Abstract
Objective: To investigate the impact of BiodivYsio dexamethazone-eluting stent versus BiodivYsio stent on the 12-month outcomes after revascularisation of patients with single vessel coronary artery disease.
Methods: From March 2003 to February 2004, 102 patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes, angina or silent ischemia after recent ST elevation myocardial infarction (<1 month) or stable angina pectoris, and single-vessel coronary artery disease were treated solely with dexamethazone-eluting stent implantation in our institution. Patients were followed up prospectively for twelve months. We compared their outcomes to a control group with similar clinical and angiographic characteristics of 160 patients treated solely with BiodivYsio stents in the preceding study enrolment period (January 2002 to March 2003).
Results: Approximately 85% of the patients in both groups were treated after an acute coronary syndrome. At 12 months, the major adverse cardiac events rates (death or non-fatal myocardial infarction or target lesion revascularization) were similar in the 2 groups (10.8% in the dexamethazone-eluting and 11.3% in the BiodivYsio group, p=1.00). No difference was found in the individual rates of death, non-fatal myocardial infarction and target lesion revascularization between the 2 groups.
Conclusions: We conclude that utilization of dexamethazone-eluting stents has no effect in reducing the incidence of major adverse cardiac events after 12 months, as compared with BiodivYsio stent implantation in the treatment of single vessel coronary artery disease.
Introduction
Drug-eluting coronary stents (DES) that elute an antiproliferative agent (paclitaxel, sirolimus or sirolimus derivatives) have been proven to reduce the risk of angiographic restenosis and repeat revascularization procedures compared to bare metal stents1-5. Taking into account the different biological mechanisms contributing to restenosis, a wide range of other pharmaceutical agents is under preclinical and clinical evaluation. Inflammatory reaction plays an important role in neointimal formation after coronary stenting and anti-inflammatory approaches may be of value to reduce in-stent restenosis6. Corticosteroids have potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects by reducing the influx of mononuclear cells, inhibiting monocyte and macrophage function, and influencing thus the smooth muscle cell proliferation in animal models of arterial injury7.
Dexamet (Abbott Vascular Devices) is a rather low price DES (60% of the price of the other DES during the study period in Greece) coated with phosphorylcholine (PC) technology and preloaded with dexamethazone (0.5 µg/mm2; in a 15-mm devise, 40 µg of the drug is bonded). In a phase II, prospective, non-controlled trial loading dexamethazone onto a PC-coated BiodivYsio coronary stent resulted in a low 6-month rate of major adverse cardiac events (MACE)8. The present study was conducted to investigate the impact of BiodivYsio dexamethazone-eluting stent implantation on the 12-month outcomes of patients with single vessel coronary artery disease as compared to the PC-coated BiodivYsio stent implantation.
Methods
Patients
In the Catheterization Laboratory of the University of Ioannina Biocompatible stents are one of the three mainly used stents; the others being Boston Scientific and Medtronic. The decision for the type of stent used in each lesion depends upon the operator’s discretion and availability. Although no formal policy exists in our Laboratory with regards which type of stent has to be implanted in different type of lesions, the operators used mainly the Biocompatible stents in proximal lesions not involving big bifurcations and not located in extremely tortuous vessels. From January 2002 to March 2003 the Biocompatible stents been available in our laboratory were the BiodivYsio and these were subsequently replaced by the Dexamet. All patients who had been treated with Dexamet stent implantation are included in a registry evaluating its efficacy. From January 2002 to March 2003 and subsequently from March 2003 to February 2004, the number of patients that had been treated with stent implantation in our catheterization laboratory were 675 and 550 respectively. Three hundred and forty eight in the first period and 275 in the later had no ST elevation acute coronary syndrome within the previous 48 hours and a single de novo native coronary lesion not located in an unprotected left main stem which could be treated with a single stent (diameter >2.5 mm and <3.5 mm, length <28 mm). Forty six percent (160/348) in the initial period (April 2002 to March 2003) and 37% (102/275) in the later were treated exclusively with BiodivYsio and Dexamet stents implantation, respectively.
All interventions were performed according to current standard guidelines9. The utilization of periprocedural glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors was left to the discretion of the operator. All patients were advised to mainitain lifelong aspirin. Clopidogrel (75 mg/d) was recommended for at least one month in the control group. In the Dexamet group, clopidogrel was prescribed for at least three months. The study was carried out according to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from every patient.
Clinical setting
The study was conducted in a confined geographical region in northwest Greece. In this region, health care is provided by private clinics, 20 small scale primary care health centres, 4 general district hospitals and 1 tertiary care hospital (University Hospital of Ioannina), in which the cardiac catheterization and cardiac surgery facilities are located. The physicians of the private clinics and the primary care health centres are in close conduct with the physicians of the tertiary centre and they can be approached directly whenever necessary for clinical or research purposes.
Clinical definitions and follow-up
The recorded MACEs include death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or target lesion revascularization. We also recorded the incidences of target vessel revascularization and thrombotic stent occlusion. Myocardial infarction was diagnosed by a rise in the creatine kinase level to more than twice the upper normal limit with an increased creatine kinase-MB. Target lesion revascularization (TLR) was defined as a repeat intervention to treat a luminal stenosis within the stent or in the 5-mm distal or proximal segments adjacent to the stent. Target vessel revascularization was defined as any re-intervention in the same epicardial vessel. Thrombotic stent occlusion was angiographically documented as a complete occlusion (TIMI flow 0 or 1) or a flow-limiting thrombus (TIMI flow 1 or 2) of a previously successfully treated artery.
Patients included in the present report were followed-up clinically according to our standard protocol, which consists of clinical reviews in the outpatient clinic at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months and a functional testing (exercise ECG or myocardial scintigraphy) at 3 and 6 months prior to clinical assessment. During the clinical follow-up period, angiography was performed only in patients with recurrence of symptoms or functional tests demonstrating the presence of myocardial ischemia. In case that a patient missed his outpatient clinic appointment the referring physician was contacted for further information. Medical records were reviewed when clinical events occurred.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were presented as mean (± SD) and were compared by means of the Student unpaired t test. Categorical variables were presented as counts and percentages and compared by means of the Fisher exact test. The Kaplan-Meier estimation technique and a log rank test made comparisons of time to an event (MACE). In measuring the time to an event for cases in which a patient had multiple MACEs, only the first event was taken into account. A p value <0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Baseline clinical and procedural characteristics of the study patients are shown in Table 1.
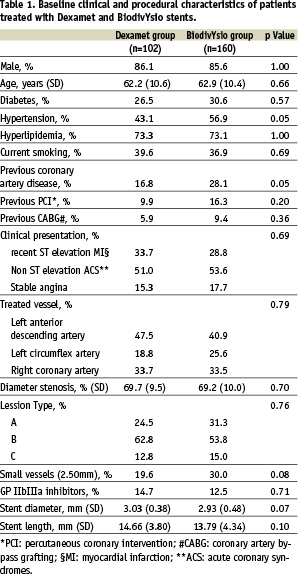
Approximately 85% of the patients in both groups were treated after an acute coronary event (non-ST elevation acute coronary syndrome, angina or silent ischemia after recent (<1 month) ST elevation myocardial infarction). The proportion of diabetics and small vessels treated did not significantly differ in the 2 groups. In 7/102 patients in the Dexamet group and 8/160 patients in the BiodivYsio group a second similar stent was implanted in order to cover a dissection after the first stent implantation or to treat a residual stenosis.
Complete follow-up information was available in all patients. There were no differences between the 2 groups in the incidence of MACE during the first month (1.96% in the Dexamet and 1.88% in the BiodivYsio group, p=1.00). Target lesion revascularization at 30 days was 0.98% in the Dexamet group and 1.25% in the BiodivYsio group (p=1.00). Repeat percutaneous intervention was performed for angiographically documented stent thrombosis in 1 patient in the Dexamet and in 2 patients in the BiodivYsio group during the initial hospitalization. No further thrombotic stent occlusion was observed during post discharge follow-up.
During the follow-up period coronary angiography was performed in 16/102 (15.7%) patients in the Dexamet and 27/160 (16.9%) in the BiodivYsio group (p=0.86). Twenty one patients (8/16 in the Dexamet and 13/27 in the BiodivYsio group) underwent coronary angiography due to typical anginal symptoms or non-fatal myocardial infarction. Twelve asymptomatic patients (5 in the Dexamet and 7 in the BiodivYsio group) underwent coronary angiography due to positive exercise tests. Coronary angiography was also performed in 6 patients (2 in the Dexamet and 4 in the BiodivYsio group) who had atypical chest pain and non-diagnostic exercise test. Finally, 4 patients (1 in the Dexamet and 3 in the BiodivYsio group) underwent coronary angiography after been rehospitalized due to chest pain although their exercise tests were negative for ischemia.
At 12 months, the incidences of MACE were similar in the 2 groups (11/102 in the Dexamet and 18/160 in the BiodivYsio group, p=1.00). The time to a first event in the first 12 months after procedure was also similar in the 2 groups (p= 0.872). Figure 1 shows the survival free from MACE in the Dexamet and BiodivYsio stent groups.
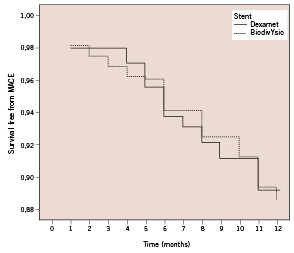
Figure 1. Survival free from MACE in the Dexamet and BiodivYsio stent groups.
The incidences of individual outcomes (death, myocardial infarction, and target lesion revascularization) were similar in the 2 groups (Table 2).
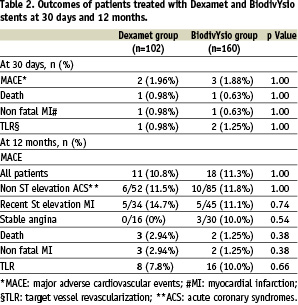
Target lesion revascularization rates did not significantly differ between the 2 groups (7.8% in the Dexamet and 10.0% in the BiodivYsio group, p=0.66). Target vessel revascularization rates did not significantly differ between the 2 groups (9.8% in the Dexamet and 11.2% in the BiodivYsio group, p=0.84). There were no differences in the MACE rates in the subgroups of patients with a) recent ST elevation myocardial infarction, b) patients with non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes and c) patients with stable angina (Table 2). None of the 16 patients with stable angina treated with Dexament stent implantation had a MACE during the follow-up. In higher risk subsets the 12-months risk of MACE was also similar; 4/27 in the Dexamet and 8/49 in the BiodivYsio group in diabetics (p=1.00), and 3/20 in the Dexamet and 6/48 in the BiodivYsio group (p=1.00) in patients with small vessels (2.50 mm).
Discussion
The present study is the only one which compared the efficacy of BiodivYsio dexamethazone eluting (Dexamet) with BiodivYsio stent in the treatment of single vessel coronary artery disease. Although the number of patients included in the present study was rather small and their risk for restenosis was not high our results indicate that the use of Dexamethazone-eluting stent has no favourable effect in reducing the outcomes of death or myocardial infarction or target lesion revascularization at 12 months compared to BiodivYsio stent implantation.
The pleiotropic mode of action been exerted by corticosteroids includes profound anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects, direct inhibition on smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis10. Thus their potential in the prevention of restenosis has gained widespread interest. Clinical studies, however, have not shown definite results.
Intravenous administration of a single dose of methylprednizolone before coronary stenting had not shown any effect on the change in minimal lumen diameter at 6 months11, while systemic treatment with prednisone was found to be effective in reducing clinical events after stent implantation in stable angina patients with elevated C-reactive protein13. A recent study indicated that in patients with unstable angina or recent myocardial infarction, 1-vessel coronary artery disease, and complex ‘culprit’ coronary lesions treated with a single stent, dexamethazone-eluting stents significantly reduced systemic C-reactive protein response after intervention12.
A pilot trial (Study of antirestenosis with the Biodivysio dexamethazone-eluting stent [STRIDE]) on the use of a stent loaded with dexamethasone (0.5 µg/mm2) reported low (3.3%) six-month MACE after Dexamet implantation8. However, angiographic restenosis rate (13.3%) was similar to the levels reported previously for non-drug-loaded BiodivYsio phosphorylcholine-coated stents14,15. Furthermore, the results of 2 recent small studies using high-dose dexamethazone-eluting stents demonstrated similar angiographic16 and intravascular17 follow-up results to bare metal stents.
Differences in study design and patient characteristics may account for the variations in the efficacy of systemic and local (dexamethazone stents) steroid therapy been observed in the different clinical trials. Although patients with unstable angina had a marginally reduced late loss at six months compared to the stable patients in the STRIDE trial8, the favourable clinical results of oral prednisone after stent implantation in IMPRESS study were extracted from a study in which only stable patients were included. It should be noted however, that these patients had systemic signs of inflammation after the procedure13. Unfortunately, in the STRIDE trial there was no data regarding the effect of Dexamet on systemic inflammatory response in subgroups of patients with unstable or stable angina. It is known that inflammation is a central pathogenic mechanism for acute coronary syndromes and the vascular response to injury after percutaneous coronary intervention and it is of possible prognostic value in both unstable and stable ischemic syndromes18-22. Recently, Patti et al. demonstrated that in patients with acute coronary syndromes, dexamethazone-eluting stents significantly reduced systemic CRP response after percutaneous coronary interventions and this effect was particularly evident in patients with elevated (>3 mg/L) preprocedural CRP values12. Corticosteroids (administered either topical or systemic) thus may have a favourable effect only in selected high-risk patients with persistent signs of inflammation (preprocedural or after the procedure) regardless their clinical syndrome.
To even date only paclitaxel, sirolimus and sirolimus derivatives eluting stents has been shown to reduce repeat revascularization in large randomized clinical trials23. Randomised studies assessing the effectiveness of other drug eluting stents reported no effectiveness or worse clinical outcomes. In the Actinomycin Eluting Stent Improves Outcomes by Reducing Neointimal Hyperplasia (ACTION) study, Serruys et al. showed that the six-month and one-year MACE was higher in actinomycin-D groups compared to the bare metal stent group24. In the Study to COmpare REstenosis Rate between QueST and QuaDDS-QP2 (SCORE) trial using the paclitaxel derivative 7-hexanoyltaxol within an acrylate polymer membrane mounted on a novel stent design, incidences of early and late stent thrombosis and MI were significantly higher in the 7-hexanoyltaxol arm, leading to premature cessation of enrolment25. Differences in drugs, polymers, coatings, and delivery systems may be responsible for these results and may indicate that, although pre-clinical models of restenosis with drug eluting stents may predict angiographic findings, they often do not accurately predict clinical events in patients.
The major limitations of this study were its design (non-randomised) and the relatively small number of patients enrolled. Other limitations were also the lack of biochemical and imaging (repeat angiogram and intracoronary ultrasound) data regarding the effect of Dexamet stent on systemic inflammatory response and neointima formation, respectively.
In conclusion, this study implies that implantation of Dexamethazone-eluting stents in patients with single de novo lesions has no effect in reducing the need of further revascularization and the incidence of major adverse cardiac events after 12 months, as compared with the implantation of PC coated BiodivYsio stent. However, large randomized studies are needed to further clarify the efficacy of corticosteroid-eluting stent in certain subsets of patients.

