Introduction
Local drug delivery as an addition to PCI has been studied over many years1. One route for administration uses the principle of low-pressure balloons with short proximal and distal occlusion regions and a non-contact reservoir area in between2.
In this report we will describe a new design for a balloon catheter based on a local drug delivery system.
Description
Basically this system consists of a balloon with a distal and proximal occlusive segment and a central segment (multiple lengths available) that allows for homogeneous transfer of paclitaxel to the vessel wall (Figure 1).
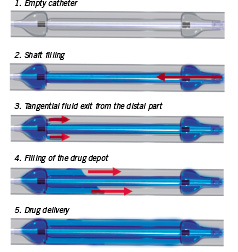
Figure 1. Schematic drawing. Function and aspect of the application device for local drug delivery.
In comparison to former local drug delivery devices, this balloon offers the advantage of drug transfer by jets that are directed coaxially to the vessel wall. Holes in the distal ramp of the catheter allow for filling of the drug depot without hydro jets due to an almost parallel flooding of the central segment.
History
Drug eluting stents have reduced the incidence of restenosis after percutaneous coronary interventions significantly, but cause concern about long term safety3,4. Local drug delivery using special application catheters is an alternative approach for intracoronary pharmacotherapy. Besides the fact, that no problematic coating as drug carrier has to be used, a local delivery independent of the stent itself by using catheter techniques offers further advantages – such as the possibility to treat the whole vessel wall, stent edges and adjacent vessel segments and not only the area close to the stent struts5,6.
Catheter-based local drug delivery for prevention of restenosis was invented before stent implantation became a routine method in percutaneous coronary intervention. Initial euphoria in the early nineties, however, was soon damped by additional vascular trauma of catheters with active, pressure-driven mode of delivery (e.g. porous balloons) and a rapid wash-out and insufficient uptake of the applied drug7,8. The combination of paclitaxel and a passive delivery system however compensates for these inherent disadvantages, because the lipophilic character of this compound allows for rapid intracellular uptake using a non-traumatic application catheter, and even a short time incubation leads to long-lasting biological effects in the vascular smooth muscle cell because of an irreversible alteration of the cytoskeleton5,9.
Therefore we followed, developed and tested a catheter-based approach to drug eluting stents, convinced that drug eluting stents are not ideal instruments for an intracoronary pharmacotherapy. Furthermore, a future preventive intracoronary pharmacotherapy (without mechanical intervention) will demand for a non-stent based application system, which is why we think it worthwhile not to abandon a catheter-based approach.
Technical specifications
Catheter characteristics
The GENIE™ device (Acrostak Corp., Winterthur, Switzerland) is based on a monorail PTCA catheter design and is compatible with a 0.014” guidewire and a 5F/0.056” guide catheter. Usable length is 138 cm; tip to monorail exit is 23 cm. Shaft markers at 90 cm, and 100 cm respectively, from the tip help in femoral and brachial approach.
The following sizes are available:
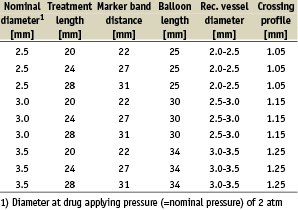
GENIE™ is deployed using standard PTCA techniques. Two radiopaque marker bands help in balloon positioning under fluoroscopy. Total balloon length is 3 mm longer than marker band distance; treatment length is about 2 mm shorter than marker band distance. Treatment lengths are available in 20, 24 and 28 mm.
The main difference to an angioplasty catheter is the balloon design with holes to fill the drug depot with a pressure of about 2 atm. The special balloon design enables filling of the drug depots without vessel traumatisation by hydro jets.
Indications for use
1. Bare metal stent + catheter-based drug delivery (stent edges, adjacent vessel segments).
2. Drug eluting stent + catheter-based drug delivery (stent edges, adjacent vessel segments).
3. PTCA + local drug delivery (small tortuous vessels, diffuse atherosclerosis).
4. Chronic total occlusions.
5. Bifurcations.
6. In-stent restenosis.
7. DES failure.
8. Alternative compounds, combination of different agents.
9. Preventive therapy.
Tips and tricks for delivery
The GENIE™ catheter is deployed using standard techniques. The balloon is continuously inflated at a low pressure of 2 atm that allows for distal and proximal occlusion of the vessel while simultaneously forming a central drug depot. A continuous pressure of 2 atm is maintained throughout application of the drug.
Preclinical experience
Local catheter-based delivery of paclitaxel proved effective in different preclinical models5,9,10. In the pig coronary stent model paclitaxel treatment via the GENIE™ catheter led to a significant reduction of neointimal proliferation. All coronary arteries showed complete endothelialisation 42 days following treatment11.
In another animal study in the denudated rabbit carotid artery, local delivery of a dimeric form of soluble Glycoprotein VI using the GENIE™ catheter, resulted in reduced thrombus formation after catheter-induced vascular injury opening a new approach of localised antithrombotic treatment of thrombogenic vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques or stented artery segments without systemic antiplatelet effects12.
Clinical experience
The potential of a local paclitaxel treatment via the GENIE™ catheter for preventing in-stent restenosis in de novo lesions is currently being evaluated in a randomised, prospective clinical trial in 204 patients (LOCAL TAX-study, EudraCT - Nr: 2005-001481-14, clinical Trials.gov identifier: NCT 00396929). Patient inclusion was completed in February of this year, and final data are expected in fall of 2007.
Meanwhile more than 35 patients with in-stent restenosis or drug eluting stent failure, as well as more than 25 patients with chronic total occlusions, were treated with local paclitaxel delivery via the GENIE catheter in our institution. Further patients with bifurcation in-stent restenosis were treated with two catheters in kissing balloon technique to allow for pharmacological treatment of the whole bifurcation without adding additional layers of metal to the bifurcation.
As an example we present the case of a 82 year old woman who was admitted to our institution because of subacute MI due to closure of the first diagonal branch (see Figure 2).
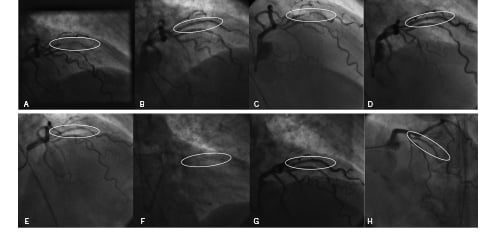
Figure 2. Angiographic findings of an 82 year old female patient at different time intervals. A: Subacute MI due to closure of diagonal branch, B: Acute result after recanalisation and bare metal stent implantation, C: In-stent-restenosis 2 months later, D: Acute result after PTCA and drug eluting stent implantation, E: In-stent restenosis in DES 4 months later, F: GENIE catheter (markers visible) covering stents and adjacent vessel segments, G: Acute result after local paclitaxel delivery via GENIE catheter, H: Control angiography 6 months after local paclitaxel delivery via GENIE catheter.
She received a bare metal stent but came back two months later suffering from acute coronary syndrome due to significant in-stent restenosis. She was then treated with a drug eluting stent (ENDEAVOR™), but again, four months later, emergency catheterisation had to be performed for acute coronary syndrome. Angiography revealed drug eluting stent failure with a new in-stent stenosis in the ENDEAVOR™ stent. By that time CABG surgery was discussed but eventually disapproved because of the poor general condition of the 82 year old patient with severely significant comorbidity. Therefore it was decided together with the patient to perform a catheter-based local delivery of paclitaxel via the GENIE™ application device as the last percutaneous attempt. After conventional PTCA, local paclitaxel delivery was performed leading to instant symptom relief of this initially highly symptomatic patient. Repeat coronary angiography seven months after this intervention revealed a patient lumen without restenosis, and the patient has stayed symptom and event free since the intervention for 10 months now.
In conclusion the GENIE™ catheter for liquid local drug delivery is an easy to use technique which can serve as an alternative for stent based local drug delivery. On-going studies will determine its future role in interventional cardiology.

