A 64-year old man with previous coronary artery bypass grafting was admitted to the hospital with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Three days before admission, multislice computed tomography (MSCT, SOMATOM Sensation Cardiac 64, Siemens Medical System, Forchheim, Germany) was performed due to an ECG abnormality. This revealed inverted T waves in leads V5 and V6 without symptoms. MSCT showed spontaneous coronary dissection in the diagonal branch (Panel 1A through F). Coronary angiography after admission demonstrated total occlusion of the diagonal branch (Panel 2A). Immediate percutaneous coronary intervention was undertaken, and coronary stents were successfully implanted with an excellent final angiogram (Panel 2B). Spontaneous coronary artery dissection is a rare condition that can cause acute myocardial infarction. MSCT is a useful device to detect spontaneous coronary artery dissection before the vessel occlusion.
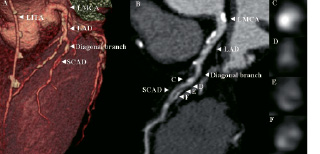
Figure 1. A. Volume-rendered image providing an anatomical overview of the diagonal branch. B. Curved multi-planar reconstructed image of the diagonal branch showing spontaneous coronary artery dissection. The arrowheads indicate cross-sectional images at different levels of the diagonal branch (C, D, E, F). LITA denotes left internal thoracic artery graft. LMCA denotes left main coronary artery. LAD denotes left anterior descending artery. SCAD denotes spontaneous coronary artery dissection.
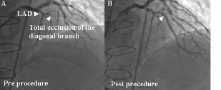
Figure 2. A. Coronary angiogram image of the diagonal branch showing total occlusion. B. Coronary angiogram after the procedure. Two coronary stents were implanted at the diagonal branch.