Thin-cap fibro atheroma (TCFA) lesions, the most prevalent precursor of plaque rupture, are composed of a lipid-rich necrotic core, a thin-fibrous cap with macrophage and lymphocyte infiltration, decreased smooth muscle cell content and expansive remodeling. Virtual Histology™ uses spectral analysis of intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) radiofrequency data to construct tissue maps that classify plaque into four major components; calcified, fibrous, fibrolipidic and necrotic core regions that are labeled white, green, greenish-yellow and red respectively. Palpography™ evaluates in vivo the mechanical properties of plaque tissue. The local strain is calculated from the radiofrequency traces using cross-correlation analysis and displayed, colour coded, from blue (for 0% strain) through yellow (for 2% strain) via red (Figure 1).
At a defined pressure, soft tissue (lipid-rich) components will deform more than hard (fibrous-calcified) components. Both techniques have been previously validated1,2.
Figure 1a shows an angiographically non-diseased proximal left anterior descending (LAD) artery. IVUS longitudinal reconstruction (Figure 1b) shows diffuse LAD disease. An eccentric mixed plaque that did not compromise the lumen was detected in the proximal LAD (Figure 1c). This segment was further analyzed with Palpography (20 MHz Eagle Eye, Volcano Therapeutics) and Virtual Histology™ (30 MHz Ultracross, Boston Scientific Corp) (Figures 1d and 1e). Despite its innocuous appearance on gray-scale IVUS, highly deformable shoulders with an underlying necrotic core-rich substrate were detected with the aid of strain and compositional imaging.
Although compatible with the presence of a vulnerable plaque, the prognostic value of these findings is currently unknown and needs to be established in large prospective randomized trials. Thus, the patient was discharged on intensive systemic therapy including lipid-lowering agents.
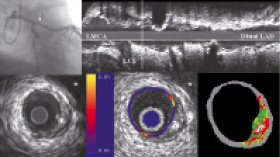
Figure 1. LAD= left anterior descending coronary artery. LCx= Left circumflex coronary artery. LMCA= Left main coronary artery. * Pericardium.

