A 39-year-old man underwent a complex percutaneous coronary intervention of the left main trifurcation due to unstable angina. Five paclitaxel-eluting stents were implanted successfully in the 3 major branches and left main trunk (Figure 1, panels A and B).
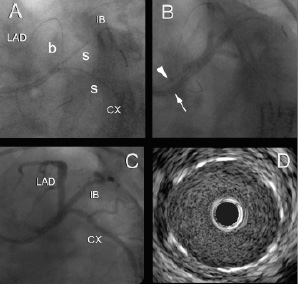
Figure 1. Two paclitaxel eluting stents (PES) were positioned simultaneously within the intermediate branch and circumflex artery (CX) together with balloon dilatation of the left anterior descending artery (LAD) to prevent plaque shift (panel A). The stent in the CX overlapped with a more distal stent in the same branch implanted at the start of the procedure. Due to dissection of the LAD ostium another PES was positioned in the proximal LAD and a fifth stent was deployed in the left main trunk (not shown). The procedure was completed with kissing balloon inflations of the 3 branches using 2 guiding catheters (one 5 and one 6 French guiding catheter), as indicated by the arrowhead and arrow (panel B). Invasive coronary angiography showed perfect patency of the 3 branches (panel C). Intravascular ultrasound confirmed the absence of neointimal hyperplasia, as shown by the IVUS cross-sectional image of the LMCA (panel D). b indicates balloon; CX, circumflex coronary artery; IB, intermediate branch; LAD, left anterior descending coronary artery; and s, stent.
Three months later follow-up 64-slice computed tomographic (MSCT) coronary angiography demonstrated excellent stent patency without signs of neointimal hyperplasia (Figure 2).
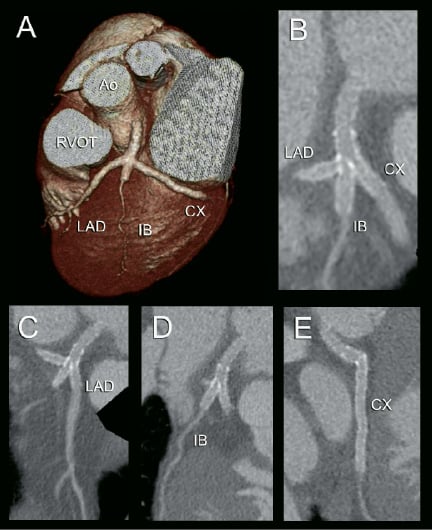
Figure 2. 64-slice CT coronary angiogram. Volume-rendered (panel A) and multiplanar reconstructed image (panel B) showing the stented left main trifurcation. The lumen within the stents is clearly visible along the 3 branches of the trifurcation (panels C, D and E). It is obvious that the 4 stents, including the stent edges, are perfectly patent without signs of neointima hyperplasia.
Ao indicates ascending aorta; CX, circumflex coronary artery; IB, intermediate branch; LAD, left anterior descending coronary artery; RVOT, right ventricular outflow tract.
Invasive coronary angiography and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) confirmed these findings (Figure 1, panels C and D).
Current MSCT scanners provide a promising non-invasive alternative to conventional coronary angiography in the follow-up of patients after stenting of the left main coronary artery.

