Abstract
BACKGROUND: Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA)-derived Murray law-based quantitative flow ratio (CT-μFR) is a novel non-invasive method for fast computation of fractional flow reserve (FFR) from CCTA images, yet its diagnostic performance remains to be prospectively validated.
AIMS: We aimed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of onsite CT-μFR in patients with coronary artery disease.
METHODS: This prospective, single-centre trial enrolled patients with ≥1 lesion with 30-90% diameter stenosis on CCTA and planned invasive coronary angiography (ICA) within 30 days. CT-μFR, ICA-derived μFR and FFR were evaluated separately in a blinded fashion. The primary endpoint was the diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR in identifying patients with haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis defined by the invasive standard: FFR ≤0.80, or μFR ≤0.80 when FFR was not available.
RESULTS: Between December 2020 and August 2023, 260 patients were consecutively enrolled. Paired comparison between CT-μFR and the invasive standard was obtained in 706 vessels from 260 patients. The patient-level accuracy of CT-μFR was 89.6% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 85.9-93.4%), which was significantly higher than the prespecified target of 72.0% (p<0.001). Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and positive and negative likelihood ratios for CT-μFR were 93.1%, 86.1%, 87.1%, 92.5%, 6.7, and 0.1, respectively. Out of the 231 vessels investigated by FFR, the accuracy of CT-μFR in vessels without extensive calcification was non-inferior to that of μFR (90.6% vs 88.9%; difference=1.8% [95% CI: −2.8 to 5.5%]; p for non-inferiority<0.001).
CONCLUSIONS: The study met its prespecified primary endpoint of the diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR in identifying patients with haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis. CT-μFR was non-inferior to ICA-derived μFR in vessels without extensive calcification. (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04665817)
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), which correlates favourably with invasive coronary angiography (ICA), is a non-invasive and convenient technology to detect patients with coronary artery disease (CAD)12. However, several randomised trials have shown that the haemodynamic significance of a coronary stenosis cannot be determined by the anatomical information obtained from CCTA or ICA345. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is an invasive procedure performed at the time of ICA to determine lesion-specific ischaemia6. It is the current reference standard in the catheterisation laboratory to determine the physiological significance of epicardial coronary stenosis7. However, the adoption of this physiological lesion assessment is limited because of the cost of the pressure wire, the need for induction of hyperaemia, and physicians’ reliance on angiographic assessment alone8.
Quantitative flow ratio (QFR) is a novel method without the need for pharmacology-induced hyperaemia for fast computation of FFR based on ICA using empirical fluid dynamic equations9. Good diagnostic concordance between QFR and FFR has been validated by several studies91011. The recent FAVOR III China trial also demonstrated that a QFR-guided strategy of lesion selection for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) improved 1-year clinical outcomes compared with standard angiography guidance12. Meanwhile, the QFR system has been upgraded with algorithms based on Murray’s bifurcation fractal law, and computation of QFR from a single angiographic view is now possible. The Murray law-based quantitative flow ratio (μFR) was shown to have high feasibility and excellent diagnostic accuracy in identifying haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis13. Recently, the μFR algorithm has been applied to CCTA images to non-invasively determine the ischaemia-causing coronary stenosis. This technology, namely CT-μFR, showed good diagnostic accuracy in retrospective studies1415161718. However, the diagnostic performance of onsite CT-μFR analysis has not been prospectively validated to date and, therefore, is the subject of the present study.
Methods
STUDY DESIGN
The Diagnostic Accuracy of CCTA-derived Versus AngiogRaphy-dErived QuantitativE Flow Ratio (CAREER; ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04665817) Study is an investigator-initiated, prospective, single-centre clinical trial designed to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of onsite CT-μFR in identifying patients with haemodynamically significant CAD by using pressure wire-based FFR or ICA-derived μFR as reference. The design and rationale of the study have been described previously19. Patients who underwent CCTA examination and were scheduled for coronary angiography within 30 days were eligible. Further eligibility criteria were stable or unstable angina pectoris or non-acute phase of myocardial infarction, with at least one lesion with a percentage diameter stenosis of 30-90% in a coronary artery with at least a 2.0 mm reference vessel diameter by visual assessment. Principal exclusion criteria included previous coronary intervention or coronary bypass surgery of the interrogated lesion; severe chronic kidney disease (defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate <30 mL/min/1.73 m²); contraindications to contrast agents, beta blockers, nitrates or adenosine drugs; previous myocardial infarction <30 days before CCTA or between CCTA and ICA; and any factors that affect the image quality of CCTA. CT-μFR and μFR were scheduled in all three epicardial coronary arteries for each included patient, blinded to each other and FFR values. Vessels were excluded from CT-μFR and μFR if the image quality was insufficient or if there was myocardial bridging on the interrogated vessel. Complete inclusion and exclusion criteria are listed in Supplementary Table 1.
The study protocol was approved by the institutional review board/independent ethics committee of Huadong Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University (2020K192). All study subjects provided written informed consent.
CCTA ACQUISITION AND CT-µFR ANALYSIS
CCTA was performed by using a dual-source computed tomography (CT) system (SOMATOM Drive [Siemens Healthineers]) or a 256-detector row scanner CT system (Revolution CT [GE HealthCare]) with prospective or retrospective electrocardiographic gating in accordance with Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography guidelines20. CCTA images were interpreted, and CT-μFR analysis was performed onsite by an experienced investigator, using dedicated software (CtaPlus [Pulse Medical Technology, Inc.]). Detailed methodologies for CT-μFR computation have been published previously16. In brief, firstly, the lumen of all coronary arteries with a reference vessel diameter ≥1.5 mm were automatically delineated and reconstructed. Subsequently, the reference lumen was reconstructed using Murray’s bifurcation fractal law, and the patient-specific hyperaemic coronary flow was derived. Finally, the CT-μFR values at each location along the entire coronary artery tree were calculated using the validated μFR algorithm. CCTA-derived percentage diameter stenosis (DS%) was obtained simultaneously for each interrogated vessel.
ICA, FFR MEASUREMENT AND µFR ANALYSIS
ICA was performed by using a 5 Fr or 6 Fr catheter, via the femoral or the radial artery pathway. Before angiography, all patients received intravenous heparin of 100 IU/kg. The contrast media (Omnipaque 350 injection [GE HealthCare]) was injected manually in a forceful and stable manner. Coronary angiography images were obtained from standard series of 6-8 projections for the left coronary artery and 2 or 3 projections for the right coronary artery using a monoplane or biplane radiographic system (Axiom Artis FC and Artis zee biplane MN [Siemens Healthineers]) at 15 frames/s. All images were digitally stored following the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) standard for analysis.
Per protocol, measurement of FFR was performed for each lesion with between 30% and 90% DS in a vessel segment ≥2 mm in diameter using a RadiAnalyzer Xpress instrument and PressureWire Certus (both St. Jude Medical, now Abbott)19.
All ICA images were analysed in the control room of the catheterisation laboratory, blinded to FFR and CT-μFR values. μFR analyses were performed by experienced analysts using dedicated software (AngioPlus Core, version V2 [Pulse Medical Technology, Inc.]), following the standard operation procedure as previously described13. Before μFR analyses, for vessels with FFR interrogation, the analysts were informed about the location of FFR measurement so that μFR could be measured at the same site. For vessels without FFR interrogation, the location distal to all visual coronary stenosis was selected as the stopping point for μFR analysis. During μFR analysis, quantitative coronary angiography (QCA) results including DS% were also available.
ENDPOINTS AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The primary endpoint of the study was the per-patient diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR in identifying a physiologically significant coronary artery stenosis defined by the invasive standard: FFR ≤0.80, or μFR ≤0.80 when FFR was not available. The major secondary endpoint was the non-inferiority of CT-μFR compared with μFR in vessels without extensively calcified lesions, defined by the combination of a cross-sectional calcium arc >90° and a thickness >1.5 mm1421. The non-inferiority threshold was set at 15% in the protocol published previously19.
The Kolmogorov-Smirnov method was used to test the normality of measurement data. Continuous variables are presented as means±standard deviations (SD) for normally distributed data, or as medians (interquartile range [IQR]) for non-normally distributed data. Categorical variables are presented as frequencies and percentages. The clinical characteristics were analysed on a per-patient basis and the lesion characteristics on a per-vessel basis. Categorical variables were compared using the χ2 or Fisher’s exact test. Comparison of SD was performed with the F-test. Spearman’s correlation coefficient and Bland-Altman plots were used to determine correlation and agreement. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive likelihood ratio (+LR), negative likelihood ratio (−LR), and diagnostic accuracy were calculated using 0.80 as the cutoff value to assess the diagnostic performance of CT-μFR in predicting haemodynamically significant stenosis with FFR and μFR values ≤0.80 as reference. Youden’s index was used as the criterion to identify the best cutoff values for CCTA-derived DS% (CCTA-DS%) and QCA-derived DS% (QCA-DS%). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of CT-μFR, CCTA-DS%, μFR and QCA-DS% were analysed, and the area under curve (AUC) was calculated and compared using the DeLong Method22. For per-patient analyses, if a patient had multiple interrogated vessels, the vessel with the lowest FFR/μFR value was used. For per-vessel analyses, in order to correct for clustering effects caused by the inclusion of multiple vessels from the same patients, the generalised estimating equation was applied.
A 2-sided value of p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using MedCalc, version 19.0.4 (MedCalc Software Ltd) and SPSS, version 23.0 (IBM).
Results
BASELINE PATIENT AND VESSEL CHARACTERISTICS
Among 307 patients who underwent study screening between December 2020 and August 2023, a total of 40 patients were excluded after CCTA. Seven patients and 28 vessels were rejected by the core laboratory for CT-μFR analysis due to the insufficient image quality from their CCTA, and 33 vessels were rejected because of prior PCI (Supplementary Figure 1). Thus, 260 patients with 740 vessels were available for coronary angiography and FFR measurement. A total of 59 patients with 59 vessels were not eligible for FFR measurement, while 34 vessels were excluded from μFR analysis; Supplementary Figure 1 provides the reasons for their exclusion. Hence, 706 vessels from 260 patients were included in the current analysis. Out of these, FFR was available for 231 vessels from 201 patients.
The baseline demographics of the study cohort are listed in Table 1. The median age was 68.0 (IQR 61.3, 74.0) years old, 168 (64.6%) patients were male, 190 (73.1%) had hypertension, 89 (34.2%) had diabetes, and 12 (4.6%) had previous myocardial infarction.
Vessel characteristics are provided in Table 2. The median FFR/μFR of the interrogated vessels was 0.90 (IQR 0.81, 0.96), and 168 (23.8%) vessels had an FFR/μFR ≤0.80. In 131 (18.6%) vessels, the FFR/μFR value fell between 0.75 and 0.85. Among the 260 patients enrolled, 49.6% did not have any haemodynamically significant lesions, 39.2% had only 1 vessel with haemodynamic significance, 8.1% had 2 vessels with FFR/μFR ≤0.80, while only 3.1% had 3 vessels with FFR/μFR ≤0.80. The CCTA characteristics included a median percentage diameter stenosis of 33.6% (IQR 25.8%, 43.3%), and there were 95 (13.5%) vessels with ≥50% DS. A total of 239 (33.9%) interrogated vessels were left anterior descending arteries (LAD).
Table 1. Baseline demographic characteristics.
| Patient level (n=260) | |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 68.0 [61.3, 74.0] |
| Male | 168 (64.6) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 24.6±3.6 |
| Hypertension | 190 (73.1) |
| Hyperlipidaemia | 70 (27.0) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 89 (34.2) |
| History of arrhythmia | 33 (12.7) |
| Previous myocardial infarction | 12 (4.6) |
| Current smoker | 36 (13.9) |
| Clinical syndrome type | |
| Stable angina | 52 (20.0) |
| Unstable angina | 190 (73.1) |
| Asymptomatic ischaemia | 18 (6.9) |
| eGFR, ml/min/1.73 m2 | 87.0 [75.0, 95.0] |
| Data are presented as median [IQR], n (%) or mean±SD. eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; IQR: interquartile range; SD: standard deviation | |
Table 2. Baseline vessel characteristics.
| Vessel level (n=706) | |
|---|---|
| Interrogated vessels | |
| Left anterior descending artery | 239 (33.9) |
| Diagonal artery | 3 (0.4) |
| Left circumflex artery | 218 (30.9) |
| Obtuse marginal artery | 3 (0.4) |
| Right coronary artery | 243 (34.4) |
| CCTA characteristics | |
| Diameter stenosis, % | 33.6 [25.8, 43.3] |
| ≥50% diameter stenosis | 95 (13.5) |
| FFR/μFR (per vessel) | 0.90 [0.81, 0.96] |
| Vessels with FFR/μFR ≤0.80 | 168 (23.8) |
| Vessels with 0.75 ≤FFR/μFR ≤0.85 | 131 (18.6) |
| FFR measurement | 231 (32.7) |
| FFR (per vessel) | 0.83 [0.75, 0.89] |
| Data are presented as n (%) or median [IQR]. CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; FFR: fractional flow reserve; IQR: interquartile range; μFR: Murray law-based quantitative flow ratio | |
EFFICIENCY OF CT-µFR ANALYSIS
The average time for CT-μFR analysis was 8.76±1.41 minutes per patient, which included image import, manual correction of the lumen contour when the automatically detected lumen contours did not follow the lumen edge, three-dimensional (3D) angiography reconstruction, CT-μFR calculation, and report generation.
DIAGNOSTIC PERFORMANCE OF CT-µFR FOR IDENTIFYING SIGNIFICANT STENOSIS
Figure 1 shows one representative example with CT-μFR and μFR computations. The per-patient diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR was 89.6% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 85.9 to 93.4%), which was significantly higher than the protocol-specified target value of 72.0% (p<0.001). Clinical discordance occurred in 27 patients: invasive standard>0.80 but CT-μFR ≤0.80 in 18 patients and invasive standard ≤0.80 but CT-μFR>0.80 in 9 patients (Supplementary Table 2). Out of these 27 patients, 18 exhibited CT-μFR or invasive FFR/μFR values ranging from 0.75 to 0.80. Among the remaining 9 cases, 4 were identified as having extensively calcified lesions. Patient-level CCTA-DS% showed a lower diagnostic accuracy (69.2% [95% CI: 63.6 to 74.9%]; difference: 20.4%; p=0.002) than CT-μFR. The AUC for CT-μFR on a patient level was significantly higher than that for CCTA-DS% (0.94 [95% CI: 0.90 to 0.97] vs 0.79 [95% CI: 0.74 to 0.84], difference: 0.15; p<0.001) (Supplementary Figure 2). The per-patient sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, +LR and −LR for CT-μFR were 93.1%, 86.1%, 87.1%, 92.5%, 6.7 and 0.1, respectively (Table 3).
Vessel-level analysis showed numerically higher diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR compared with patient-level analysis: 93.5% (95% CI: 91.7 to 95.3%). Other vessel-level diagnostic performance metrics of CT-μFR and CCTA-DS% are listed in Table 3 and Supplementary Table 2.
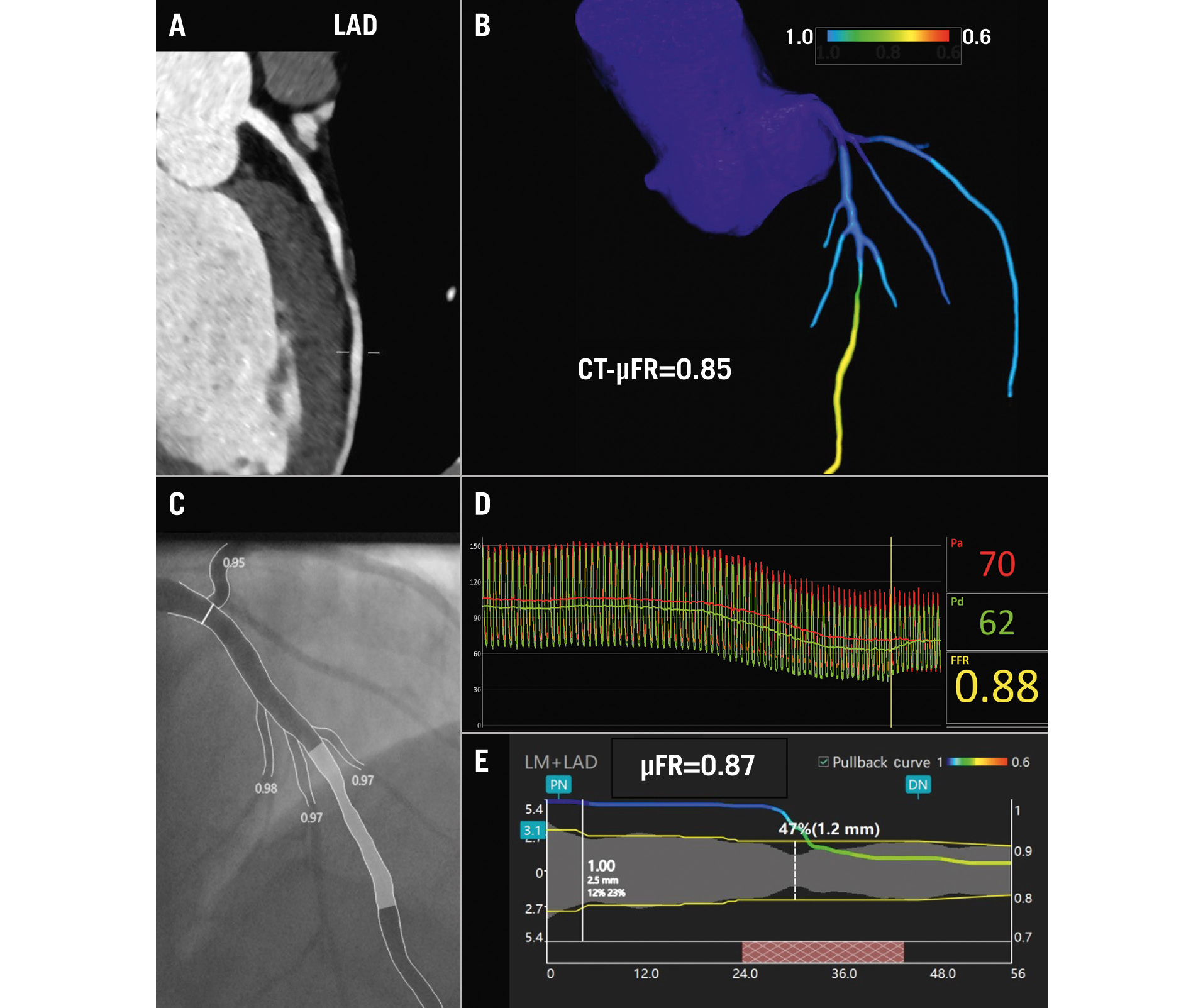
Figure 1. Representative example of CT-μFR and μFR computations for identifying the haemodynamic significance of coronary stenosis. A) Reconstructed image of the left anterior descending artery (LAD) obtained through CCTA. B) CT-μFR analysis result showed CT-μFR value of the LAD was calculated as 0.85. C) Invasive coronary angiogram of the interrogated LAD. D) Invasive FFR value was measured as 0.88. E) μFR analysis result showed μFR value of the LAD was calculated as 0.87. μFR: Murray law-based quantitative flow ratio; CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; CT-μFR: CCTA-derived μFR; FFR: fractional flow reserve; LM: left main
Table 3. Diagnostic performance of CT-μFR and CCTA-DS% in predicting invasive standard ≤0.80.
| Patient-level (n=260) | Vessel-level (n=706) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT-μFR ≤0.80 | CCTA-DS% ≥50% | CT-μFR ≤0.80 | CCTA-DS% ≥50% | |
| Accuracy | 89.6 (85.9, 93.4) | 69.2 (63.6, 74.9) | 93.5 (91.7, 95.3) | 83.8 (80.9, 86.7) |
| Sensitivity | 93.1 (87.4, 96.8) | 55.0 (46.0, 63.7) | 86.3 (80.2, 91.1) | 47.6 (39.8, 55.5) |
| Specificity | 86.1 (78.8, 91.5) | 83.7 (76.2, 89.6) | 95.7 (93.7, 97.3) | 97.1 (95.1, 98.5) |
| PPV | 87.1 (80.4, 92.2) | 77.4 (67.6, 85.4) | 86.3 (80.2, 91.1) | 85.9 (77.0, 92.3) |
| NPV | 92.5 (86.2, 96.5) | 64.7 (56.9, 71.9) | 95.7 (93.7, 97.3) | 83.4 (79.9, 86.5) |
| +LR | 6.7 (4.3, 10.3) | 3.4 (2.2, 5.1) | 20.2 (13.5, 30.3) | 16.5 (9.4, 28.8) |
| −LR | 0.1 (0.0, 0.2) | 0.5 (0.4, 0.7) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.2) | 0.5 (0.5, 0.6) |
| Data are presented with 95% CI. CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; CCTA-DS%: CCTA-derived percentage diameter stenosis; CI: confidence interval; CT-μFR: CCTA-derived quantitative flow ratio; DS%: percentage diameter stenosis; NPV: negative predictive value; PPV: positive predictive value; +LR: positive likelihood ratio; −LR: negative likelihood ratio | ||||
COMPARISON OF CT-µFR AND µFR IN NON-EXTENSIVELY CALCIFIED LESIONS
Out of the 231 vessels successfully investigated by invasive FFR measurements, 60 were identified as having extensively calcified lesions, defined by the combination of a cross-sectional calcium arc >90° and a thickness >1.5 mm on CCTA. The diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR for identifying physiological significance in vessels without extensively calcified lesions was non-inferior to that of μFR (90.6% [95% CI: 86.2 to 95.1%] vs 88.9% [95% CI: 84.1 to 93.7%]; difference: 1.8% [95% CI: −2.8 to 5.5%]; p for non-inferiority<0.001). The presence of extensively calcified lesions reduced the diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR numerically, albeit statistically non-significantly (81.7% [95% CI: 71.6 to 91.8%]; difference: 9.0%; p=0.06). On the other hand, the impact of extensively calcified lesions on the computation of μFR was less obvious (86.7% [95% CI: 77.8 to 95.5%]; difference: 2.2%; p=0.65). Other diagnostic performance metrics of CT-μFR and μFR in vessels with or without extensively calcified lesions are listed in Table 4.
Table 4. Diagnostic performance of CT-μFR and μFR in vessels with or without extensively calcified lesions.
| Non-extensively calcified lesions (n=171) | Extensively calcified lesions (n=60) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT-μFR ≤0.80 | μFR ≤0.80 | CT-μFR ≤0.80 | μFR ≤0.80 | |
| Accuracy | 90.6 (86.2, 95.1) | 88.9 (84.1, 93.7) | 81.7 (71.6, 91.8) | 86.7 (77.8, 95.5) |
| Sensitivity | 86.7 (75.4, 94.1) | 81.67 (69.6, 90.5) | 90.0 (73.5, 97.9) | 83.3 (65.3, 94.4) |
| Specificity | 92.8 (86.3, 96.8) | 92.8 (86.3, 96.8) | 73.3 (54.1, 87.7) | 90.0 (73.5, 97.9) |
| PPV | 86.7 (75.4, 4.1) | 86.0 (74.2, 93.7) | 77.1 (59.9, 89.6) | 89.3 (71.8, 97.7) |
| NPV | 92.8 (86.3, 96.8) | 90.4 (83.4, 95.1) | 88.0 (68.8, 97.5) | 84.4 (67.2, 94.7) |
| +LR | 12.0 (6.1, 23.6) | 11.3 (5.8, 22.3) | 3.4 (1.8, 6.2) | 8.3 (2.8, 24.7) |
| −LR | 0.1 (0.1, 0.3) | 0.2 (0.1, 0.3) | 0.1 (0.1, 0.4) | 0.2 (0.1, 0.4) |
| Data are presented with 95% CI. CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; CI: confidence interval; CT-μFR: CCTA-derived quantitative flow ratio; DS%: percentage diameter stenosis; NPV: negative predictive value; PPV: positive predictive value; μFR: Murray law-based quantitative flow ratio; +LR: positive likelihood ratio; −LR: negative likelihood ratio | ||||
OTHER SECONDARY ENDPOINTS
In 231 vessels with successful invasive FFR measurements, the diagnostic concordance with FFR on a per-vessel basis for CT-μFR was similar to that for μFR (88.3% [95% CI: 84.1 to 92.5%] vs 88.3% [95% CI: 84.1 to 92.5%]; p=1.00). Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, +LR and −LR were 87.8%, 88.7%, 83.2%, 91.1%, 7.74 and 0.14 for CT-μFR, and 82.2%, 92.2%, 87.1%, 89.0%, 10.5 and 0.19 for μFR, respectively (Supplementary Table 3). Good correlation (r=0.76 [95% CI: 0.70 to 0.81]; p<0.001) and agreement (0.00±0.07; p=0.99) between CT-μFR and FFR were observed (Figure 2). μFR also showed good correlation with FFR (r=0.79 [95% CI: 0.73 to 0.83]; p<0.001). The Bland-Altman plots showed a similar trend in the limit of agreement with FFR compared with CT-μFR (SD of the difference=0.07 vs 0.07; p=1.00).
The AUC for CT-μFR, μFR, CCTA-DS% and QCA-DS% to identify FFR ≤0.80 were 0.92 (95% CI: 0.87 to 0.95), 0.94 (95% CI: 0.90 to 0.97), 0.76 (95% CI: 0.70 to 0.82), and 0.79 (95% CI: 0.74 to 0.84), respectively (Figure 3).
The per-vessel diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR in identifying physiologically significant stenosis, defined by μFR ≤0.80, was numerically higher than that defined by FFR ≤0.80 (89.6% [95% CI: 84.9 to 93.2%] vs 88.3% [95% CI: 84.1 to 92.5%]), although statistically non-significant (p=0.656). The per-vessel sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, +LR and −LR for CT-μFR were 82.1%, 94.9%, 91.8%, 88.4%, 16.0 and 0.2, respectively (Supplementary Table 4).
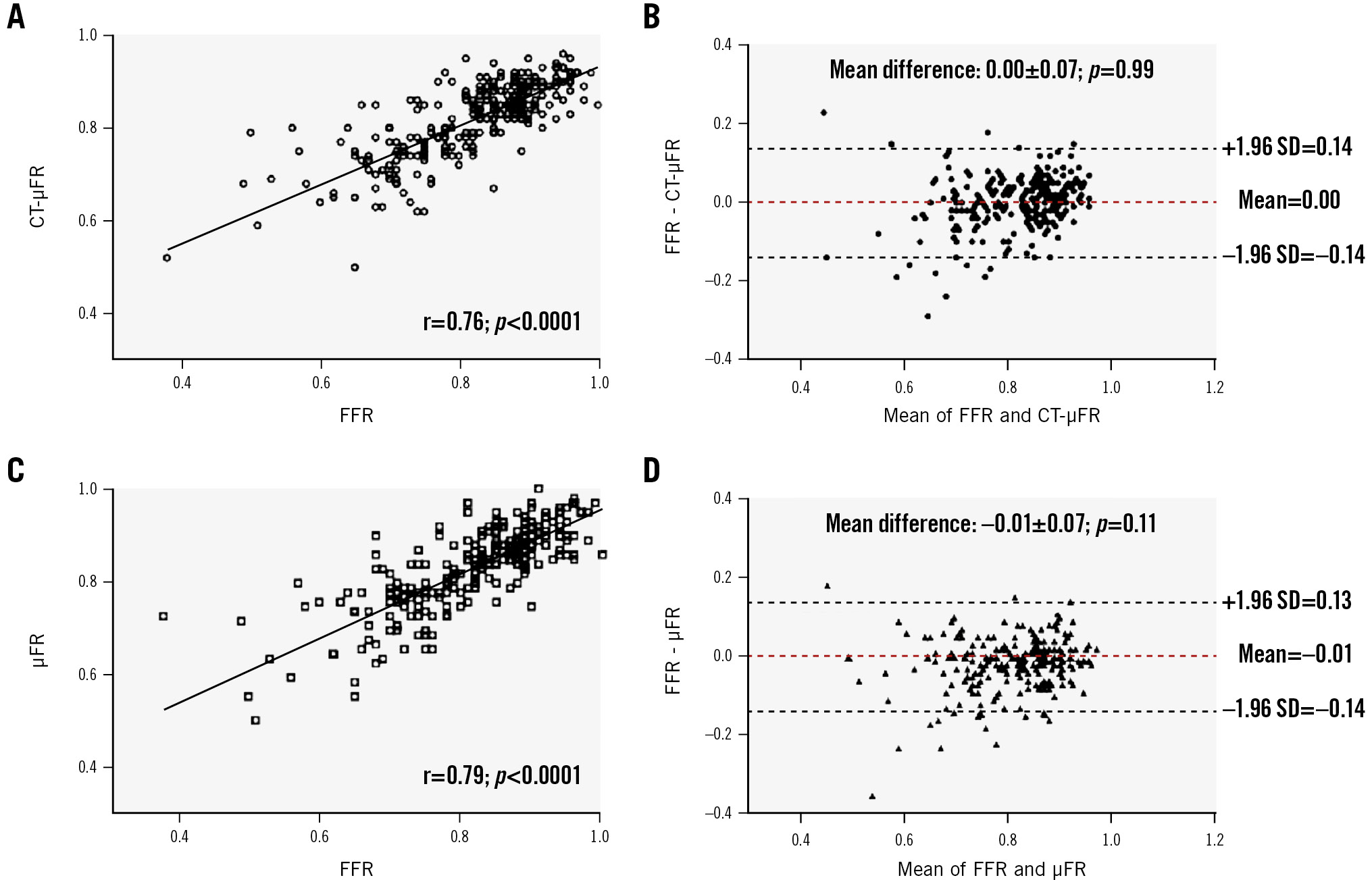
Figure 2. Correlation and agreement of CT-μFR and μFR compared with FFR. A) Correlation between CT-μFR and FFR. B) Agreement between CT-μFR and FFR. C) Correlation between μFR and FFR. D) Agreement between μFR and FFR. μFR: Murray law-based quantitative flow ratio; CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; CT-μFR: CCTA-derived μFR; FFR: fractional flow reserve
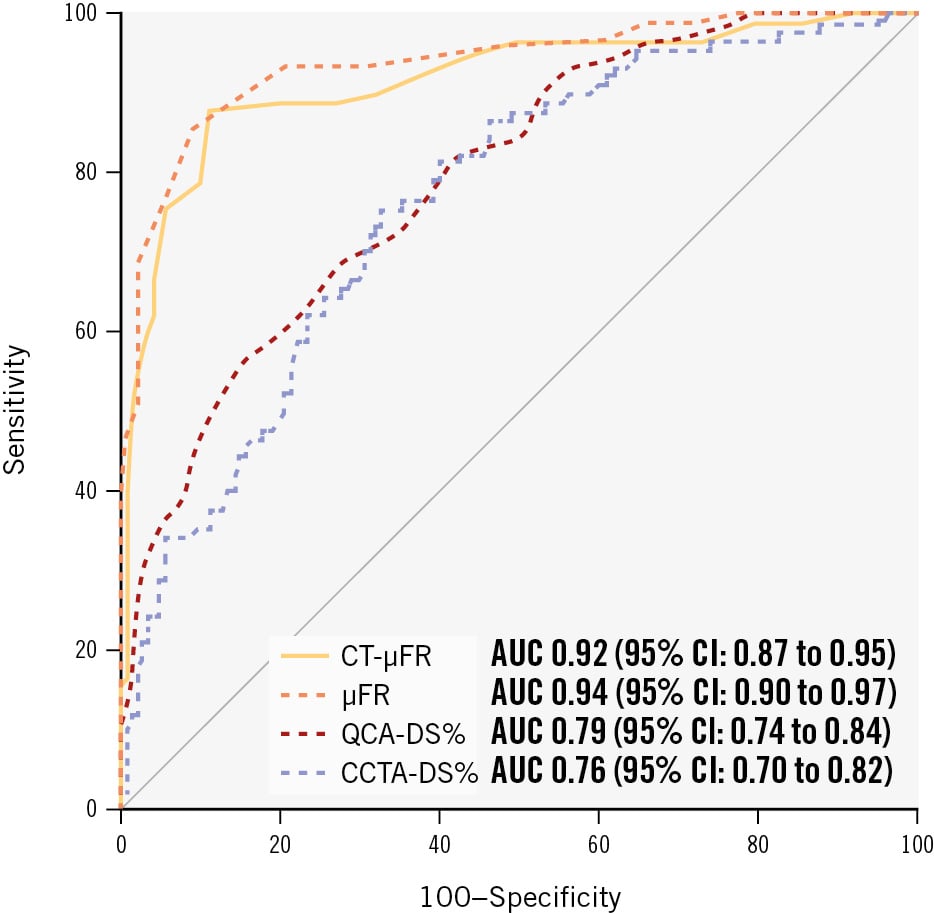
Figure 3. Comparison of per-vessel diagnostic performance for CT-μFR, μFR, CCTA-DS%, and QCA-DS%. μFR: Murray law-based quantitative flow ratio; AUC: area under the curve; CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; CCTA-DS%: CCTA-derived percentage diameter stenosis; CI: confidence interval; CT-μFR: CCTA-derived μFR; DS%: percentage diameter stenosis; QCA: quantitative coronary angiography; QCA-DS%: QCA-derived percentage diameter stenosis
Discussion
In this adequately powered prospective study, we investigated the diagnostic performance of CT-μFR, a novel CCTA-derived method to quickly compute FFR and identify ischaemia-causing lesions and observed the following main findings: (1) the onsite non-invasive CT-μFR analyses demonstrated good diagnostic accuracy in identifying patients with haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis defined by the invasive standard. Patient-level diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR was 89.6% (95% CI: 85.9% to 93.4%), which was significantly higher than the predefined target value (p<0.001). 2) In vessels with non-extensively calcified lesions identified by CCTA, the diagnostic performance of CT-μFR was non-inferior to the ICA-derived μFR (Central illustration). Thus, the study met both the prespecified primary endpoint and major secondary endpoint goals.
The results of this study expand on findings from previous validation studies of CT-μFR, in which the diagnostic performance of CT-μFR was retrospectively validated1415161718. The present study was the first prospective trial with adequate power to assess the diagnostic accuracy of onsite CT-μFR, and it documented good per-patient diagnostic accuracy of 89.6%, with high sensitivity of 93.1% and specificity of 86.1% for CT-μFR in a consecutively enrolled real-world patient population. Of note, when evaluated at a per-vessel level, we observed increased specificity of 95.7%, while decreased sensitivity of 86.3% was found. Compared with per-patient analyses, more vessels without haemodynamic significance were included. This resulted in lower disease prevalence at a vessel level (23.8% vs 50.4%) and a subsequent major increase in true negatives classified by CT-μFR (515 vs 111). Importantly, the calculation of CT-μFR required no modification of the CCTA acquisition protocols, nor additional imaging or administration of medications. The CT-μFR analyses were timely obtained onsite using a normal computer, with an average analysis time of less than 9 minutes. The results of the present study further proved the feasibility and accuracy of CT-μFR for the non-invasive determination of the physiological consequences of CAD and support the utility for applying CT-μFR in patients undergoing CCTA.
CCTA has been used routinely for the evaluation of patients with suspected CAD, and a diameter stenosis of 50% according to CCTA is generally considered the cutoff to identify physiologically significant coronary stenosis. Nevertheless, the accuracy of CCTA-DS% for identifying ischaemia-causing coronary stenosis is limited17. In particular, significant false positive rates revealed a general overestimation of CAD severity by CCTA. Even in obstructive lesions that were detected with CCTA and confirmed by ICA, not all were identified as haemodynamically significant by FFR17. Previous studies have demonstrated an improved clinical outcome with additional physiological assessment of coronary stenosis by FFR23. In this regard, the addition of CT-μFR on top of CCTA might improve clinical decision-making and outcomes for patients with CAD identified by CCTA. This was supported in the present study by the fact that the diagnostic performance of CCTA-DS% improved when CT-μFR was added to CCTA: accuracy increased from 69.2% to 89.6%, sensitivity from 55.0% to 93.1%, and specificity remained similar, with a small increase from 83.7% to 86.1%.
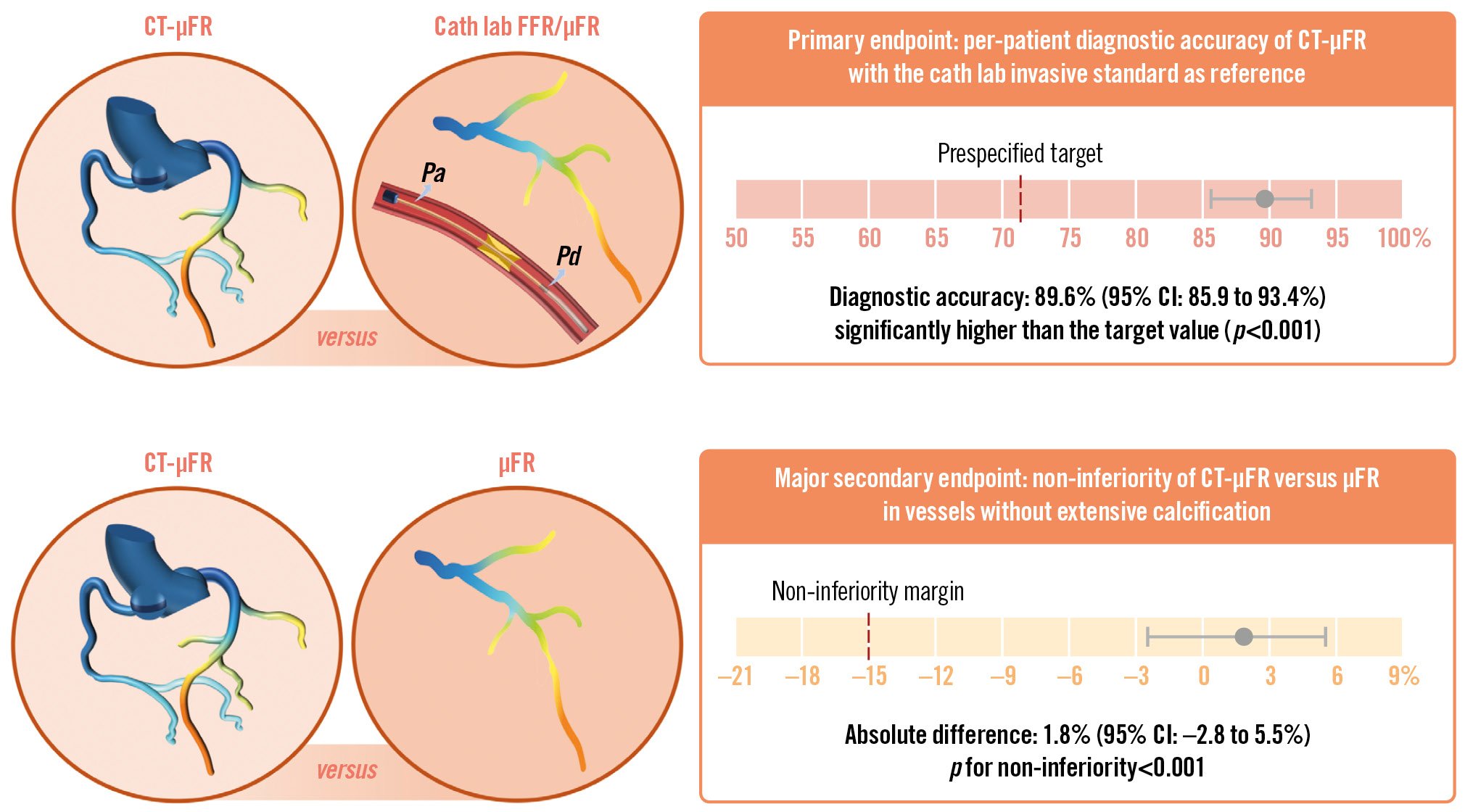
Central illustration. The CAREER Study. Schematic overview of the prospective clinical trial, the CAREER Study, aimed at evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR. Patients with 30-90% diameter stenosis on CCTA and scheduled for ICA and/or FFR within 30 days were included. CT-μFR analysis based on CCTA scans was performed onsite. Angiography-based μFR analysis was performed in the catheterisation laboratory. The primary endpoint was the per-patient diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR for identifying patients with physiologically significant coronary stenosis defined by the cath lab physiology standard: FFR ≤0.80, or μFR ≤0.80 when FFR was not available. The major secondary endpoint is the non-inferiority of CT-μFR compared with μFR in vessels without extensive calcification. Both the primary endpoint and the major secondary endpoint were achieved. μFR: Murray law-based quantitative flow ratio; CCTA: coronary computed tomography angiography; CI: confidence interval; CT-μFR: CCTA-derived μFR; FFR: fractional flow reserve; ICA: invasive coronary angiography; Pa: aortic pressure; Pd: distal coronary pressure
CT-µFR COMPARED WITH OTHER FUNCTIONAL CT-ASSESSMENT TECHNIQUES
Currently, CCTA-derived FFR (FFRCT) is the most extensively validated method for the computation of FFR. It integrates patient-specific models of coronary anatomy with 3D computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models and computes coronary flow and pressure under simulated hyperaemic conditions. A large amount of evidence showed that it had good diagnostic performance and effectively reduced unnecessary ICA242526. Three studies – DISCOVER-FLOW, DeFACTO, and HFNXT – demonstrated a per-patient diagnostic accuracy of 73-87% (95% CI: 67 to 93%) for FFRCT. Additionally, recent meta-analyses272829 have demonstrated that the sensitivity and specificity of FFRCT were 89-90% (95% CI: 85 to 93%) and 71-81% (95% CI: 65 to 87%), respectively. The present study showed that CT-μFR yields equal if not superior diagnostic performance compared with FFRCT. Importantly, CT-μFR is based on fluid dynamic equation computation rather than complicated CFD. By using the CT-μFR algorithm, the limitations of the CFD-based method can be avoided, including the high demand for computational power and analysis time, and the need to transfer imaging data to a core laboratory for centralised offsite analysis. The simplified procedure and fast analysis time make CT-μFR a more promising tool to be integrated into daily practice. Future application of artificial intelligence has the potential to further automate the CT-μFR algorithm and reduce manual interactions to a minimum.
THE IMPACT OF EXTENSIVELY CALCIFIED LESIONS ON CT-µFR
The present study affirmed that CT-μFR was non-inferior to μFR in terms of its diagnostic accuracy for non-extensively calcified lesions, which was consistent with the findings of a previous retrospective study conducted by Li et al16. The diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR appeared numerically reduced by the presence of extensively calcified lesions despite the lack of a statistically significant difference (81.7% [95% CI: 71.6 to 91.8%]; difference: 9.0%; p=0.06). As numerous studies have demonstrated, a significant limitation of CCTA is the potential for overestimation of stenosis severity due to blurring caused by partial volume effects and beam hardening artefacts when imaging dense materials3031. The presence of extensively calcified lesions, however, did not significantly impact the diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR. Therefore, additional CT-μFR analysis in the field of CCTA can appropriately mitigate the false-positive findings due to severely calcified lesions. The observed improvement could be attributed to the iteration of the CT-μFR algorithm, which augments the automatic lumen segmentation capability.
Limitations
The present study has several limitations. Firstly, the study was limited because of the nature of its single-centre design, which may limit the generalisability and applicability of the recruited subjects. Of note, in a recent, retrospective, multicentre study18 enrolling 309 vessels with 30-90% diameter stenosis from 240 patients who underwent CCTA, ICA, and FFR examinations within 2 months, CT-μFR analysis showed high feasibility of 100%, with a sensitivity of 91% and a specificity of 92% in predicting invasive FFR ≤0.80. Future prospective multicentre studies are warranted to verify the findings of this study. Secondly, FFR was not measured in all three vessels. We performed ICA-derived μFR in those vessels and used it as the reference standard to validate CT-μFR, since previous studies have demonstrated high diagnostic concordance between μFR and FFR1332. Thirdly, as photon-counting CT technology is starting to be applied in clinical practice, we eagerly anticipate the future outcomes of applying CT-μFR technology to images obtained from this kind of CT. Furthermore, in line with the design of the CAREER trial, our analysis focused on coronary physiology, while high-risk plaques, another important factor associated with patient vulnerability and prognosis, were not evaluated. Future post hoc analysis of high-risk plaques based on the current population is highly welcome.
Conclusions
The CAREER Study met its prespecified primary endpoint of the diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR in identifying patients with haemodynamically significant coronary stenosis. The diagnostic accuracy of CT-μFR was non-inferior to μFR in vessels without extensively calcified lesions. The study indicated that in patients undergoing CCTA examination, the addition of CT-μFR has the potential of improving CCTA-based identification of haemodynamically significant stenosis and reducing unnecessary ICA and coronary interventions.
Impact on daily practice
The prospective CAREER Study showed that the per-patient diagnostic accuracy of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA)-derived Murray law-based quantitative flow ratio (CT-μFR) was 89.6%, with high sensitivity of 93.1% and specificity of 86.1%, in a consecutively enrolled real-world patient population. The results of this study proved the feasibility and accuracy of CT-μFR for the non-invasive determination of the physiological consequences of coronary artery disease and support the utility of applying CT-μFR in patients undergoing CCTA.
Funding
The CAREER Study is an investigator-initiated clinical trial with external funding from the Clinical Research Plan of Shanghai Hospital Development Center (SHDC) (No. SHDC2020CR3024B), issued by SHDC, and Clinical Medical Research Center of Geriatric Coronary Disease (No. LCXZ2205).
Conflict of interest statement
S. Tu is a co-founder of and reports research grants and consultancy from Pulse Medical Technology, Inc. W. Wijns reports grants and consulting fees from MicroPort; is a medical adviser for Corrib Core Laboratory and Rede Optimus; and is a co-founder of Argonauts, which is an innovation facilitator. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare relevant to the contents of this paper.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

