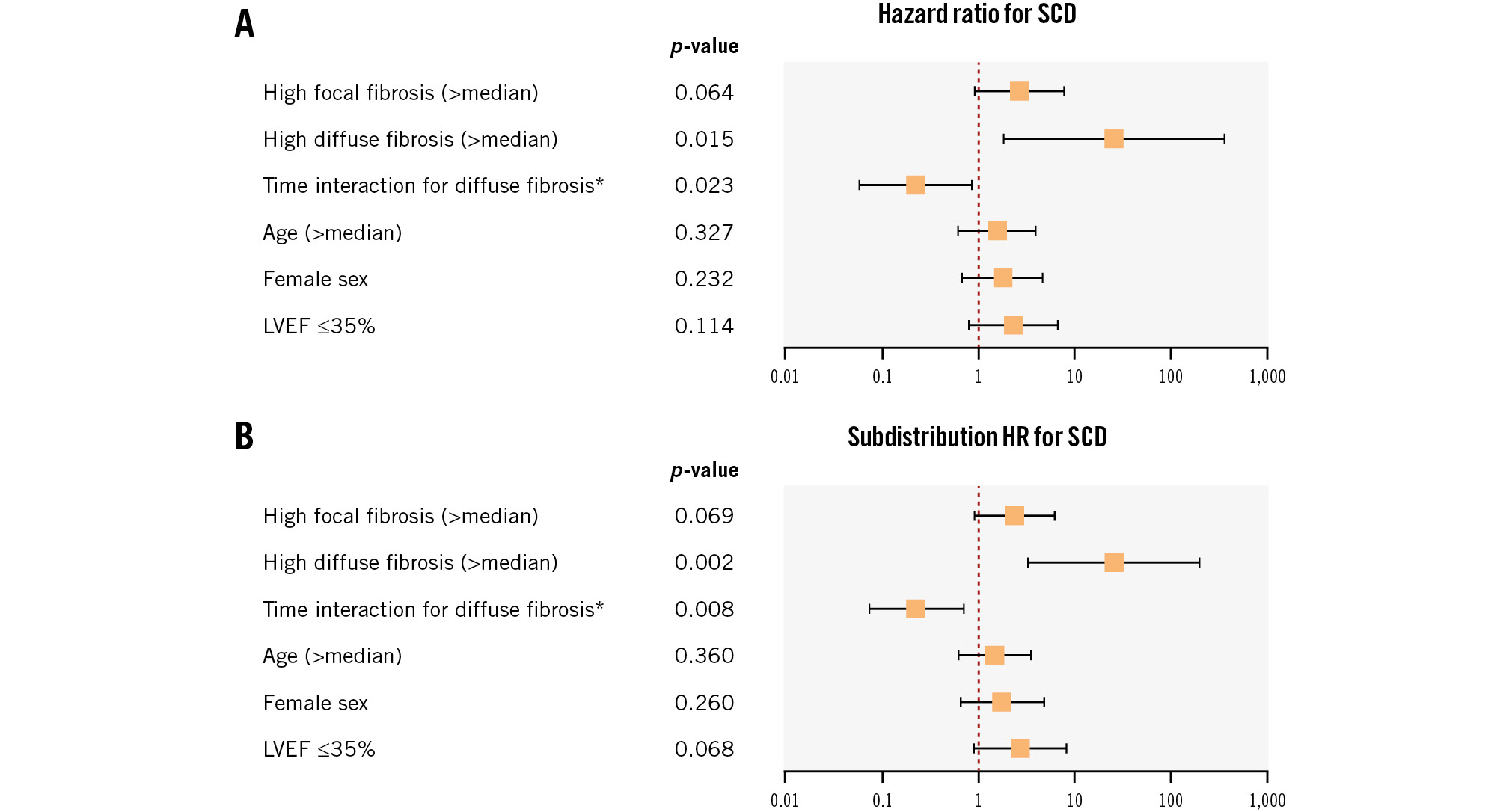
Figure 4. Multivariate analysis for predicting SCD. The results of the multivariate Cox proportional hazards model (A) and the Fine-Gray competing risk model (B) to predict SCD events in our cohort are shown. The fibrosis variables (with the time covariate for the diffuse subtype) and variables of age (above or below median), sex and EF (above or below 35%, which is the cutoff point for ICD indication in the guidelines for heart failure management30) were included in this model (21 SCD events in total, 26 patients with EF ≤35%). The variable of high diffuse fibrosis and its time interaction variate remained significant, as opposed to focal fibrosis and EF, probably suggesting independent SCD predictivity. *time in years. EF: ejection fraction; HR: hazard ratio; ICD: implantable cardioverter-defibrillator; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; SCD: sudden cardiac death
Discussion
As the first study of its kind, we have been able to investigate, in our current research, the link between specific subtypes of cardiac fibrosis (assessed histologically) and SCD events after TAVI (Central illustration). We were able to evaluate the LV biopsies from more than 160 patients in a valid quantitative way, and cardiac fibrosis was classified into two subtypes: diffuse (interstitial and perivascular) fibrosis and focal (replacement) fibrosis, with the focal subtype being the dominant form of fibrosis in our study cohort. Our findings clearly indicated the utility of fibrosis topography as a prognostic tool for TAVI patients.
First, we assessed in our study the correlations of diffuse and focal fibrosis with all other variables in our cohort. While no evidence for significant correlation could be found for age, sex, CKD, atrial fibrillation or diabetes, surprisingly, diffuse fibrosis was significantly less severe in hypertensive patients. Accordingly, we may speculate that LV (diffuse) fibrosis burden could primarily be related to the pressure overload of aortic stenosis. That might also be an explanation for the higher burden of diffuse fibrosis in patients with lower blood pressure, as it could reflect diminished LV power due to increased fibrotic changes.
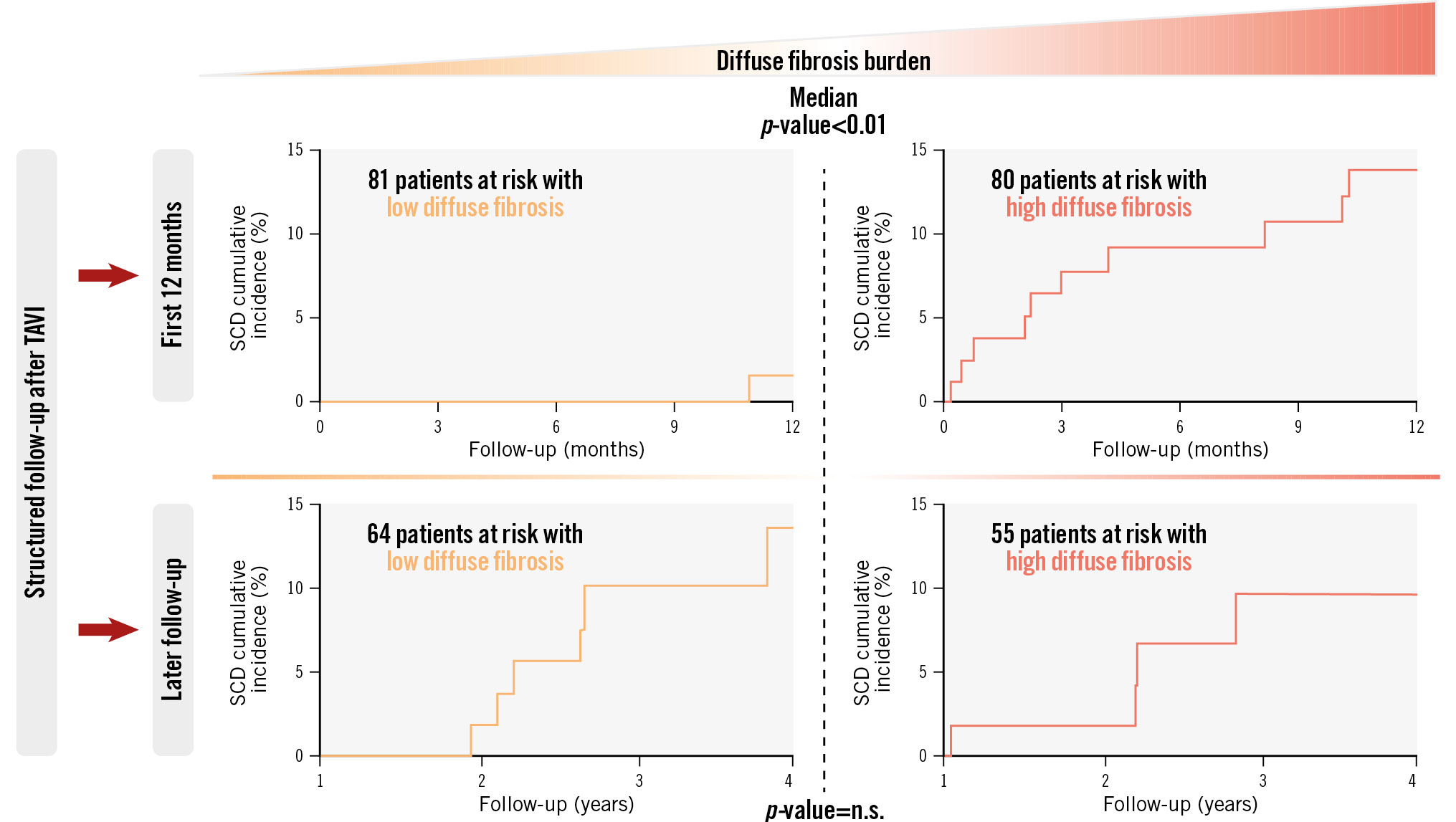
Central illustration. Progress of SCD events after TAVI depending on the burden of diffuse cardiac fibrosis. The main findings of this research work are presented above. Our study aimed to investigate the prognostic value of cardiac fibrosis subtypes (evaluated histologically in the endomyocardial biopsies of 161 patients) regarding SCD after TAVI (median follow-up period of 847 days, 21 SCD events in total). A high burden of diffuse fibrosis upon intervention (above the median) has been found to represent an important predictor of SCD, specifically for early events after TAVI. The progress of SCD events is shown here as cumulative incidence curves, with p-values for comparisons in the first 12 months after the intervention and during follow-up thereafter. n.s.: non-significant, SCD: sudden cardiac death; TAVI: transcatheter aortic valve implantation
CARDIAC FIBROSIS SUBTYPES AS SCD PREDICTORS AFTER TAVI
Vulnerability to SCD is still an important clinical problem for patients with aortic stenosis, even after replacing their diseased valve223. A high burden of both fibrosis subtypes showed a significant association with SCD events after TAVI in our cohort as a univariate variable. However, histological diffuse fibrosis was a better predictor for the early SCD cases, with the highest AUC value of all the variables at 6 months after TAVI, and independent of the variables of age, sex and EF (as concluded from our multivariate analyses). To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first to point out such an important association. Our findings do not dismiss the proven significance of scar fibrosis as a well-known cause of ventricular tachycardia/SCD. Our study should be evaluated comprehensively; several previous studies showed focal fibrosis as a good predictor of arrhythmic events, but patients were assessed mostly using MRI with a focus on late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) as a surrogate of this fibrosis subtype only891012.
Comparing the results of MRI-based studies concerning cardiac fibrosis with studies depending on heart biopsies is not free of problems. A recent study from our centre confirmed the expressiveness of our histological fibrosis assessment methodology in the heart biopsies of 46 patients undergoing TAVI. This study showed a significant association between diffuse fibrosis, histologically evaluated with Masson’s trichrome staining, and MRI mapping-derived LV matrix volume or extracellular volume fraction as parameters for the fibrotic remodelling process in the LV, as assessed with baseline MRIs25. Therefore, we speculate that a stronger correlation between these two methods would be detected in the case of reactive diffuse fibrosis within the entire heart, due to its diffuse nature, with histological results that may not necessarily depend on the origin of the biopsy when compared to global MRI mapping values. Conversely, since a histological evaluation will always be restricted to the scope of the biopsied area, significantly more discrepancy is to be expected compared to LGE-based evaluation of the (focally distributed) focal fibrosis subtype in MRI.
THE ARRHYTHMOGENIC ROLE OF DIFFUSE FIBROSIS
Very few previous studies have addressed the importance of diffuse cardiac fibrosis as an arrhythmic substrate. In the work of Bui et al, diffuse interstitial fibrosis, without the presence of replacement fibrosis, was reported to play an essential role in the mechanism of ventricular arrhythmia in patients with mitral valve prolapse11. Apart from this, we are aware of only one previous study which directly compared both fibrosis subtypes, assessed histologically, regarding their association with SCD in patients with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy7. In this work from Almaas et al, areas of interstitial fibrosis were found to be more arrhythmogenic than the areas of reparative, confluent fibrosis, probably because of the altered composition of the extracellular matrix along with preserved myocytes. Nguyen et al suggested a similar explanation in their review about the arrhythmogenic impact of different subtypes of cardiac fibrosis6.
THE DYNAMIC NATURE OF DIFFUSE FIBROSIS AND ITS DIAGNOSTIC AND THERAPEUTIC IMPLICATIONS
Another important de novo finding of our study is the significant interaction between follow-up time after TAVI and the ability of diffuse fibrosis to predict SCD, which we did not observe in the case of focal fibrosis or for other variables. After 1 year of follow-up, the association between SCD and a higher burden of diffuse fibrosis lost most of its magnitude in our cohort. One possible explanation for this finding is the reversible nature of diffuse fibrosis, as opposed to reparative fibrosis3526, which may have caused a decrease in the arrhythmogenic effect of diffuse fibrosis at later timepoints to such an extent that it was not large enough to be detected or was possibly overshadowed by other factors. Testing this hypothesis about the dynamic prognostic role of fibrosis measures in aortic stenosis patients after solving the problem of the narrowed valve (interventionally or surgically) requires repeated biopsies from a large cohort of patients, which is practically impossible. That currently leaves us with repeated MRIs as the only alternative to assess the dynamic of fibrosis subsets; measureable biomarkers of cardiac fibrosis may represent another option in the future327. Such an approach could help to identify the best candidates for any additional antifibrotic therapy326.
Obviously, future studies are also needed to investigate potential differences in the molecular pathomechanisms involved in the fibrogenesis process for each fibrosis subtype, including the question of whether different collagen subtypes and different inflammatory reactions are involved28. In this respect, the significant association between NT-proBNP levels – interpreted as inflammation markers/mediators29 – and SCD events in our cohort suggests a relevant aetiological role of the inflammatory processes in SCD with promising translational implications.
Finally, another preventive option for SCD that could be considered is primary ICD implantation. Our findings showed very strong predictivity for diffuse fibrosis regarding SCD early after TAVI − independent of EF value, which represents the most important parameter regarding ICD indication according to current guidelines30. Accordingly, it may be justified to consider initiating a prospective study in which TAVI patients with very risky fibrosis topography (assessed in biopsies obtained during the valve intervention, or alternatively with the help of MRI) would be randomised for antifibrotic therapy and/or ICD implantation irrespective of their EF values. Cost-effectiveness issues should be carefully considered, especially because of the relatively high incidence of death from non-cardiac reasons in TAVI patients12. It is also worth mentioning, in this regard, that our results disagree with the data published by Urena et al2, specifically concerning the role of EF as an independent SCD predictor after TAVI. However, that study did not include any histological analysis or any other variables as surrogates for LV fibrotic changes (no MRI or fibrosis biomarkers data). The reversibility of LV systolic dysfunction after removing the pressure overload of the stenotic valve should also be evaluated as a possible (favourable) prognostic parameter in this context. This reversibility needs to be addressed in detail, also in correlation with the baseline fibrosis topography, in further studies.
Limitations
Our current research work is a monocentric study with a limited number of events (in total, 21 SCD events); this represents the primary limitation that can affect the conclusion validity of any multivariate analysis approach. We are not able to prove a causal relationship between fibrosis patterns and the occurrence of SCD after TAVI. Any generalisation of our results requires the conduction of validating studies with larger/external cohorts. Our study did not include any analysis of electrocardiographic data or detailed echocardiographic parameters (such as strain analysis), which is beyond the scope of this histologically oriented research.
Conclusions
The results of our study outline the great clinical significance of SCD as a major reason for mortality after TAVI. Our research indicates the importance of a more detailed characterisation of the LV fibrotic changes in patients with aortic stenosis. Cardiac fibrosis patterns, assessed histologically, seem to play a key prognostic role in this context; understanding cardiac fibrosis here as a dynamic process with different entities is of pivotal importance. Our findings, therefore, may be hypothesis-generating for other studies in the future, hopefully leading to individualised treatment strategies for patients with aortic stenosis, to be approached as a complex illness of the whole heart, not only as an isolated mechanical valve lesion.
Impact on daily practice
Sudden cardiac death (SCD) remains a major reason for cardiovascular mortality in aortic stenosis patients, even after replacing their stenotic valve surgically or interventionally. Because patients at risk for SCD may require a specific management strategy, it is important to establish meaningful methods to identify these individuals. Despite the indisputable role of myocardial fibrosis in the pathophysiology of heart diseases, the clinical applicability of research efforts in this field is still considerably restricted, mainly because of methodological obstacles. Our study provides novel results which may help to identify patients at risk of SCD; it can assist in establishing histological fibrosis patterning as a promising tool to identify patients who may benefit from fibrosis-guided therapeutic measures (specific antifibrotic drugs and/or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator), possibly also through non-invasive evaluation of left ventricular fibrotic changes with magnetic resonance imaging techniques.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mrs Annika Erdmann for her substantial contribution to this research work.
Funding
This work was supported by the Collaborative Research Centre (CRC) 1002: Modulatory Units in Heart Failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

