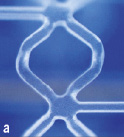
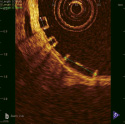
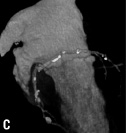
A biodegradable everolimus-eluting stent, developed by Bioabsorbable Vascular Solutions, Inc., an affiliate of Abbott Laboratories, located in Mountain View, CA, is currently undergoing clinical evaluation. The stent consists of a Polylactic acid (PLA) stent backbone processed for increased radial strength to provide stent integrity and a thin amorphous everolimus/PLA matrix coating (1:1 ratio of Everolimus/PLA matrix) for controlled drug release. Panel (a) shows the stent ex vivo: the stent is transparent apart from 2 radio-opaque markers at both proximal and distal edges. The appearances on optical coherence tomography (OCT) (Panel b) are quite unlike conventional stents; OCT can detect the interface between the stent and other tissues or fluid, but the inside of the strut consists of exactly the same material all the way through so it appears black, giving this a unique box appearance. The stent is radiolucent and invisible on fluoroscopy and multi-slice computed tomography (MSCT). Panels (c) and (d) demonstrate that the radiopaque markers (arrows) are clearly visible on MSCT, although due to a blooming effect the 2 markers appear as one continuous object. Calcification can be seen in the vessel proximal to the stent.