Abstract
Background: Microvascular angina (MVA) is an important contributor to morbidity and mortality in patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease. Despite improvements in its recognition and diagnosis, uncertainty remains around the most effective treatment strategy, and more data are needed.
Aims: We aimed to evaluate the quality of patient selection in treatment studies of MVA and provide a contemporary overview of the evidence base for the treatment of MVA.
Methods: PubMed, the Cochrane Library and Google Scholar were searched from inception to 4 November 2023 for all treatment studies in patients with angina and non-obstructive coronary artery disease or coronary microvascular dysfunction. Populations with acute coronary syndrome were excluded (PROSPERO: CRD42023383075).
Results: Forty-three studies were included. By contemporary definitions of MVA according to the Coronary Vasomotor Disorders International Study Group criteria, 11 (26%) studies enrolled patients with “definitive” MVA, 24 (56%) with “suspected” MVA, and 8 (19%) did not enrol patients who met the diagnostic criteria. A total of 24 unique treatment interventions were investigated. Most studies were observational and single armed (12/24, 50%) or had a single randomised study (9/24, 38%). Ranolazine is the most well-studied intervention drug. Double-blind randomised controlled trials of ranolazine (n=6) have shown inconsistent improvements in Seattle Angina Questionnaire scores and coronary flow reserve with short-term follow-up.
Conclusions: Treatment studies of MVA enrolled a heterogeneous population, with only a quarter meeting contemporary diagnostic criteria for definitive MVA. There is a paucity of high quality, randomised data to support any specific treatment intervention. Larger studies with robust selection criteria, blinded patient-reported outcomes, and long-term follow-up are needed.
Up to half of all patients with angina referred for coronary angiography have non-obstructive coronary arteries1. In the presence of myocardial ischaemia, a diagnosis of “microvascular angina” (MVA) should be considered. MVA is an umbrella term encompassing several endotypes with distinct yet overlapping pathophysiological mechanisms, including structural (increased resistance) and functional abnormalities (impaired vasodilation and/or enhanced susceptibility to microvascular constriction). These microcirculatory changes lead to reductions in coronary blood flow and subsequent myocardial ischaemia2.
MVA is associated with impaired quality of life and poor outcomes3. It often coexists with common cardiovascular comorbidities including hypertension, dyslipidaemia and diabetes mellitus, complicating the diagnosis and management of MVA itself. Formal MVA diagnostic criteria were established by the Coronary Vasomotor Disorders International Study Group (COVADIS) in 20184, and these were endorsed in a consensus document by the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI) (Table 1)5. Microvascular assessment in patients with suspected angina and non-obstructed coronary arteries (ANOCA) has been upgraded to a Class I, Level of Evidence B recommendation in the current European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines6.
Despite improvements in the recognition and diagnosis of MVA, to date, no treatment has been shown to improve major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in this population. It is possible that previously published treatment studies enrolled heterogeneous populations that would not now meet contemporary definitions of MVA, and this may in part explain the observed lack of treatment effect. This systematic review therefore has two main aims:
1. To evaluate the quality of patient selection in treatment studies of MVA.
2. To summarise the current evidence base for the treatment of MVA.
Table 1. Consensus-based diagnostic criteria for microvascular angina.
| Criteria | Evidence | Diagnostic parameters |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Symptoms of myocardial ischaemia | Effort or rest anginaExertional dyspnoea |
| 2 | Absence of obstructive CAD(<50% diameter reduction or FFR >0.80) | CT coronary angiographyInvasive coronary angiography |
| 3 | Objective evidence of myocardial ischaemia | Presence of reversible perfusion defect or wall motion abnormality on functional imaging testingIschaemic ECG changes |
| 4 | Evidence of impaired coronary microvascular function | Impaired coronary flow reserve (<2.5), determined invasively or non-invasivelyCoronary microvascular spasm, defined as reproduction of symptoms, ischaemic ECG shifts but no epicardial spasm during acetylcholine testingAbnormal coronary microvascular resistance indices (e.g., IMR ≥25) |
| Adapted from COVADIS/EAPCI recommendations45. A “definitive” diagnosis of microvascular angina is made when all 4 criteria are met; “suspected” microvascular angina is when 3 or 4 criteria are met. CAD: coronary artery disease; CT: computed tomography; ECG: electrocardiogram; FFR: fractional flow reserve; IMR: index of microvascular resistance | ||
Methods
Search strategy
PubMed, the Cochrane Library and Google Scholar were searched from inception up to 4 November 2023 for all original studies evaluating the effects of any intervention (including non-pharmacological) on patients defined by the authors as having “microvascular angina” or “ischaemia with non-obstructed coronary arteries” (INOCA) caused by coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMD). Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and myocardial infarction with non-obstructed coronary arteries (MINOCA) populations, paediatric populations (<18 years), conference abstracts, case reports, systematic reviews, editorials, and non-English language manuscripts were excluded. Studies investigating the treatment of epicardial coronary artery disease (CAD), including vasospastic angina, were excluded. The full search strategy, including search terms, is provided in Supplementary Appendix 1. The protocol for this systematic review was submitted prospectively to PROSPERO (identification number: CRD42023383075) on 10 March 2023.
All records were independently reviewed by two reviewers (M. Hammond-Haley and K. Chiew). Studies were systematically excluded by title, abstract, and finally full text (Figure 1). Disagreements were independently resolved by a third reviewer (F. Ahmed-Jushuf). Reference lists of included articles were screened for relevant publications that were not identified by the initial search. Studies were classified as double blind if the patient, the research team, and clinical team were all blinded to treatment allocation.
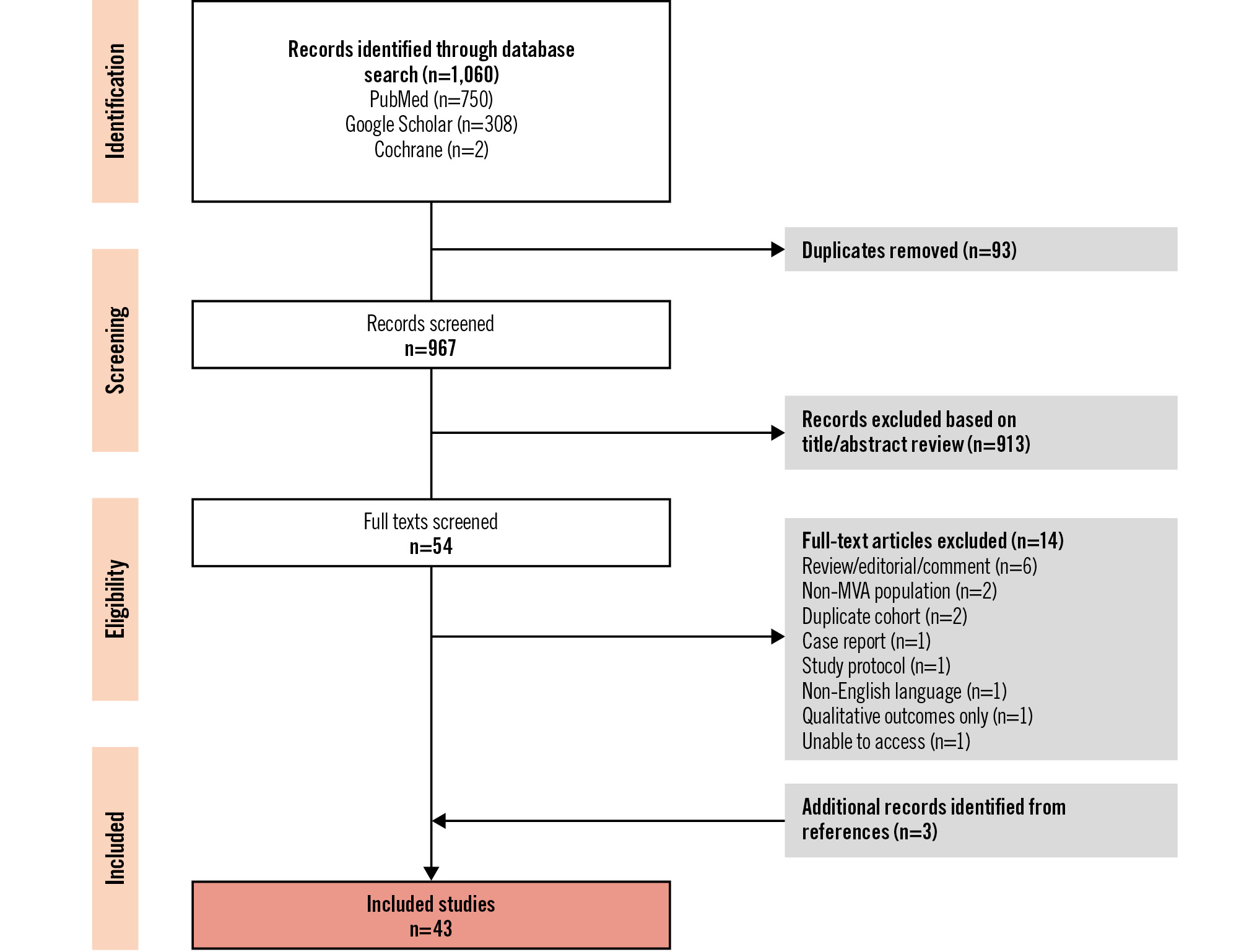
Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram. MVA: microvascular angina
Data extraction and statistical analysis
The following data were extracted from each study: study characteristics (including year of publication, type of intervention being studied, sample size, baseline study population characteristics), study design and quality assessment (including inclusion and exclusion criteria, use of blinding, placebo control, and risk of bias assessment), data to support the definition of MVA (including objective evidence of ischaemia, tests for microvascular dysfunction, and definitions of non-obstructive coronary arteries) and study outcomes (primary and secondary outcome data). Continuous variables are presented as mean±standard deviation, and categorical variables as total numbers and percentages (%).
Results
A total of 1,060 studies were identified from the search strategy (967 following the removal of duplicates) (Figure 1). The inclusion criteria were met by 43 studies, including 1,763 patients. A summary of the included studies is provided in Supplementary Table 1.
Patient population
Most study participants were female (n=1,212, 69%), with a moderate burden of cardiovascular comorbidities (Table 2). Frequently reported exclusion criteria included a history of valvular heart disease (20 studies, 47%), chronic kidney disease (CKD; 20 studies, 47%), previous myocardial infarction (MI; 12 studies, 28%), heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF; 12 studies, 28%), hypertension (11 studies, 26%), atrial fibrillation (AF; 10 studies, 23%), significant pulmonary disease (7 studies, 16%), previous percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG; 5 studies, 12%) or congenital heart disease (4 studies, 9%). In studies that excluded patients with HFrEF, several different left ventricular ejection fraction thresholds were used: <55% (n=1), <50% (n=3), <45% (n=3), <40% (n=2) and unspecified (n=3).
Table 2. Baseline patient characteristics.
| Total (n=1,763) | Intervention (n=1,208) | Control (n=559) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female | 1,145 (65) | 831 (69) | 314 (56) |
| Age, years | 58±10 (n=1,431) | 58±10 (n=988) | 59±10 (n=443) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 27.8±6.3 (n=881) | 27.9±6.4 (n=594) | 27.6±6.1 (n=287) |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Hypertension | 742/1,311 (57) | 556/917 (61) | 186/394 (47) |
| Diabetes | 281/1,512 (19) | 189/983 (19) | 92/529 (17) |
| Smoking history | 238/1,282 (19) | 144/833 (17) | 94/449 (21) |
| Hypercholesterolaemia/dyslipidaemia | 747/1,207 (62) | 479/754 (64) | 268/453 (59) |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction, % | 61.4±8.1 (n=416) | 62.6±8.3 (n=292) | 58.6±6.8 (n=124) |
| Medications | |||
| Beta blockers | 688/1,289 (53) | 483/886 (55) | 205/403 (51) |
| ACEi/ARB | 461/860 (54) | 313/580 (54) | 148/280 (53) |
| Nitrates | 386/968 (40) | 266/651 (41) | 120/317 (38) |
| Calcium antagonists | 322/989 (33) | 251/733 (34) | 71/256 (28) |
| Statins | 780/1,158 (67) | 550/796 (69) | 230/362 (64) |
| Data are presented as n (%), n/N (%) or mean±SD. For studies using a crossover trial design, participants were included in the intervention group. ACEi: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB: angiotensin receptor blocker; BMI: body mass index; SD: standard deviation | |||
Diagnosis of MVA
We investigated enrolment criteria based on the COVADIS/EAPCI recommendations for diagnosis of MVA across the 4 key domains (Central illustration)45. Of the studies included in this review, 27 (62%) were published prior to the publication of these criteria. According to the COVADIS criteria, 11 (26%) studies enrolled patients with “definitive” MVA, 24 (56%) with “suspected” MVA, and 8 (19%) did not enrol patients who met the diagnostic criteria (Central illustration).
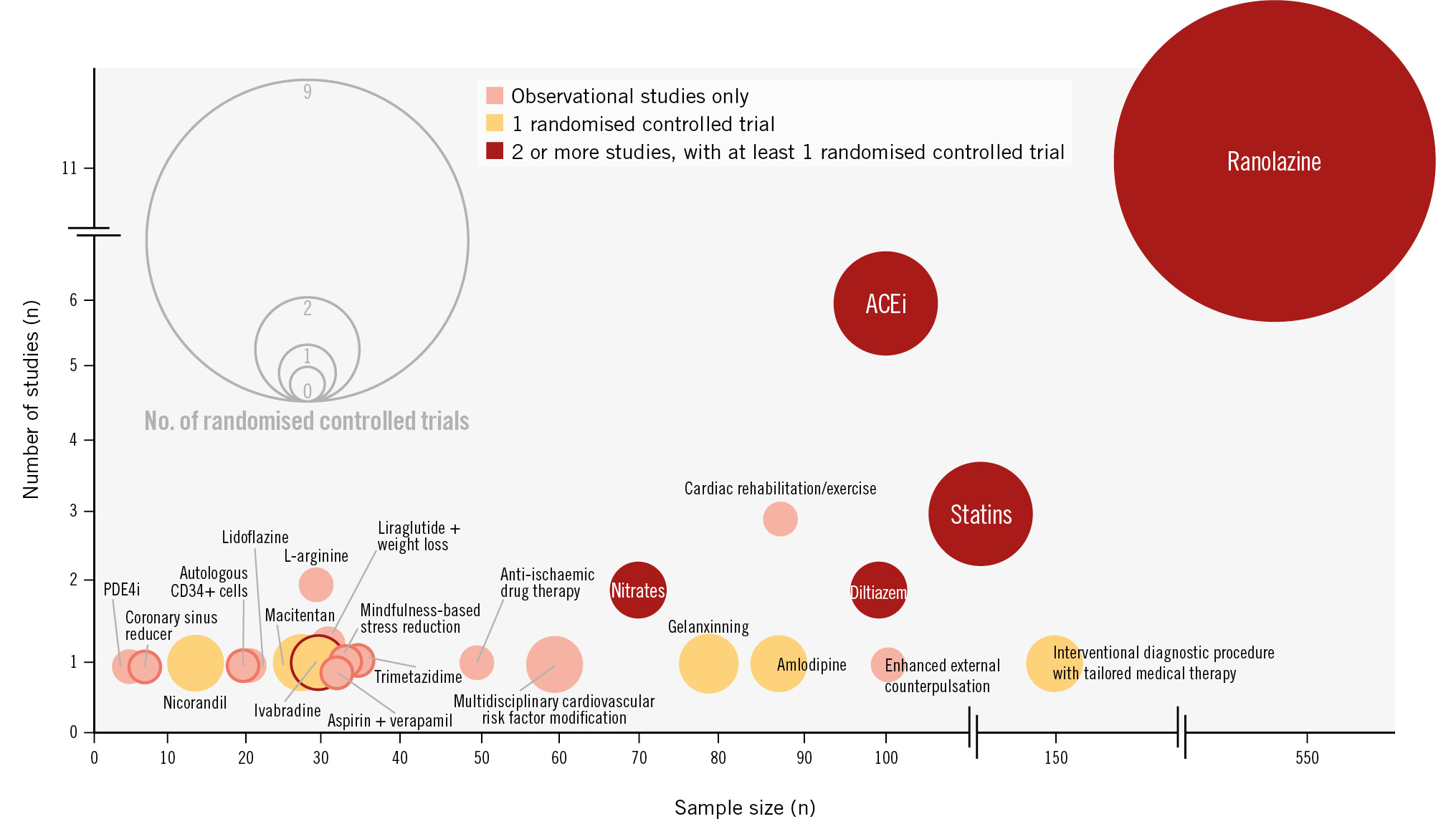
Central illustration. Proportion of treatment studies meeting COVADIS criteria for the diagnosis of microvascular angina. Bubble chart of all treatments for microvascular angina, displayed by sample size, total number of studies, and study type. The size of a bubble represents the number of randomised controlled trials. The bubble colours represent observational studies only (pink), a single randomised controlled trial (orange), and 2 or more studies with at least 1 randomised controlled trial (red). ACEi: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; PDE4i: phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor
Domain 1: symptoms of myocardial ischaemia
All studies recruited patients with a history of chest pain. A total of 24 (56%) studies reported a baseline angina score, with the Seattle Angina Questionnaire (SAQ) being the most frequently used score (n=22, 51%), followed by the Canadian Cardiovascular Society (CCS) angina class (n=6, 14%). Other functional or angina scores used included the EuroQol-5D (EQ-5D; n=6), Duke Activity Status Index (DASI; n=5), Short Form Survey (SF-36; n=1), Ferrans & Powers Quality of Life Index Cardiac version IV questionnaire (n=1), Symptom Checklist-90-Revised (SCL-90-R; n=1), Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire – Short Form (Q-LES-Q-SF; n=1), and the Rose Dyspnea Scale (n=1).
Domain 2: absence of obstructive CAD
Overall, 25 studies (58%) reported the criteria used to describe non-obstructive coronaries based on invasive coronary angiography. Four studies (9%) used computed tomography (CT) coronary angiography to exclude obstructive CAD. A total of 22 studies (51%) met the COVADIS/EAPCI recommended criteria of <50% coronary diameter reduction and/or fractional flow reserve (FFR)>0.80. None of the studies used intravascular imaging, such as intravascular ultrasound or optical coherence tomography.
Domain 3: objective evidence of myocardial ischaemia
Five studies (12%) reported the use of FFR or instantaneous wave-free ratio (iFR). A total of 29 studies (67%) reported the use of a functional test for myocardial ischaemia, which included stress electrocardiography (ECG; n=16), stress echocardiography (n=3), positron emission tomography (PET)-CT/myocardial perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT; n=2), stress cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMRI; n=2), and an unspecified test (n=6).
Domain 4: evidence of impaired coronary microvascular function
Ten studies (23%) reported the use of invasive tests of the coronary microcirculation, of which 6 (60%) used cutoff points in keeping with COVADIS criteria (Table 1). Different CFR cutoff points were used to define CMD: <2 (n=3), <2.5 (n=3), <3 (n=1), and unspecified (n=3). Three studies reported use of the index of microcirculatory resistance (IMR), with a value of >25 used in two studies and >20 used in the other to define CMD. Non-invasive assessments of CMD were used in 14 studies (33%), including transthoracic Doppler echocardiography (n=7), CMRI (n=1) and PET-CT (n=5). Coronary flow velocity reserve (CFVR) cutoff points by Doppler echocardiography included <2.5 (n=3), <2.2 (n=1) and unspecified (n=3). Only 13 studies (30%) reported the use of a provocation test to exclude epicardial spasm.
Treatment of MVA
In total, 24 unique interventions have been investigated for the treatment of MVA (Figure 2), including 7 drug therapies, 3 lifestyle interventions, 1 combination of medication and lifestyle intervention, 2 device therapies and 1 stem cell therapy (Table 3). Seven interventions (29%) were investigated in more than 1 study, and 12 interventions (50%) were investigated in only observational studies. Nine interventions (38%) were studied in a single randomised controlled trial (RCT). Most studies (28/43, 65%) enrolled fewer than 50 participants (Table 3). Of the 43 studies, 20 (47%) were RCTs. Studies which met the criteria for a double-blind RCT (n=15) are listed in Table 4.
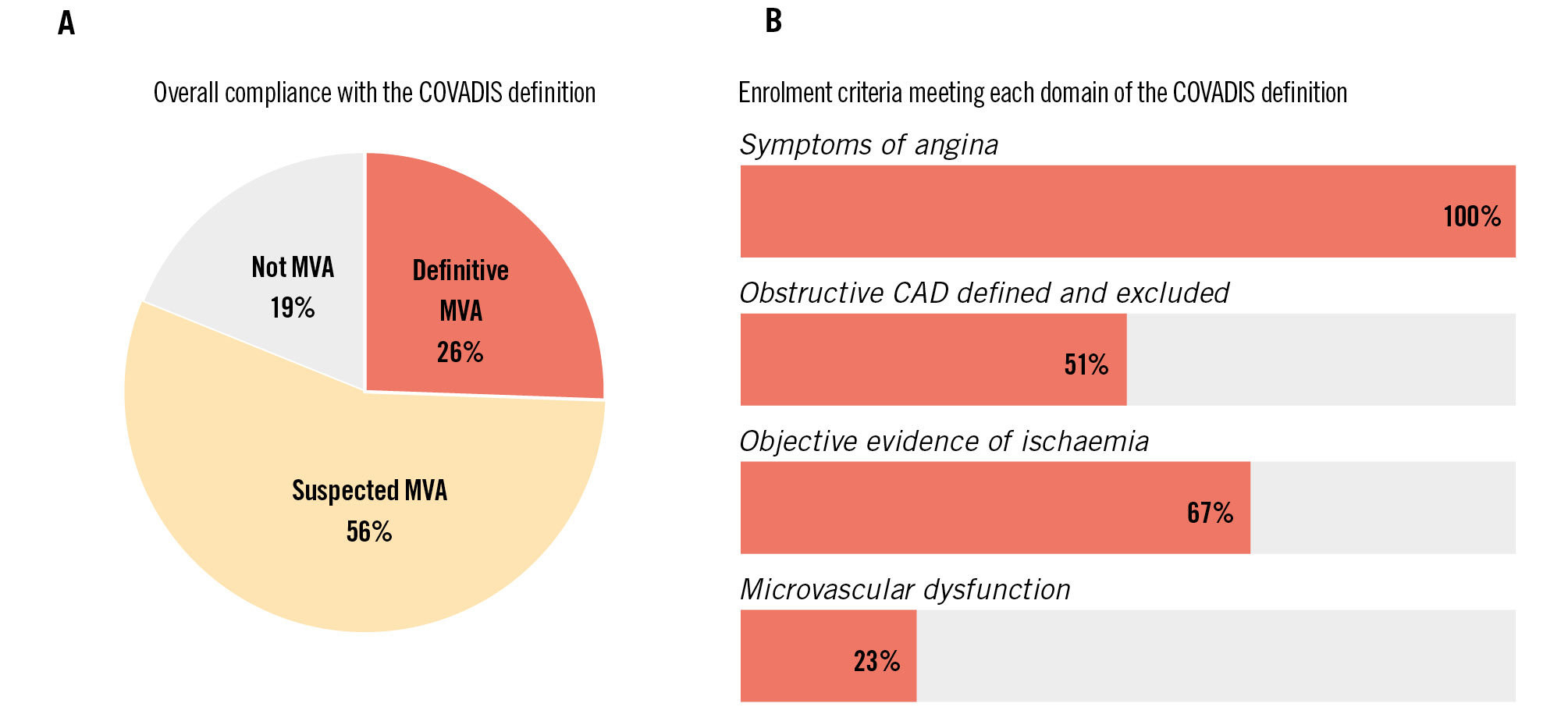
Figure 2. Proportion meeting COVADIS criteria overall (A), and by each domain (B). CAD: coronary artery disease; COVADIS: Coronary Vasomotion Disorders International Study Group; MVA: microvascular angina
Table 3. All included studies, stratified by treatment intervention.
| Intervention | Number of randomised controlled trials | Total sample size from randomised controlled trials | Number of observational studies | Total sample size from observational studies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ranolazine | 9 | 483 | 2 | 38 |
| Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor | 2 | 41 | 4 | 57 |
| Statin | 2 | 124 | 1 | 23 |
| Diltiazem | 1 | 85 | 1 | 11 |
| Nitrates | 1 | 20 | 1 | 53 |
| Interventional diagnostic procedure with tailored drug therapy | 1 | 151 | 0 | - |
| Amlodipine | 1 | 87 | 0 | - |
| Gelanxinning | 1 | 78 | 0 | - |
| Ivabradine | 1 | 31 | 0 | - |
| Nicorandil | 1 | 13 | 0 | - |
| Macitentan | 1 | 28 | 0 | - |
| Multidisciplinary cardiovascular risk factor modification | 1 | 62 | 0 | - |
| Cardiac rehabilitation or exercise program | 0 | - | 3 | 87 |
| L-arginine | 0 | - | 2 | 31 |
| Enhanced external counterpulsation | 0 | - | 1 | 101 |
| Trimetazidine | 0 | - | 1 | 35 |
| Mindfulness-based stress reduction | 0 | - | 1 | 34 |
| Aspirin and verapamil | 0 | - | 1 | 32 |
| Autologous CD34+ cells | 0 | - | 1 | 20 |
| Coronary sinus reducer | 0 | - | 1 | 8 |
| Phosphodiesterase inhibitor | 0 | - | 1 | 5 |
| Lidoflazine | 0 | - | 1 | 22 |
| Anti-ischaemic drug therapy (at physician’s discretion) | 0 | - | 1 | 51 |
| Liraglutide and weight loss | 0 | - | 1 | 33 |
| Treatments are listed in descending order based on the total number of randomised studies, then the total number of non-randomised studies. | ||||
Table 4. All included double-blind, randomised controlled trials and randomised crossover trials.
| Double-blind, randomised control trials and randomised crossover trials | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First author | Year | Country | Study design | Total sample size | Key inclusion criteria | Key exclusion criteria | Treatment | Treatment group size | Comparator | Comparator group size | Follow-up, weeks |
| Jansen21 | 2022 | Netherlands | RCT | 85 | <50% epicardial stenosis or 50-80% with FFR >0.8 or iFR >0.89 on invasive coronary angiography, coronary vasospasm (acetylcholine) and/or CFR <2 or IMR >25 (adenosine) using thermodilution | Previous PCI/CABG, LVEF <50% | Diltiazem 120-360 mg OD | 41 | Placebo | 44 | 6 |
| Solberg15 | 2019 | Norway | RCT | 66 | Females only, age 30-70 years, FFR >0.8 on invasive coronary angiography, ischaemia on bicycle ergometry | Coronary artery stenosis >33%, valvular heart disease | Rosuvastatin20 mg OD | 33 | Placebo | 33 | 24 |
| Kabaklic16 | 2017 | Slovenia | RCT | 58 | <50% epicardial stenosis on invasive coronary angiography, ischaemia on myocardial perfusion scan or exercise treadmill test | Lipid-lowering drug treatment within 1 month, diabetes mellitus, smoker, previous MI | Atorvastatin20 mg OD | 27 | Placebo | 31 | 24 |
| Michelsen14 | 2018 | Denmark | RCT | 63 | Females only, <50% epicardial stenosis on invasive coronary angiography, CFVR <2.2 from TTDE | Valvular heart disease, previous MI, LVEF <45% | Ramipril at maximum tolerated dose | 28 | Placebo | 27 | 24 |
| Safdar9 | 2017 | USA | RCT | 31 | Absence of coronary calcification on CT, CFR <2.5 from PET | Previous MI | Ranolazine 500-1,000 mg BD | 21 | Placebo | 10 | 4 |
| Tagliamonte10 | 2015 | Italy | RCT | 58 | <70% epicardial stenosis on CT coronary angiography, ischaemia on myocardial perfusion scan | Previous MI, LVEF <55% | Ranolazine 350-500 mg BD | 29 | Placebo | 29 | 8 |
| Mehta12 | 2011 | USA | Crossover | 20 | Females only, <50% epicardial stenosis on invasive coronary angiography | - | Ranolazine 500-1,000 mg BD | 20 | Placebo | 20 | 4 |
| Bairey Merz7 | 2016 | USA | Crossover | 142 | <50% epicardial stenosis on invasive coronary angiography, CFR <2.5 or MPRI <2 from CMRI | Valvular heart disease, LVEF <45%, ACS | Ranolazine 500-1,000 mg BD | 70 | Placebo | 72 | 2 |
| Shah11 | 2017 | USA | Crossover | 40 | Diabetes, <50% epicardial stenosis on invasive or CT coronary angiography | Valvular heart disease, LVEF <40% | Ranolazine 500-1,000 mg BD | 21 | Placebo | 19 | 4 |
| Villano8 | 2013 | Italy | RCT | 31 | Normal coronary angiography, CFVR <2.5 from TTDE, ischaemia on exercise test | Left ventricular hypertrophy | Ivabradine 5 mg BD or ranolazine 375 mg BD | 16 | Placebo | 15 | 4 |
| Feenstra40 | 2023 | Netherlands | Crossover | 28 | Epicardial or microvascular coronary artery spasm, >3 anginal attacks per week despite pharmacological treatment | Pregnancy, women of childbearing age, acute or severe liver disease, renal impairment | Macitentan10 mg OD | 14 | Placebo | 15 | 4 |
| Wu18 | 2015 | Italy | Crossover | 20 | Normal coronary angiogram, ischaemia on exercise test, CFR <2 from TTDE | - | ISMN60 mg OD | 20 | Placebo | 20 | 4 |
| Chen41 | 1997 | Taiwan | Crossover | 13 | Normal coronary angiogram, CFR <3 | Valvular heart disease, previous MI, left ventricular hypertrophy | Nicorandil5 mg TDS | 13 | Placebo | 13 | 2 |
| Kaski13 | 1994 | UK | Crossover | 10 | Normal coronary angiogram, ischaemia on exercise test, PET or technetium scan | Valvular heart disease, AF | Enalapril10 mg OD | 10 | Placebo | 10 | 2 |
| ACS: acute coronary syndrome; AF: atrial fibrillation; BD: twice a day; CABG: coronary artery bypass graft; CFR: coronary flow reserve; CFVR: coronary flow velocity reserve; CMRI: cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; CT: computed tomography; FFR: fractional flow reserve; iFR: instantaneous wave-free ratio; IMR: index of microvascular resistance; ISMN: isosorbide mononitrate; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; MI: myocardial infarction; MPRI: myocardial perfusion reserve index; OD: once daily; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; PET: positron emission tomography; RCT: randomised controlled trial; TDS: three times a day; TTDE: transthoracic Doppler echocardiography | |||||||||||
Randomised controlled trials of pharmacological therapy
Ranolazine
Nine RCTs (total n=488) investigated the effect of ranolazine on MVA (Table 5). Six were double-blind studies and used a placebo comparator, with a follow-up period of 2 to 8 weeks. Of the double-blind RCTs (including 321 individuals), 4 used the change in SAQ score as a primary outcome with variable results ranging from no improvement7 to significant improvements across all domains8. Three studied changes in coronary flow reserve (CFR) invasively (n=1)9 or with Doppler transthoracic echocardiography (n=2)1011. Only one of these demonstrated an improvement in CFR, from 1.91±0.31 to 2.54±0.44 (p=0.005)10. Two RCTs assessed the myocardial perfusion reserve index (MPRI) without any demonstrable improvements712. One RCT found a 47 second improvement in exercise time (p<0.05) and a 122 second improvement in time to 1 mm ST depression (p<0.01) on the exercise treadmill test8.
Table 5. All included randomised controlled trials of ranolazine.
| First author | Year | Total sample size | Blinding | Key inclusion criteria | Key exclusion criteria | Treatment | Treatment group size | Comparator | Comparator group size | Follow-up duration, weeks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sinha42 | 2023 | 87 | Partial | LVEF >50%, FFR >0.8 | Previous ACS or revascularisation, vasospastic angina | Ranolazine 375-750 mg BD | 87 | Amlodipine 5-10 mg OD | 87 | 4 |
| Golino43 | 2018 | 15 | Partial | Recent PCI within 6 months with no residual stenosis >20%, ischaemia on exercise test | - | Ranolazine375 mg BD | 15 | ISMN20 mg BD | 15 | 3 |
| Saha44 | 2017 | 65 | None | <50% epicardial stenosis on invasive coronary angiography, ischaemia on exercise test | - | Ranolazine 500-1,000 mg BD | 35 | Usual antianginals | 30 | 6 |
| Shah11 | 2017 | 40 | Double | Diabetes, <50% epicardial stenosis on invasive or CT coronary angiography | Valvular heart disease, LVEF <40% | Ranolazine 500-1,000 mg BD | 21 | Placebo | 19 | 4 |
| Safdar9 | 2017 | 31 | Double | Absence of coronary calcification on CT, CFR <2.5 from PET | Previous MI | Ranolazine 500-1,000 mg BD | 21 | Placebo | 10 | 4 |
| Bairey Merz7 | 2016 | 142 | Double | <50% epicardial stenosis on invasive coronary angiography, CFR <2.5 or MPRI <2 from CMRI | Valvular heart disease, LVEF <45%, ACS | Ranolazine 500-1,000 mg BD | 70 | Placebo | 72 | 2 |
| Tagliamonte10 | 2015 | 58 | Double | <70% epicardial stenosis on CT coronary angiography, ischaemia on myocardial perfusion scan | Previous MI, LVEF <55% | Ranolazine 350-500 mg BD | 29 | Placebo | 29 | 8 |
| Villano8 | 2013 | 30 | Double | Normal coronary angiogram, CFR <2.5 on transthoracic Doppler echocardiography, ischaemia on exercise test | Vasospastic angina | Ranolazine375 mg BD | 15 | Placebo | 15 | 4 |
| Mehta12 | 2011 | 20 | Double | Females only, <50% epicardial stenosis on invasive coronary angiography | - | Ranolazine 500-1,000 mg BD | 20 | Placebo | 20 | 4 |
| ACS: acute coronary syndrome; BD: twice a day; CFR: coronary flow reserve; CMRI: cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; CT: computed tomography; FFR: fractional flow reserve; ISMN: isosorbide mononitrate; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; MI: myocardial infarction; MPRI: myocardial perfusion reserve index; OD: once daily; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; PET: positron emission tomography | ||||||||||
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
Two RCTs studied angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi) against placebo. The first was a single-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial of 10 patients treated with enalapril for 2 weeks13. It showed improvements in exercise time and time to 1 mm ST depression. The second was a double-blind, randomised, parallel-group trial involving 63 female patients, comparing ramipril with placebo14. After 24 weeks, there were no differences in CFVR or echocardiographic parameters of systolic or diastolic function. There was an improvement in 3 out of 5 SAQ domains.
Other pharmacological therapies with at least 2 studies
Statins were investigated in 3 studies. A placebo-controlled RCT of once-daily 20 mg rosuvastatin for 6 months did not improve CFR, IMR, SF-36 or EQ-5D scores in 66 female patients with MVA15. Another placebo-controlled RCT of atorvastatin 20 mg once daily for 6 months in 58 individuals showed a higher flow-mediated dilatation of the brachial artery but no change in the reactive hyperaemia index (RHI)16. Finally, an observational study of once-daily 20 mg of simvastatin in 23 individuals showed an improvement in CFR (2.2 to 2.64; p<0.01)17.
Nitrates were investigated in 2 studies. A randomised crossover trial of 60 mg of modified release isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN) in 20 individuals demonstrated no improvements in coronary blood flow response to nitrate or the cold pressor test nor in flow-mediated dilatation of the brachial artery at 4 weeks18. Nine individuals did not complete the ISMN phase due to adverse side effects. An observational study of 5 mg of sublingual isosorbide dinitrate given to 53 patients prior to exercise stress testing showed no improvement in rate-pressure product at 1 mm ST-segment depression19.
Diltiazem was investigated in 2 studies. In a study of 5 patients treated with 10 mg of intravenous diltiazem during coronary angiography, there was no improvement in CFR20. A recent RCT of 86 patients given 120-360 mg of diltiazem once a day for 6 weeks showed no improvements in CFR, IMR, SAQ scores or CCS class21.
L-arginine was investigated in 2 observational studies. A total of 18 patients received an intracoronary L-arginine infusion during angiography22 which improved coronary blood flow response to acetylcholine compared to controls. In another study, 13 hypertensive patients taking 2 g of oral L-arginine 3 times a day for 4 weeks demonstrated a significant reduction in blood pressure and improvements in maximal forearm blood flow and CCS class23.
Patient-stratified medical therapy
Stratified medical therapy was evaluated in 2 studies. An observational study of 51 individuals treated with classical anti-ischaemic drugs at their physicians’ discretion24 showed an improvement in the EuroQol score of 10 or more in 25/51 (49%) patients after 52 weeks. Within this subgroup, there was no association between the angina status and changes in coronary microvascular function measured by coronary blood flow response to adenosine and the cold pressor test.
A stratified treatment strategy based on invasive coronary microvascular function testing was investigated in the CorMicA trial25. After invasive comprehensive microvascular function testing to identify the endotypes of CMD or vasospasm, 391 patients were randomised to treatment informed by knowledge of the endotype compared to standard care. Improvements in SAQ (p=0.015) and EQ-5D scores (p=0.024) were seen in endotype-guided care.
Lifestyle interventions
Cardiac rehabilitation or exercise programmes were evaluated in 3 small observational studies262728. All were positive in meeting their primary outcomes at 12- to 16-week follow-up, including improvements in VO2 max, proportion of ischaemic myocardium on myocardial perfusion SPECT imaging, and CFR measured with transthoracic Doppler echocardiography.
Mindfulness-based stress reduction was shown by Kim et al in 1 study of 34 females to reduce global longitudinal strain on transthoracic echocardiography and reactive brachial flow-mediated dilatation at 8 weeks29.
Multidisciplinary risk factor management in 62 overweight female patients, involving weight loss, exercise training, and blood pressure, lipid and glycaemic optimisation, was compared to standard care in a randomised study by Bove et al30. After 24 weeks, there were improvements in 3 out of 5 domains in the SAQ but no change in CFVR.
Device interventions
A coronary sinus reducer was investigated in 1 observational study of 8 individuals with refractory angina31. At 16 weeks, there were improvements in the median CCS class, 4 out of 5 SAQ domains and distance walked during the 6-minute walk test.
Enhanced external counterpulsation (EEC) was evaluated in an observational study of 101 individuals32. After a median follow-up of 31 weeks, the proportion of those in CCS class III or IV reduced from 100% to 45.5% (p<0.001), with improvements in distance walked during the 6-minute walk test, and SAQ and DASI scores.
Discussion
In this comprehensive systematic review of MVA treatment studies, we found only a quarter of studies would meet the contemporary diagnostic criteria for definitive MVA. Almost 1 in 5 studies did not enrol patients with MVA at all. Secondly, whilst a range of interventions have been investigated, these are limited to mostly small, unblinded, observational studies, with short follow-up periods. There is a lack of quality data to support any particular treatment strategy. To date, no published studies have investigated long-term MACE in this population. Most enrolled patients were female, reflecting both a higher prevalence of CMD in females33 and an effort to advance diagnosis and treatment options in this historically underrepresented demographic.
Diagnosis of MVA
Diagnostic criteria for MVA were standardised by COVADIS in 20184, with over half of the included studies reported prior to the publication of these criteria. COVADIS/EAPCI require patients to meet the criteria in 4 domains to confirm a definitive diagnosis of MVA. All the included studies provided some description of symptoms in keeping with myocardial ischaemia; however, the definitions used were highly variable. Validated questionnaires were used to assess symptom burden and/or quality of life in just over half of the studies.
The COVADIS criteria for excluding obstructive CAD were not met by almost half of the included studies. Coronary physiology (FFR or iFR) was rarely utilised, and none of the studies used intravascular imaging. Importantly, visual assessment of the haemodynamic significance of an angiographically intermediate stenosis (typically defined as a 40-70% diameter stenosis) does not predictably correlate with FFR assessment34. Given that most of the studies included patients with up to 50% stenoses, the prevalence of significant flow-limiting epicardial coronary disease could have been underappreciated. CT coronary angiography is likely to be increasingly utilised in the assessment of patients presenting with chronic coronary syndromes, in line with current international guidelines635, but it was used by less than 10% of the included studies.
The third COVADIS domain relates to objective evidence of myocardial ischaemia. Traditional non-invasive tests for this include stress ECG, stress echocardiography and SPECT. These methods were used by 29 (67%) of the included studies. However, such methods rely on the detection of large regional differences in myocardial perfusion or ventricular wall motion in epicardial coronary artery vascular territories5. CMD, by contrast, typically has a more diffuse disease pattern, and hence, these modalities have a relatively low sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing CMD5.
The fourth diagnostic domain is objective evidence of microvascular dysfunction. Once severe obstructive epicardial disease has been excluded, an abnormally low CFR (<2.5) can be used as a surrogate for ischaemia and a diagnostic parameter for CMD. However, the presence of non-obstructive epicardial coronary disease can influence CFR, rendering interpretation challenging, particularly when a broad range of non-obstructive stenoses are included for summative analyses. IMR − a measure of microvascular resistance assessed during hyperaemia using a pressure wire − is independent of epicardial stenoses and haemodynamic changes. IMR therefore overcomes some of the key limitations of CFR, although it can only be measured invasively. Despite these advantages, IMR was reported by only 3 of the included studies.
Exclusion of epicardial vasospasm by demonstration of no or less than 90% epicardial coronary artery diameter reduction with acetylcholine is an important part of the COVADIS/EAPCI definition of CMD. Once excluded, provocation testing that reproduces symptoms and generates ischaemic ECG changes suggests microvascular spasm. Abnormal epicardial coronary vasoconstrictive reactivity accounts for a significant proportion of INOCA, and differentiating between these discrete pathophysiological mechanisms has important therapeutic implications25. Despite this, methods to exclude epicardial vasospasm were only reported in less than a third of the included studies, further highlighting the need for careful diagnosis and stratification of INOCA endotypes in future treatment studies.
Treatment of MVA
Despite a global effort to improve the recognition of MVA5 and an expansion in both invasive and non-invasive diagnostics for CMD, there are no well-established treatments to date. The data are mainly comprised of small, observational studies with short follow-up periods, variable inclusion criteria, and poor reproducibility. Despite studies of 24 different interventions being published, only half of all the studies were RCTs, and less than a third of treatments were investigated in more than one study. As such, there remains a lack of strong evidence to inform clinical guidelines, with current recommendations largely based on expert consensus5.
In practice, two broad approaches are used to manage MVA: firstly, addressing cardiovascular risk factors through lifestyle modifications or pharmacological treatment; secondly, using antianginal medication to improve symptom burden and quality of life.
Ranolazine is the most studied treatment. A previous meta-analysis of 6 RCTs demonstrated partial improvements in SAQ scores: it found improvements in angina stability, quality of life and physical functioning but no improvements in angina frequency or treatment satisfaction36. Whilst there was some improvement in CFR (mean difference 0.27, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.09-0.45), there was no improvement in MPRI. These contradicting results from an analysis of highly heterogeneous studies limit the assessment of ranolazine’s mechanism of action and its unblinded effect on symptoms.
Lifestyle interventions, albeit all from unblinded observational data, have been the most consistent in showing benefit. Exercise programmes have demonstrated improvements in exercise capacity as well as objective features of ischaemia on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and invasive testing. Additionally, mindfulness training may improve brachial artery flow-mediated dilatation. The impacts of stress reduction and improved fitness on overall cardiovascular health are well recognised, and the participants included in the treatment trials had a significant burden of cardiovascular risk factors. As such, in the absence of controls, it is unclear if this observed benefit can be directly attributed to an improvement in microvascular function.
Upcoming studies
The ongoing Women’s Ischemia Trial to Reduce Events in Non-Obstructive CAD (WARRIOR) trial37 will evaluate the effect of combining a high-dose statin, ACE inhibitors and aspirin compared to usual care in over 4,000 female patients with ANOCA over a 3-year follow-up period. It is the first large RCT to evaluate MACE as a primary outcome. However, this trial is not enrolling a “definitive” CMD population because objective evidence of CMD is not mandated as an inclusion criteria.
The International Study of Coronary Microvascular Angina (iCorMicA) is a multinational trial investigating whether an interventional diagnostic procedure with stratified medical therapy according to ANOCA endotype will improve SAQ summary scores in 1,500 participants (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04674449)38.
Finally, the Precision Medicine with Zibotentan in Microvascular Angina (PRIZE) study will determine the efficacy of zibotentan, an endothelin-receptor antagonist, compared to placebo in a population enriched with a high genetic expression of endothelin-1 on the treadmill exercise test39.
Limitations
This systematic review did not identify sufficiently homogeneous RCTs to conduct a meta-analysis. Of note, more than half of the identified studies were published before the 2018 COVADIS definition of MVA. This review therefore provides the historical and contemporary context for evaluation of the current evidence base and its application to clinical practice.
Furthermore, while COVADIS criteria have been endorsed by the EAPCI, the use of these criteria is not mandated by international guidelines. In addition, individual investigators may be constrained by factors such as budget and the availability of diagnostic tests within local institutions. This should not deter future research in the field, but every possible effort should be made to ensure that the enrolment criteria are well defined and targeted to select the most appropriate study population.
A number of endotypes for INOCA have been identified; this present review does not attempt to describe populations with vasospastic angina or to separate the structural and functional causes for CMD.
Conclusions
Despite recent renewed enthusiasm for the diagnosis and management of MVA, there remains a paucity of high-quality randomised data to support any specific treatment strategy. Almost 1 in 5 studies to date in MVA did not enrol patients who met contemporary COVADIS criteria. Less than a third of treatments were used in more than 1 study, suggesting caution is needed before translating the results into clinical practice. Future studies should enforce robust enrolment criteria to ensure the selection of a truly representative population with MVA. Large placebo-controlled RCTs evaluating long-term clinical outcomes are needed to accurately inform clinical decision-making in patients with MVA.
Impact on daily practice
Most patients recruited to previous treatment studies of microvascular angina do not meet the current consensus-based definitions of definitive microvascular angina. The existing literature should therefore be interpreted with caution, and future studies should enrol participants who strictly meet these diagnostic criteria. At present, a wide range of pharmacological and non-pharmacological management strategies have been investigated, but there is a lack of high-quality evidence to support any specific treatment strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Hammond-Haley and K. Chiew are supported by the National Institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) Academic Clinical Fellowship. F. Ahmed-Jushuf has grant support from the Medical Research Council (MRC). C.A. Rajkumar has grant support from the MRC; reports consulting fees from Philips; and speaker fees from Menarini. M.J. Foley has grant support from the MRC; and reports speaker fees from Menarini and Philips. S. Chotai has grant support from the NIHR. M.J. Shun-Shin reports consulting fees from MyCardium AI and Medtronic. R. Al-Lamee has grant support from the British Heart Foundation; reports being on a trial steering committee for Janssen Pharmaceuticals; being on an advisory board for Abbott and Philips; and reports speaker honoraria from Abbott, Philips, Medtronic, Servier, Omniprex, and Menarini. F.A. Simader has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary data
To read the full content of this article, please download the PDF.

